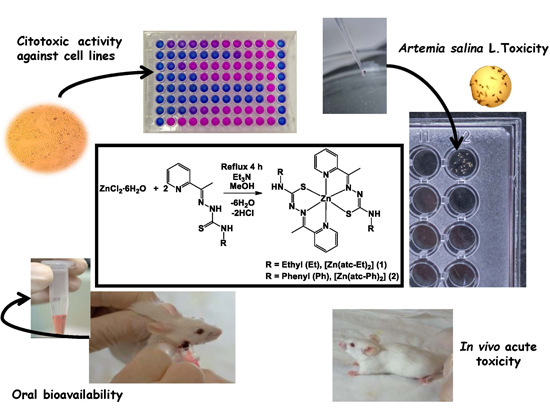
Novel Zinc(II) Complexes [Zn(atc-Et)2] and [Zn(atc-Ph)2]: In Vitro and in Vivo Antiproliferative Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Cytotoxic Activity toward MRC-5, HepG2, HeLa, MDA-MB-231, K-562 and DU 145 Cell Lines
2.3. Toxicity in Artemia salina L.
2.4. Acute Toxicity in Vivo
2.5. Quantification of the Enzymatic Activity Levels of Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST) and Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT) in the Serum of BALB/c Mice
2.6. Oral Bioavailability in Vivo
3. Experimental
3.1. Inorganic Complexes
3.2. Synthesis of the Complexes
3.3. Cell Culture
3.4. Cytotoxic Analysis (IC50) of Adherent Cell Lines
3.5. Cytotoxic Analysis (IC50) of Suspended Cells
3.6. SI Measurement
3.7. Artemia salina L. Toxicity Assay
3.8. In Vivo Oral Bioavailability Tests
3.9. Specimen Preparation for Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectrometry (ICP-OES)
3.10. Specimen Preparation for Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS)
3.11. In Vivo Acute Toxicity Assay
3.12. Quantification of the Serum AST and ALT Enzymatic Activity Levels in BALB/c Mice
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization (WHO). Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs297/es/ (accessed on 6 April 2015).
- American Cancer Society. Available online: http://www.cancer.org/research/cancerfactsstatistics/cancerfactsfigures2014/ (accessed on 15 May 2015).
- National Cancer Institute (NCI). Available online: www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/types (accessed on 6 April 2015).
- Kelland, L. The resurgence of platinum-based cancer chemotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielawski, K.; Czarnomysy, R.; Muszynska, A.; Bielawska, A.; Poplawska, B. Cytotoxicity and induction of apoptosis of human breast cancer cells by novel platinum(II) complexes. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2013, 35, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Xie, Z.; Sun, G.; Yang, P.; Li, J.; Yang, H.; Xiao, S.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, H.; Qiu, L.; et al. Reversing drug resistance of cisplatin by hsp90 inhibitors in human ovarian cancer cells. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 687–701. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.M.; Jiang, Z.F.; Ding, P.S.; Shao, L.J.; Lui, R.Y. Hypoxia-induced autophagy mediates cisplatin resistance in lung cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenzuela, M.M.; Neidigh, J.W.; Wall, N.R. Antimetabolite treatment for pancreatic cancer. Chemotherapy (Los Angel) 2014, 3, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lui, J.; Li, L.; Nie, D.; Tao, Q.; Wu, J.; Fan, J.; Lin, C.; Zhao, S.; Ju, D. Inhibition of autophagy potentiated the antitumor effect of nedaplatin in cisplatin-resistant nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florea, A.M.; Busselberg, D. Cisplatin as an anti-tumor drug: cellular mechanisms of activity, drug resistance and induced side effects. Cancers (Basel) 2011, 3, 1351–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do Nascimento, F.B.; Poelhsitz, G.V.; Pavan, F.R.; Sato, D.N.; Leite, C.Q.F.; Araújo, H.S.S.; Ellena, J.; Castellano, E.E.; Deflon, V.M.; Bastista, A.A. Synthesis, characterization, X-ray structure and in vitro antimycobacterial and antitumoral activities of Ru(II) phosphine/diimine complexes containing the “SpymMe2” ligand, SpymMe2=4,6-dimethyl-2-mercaptopyrimidine. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2008, 102, 1783–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondelli, M.A.; Graminha, A.E.; Côrrea, R.S.; Silva, M.M.; Carnizello, A.P.; Poelhsitz, G.V.; Ellena, J.; Deflon, V.M.; Caramori, G.F.; Torre, M.H.; et al. Ruthenium(II)/4,6-dimethyl-2-mercaptopyrimidine complexes: Synthesis, characterization, X-ray structures and in vitro cytotoxicity activities on cancer cell lines. Polyhedron 2014, 68, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, R. Bioinorganic Chemistry: A Short Course, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New Jersey, NJ, USA, 2002; pp. 1–368. [Google Scholar]
