Production of Bioactive Recombinant Bovine Chymosin in Tobacco Plants
Abstract
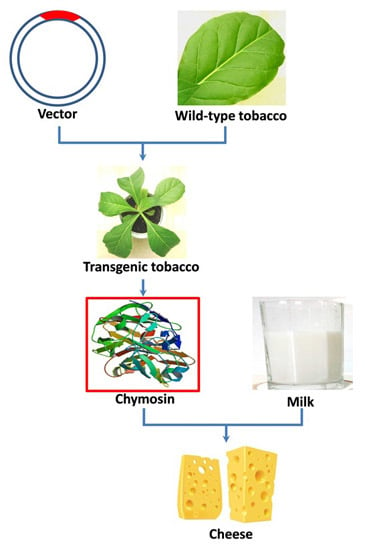
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Vector Construction and Tobacco Transformation
2.2. Molecular Analyses
2.3. Expression of Recombinant Bovine Chymosin and Detection of Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Vector Construction
4.2. Tobacco Transformation and Generation of Transgenic Tobacco
4.3. Molecular Analysis
4.3.1. PCR and Southern Blotting Analysis
4.3.2. RT-PCR Analyses
4.4. Immunoblotting and ELISA Analyses
4.5. Bioactivity Detection of Recombinant Bovine Chymosin
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, T.; Drake, M.; Cadwallader, K. Flavor of cheddar cheese: A chemical and sensory perspective. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2003, 2, 166–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, P.; Wallace, J. Formation of flavor compounds in cheese. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 1997, 45, 17–86. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Gunasekaran, S.; Olson, N. Combined use of chymosin and protease from Cryphonectria parasitica for control of meltability and firmness of cheddar cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2004, 87, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corredig, M.; Salvatore, E. Enzymatic coagulation of milk. In Advanced Dairy Chemistry; McSweeney, H.P.L., O’Mahony, A.J., Eds.; Springer New York: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 1B, pp. 287–307. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty, A.; Mukhopadhyay, U.; Grover, S.; Batish, V. Bovine chymosin: Production by rDNA technology and application in cheese manufacture. Biotechnol. Adv. 1999, 17, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feijoo-Siota, L.; Blasco, L.; Rodriguez-Rama, J.; Barros-Velazquez, J.; Miguel, T.; Sanchez-Perez, A.; Villa, T. Recent patents on microbial proteases for the dairy industry. Recent Adv. DNA Gene Seq. 2013, 8, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.A.; Mir, S.A.; Paray, M.A. Plant proteases as milk-clotting enzymes in cheesemaking: A review. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2014, 94, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çepoğlu, F.; Güler-Akın, M.B. Effects of coagulating enzyme types (commercial calf rennet, Aspergillus niger var. awamori as recombinant chymosin and Rhizomucor miehei as microbial rennet) on the chemical and sensory characteristics of white pickled cheese. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 12, 5588. [Google Scholar]
- Kappeler, S.; Farah, Z.; Budtz, P.; Rahbek-Nielsen, H.; van den Brink, J.M. Method of Producing Non-Bovine Chymosin and Use Hereof. Patent WO2002036752A3, 26 September 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Stressler, T.; Leisibach, D.; Lutz-Wahl, S.; Kuhn, A.; Fischer, L. Homologous expression and biochemical characterization of the arylsulfatase from Kluyveromyces. lactis and its relevance in milk processing. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Wang, X.-P.; Yan, Q.-J.; Chen, W.; Jiang, Z.-Q. Purification and characterization of a chymosin from Rhizopus microsporus var. rhizopodiformis. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 174, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tyagi, A.; Kumar, A.; Yadav, A.K.; Saklani, A.C.; Grover, S.; Batish, V.K. Functional expression of recombinant goat chymosin in Pichia pastoris bioreactor cultures: A commercially viable alternate. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 69, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, M.; Boran, O.S.; Hayaloglu, A.A. Effect of various blends of camel chymosin and microbial rennet (Rhizomucor miehei) on microstructure and rheological properties of Iranian UF White cheese. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 68, 724–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, T.; Lowe, P.; Lyons, A.; Thomas, P.; Eaton, M.; Millican, T.; Patel, T.; Bose, C.; Carey, N.; Doel, M. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of cDNA coding for calf preprochymosin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982, 10, 2177–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimori, K.; Kawauchi, Y.; Hidaka, M.; Uozumi, T.; Beppu, T. Nucleotide sequence of calf prorennin cDNA cloned in Escherichia coli. J. Biochem. 1982, 91, 1085–1088. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Badiefar, L.; Khodabande, M.; Ahmadian, G. Evaluation of the recombinant E. coli BL21 strains producing prochymosin in the biotechnological processes. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 150, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Song, X.; He, X.; Gan, B. Optimization of culture media of Bacillus licheniformis with high yield of chymosin. China Brew. 2011, 2, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Cardoza, R.E.; Gutierrez, S.; Ortega, N.; Colina, A.; Casqueiro, J.; Martin, J.F. Expression of a synthetic copy of the bovine chymosin gene in Aspergillus awamori from constitutive and pH-regulated promoters and secretion using two different pre-pro sequences. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2003, 83, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.; Kikuma, T.; Maruyama, J.; Kitamoto, K. Enhanced production of bovine chymosin by autophagy deficiency in the filamentous fungus Aspergillus oryzae. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallejo, J.A.; Ageitos, J.M.; Poza, M.; Villa, T.G. Short communication: A comparative analysis of recombinant chymosins. J. Dairy Sci. 2012, 95, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellmuth, K. Industrial scale production of chymosin with Aspergillus niger. Microb. Cell Fact. 2006, 5, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingston, D.; Novelli, G.F.; Cerrutti, P.; Recupero, M.N.; Blasco, M.; Galvagno, M.A. Use of grape pomaces to produce biomass of a Komagataella pastoris strain expressing a bovine chymosin activity. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 2, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noseda, D.G.; Blasco, M.; Recúpero, M.; Galvagno, M.Á. Bioprocess and downstream optimization of recombinant bovine chymosin b in Pichia (Komagataella) pastoris under methanol-inducible AOX1 promoter. Protein Expres. Purif. 2014, 104, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noseda, D.G.; Recúpero, M.N.; Blasco, M.; Ortiz, G.E.; Galvagno, M.Á. Cloning, expression and optimized production in a bioreactor of bovine chymosin B in Pichia (Komagataella) pastoris under AOX1 promoter. Protein Expres. Purif. 2013, 92, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.P.; Yin, M.L.; Chen, P.; Yang, Q. Constitutive expression, purification and characterization of bovine prochymosin in Pichia pastoris GS115. World J. Microb. Biotechnol. 2012, 28, 2087–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, R.; Shi, Z.; Gan, B.; Hu, Y. Researh advancment of chymosin. China Dairy Ind. 2010, 38, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Mundle, M. Are transgenic food crops safe for human consumption? J. Compr. Health 2014, 2, 8–17. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, D.R.; Penney, C.A.; Majumder, A.; Walmsley, A.M. Evolution of plant-made pharmaceuticals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 3220–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuse, D.; Tu, T.; McDonald, K.A. Manufacturing economics of plant-made biologics: Case studies in therapeutic and industrial enzymes. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 256135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleba, Y.Y.; Tuse, D.; Giritch, A. Plant viral vectors for delivery by Agrobacterium. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2014, 375, 155–192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abiri, R.; Valdiani, A.; Maziah, M.; Shaharuddin, N.A.; Sahebi, M.; Yusof, Z.N.B.; Atabaki, N.; Talei, D. A critical review of the concept of transgenic plants: Insights into pharmaceutical biotechnology and molecular farming. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2015, 18, 21–42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Twyman, R.M.; Schillberg, S.; Fischer, R. Transgenic plants in the biopharmaceutical market. Expert Opin. Emerg. Drugs 2005, 10, 185–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ommundsen, D.; Skjaervik, H. Chymosin for the Prevention and Treatment of Gastrointestinal Disorders. Canada Patent 2671303, 28 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Willmitzer, L.; Sonnewald, U.; Rober, M.; Carlsen, S.K. Transgenic Plants Expressing Industrial Enzymes. Patent WO1992001042 A1, 23 January 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Van Rooijen, G.; Glenn, K.R.; Shen, Y.; Boothe, J. Commercial Production of Chymosin in Plants. Patent US7390936B1, 24 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Vallejo, J.A.; Ageitos, J.M.; Poza, M.; Villa, T.G. Cloning and expression of buffalo active chymosin in Pichia pastoris. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 10606–10610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, P.M.; Li, W.-H. The codon adaptation index-a measure of directional synonymous codon usage bias, and its potential applications. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987, 15, 1281–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustafsson, C.; Govindarajan, S.; Minshull, J. Codon bias and heterologous protein expression. Trends Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kermode, A.R. Plants as factories for production of biopharmaceutical and bioindustrial proteins: Lessons from cell biology. Botany 2006, 84, 679–694. [Google Scholar]
