The miRacle in Pancreatic Cancer by miRNAs: Tiny Angels or Devils in Disease Progression
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Biosynthesis of miRNAs
3. OncomiRs in Pancreatic Cancer
3.1. MicroRNA 21 (miR-21)
3.2. MicroRNA 221 (miR-221)
3.3. MicroRNA-155 (miR-155)
3.4. MicroRNA 10b (miR-10b)
3.5. MicroRNA-208 (miR-208)
3.6. Additional OncomiRs in Pancreatic Cancer
4. Tumor Suppressor miRNAs (TSmiRs) in Pancreatic Cancer
4.1. The miRNA-200 Family
4.2. MicroRNA-34a (miR-34a)
4.3. MicroRNA-146a (miR-146a)
4.4. MicroRNA-124 (miR-124)
4.5. MicroRNA-203 (miR-203)
4.6. Other TSmiRs in Pancreatic Cancer
5. The Therapeutic Potential of MicroRNAs in Pancreatic Cancer
6. Pitfalls of miRNA Therapy
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arora, S.; Bhardwaj, A.; Singh, S.; Srivastava, S.K.; McClellan, S.; Nirodi, C.S.; Piazza, G.A.; Grizzle, W.E.; Owen, L.B.; Singh, A.P. An undesired effect of chemotherapy: Gemcitabine promotes pancreatic cancer cell invasiveness through reactive oxygen species-dependent, nuclear factor κb- and hypoxia-inducible factor 1α-mediated up-regulation of CXCR4. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 21197–21207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haque, I.; Mehta, S.; Majumder, M.; Dhar, K.; De, A.; McGregor, D.; Van Veldhuizen, P.J.; Banerjee, S.K.; Banerjee, S. Cyr61/ccn1 signaling is critical for epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stemness and promotes pancreatic carcinogenesis. Mol. Cancer 2011, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebolt-Leopold, J.S.; English, J.M. Mechanisms of drug inhibition of signalling molecules. Nature 2006, 441, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Marin-Muller, C.; Bharadwaj, U.; Chow, K.H.; Yao, Q.; Chen, C. MicroRNAs: Control and loss of control in human physiology and disease. World J. Surg. 2009, 33, 667–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, X.; Yang, J.; Li, M. Imaging-guided curative surgical resection of pancreatic cancer in a xenograft mouse model. Cancer Lett. 2012, 324, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Yao, W.; Xu, J.; Long, J.; Liu, C.; Yu, X. Combinational therapy: New hope for pancreatic cancer? Cancer Lett. 2012, 317, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar]
- Calin, G.A.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA signatures in human cancers. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calin, G.A.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNAs and chromosomal abnormalities in cancer cells. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6202–6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calin, G.A.; Sevignani, C.; Dumitru, C.D.; Hyslop, T.; Noch, E.; Yendamuri, S.; Shimizu, M.; Rattan, S.; Bullrich, F.; Negrini, M.; et al. Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 2999–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Pan, X.; Cobb, G.P.; Anderson, T.A. MicroRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Dev. Biol. 2007, 302, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farhana, L.; Dawson, M.I.; Fontana, J.A. Down regulation of miR-202 modulates Mxd1 and Sin3a repressor complexes to induce apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2015, 16, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Di, Y.; Liang, M.; Yang, F.; Yao, L.; Hao, S.; Li, J.; Jiang, Y.; Jin, C.; Fu, D. The microRNA-218 and robo-1 signaling axis correlates with the lymphatic metastasis of pancreatic cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Li, Z.; Yu, C.; Chen, M.; Tian, S.; Sun, C. MiR-1181 inhibits stem cell-like phenotypes and suppresses sox2 and stat3 in human pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett. 2015, 356, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Sun, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, J.; Yu, S.; Chang, X.; Lu, Z.; Chen, J. Deregulation of the miR-193b-kras axis contributes to impaired cell growth in pancreatic cancer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Li, B.; Chen, D.; Liu, L.; Huang, C.; Lu, Z.; Lun, L.; Wan, X. MiR-139 and miR-200c regulate pancreatic cancer endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, J.G.; Yang, M.; Qin, Q.; Deng, S.C.; Wang, B.; Tian, K.; Liu, L.; et al. Ectopic expression of miR-494 inhibited the proliferation, invasion and chemoresistance of pancreatic cancer by regulating sirt1 and c-Myc. Gene Ther. 2015, 22, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Peng, F.; Yu, C.; Wang, M.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Jiang, J.; Sun, C. MicroRNA-137 modulates pancreatic cancer cells tumor growth, invasion and sensitivity to chemotherapy. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 7442–7450. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.L.; Bai, Z.H.; Wang, X.B.; Bai, L.; Miao, F.; Pei, H.H. MiR-186 and 326 predict the prognosis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and affect the proliferation and migration of cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, S.S.; Mak, A.S.; Yam, J.W.; Cheung, A.N.; Ngan, H.Y.; Wong, A.S. Targeting estrogen-related receptor α inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stem cell properties of ovarian cancer cells. Mol. Ther. 2014, 22, 743–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.S.; Chen, W.C.; Huang, J.X.; Gao, H.J.; Sheng, H.H. Aberrant expression of microRNAs in serum may identify individuals with pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 7, 5226–5234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Papaconstantinou, I.G.; Lykoudis, P.M.; Gazouli, M.; Manta, A.; Polymeneas, G.; Voros, D. A review on the role of microRNA in biology, diagnosis, and treatment of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Pancreas 2012, 41, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Abou Tayoun, A.N.; Abo, K.M.; Pipas, J.M.; Gordon, S.R.; Gardner, T.B.; Barth, R.J., Jr.; Suriawinata, A.A.; Tsongalis, G.J. MicroRNAs as diagnostic markers for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and its precursor, pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasm. Cancer Genet. 2013, 206, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Li, A.; Hong, S.M.; Hruban, R.H.; Goggins, M. MicroRNA alterations of pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasias. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, B.; Ali, S.; Banerjee, S.; Wang, Z.; Logna, F.; Azmi, A.S.; Kong, D.; Ahmad, A.; Li, Y.; Padhye, S.; et al. Curcumin analogue CDF inhibits pancreatic tumor growth by switching on suppressor microRNAs and attenuating EZH2 expression. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovannetti, E.; Funel, N.; Peters, G.J.; Del Chiaro, M.; Erozenci, L.A.; Vasile, E.; Leon, L.G.; Pollina, L.E.; Groen, A.; Falcone, A.; et al. MicroRNA-21 in pancreatic cancer: Correlation with clinical outcome and pharmacologic aspects underlying its role in the modulation of gemcitabine activity. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 4528–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribas, J.; Ni, X.; Castanares, M.; Liu, M.M.; Esopi, D.; Yegnasubramanian, S.; Rodriguez, R.; Mendell, J.T.; Lupold, S.E. A novel source for miR-21 expression through the alternative polyadenylation of VMP1 gene transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 6821–6833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, R.V.; Erickson, L.A.; Jin, L.; Kulig, E.; Qian, X.; Cheville, J.C.; Scheithauer, B.W. p27kip1: A multifunctional cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor with prognostic significance in human cancers. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 154, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, T.; Komatsu, S.; Ichikawa, D.; Morimura, R.; Tsujiura, M.; Konishi, H.; Takeshita, H.; Nagata, H.; Arita, T.; Hirajima, S.; et al. Clinical impact of circulating miR-221 in plasma of patients with pancreatic cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galardi, S.; Mercatelli, N.; Giorda, E.; Massalini, S.; Frajese, G.V.; Ciafre, S.A.; Farace, M.G. MiR-221 and miR-222 expression affects the proliferation potential of human prostate carcinoma cell lines by targeting p27kip1. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 23716–23724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, A.; He, S.; Tian, B.; Hu, W.; Zhang, Z. MicroRNA-221 mediates the effects of pdgf-bb on migration, proliferation, and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, W. Identification and characterization of human bic, a gene on chromosome 21 that encodes a noncoding RNA. Gene 2001, 274, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seux, M.; Peuget, S.; Montero, M.P.; Siret, C.; Rigot, V.; Clerc, P.; Gigoux, V.; Pellegrino, E.; Pouyet, L.; N’Guessan, P.; et al. Tp53inp1 decreases pancreatic cancer cell migration by regulating SPARC expression. Oncogene 2011, 30, 3049–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gironella, M.; Seux, M.; Xie, M.J.; Cano, C.; Tomasini, R.; Gommeaux, J.; Garcia, S.; Nowak, J.; Yeung, M.L.; Jeang, K.T.; et al. Tumor protein 53-induced nuclear protein 1 expression is repressed by miR-155, and its restoration inhibits pancreatic tumor development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16170–16175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, L. Role of miR-10b in breast cancer metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. 2010, 12, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Weinberg, R.A. Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast cancer. Nature 2007, 449, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, M.; Li, Y.; Ye, S.; Ma, J.; Lu, L.; Lv, W.; Chang, G.