TOR Pathway-Mediated Juvenile Hormone Synthesis Regulates Nutrient-Dependent Female Reproduction in Nilaparvata lugens (Stål)
Abstract
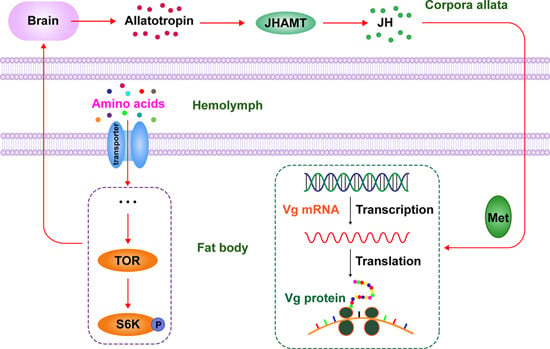
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of Target of Rapamycin (TOR) Pathway Genes and Phylogenetic Analysis
2.2. Expression of TOR Pathway Genes Is Regulated by Amino Acids (AAs) Signaling
2.3. TOR Pathway Transduces AAs Signaling that Regulates Vitellogenin (Vg) Synthesis
2.4. TOR Pathway Works through Juvenile Hormone (JH) Biosynthesis to Regulate Vg Synthesis
2.5. TOR Pathway and JH Are Required for AA-Mediated Ovary Development and Fecundity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Insect Rearing
4.2. Chemical Reagents and Treatments
4.3. Sequence and Phylogenetic Analysis
4.4. RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis and Reverse Transcriptase Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
4.5. Protein Extraction and Western Blot Analysis
4.6. RNA Interference
4.7. Ovary Dissection and Fecundity Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Attardo, G.M.; Hansen, I.A.; Raikhel, A.S. Nutritional regulation of vitellogenesis in mosquitoes: Implications for anautogeny. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2005, 35, 661–675. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clifton, M.E.; Noriega, F.G. Nutrient limitation results in juvenile hormone-mediated resorption of previtellogenic ovarian follicles in mosquitoes. J. Insect Physiol. 2011, 57, 1274–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parthasarathy, R.; Palli, S.R. Molecular analysis of nutritional and hormonal regulation of female reproduction in the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 41, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smykal, V.; Raikhel, A.S. Nutritional control of insect reproduction. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2015, 11, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sappington, T.W.; Raikhel, A.S. Molecular characteristics of insect vitellogenins and vitellogenin receptors. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1998, 28, 277–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufail, M.; Takeda, M. Molecular characteristics of insect vitellogenins. J. Insect Physiol. 2008, 54, 1447–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tufail, M.; Takeda, M. Insect vitellogenin/lipophorin receptors: Molecular structures, role in oogenesis, and regulatory mechanisms. J. Insect Physiol. 2009, 55, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abrisqueta, M.; Suren-Castillo, S.; Maestro, J.L. Insulin receptor-mediated nutritional signalling regulates juvenile hormone biosynthesis and vitellogenin production in the German cockroach. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 49, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, I.A.; Attardo, G.M.; Park, J.H.; Peng, Q.; Raikhel, A.S. Target of rapamycin-mediated amino acid signaling in mosquito anautogeny. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10626–10631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, S.-H.; Yeh, W.-L.; Young, S.-C.; Lin, P.-L.; Li, S. TOR signaling is involved in PTTH-stimulated ecdysteroidogenesis by prothoracic glands in the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 42, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howell, J.J.; Manning, B.D. mTOR couples cellular nutrient sensing to organismal metabolic homeostasis. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 22, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, X.H.; Majithia, A.; Huang, X.; Kimmel, A.R. Growth control via TOR kinase signaling, an intracellular sensor of amino acid and energy availability, with crosstalk potential to proline metabolism. Amino Acids 2008, 35, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Hedo, M.; Rivera-Perez, C.; Noriega, F.G. The insulin/TOR signal transduction pathway is involved in the nutritional regulation of juvenile hormone synthesis in Aedes aegypti. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 43, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.G.; Raikhel, A.S. The small GTPase Rheb is a key component linking amino acid signaling and TOR in the nutritional pathway that controls mosquito egg development. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 41, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arsic, D.; Guerin, P.M. Nutrient content of diet affects the signaling activity of the insulin/target of rapamycin/p70 S6 kinase pathway in the African malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae. J. Insect Physiol. 2008, 54, 1226–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, I.A.; Attardo, G.M.; Roy, S.G.; Raikhel, A.S. Target of rapamycin-dependent activation of S6 kinase is a central step in the transduction of nutritional signals during egg development in a mosquito. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 20565–20572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maestro, J.L.; Cobo, J.; Belles, X. Target of rapamycin (TOR) mediates the transduction of nutritional signals into juvenile hormone production. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 5506–5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, Z.; Xu, J.; Bai, H.; Zhu, F.; Palli, S.R. Juvenile hormone regulates vitellogenin gene expression through insulin-like peptide signaling pathway in the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 41924–41936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corona, M.; Velarde, R.A.; Remolina, S.; Moran-Lauter, A.; Wang, Y.; Hughes, K.A.; Robinson, G.E. Vitellogenin, juvenile hormone, insulin signaling, and queen honey bee longevity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7128–7133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.R.; Sieglaff, D.H.; Rees, H.H. Gonadal ecdysteroidogenesis in arthropoda: Occurrence and regulation. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2009, 54, 105–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.J.; Xue, J.; Lu, B.; Zhang, X.C.; Zhuo, J.C.; He, S.F.; Ma, X.F.; Jiang, Y.Q.; Fan, H.W.; Xu, J.Y.; et al. Two insulin receptors determine alternative wing morphs in planthoppers. Nature 2015, 519, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, C.X.; Yu, L.L.; Fan, H.W.; Wang, Z.; Xu, H.J.; Xi, Y.; Zhu, Z.R.; Zhou, W.W.; et al. Genomes of the rice pest brown planthopper and its endosymbionts reveal complex complementary contributions for host adaptation. Genome Biol. 2014, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noda, H.; Kawai, S.; Koizumi, Y.; Matsui, K.; Zhang, Q.; Furukawa, S.; Shimomura, M.; Mita, K. Annotated ESTs from various tissues of the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens: A genomic resource for studying agricultural pests. BMC Genom. 2008, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.J.; Chen, T.; Ma, X.F.; Xue, J.; Pan, P.L.; Zhang, X.C.; Cheng, J.A.; Zhang, C.X. Genome-wide screening for components of small interfering RNA (siRNA) and micro-RNA (miRNA) pathways in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Insect Mol. Biol. 2013, 22, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Q.; Zhang, Z.T.; Hu, C.; Lai, F.X.; Sun, Z.X. A chemically defined diet enables continuous rearing of the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål) (Homoptera: Delphacidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2001, 36, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Lu, K.; Qi, S.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, Q. The content of amino acids in artificial diet influences the development and reproduction of brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens (Stål). Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2014, 86, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.; Shu, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, M.; Yao, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, W. Molecular characterization and RNA interference analysis of vitellogenin receptor from Nilaparvata lugens (Stål). J. Insect Physiol. 2015, 73, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tufail, M.; Naeemullah, M.; Elmogy, M.; Sharma, P.N.; Takeda, M.; Nakamura, C. Molecular cloning, transcriptional regulation, and differential expression profiling of vitellogenin in two wing-morphs of the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens Stal (Hemiptera: Delphacidae). Insect Mol. Biol. 2010, 19, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.; Chen, X.; Liu, W.-T.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Chen, M.-X.; Zhou, Q. Nutritional signaling regulates vitellogenin synthesis and egg development through juvenile hormone in Nilaparvata lugens (Stål). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fronstin, R.B.; Hatle, J.D. A cumulative feeding threshold required for vitellogenesis can be obviated with juvenile hormone treatment in lubber grasshoppers. J. Exp. Biol. 2008, 211, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiao, S.H.; Hansen, I.A.; Zhu, J.; Sieglaff, D.H.; Raikhel, A.S. Juvenile hormone connects larval nutrition with target of rapamycin signaling in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. J. Insect Physiol. 2008, 54, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, C.; Denlinger, D.L. Insulin signaling and FOXO regulate the overwintering diapause of the mosquito Culex pipiens. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 6777–6781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatar, M.; Kopelman, A.; Epstein, D.; Tu, M.-P.; Yin, C.-M.; Garofalo, R. A mutant Drosophila insulin receptor homolog that extends life-span and impairs neuroendocrine function. Science 2001, 292, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, M.-P.; Yin, C.-M.; Tatar, M. Mutations in insulin signaling pathway alter juvenile hormone synthesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2005, 142, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parthasarathy, R.; Sun, Z.; Bai, H.; Palli, S.R. Juvenile hormone regulation of vitellogenin synthesis in the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 40, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urano, J.; Comiso, M.J.; Guo, L.; Aspuria, P.J.; Deniskin, R.; Tabancay, A.P.; Kato-Stankiewicz, J.; Tamanoi, F. Identification of novel single amino acid changes that result in hyperactivation of the unique GTPase, Rheb, in fission yeast. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 58, 1074–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, X.; Lin, Y.; Ortiz-Vega, S.; Yonezawa, K.; Avruch, J. Rheb binds and regulates the mTOR kinase. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, X.; Ortiz-Vega, S.; Lin, Y.; Avruch, J. Rheb binding to mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is regulated by amino acid sufficiency. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 23433–23436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noriega, F.G. Nutritional regulation of JH synthesis: A mechanism to control reproductive maturation in mosquitoes? Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2004, 34, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Martínez, S.; Mayoral, J.G.; Li, Y.; Noriega, F.G. Role of juvenile hormone and allatotropin on nutrient allocation, ovarian development and survivorship in mosquitoes. J. Insect Physiol. 2007, 53, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caroci, A.S.; Li, Y.; Noriega, F.G. Reduced juvenile hormone synthesis in mosquitoes with low teneral reserves reduces ovarian previtellogenic development in Aedes aegypti. J. Exp. Biol. 2004, 207, 2685–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Unnithan, G.C.; Veenstra, J.A.; Feyereisen, R.; Noriega, F.G. Stimulation of JH biosynthesis by the corpora allata of adult female Aedes aegypti in vitro: Effect of farnesoic acid and Aedes allatotropin. J. Exp. Biol. 2003, 206, 1825–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Martínez, S.; Li, Y.; Rodriguez, M.; Lanz-Mendoza, H.; Noriega, F. Allatotropin and PISCF-and YXFGL-amide-allatostatins distribution in Aedes aegypti and Anopheles albimanus mosquitoes. Cell Tissue Res. 2005, 321, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Hernandez-Martinez, S.; Fernandez, F.; Mayoral, J.G.; Topalis, P.; Priestap, H.; Perez, M.; Navare, A.; Noriega, F.G. Biochemical, molecular, and functional characterization of PISCF-allatostatin, a regulator of juvenile hormone biosynthesis in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 34048–34055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCt method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, D.; Yao, Q.; Zhang, J.; Dong, X.; Tian, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W. Feeding-based RNA interference of a trehalose phosphate synthase gene in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Insect Mol. Biol. 2010, 19, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, K.; Chen, X.; Liu, W.; Zhou, Q. Identification of a heat shock protein 90 gene involved in resistance to temperature stress in two wing-morphs of Nilaparvata lugens (Stål). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2016, 197, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Ding, Z.; Zhang, C.; Yang, B.; Liu, Z. Gene knockdown by intro-thoracic injection of double-stranded RNA in the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 40, 666–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.R.; Clark, K.D.; Gulia, M.; Zhao, Z.; Garczynski, S.F.; Crim, J.W.; Suderman, R.J.; Strand, M.R. An insulin-like peptide regulates egg maturation and metabolism in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 5716–5721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.G.; Hansen, I.A.; Raikhel, A.S. Effect of insulin and 20-hydroxyecdysone in the fat body of the yellow fever mosquito, Aedes aegypti. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 37, 1317–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, I.A.; Attardo, G.M.; Rodriguez, S.D.; Drake, L.L. Four-way regulation of mosquito yolk protein precursor genes by juvenile hormone-, ecdysone-, nutrient-, and insulin-like peptide signaling pathways. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, K.; Chen, X.; Liu, W.-T.; Zhou, Q. TOR Pathway-Mediated Juvenile Hormone Synthesis Regulates Nutrient-Dependent Female Reproduction in Nilaparvata lugens (Stål). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040438
Lu K, Chen X, Liu W-T, Zhou Q. TOR Pathway-Mediated Juvenile Hormone Synthesis Regulates Nutrient-Dependent Female Reproduction in Nilaparvata lugens (Stål). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(4):438. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040438
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Kai, Xia Chen, Wen-Ting Liu, and Qiang Zhou. 2016. "TOR Pathway-Mediated Juvenile Hormone Synthesis Regulates Nutrient-Dependent Female Reproduction in Nilaparvata lugens (Stål)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 4: 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040438
APA StyleLu, K., Chen, X., Liu, W. -T., & Zhou, Q. (2016). TOR Pathway-Mediated Juvenile Hormone Synthesis Regulates Nutrient-Dependent Female Reproduction in Nilaparvata lugens (Stål). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(4), 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17040438