- Das, A.K. Metallotherapy: A Textbook on Medicinal Aspects of Bioinorganic Chemistry; CBS Publishers and Distributors: New Dehli, India, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.X.; Zhang, L.Z.; Yang, M.; Niu, J.Y.; Zhou, J. Synthesis, crystal structures, in vitro biological evaluation of zinc(II) and bismuth(III) complexes of 2-acetylpyrazine N(4)-phenylthiosemicarbazone. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2012, 22, 2418–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.X.; Chen, C.L.; Zhang, D.; Niu, J.Y.; Ji, B.S. Mn(II), Co(II) and Zn(II) complexes with heterocyclic substituted thiosemicarbazones: Synthesis, characterization, X-ray crystal structures and antitumor comparison. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 3169–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, C.G.; Maia, P.I.S.; Souza, P.C.; Pavan, F.R.; Leite, C.Q.F.; Vianna, R.B.; Batista, A.A.; Nascimento, O.R.; Deflon, V.M. Manganese(II) complexes with thiosemicarbazones as potential anti-Mycobacterium tuberculosis agents. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2013, 132, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, C.G.; Maia, P.I.S.; Miyata, M.; Pavan, F.R.; Leite, C.Q.F.; Almeida, E.T.; Deflon, V.M. Cobalt(III) complexes with thiosemicarbazones as potential anti-Mycobacterium tuberculosis agents. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2014, 25, 1848–1856. [Google Scholar]
- Stefani, C.; Jansson, P.J.; Gutierrez, E.; Bernhardt, P.V.; Richardson, D.R.; Kalinowski, D.S. Alkyl substituted 2'-benzoylpyridine thiosemicarbazone chelators with potent and selective anti-neoplastic activity: Novel ligands that limit methemoglobin formation. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelopo, M.P.; Pawar, S.A.; Sokhela, M.K.; Govender, T.; Kruger, H.G.; Maguire, G.E.M. Anticancer activity of ruthenium(II) arene complexes bearing 1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline amino alcohol ligands. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 66, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra, A.L.; Yhebra, R.S.; Sardiñas, I.G.; Buela, L.I. Comparative study of the assay of Artemia salina L. and the estimate of the medium lethal dose (LD50 value) in mice, to determine oral acute toxicity of plant extracts. Phytomedicine 2001, 8, 395–400. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, B.N.; Ferrigni, N.R.; Putnam, J.E.; Jacobsen, L.B.; Nichols, D.E.; McLaughlin, J.L. Brine shrimp: A convenient general bioassay for active plant constituents. Planta Med. 1982, 45, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraz, K.O.; Wardell, S.M.S.V.; Wardell, J.L.; Louro, S.R.W.; Beraldo, H. Copper(II) complexes with 2-pyridineformamide-derived thiosemicarbazones: Spectral studies and toxicity against Artemia salina. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2009, 73, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krstic, N.M.; Matuc, I.Z.; Juranic, Z.D.; Novakovic, I.T.; Sladic, D.M. Steroid dimers-in vitro cytotoxic and antimicrobial activities. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 143, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, M.C.R.; Antonio, J.M.S.; Ziolli, R.L.; Yoshida, M.I.; Rey, N.A.; Diniz, R. Synthesis and structural characterization of a zinc(II) complex of the mycobactericidal drug isoniazid—Toxicity against Artemia salina. Polyhedron 2011, 30, 1922–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD, 2011. Guideline 423: Acute Oral Toxicity - Acute Toxic Class Method. Paris: Head of Publications Service. Available online: http://www.oecd.org/publications (accessed on 18 November 2014).