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, S.; et al. MicroRNA profiling implies new markers of chemoresistance of triple-negative breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.; Shao, C.; Jin, G.; Liu, R.; Hao, J.; Song, B.; Ouyang, L.; Hu, X. MiR-208-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition of pancreatic cancer cells promotes cell metastasis and invasion. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 69, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zheng, D.; Zhang, B.; Liu, L.; Ou, J.; Chen, W.; Xiong, S.; Gu, Y.; Yang, J. MiR-208 promotes cell proliferation by repressing sox6 expression in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Cong, S.; Zhang, X.; Bao, X.; Wang, W.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, G.; Xu, J.; Du, B.; et al. MicroRNA-192 targeting retinoblastoma 1 inhibits cell proliferation and induces cell apoptosis in lung cancer cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 6669–6678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Yu, D.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Q.; Shi, M.; Ni, C.; Zhu, M. Diagnostic and biological significance of microRNA-192 in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Hu, G.; He, X.; Zhou, P.; Li, J.; He, B.; Sun, W. MicroRNA-424-5p suppresses the expression of socs6 in pancreatic cancer. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2013, 19, 739–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, X.; Shao, C. MicroRNA 483-3p suppresses the expression of DPC4/SMAD4 in pancreatic cancer. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, C.; Hu, X.; Shao, C. MicroRNA 421 suppresses DPC4/SMAD4 in pancreatic cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 406, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.K.; Henry, J.C.; Jiang, J.; Esau, C.; Gusev, Y.; Lerner, M.R.; Postier, R.G.; Brackett, D.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. MiR-132 and miR-212 are increased in pancreatic cancer and target the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 406, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Xu, X.F.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, M.C.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Lu, J.; Gao, F.H. MicroRNA-191 promotes pancreatic cancer progression by targeting usp10. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 12157–12163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Nong, K.; Wu, B.; Dong, B.; Bai, Y.; Zhu, H.; Wang, W.; Huang, X.; Yuan, Z.; Ai, K. MiR-212 promotes pancreatic cancer cell growth and invasion by targeting the hedgehog signaling pathway receptor patched-1. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 33, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Wang, Z.; Fillmore, R.; Xi, Y. MiR-200, a new star miRNA in human cancer. Cancer Lett. 2014, 344, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.F.; Xu, L.Y.; Li, E.M. A family of pleiotropically acting microRNAs in cancer progression, miR-200: Potential cancer therapeutic targets. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 1896–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilmarsdottir, B.; Briem, E.; Bergthorsson, J.T.; Magnusson, M.K.; Gudjonsson, T. Functional role of the microRNA-200 family in breast morphogenesis and neoplasia. Genes 2014, 5, 804–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, S.M.; Gaur, A.B.; Lengyel, E.; Peter, M.E. The miR-200 family determines the epithelial phenotype of cancer cells by targeting the E-cadherin repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 894–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altuvia, Y.; Landgraf, P.; Lithwick, G.; Elefant, N.; Pfeffer, S.; Aravin, A.; Brownstein, M.J.; Tuschl, T.; Margalit, H. Clustering and conservation patterns of human microRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 2697–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlmann, S.; Zhang, J.D.; Schwager, A.; Mannsperger, H.; Riazalhosseini, Y.; Burmester, S.; Ward, A.; Korf, U.; Wiemann, S.; Sahin, O. MiR-200bc/429 cluster targets PLCγ1 and differentially regulates proliferation and EGF-driven invasion than miR-200a/141 in breast cancer. Oncogene 2010, 29, 4297–4306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphries, B.; Yang, C. The microRNA-200 family: Small molecules with novel roles in cancer development, progression and therapy. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 6472–6498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamieson, N.B.; Morran, D.C.; Morton, J.P.; Ali, A.; Dickson, E.J.; Carter, C.R.; Sansom, O.J.; Evans, T.R.; McKay, C.J.; Oien, K.A. MicroRNA molecular profiles associated with diagnosis, clinicopathologic criteria, and overall survival in patients with resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 534–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, G.; Long, J.; Cui, X.; Xiao, Z.; Liu, Z.; Shi, S.; Liu, L.; Liu, C.; Xu, J.; Li, M.; et al. Highly lymphatic metastatic pancreatic cancer cells possess stem cell-like properties. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 42, 979–984. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ji, Q.; Hao, X.; Zhang, M.; Tang, W.; Yang, M.; Li, L.; Xiang, D.; Desano, J.T.; Bommer, G.T.; Fan, D.; et al. MicroRNA miR-34 inhibits human pancreatic cancer tumor-initiating cells. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e6816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodygin, D.; Tarasov, V.; Epanchintsev, A.; Berking, C.; Knyazeva, T.; Korner, H.; Knyazev, P.; Diebold, J.; Hermeking, H. Inactivation of miR-34a by aberrant CpG methylation in multiple types of cancer. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 2591–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalls, D.; Tang, S.N.; Rodova, M.; Srivastava, R.K.; Shankar, S. Targeting epigenetic regulation of miR-34a for treatment of pancreatic cancer by inhibition of pancreatic cancer stem cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azmi, A.S.; Ali, S.; Banerjee, S.; Bao, B.; Maitah, M.N.; Padhye, S.; Philip, P.A.; Mohammad, R.M.; Sarkar, F.H. Network modeling of CDF treated pancreatic cancer cells reveals a novel c-myc-p73 dependent apoptotic mechanism. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2011, 3, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Vandenboom, T.G., 2nd; Wang, Z.; Kong, D.; Ali, S.; Philip, P.A.; Sarkar, F.H. MiR-146a suppresses invasion of pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1486–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; VandenBoom, T.G., 2nd; Wang, Z.; Kong, D.; Ali, S.; Philip, P.A.; Sarkar, F.H. Up-regulation of miR-146a contributes to the inhibition of invasion of pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 5703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, S.; Jones, A.V.; Hinsley, E.E.; Whawell, S.A.; Lambert, D.W. MicroRNA-124 suppresses oral squamous cell carcinoma motility by targeting itgb1. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, F.; Liao, Y.J.; Cai, M.Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Liu, T.H.; Chen, S.P.; Bian, X.W.; Guan, X.Y.; Lin, M.C.; Zeng, Y.X.; et al. The putative tumour suppressor microRNA-124 modulates hepatocellular carcinoma cell aggressiveness by repressing ROCK2 and EZH2. Gut 2012, 61, 278–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.D.; Yuan, Y.; Zhuang, C.W.; Li, B.L.; Gong, D.J.; Wang, S.G.; Zeng, Z.Y.; Cheng, H.Z. MicroRNA-98 and microRNA-214 post-transcriptionally regulate enhancer of zeste homolog 2 and inhibit migration and invasion in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2012, 11, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Zhang, Z.; Tan, Z.; He, R.; Zeng, X.; Xie, Y.; Li, S.; Tang, G.; Tang, H.; He, X. MicroRNA-124 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis by directly repressing EZH2 in gastric cancer. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2014, 392, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Chen, L.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H.; Fan, J.; Wang, K.; Luo, J.; Chen, Z.; Meng, Z.; Liu, L. Methylation-mediated silencing of the miR-124 genes facilitates pancreatic cancer progression and metastasis by targeting Rac1. Oncogene 2014, 33, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Gu, M.; Zhang, K.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Z.; Da, J. MiR-203 inhibition of renal cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting of FGF2. Diagn. Pathol. 2015, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, L.; Xiong, X.; Lin, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, N. MiR-203 inhibits tumor cell migration and invasion via caveolin-1 in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2014, 7, 658–662. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, L.J.; Zhang, W.J.; Chang, Z.W.; Pan, Y.F.; Zong, H.; Fan, Q.X.; Wang, L.X. Pu.1 is identified as a novel metastasis suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma regulating the miR-615-5p/IGF2 axis. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 3667–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Tayebi, H.M.; Hosny, K.A.; Esmat, G.; Breuhahn, K.; Abdelaziz, A.I. MiR-615-5p is restrictedly expressed in cirrhotic and cancerous liver tissues and its overexpression alleviates the tumorigenic effects in hepatocellular carcinoma. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 3309–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, C.; Jin, X.; Jia, C.; Yu, S.; Chen, J. MiRNA-615-5p functions as a tumor suppressor in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by targeting AKT2. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119783. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, W.; Gu, Y.; Li, Z.; Cai, H.; Peng, Q.; Tu, M.; Kondo, Y.; Shinjo, K.