- Benchabane, M.; Goulet, C.; Rivard, D.; Faye, L.; Gomord, V.; Michaud, D. Preventing unintended proteolysis in plant protein biofactories. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2008, 6, 633–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, D.E.; Thomas, M.C. Post-translational modification of plant-made foreign proteins; glycosylation and beyond. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, M.; Smith, A.E.; Pielak, G.J. Impact of reconstituted cytosol on protein stability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 19342–19347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streatfield, S.J. Approaches to achieve high-level heterologous protein production in plants. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2007, 5, 2–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, S.M.; Doran, P.M. Foreign protein production using plant cell and organ cultures: Advantages and limitations. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doran, P.M. Foreign protein degradation and instability in plants and plant tissue cultures. Trends Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vibeke, B.P.; Kurt, A.C.; Bent, F. Investigations on the activation of bovine prochymosin. Eur. J. Biochem. 1979, 94, 573–580. [Google Scholar]
- Felle, H.H. pH: Signal and messenger in plant cells. Plant Biol. 2001, 3, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gout, E.; Bligny, R.; Douce, R. Regulation of intracellular pH values in higher plant cells. Carbon-13 and phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance studies. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 13903–13909. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sleight, S.C.; Bartley, B.A.; Lieviant, J.A.; Sauro, H.M. In-fusion biobrick assembly and re-engineering. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 2624–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, A.A.; Liu, Z.; Binns, A.N. Three methods for the introduction of foreign DNA into Agrobacterium. Agrobacterium Protoc. 2006, 343, 43–53. [Google Scholar]
- Murashige, T.; Skoog, F. A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 1962, 15, 473–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, S. Western blotting using pvdf membranes and its downstream applications. In Western Blotting: Methods and Protocols; Kurien, T.B., Scofield, H.R., Eds.; Springer New York: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 227–236. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, M.F.; Adams, A. Characteristics of the microplate method of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of plant viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 1977, 34, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arima, K.; Yu, J.; Iwasaki, S.; Tamura, G. Milk-clotting enzyme from microorganisms: V. Purification and crystallization of Mucor rennin from Mucor pusillus var. Lindt. Appl. Microbiol. 1968, 16, 1727–1733. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]




© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, Z.-Y.; Zhang, Y.-Y.; Wang, Y.-P.; Fan, M.-X.; Zhong, X.-F.; Xu, N.; Lin, F.; Xing, S.-C. Production of Bioactive Recombinant Bovine Chymosin in Tobacco Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050624
Wei Z-Y, Zhang Y-Y, Wang Y-P, Fan M-X, Zhong X-F, Xu N, Lin F, Xing S-C. Production of Bioactive Recombinant Bovine Chymosin in Tobacco Plants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(5):624. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050624
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Zheng-Yi, Yu-Ying Zhang, Yun-Peng Wang, Ming-Xia Fan, Xiao-Fang Zhong, Nuo Xu, Feng Lin, and Shao-Chen Xing. 2016. "Production of Bioactive Recombinant Bovine Chymosin in Tobacco Plants" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 5: 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050624
APA StyleWei, Z. -Y., Zhang, Y. -Y., Wang, Y. -P., Fan, M. -X., Zhong, X. -F., Xu, N., Lin, F., & Xing, S. -C. (2016). Production of Bioactive Recombinant Bovine Chymosin in Tobacco Plants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(5), 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050624