- Muscella, A.; Vetrugno, C.; Migoni, D.; Biagioni, F.; Fanizzi, F.P.; Fornai, F.; De Pascali, S.A.; Marsigliante, S. Antitumor activity of [Pt(O,O′-acac)(gamma-acac)(DMS)] in mouse xenograft model of breast cancer. Cell. Death Dis. 2014, 5, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xiel, X. Change trends of organ weight background data in sprague dawley rats at diferente ages. J. Toxicol. Pathol. 2013, 26, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ping, K.Y.; Darah, I.; Chen, Y.; Sreeramanan, S.; Sasidharan, S. Acute and subchronic toxicity study of Euphorbia hirta L. methanol extract in rats. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.-J.; Choi, Y.-K.; Im, H.-S.; Yarimaga, O.; Yoon, E.; Kim, H.-S. Aspartate aminotransferase (AST/GOT) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT/GPT) detection techniques. Sensors 2006, 6, 756–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, R.C.P.; Neves, F.A.R.; Formagio, A.S.N.; Kasseya, C.A.L.; Stefanello, M.E.A.; Souza, V.V.; Pavan, F.R.; Croda, J. Evaluation of the anti-mycobacterium tuberculosis activity and in vivo acute toxicity of Annona sylvatic. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, N.; Zhang, H.; Yao, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, L. Pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of zinc-enriched yeast in rats. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- G.M. Sheldrick, SHELXL97. Program. for the Refinement of Crystal Structures; University of Göttingen: Göttingen, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- O’brien, J.; Wilson, I.; Orton, T.; Pognan, F. Investigation of the Alamar Blue (resazurin) fluorescent dye for the assessment of mammalian cell cytotoxicity. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 5421–5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhtar, M.N.; Zareen, S.; Yeap, S.K.; Ho, W.Y.; Lo, K.M.; Hasan, A.; Alitheen, B. Total synthesis, cytotoxic effects of damnacanthal, nordamnacanthal and related anthraquinone analogues. Molecules 2013, 18, 10042–10055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruppo, V.; Johnson, C.M.; Marietta, K.S.; Scherman, H.; Zink, E.E.; Crick, D.C.; Adams, L.B.; Orme, I.M.; Lenaerts, J.A. Rapid microbiologic and pharmacologic evaluation of experimental compounds against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 1245–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golde, W.T.; Gollobin, P.; Rodriguez, L.L. A rapid, simple, and humane method for submandibular bleeding of mice using a lancet. Lab. Anim. 2005, 34, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batista, B.L.; Rodrigues, J.L.; Nunes, J.A.; Souza, V.C.O.; Barbosa, F.J. Exploiting dynamic reaction cell inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (DRC-ICP-MS) for sequential determination of trace elements in blood using a dilute-and-shoot procedure. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 639, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| 1 | 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Bond Lengths | ||
| Zn(1)-N(2)/Zn(1)-N(2’) | 2.1586(18)/2.1527(17) | 2.1549(17) |
| Zn(1)-N(1)/Zn(1)-N(1’) | 2.203(2)/2.2482(18) | 2.2139(18) |
| Zn(1)-S(1)/Zn(1)-S(1’) | 2.4539(10)/2.4464(9) | 2.4452(6) |
| S(1)-C(8)/S(1’)-C(8’) | 1.739(2)/1.719(2) | 1.729(2) |
| N(3)-C(8)/N(3’)-C(8’) | 1.321(3)/1.338(3) | 1.323(3) |
| Angles | ||
| N(2’)-Zn(1)-N(2) | 161.22(5) | 169.60(9) |
| N(2’)-Zn(1)-N(1) | 104.79(7) | 98.88(6) |
| N(2)-Zn(1)-N(1) | 73.95(7) | 73.62(7) |
| N(2’)-Zn(1)-N(1’) | 73.58(7) | 73.62(7) |
| N(2)-Zn(1)-N(1’) | 87.64(7) | 98.88(6) |
| N(1)-Zn(1)-N(1’) | 87.97(6) | 90.55(9) |
| N(2’)-Zn(1)-S(1’) | 79.18(6) | 79.08(5) |
| N(1)-Zn(1)-S(1) | 151.47(5) | 152.54(5) |
| N(1’)-Zn(1)-S(1’) | 150.67(5) | 152.54(5) |
| C(8)-S(1)-Zn(1) | 96.13(8) | 95.93(7) |
| C(1)-N(1)-C(5) | 118.95(19) | 118.58(19) |