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. MiR-615-5p is epigenetically inactivated and functions as a tumor suppressor in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 2015, 34, 1629–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keklikoglou, I.; Hosaka, K.; Bender, C.; Bott, A.; Koerner, C.; Mitra, D.; Will, R.; Woerner, A.; Muenstermann, E.; Wilhelm, H.; et al. MicroRNA-206 functions as a pleiotropic modulator of cell proliferation, invasion and lymphangiogenesis in pancreatic adenocarcinoma by targeting ANXA2 and KRAS genes. Oncogene 2014, 34, 4867–4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Lv, W.; Zhang, J.H.; Lu, D.L. MiR96 functions as a tumor suppressor gene by targeting NUAK1 in pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 34, 1599–1605. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Yu, J.; Pan, X.; Li, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, W.; Wang, B.; Yang, L.; Xu, H.; Zhang, G.; et al. Herg1 functions as an oncogene in pancreatic cancer and is downregulated by miR-96. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 5832–5844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.; Lu, Z.; Liu, C.; Meng, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, W.; Liu, J.; Yu, J.; Chen, J. MiRNA-96 suppresses Kras and functions as a tumor suppressor gene in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 6015–6025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.; Gu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Gu, C. MicroRNA-410 functions as a tumor suppressor by targeting angiotensin ii type 1 receptor in pancreatic cancer. IUBMB Life 2015, 67, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuda, N.; Ishiyama, S.; Li, Y.; Ioannides, C.G.; Abbruzzese, J.L.; Chang, D.Z. Synthetic microrna designed to target glioma-associated antigen 1 transcription factor inhibits division and induces late apoptosis in pancreatic tumor cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 6557–6564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macfarlane, L.A.; Murphy, P.R. MicroRNA: Biogenesis, function and role in cancer. Curr. Genom. 2010, 11, 537–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, M.; Han, J.; Yeom, K.H.; Lee, S.; Baek, S.H.; Kim, V.N. MicroRNA genes are transcribed by rna polymerase II. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 4051–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.; Lee, Y.; Yeom, K.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Jin, H.; Kim, V.N. The DROSHA-DGCR8 complex in primary microrna processing. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 3016–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, V.N. MicroRNA precursors in motion: Exportin-5 mediates their nuclear export. Trends Cell Biol. 2004, 14, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.J.; Gusev, Y.; Jiang, J.; Nuovo, G.J.; Lerner, M.R.; Frankel, W.L.; Morgan, D.L.; Postier, R.G.; Brackett, D.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Expression profiling identifies microRNA signature in pancreatic cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 120, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloomston, M.; Frankel, W.L.; Petrocca, F.; Volinia, S.; Alder, H.; Hagan, J.P.; Liu, C.G.; Bhatt, D.; Taccioli, C.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA expression patterns to differentiate pancreatic adenocarcinoma from normal pancreas and chronic pancreatitis. JAMA 2007, 297, 1901–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillhoff, M.; Liu, J.; Frankel, W.; Croce, C.; Bloomston, M. MicroRNA-21 is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer and a potential predictor of survival. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2008, 12, 2171–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriyama, T.; Ohuchida, K.; Mizumoto, K.; Yu, J.; Sato, N.; Nabae, T.; Takahata, S.; Toma, H.; Nagai, E.; Tanaka, M. MicroRNA-21 modulates biological functions of pancreatic cancer cells including their proliferation, invasion, and chemoresistance. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagao, Y.; Hisaoka, M.; Matsuyama, A.; Kanemitsu, S.; Hamada, T.; Fukuyama, T.; Nakano, R.; Uchiyama, A.; Kawamoto, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; et al. Association of microRNA-21 expression with its targets, pdcd4 and timp3, in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Mod. Pathol. 2012, 25, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szafranska, A.E.; Doleshal, M.; Edmunds, H.S.; Gordon, S.; Luttges, J.; Munding, J.B.; Barth, R.J., Jr.; Gutmann, E.J.; Suriawinata, A.A.; Marc Pipas, J.; et al. Analysis of microRNAs in pancreatic fine-needle aspirates can classify benign and malignant tissues. Clin. Chem. 2008, 54, 1716–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du Rieu, M.C.; Torrisani, J.; Selves, J.; Al Saati, T.; Souque, A.; Dufresne, M.; Tsongalis, G.J.; Suriawinata, A.A.; Carrere, N.; Buscail, L.; et al. MicroRNA-21 is induced early in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma precursor lesions. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Ahmad, A.; Banerjee, S.; Padhye, S.; Dominiak, K.; Schaffert, J.M.; Wang, Z.; Philip, P.A.; Sarkar, F.H. Gemcitabine sensitivity can be induced in pancreatic cancer cells through modulation of miR-200 and miR-21 expression by curcumin or its analogue CDF. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 3606–3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.K.; Lee, E.J.; Esau, C.; Schmittgen, T.D. Antisense inhibition of microRNA-21 or -221 arrests cell cycle, induces apoptosis, and sensitizes the effects of gemcitabine in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Pancreas 2009, 38, e190–e199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Wang, X.J.; Liu, Y.; Cui, Y.F. Pi3K/AKT/mTOR signaling is involved in (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate-induced apoptosis of human pancreatic carcinoma cells. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2013, 41, 629–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mace, T.A.; Collins, A.L.; Wojcik, S.E.; Croce, C.M.; Lesinski, G.B.; Bloomston, M. Hypoxia induces the overexpression of microRNA-21 in pancreatic cancer cells. J. Surg. Res. 2013, 184, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, A.; Alder, H.; Khiyami, A.; Leahy, P.; Croce, C.M.; Haldar, S. MicroRNA-375 and microRNA-221: Potential noncoding RNAs associated with antiproliferative activity of benzyl isothiocyanate in pancreatic cancer. Genes Cancer 2011, 2, 108–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, S.; Dubaybo, H.; Ali, S.; Goncalves, P.; Kollepara, S.L.; Sethi, S.; Philip, P.A.; Li, Y. Down-regulation of miR-221 inhibits proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells through up-regulation of PTEN, p27(kip1), p57(kip2), and PUMA. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2013, 3, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Volinia, S.; Calin, G.A.; Liu, C.G.; Ambs, S.; Cimmino, A.; Petrocca, F.; Visone, R.; Iorio, M.; Roldo, C.; Ferracin, M.; et al. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2257–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Zhang, H.W.; Lu, M.H.; He, X.H.; Li, Y.; Gu, H.; Liu, M.F.; Wang, E.D. MicroRNA-155 functions as an oncomir in breast cancer by targeting the suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 gene. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 3119–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, W.; He, L.; Coppola, M.; Guo, J.; Esposito, N.N.; Coppola, D.; Cheng, J.Q. MicroRNA-155 regulates cell survival, growth, and chemosensitivity by targeting FOXO3a in breast cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 17869–17879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sochor, M.; Basova, P.; Pesta, M.; Dusilkova, N.; Bartos, J.; Burda, P.; Pospisil, V.; Stopka, T. Oncogenic microRNAs: MiR-155, miR-19a, miR-181b, and miR-24 enable monitoring of early breast cancer in serum. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.M.; Zhao, J.; Deng, H.Y. MiR-155 promotes proliferation of human breast cancer MCF-7 cells through targeting tumor protein 53-induced nuclear protein 1. J. Biomed. Sci. 2013, 20, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babar, I.A.; Czochor, J.; Steinmetz, A.; Weidhaas, J.B.; Glazer, P.M.; Slack, F.J. Inhibition of hypoxia-induced miR-155 radiosensitizes hypoxic lung cancer cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2011, 12, 908–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raponi, M.; Dossey, L.; Jatkoe, T.; Wu, X.; Chen, G.; Fan, H.; Beer, D.G. MicroRNA classifiers for predicting prognosis of squamous cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 5776–5783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, D.; Haddadin, S.; Wang, Y.; Gu, L.Q.; Perry, M.C.; Freter, C.E.; Wang, M.X. Plasma microRNAs as novel biomarkers for early detection of lung cancer. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2011, 4, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nikiforova, M.N.; Tseng, G.C.; Steward, D.; Diorio, D.; Nikiforov, Y.E. MicroRNA expression profiling of thyroid tumors: Biological significance and diagnostic utility. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 1600–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Zuo, K.; Li, D.; Ye, M.; Ding, L.; Cai, H.; Fu, D.; Fan, Y.; Lv, Z. Upregulated miR-155 in papillary thyroid carcinoma promotes tumor growth by targeting apc and activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E1305–E1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.K.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Y.B.; Gu, M.; Zheng, D.C.