| Complexes | IC50 (µM) ± SD | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MRC-5 1 | HepG2 2 | SI * | HeLa 2 | SI * | MDA-MB-231 2 | SI * | K-562 2 | SI * | DU 145 2 | SI * | |
| ZnCl2·6H2O | 239.9 ± 16.8 | 698.4 ± 10.9 | 0.3 | 864.5 ± 14.0 | 0.3 | 475.4 ± 64.3 | 0.5 | 1088.7 ± 73.8 | 0.2 | 382.9 ± 7.8 | 0.6 |
| Hatc-Et | 9.0 ± 0.0 | 552.8 ± 45.0 | 0.0 | 746.0 ± 23.2 | 0.0 | 903.5 ± 65.3 | 0.0 | 420.3 ± 3.7 | 0.0 | 531.5 ± 12.6 | 0.0 |
| Hatc-Ph | 7.4 ± 0.0 | 36.3 ± 1.5 | 0.2 | 25.0 ± 0.2 | 0.3 | 24.3 ± 5.0 | 0.3 | 11.1 ± 0.6 | 0.7 | 15.1 ± 2.1 | 0.5 |
| [Zn(atc-Et)2] (1) | 12.1 ± 4.0 | 7.1 ± 3.7 | 1.7 | 102.0 ± 17.6 | 0.1 | 3.9 ± 0.0 | 3.1 | 52.0 ± 8.6 | 0.2 | 9.4 ± 3.4 | 1.3 |
| [Zn(atc-Ph)2] (2) | 12.1 ± 3.0 | 3.3 ± 0.0 | 3.6 | 325.0 ± 58.4 | 0.0 | 5.5 ± 3.1 | 2.2 | 14.1 ± 3.8 | 1.0 | 34.1 ± 7.0 | 0.3 |
| Cisplatin | 46.2 ± 4.9 | 60.3 ± 15.1 | 0.8 | 85.0 ± 10.1 | 0.5 | 143.3 ± 3.3 | 0.3 | 75.4 ± 6.0 | 0.6 | 56.5 ± 6.8 | 0.8 |
| Complexes | LC50 (µM) ± SD |
|---|---|
| [Zn(atc-Et)2] (1) | 962.6 ± 19.2 |
| [Zn(atc-Ph)2] (2) | 1672.7 ± 15.0 |
| Cisplatin | 295.1 ± 35.1 |
| 1 | 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Empirical formula | C20H26N8S2Zn | C28H26N8S2Zn |
| Formula weight | 507.98 | 604.06 |
| Temperature (K) | 293(2) | 296(2) |
| Wavelength (Å) | 0.71073 | 0.71073 |
| Crystal system | Monoclinic | Monoclinic |
| Space group | P21 | C2/c |
| Unit cell dimensions | a = 8.8919(5) Å α = 90° b = 14.738(5) Å β = 103.917(5)° c = 9.248(5) Å γ = 90° | a = 13.4421(10) Å α = 90° b = 18.9640(14) Å β = 95.5940(10)° c = 10.9390(8) Å γ = 90° |
| V (Å3) | 1,176.4(10) | 2775.2(4) |
| Z | 2 | 4 |
| Density (calculated) (Mg m−3) | 1.434 | 1.446 |
| Absorption coefficient (mm−1) | 1.246 | 1.069 |
| Crystal size/mm3 | 0.66 × 0.55 × 0.29 | 0.41 × 0.09 × 0.08 |
| Theta range for data collection | 2.36 to 25.12 | 1.86 to 25.07 |
| Index ranges | −10←h←10, −17←k←17, −11←l←9 | −16←h←16, −20←k←22, −12←l←13 |
| Reflections collected | 8001 | 8543 |
| Independent reflections | [R(int) = 0.0161] | [R(int) = 0.0227] |
| Abs. Corr. | Semi-empirical from equivalents | Semi-empirical from equivalents |
| Final R indices [I > 2sigma(I)] | R1 = 0.0184, wR2 = 0.0484 | R1 = 0.0296, wR2 = 0.0668 |
| R indices (all data) | R1 = 0.0189, wR2 = 0.0485 | R1 = 0.0368, wR2 = 0.0699 |
| Goodness-of-fit on F2 | S = 1.047 | S = 1.037 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lopes, E.D.O.; Oliveira, C.G.d.; Silva, P.B.d.; Eismann, C.E.; Suárez, C.A.; Menegário, A.A.; Leite, C.Q.F.; Deflon, V.M.; Pavan, F.R. Novel Zinc(II) Complexes [Zn(atc-Et)2] and [Zn(atc-Ph)2]: In Vitro and in Vivo Antiproliferative Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 781. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050781
Lopes EDO, Oliveira CGd, Silva PBd, Eismann CE, Suárez CA, Menegário AA, Leite CQF, Deflon VM, Pavan FR. Novel Zinc(II) Complexes [Zn(atc-Et)2] and [Zn(atc-Ph)2]: In Vitro and in Vivo Antiproliferative Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(5):781. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050781
Chicago/Turabian StyleLopes, Erica De O., Carolina G. de Oliveira, Patricia B. da Silva, Carlos E. Eismann, Carlos A. Suárez, Amauri A. Menegário, Clarice Q. F. Leite, Victor M. Deflon, and Fernando R. Pavan. 2016. "Novel Zinc(II) Complexes [Zn(atc-Et)2] and [Zn(atc-Ph)2]: In Vitro and in Vivo Antiproliferative Studies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 5: 781. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050781
APA StyleLopes, E. D. O., Oliveira, C. G. d., Silva, P. B. d., Eismann, C. E., Suárez, C. A., Menegário, A. A., Leite, C. Q. F., Deflon, V. M., & Pavan, F. R. (2016). Novel Zinc(II) Complexes [Zn(atc-Et)2] and [Zn(atc-Ph)2]: In Vitro and in Vivo Antiproliferative Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(5), 781. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050781