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Z. MicroRNA-155 promotes the proliferation of prostate cancer cells by targeting annexin 7. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Habbe, N.; Koorstra, J.B.; Mendell, J.T.; Offerhaus, G.J.; Ryu, J.K.; Feldmann, G.; Mullendore, M.E.; Goggins, M.G.; Hong, S.M.; Maitra, A. MicroRNA miR-155 is a biomarker of early pancreatic neoplasia. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2009, 8, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.K.; Hong, S.M.; Karikari, C.A.; Hruban, R.H.; Goggins, M.G.; Maitra, A. Aberrant microRNA-155 expression is an early event in the multistep progression of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Pancreatology 2010, 10, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Zhu, C.F.; Ma, M.Z.; Chen, G.; Song, M.; Zeng, Z.L.; Lu, W.H.; Yang, J.; Wen, S.; Chiao, P.J.; et al. Micro-RNA-155 is induced by K-Ras oncogenic signal and promotes ros stress in pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 21148–21158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Li, H.; Wu, W.; Jiang, T.; Qiu, Z. Regulation of miR-155 affects pancreatic cancer cell invasiveness and migration by modulating the stat3 signaling pathway through socs1. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 1223–1230. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, A.; Ghosh, S.; Maiti, G.P.; Sabbir, M.G.; Zabarovsky, E.R.; Roy, A.; Roychoudhury, S.; Panda, C.K. Frequent alterations of the candidate genes hMLH1, ITGA9 and RBSP3 in early dysplastic lesions of head and neck: Clinical and prognostic significance. Cancer Sci. 2010, 101, 1511–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greither, T.; Grochola, L.F.; Udelnow, A.; Lautenschlager, C.; Wurl, P.; Taubert, H. Elevated expression of microRNAs 155, 203, 210 and 222 in pancreatic tumors is associated with poorer survival. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishi, K.; Doki, Y.; Yano, M.; Yasuda, T.; Fujiwara, Y.; Takiguchi, S.; Kim, S.; Higuchi, I.; Monden, M. Reduced MLH1 expression after chemotherapy is an indicator for poor prognosis in esophageal cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 4368–4375. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.J.; Zhao, Y.P.; Zhang, T.P.; Zhou, L.; Cui, Q.C.; Zhou, W.X.; You, L.; Chen, G.; Shu, H. MLH1 as a direct target of miR-155 and a potential predictor of favorable prognosis in pancreatic cancer. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2013, 17, 1399–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackay, H.J.; Cameron, D.; Rahilly, M.; Mackean, M.J.; Paul, J.; Kaye, S.B.; Brown, R. Reduced MLH1 expression in breast tumors after primary chemotherapy predicts disease-free survival. J. Clin. Oncol. 2000, 18, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sinha, S.; Singh, R.K.; Alam, N.; Roy, A.; Roychoudhury, S.; Panda, C.K. Frequent alterations of hMLH1 and RBSP3/HYA22 at chromosomal 3p22.3 region in early and late-onset breast carcinoma: Clinical and prognostic significance. Cancer Sci. 2008, 99, 1984–1991. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Haque, I.; Banerjee, S.; Mehta, S.; De, A.; Majumder, M.; Mayo, M.S.; Kambhampati, S.; Campbell, D.R.; Banerjee, S.K. Cysteine-rich 61-connective tissue growth factor-nephroblastoma-overexpressed 5 (ccn5)/wnt-1-induced signaling protein-2 (wisp-2) regulates microRNA-10b via hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha-twist signaling networks in human breast cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 43475–43485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allaya, N.; Khabir, A.; Sallemi-Boudawara, T.; Sellami, N.; Daoud, J.; Ghorbel, A.; Frikha, M.; Gargouri, A.; Mokdad-Gargouri, R.; Ayadi, W. Over-expression of miR-10b in npc patients: Correlation with lmp1 and twist1. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 3807–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, X.D.; Jiang, Z.W.; Jiang, C.C. MiR-10b promotes migration and invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 5533–5537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.G.; Wu, W.K.; Feng, S.Y.; Wang, X.J.; Shao, J.F.; Qiao, J. Co-inhibition of microRNA-10b and microRNA-21 exerts synergistic inhibition on the proliferation and invasion of human glioma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 41, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sasayama, T.; Nishihara, M.; Kondoh, T.; Hosoda, K.; Kohmura, E. MicroRNA-10b is overexpressed in malignant glioma and associated with tumor invasive factors, upar and rhoc. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 1407–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garzon, R.; Garofalo, M.; Martelli, M.P.; Briesewitz, R.; Wang, L.; Fernandez-Cymering, C.; Volinia, S.; Liu, C.G.; Schnittger, S.; Haferlach, T.; et al. Distinctive microRNA signature of acute myeloid leukemia bearing cytoplasmic mutated nucleophosmin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 3945–3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Luo, A.; Cai, Y.; Su, Q.; Ding, F.; Chen, H.; Liu, Z. MicroRNA-10b promotes migration and invasion through klf4 in human esophageal cancer cell lines. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 7986–7994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, N.; Yamashita, S.; Mimori, K.; Sudo, T.; Tanaka, F.; Shibata, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Ishii, H.; Doki, Y.; Mori, M. MicroRNA-10b is a prognostic indicator in colorectal cancer and confers resistance to the chemotherapeutic agent 5-fluorouracil in colorectal cancer cells. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 19, 3065–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, G.; Liu, N.; Ma, J.; Li, H.; Oblinger, J.L.; Prahalad, A.K.; Gong, M.; Chang, L.S.; Wallace, M.; Muir, D.; et al. MicroRNA-10b regulates tumorigenesis in neurofibromatosis type 1. Cancer Sci. 2010, 101, 1997–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakata, K.; Ohuchida, K.; Mizumoto, K.; Kayashima, T.; Ikenaga, N.; Sakai, H.; Lin, C.; Fujita, H.; Otsuka, T.; Aishima, S.; et al. MicroRNA-10b is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer, promotes its invasiveness, and correlates with a poor prognosis. Surgery 2011, 150, 916–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preis, M.; Gardner, T.B.; Gordon, S.R.; Pipas, J.M.; Mackenzie, T.A.; Klein, E.E.; Longnecker, D.S.; Gutmann, E.J.; Sempere, L.F.; Korc, M. MicroRNA-10b expression correlates with response to neoadjuvant therapy and survival in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 5812–5821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, C.G.; Kong, L.M.; Zhou, P.; Yang, X.L.; Huang, J.G.; Zhang, H.L.; Lu, N. MiR-10b is overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion through rhoc, upar and mmps. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Xu, Y.; Fu, Q. Curcumin inhibits growth of prostate carcinoma via miR-208-mediated cdkn1a activation. Tumour Biol. 2015, 36, 8511–8517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.C.; Jin, X.L.; Zhang, X.; Piao, Y.S.; Liu, S.P. Effect of osw-1 on microRNA expression profiles of hepatoma cells and functions of novel microRNAs. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 7, 1831–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halkova, T.; Cuperkova, R.; Minarik, M.; Benesova, L. MicroRNAs in pancreatic cancer: Involvement in carcinogenesis and potential use for diagnosis and prognosis. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2015, 2015, 892903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, B.; Wang, Y.; Kudo, K.; Gavin, E.J.; Xi, Y.; Ju, J. MiR-192 regulates dihydrofolate reductase and cellular proliferation through the p53-microRNA circuit. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 8080–8086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korpal, M.; Kang, Y. The emerging role of miR-200 family of microRNAs in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer metastasis. RNA Biol. 2008, 5, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, J.X.; Yan, B.; Zhao, Z.N.; Xiao, X.; Qin, W.W.; Zhang, R.; Jia, L.T.; Meng, Y.L.; Jin, B.Q.; Fan, D.M.; et al. Tamoxifen represses miR-200 microRNAs and promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by up-regulating c-myc in endometrial carcinoma cell lines. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 635–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphries, B.; Wang, Z.; Oom, A.L.; Fisher, T.; Tan, D.; Cui, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, C. MicroRNA-200b targets protein kinase cα and suppresses triple-negative breast cancer metastasis. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 2254–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knezevic, J.; Pfefferle, A.D.; Petrovic, I.; Greene, S.B.; Perou, C.M.; Rosen, J.M. Expression of miR-200c in claudin-low breast cancer alters stem cell functionality, enhances chemosensitivity and reduces metastatic potential. Oncogene 2015, 34, 5997–6006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdigao-Henriques, R.; Petrocca, F.; Altschuler, G.; Thomas, M.P.; Le, M.T.; Tan, S.M.; Hide, W.; Lieberman, J. MiR-200 promotes the mesenchymal to epithelial transition by suppressing multiple members of the zeb2 and snail1 transcriptional repressor complexes. Oncogene 2015, 35, 158–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.H.; Chen, C.L.; More, S.V.; Hsiao, P.W.; Hung, W.C.; Li, W.S. The tetraindole sk228 reverses the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cells by up-regulating members of the miR-200 family. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duns, G.; van den Berg, A.; van Dijk, M.C.; van Duivenbode, I.; Giezen, C.; Kluiver, J.; van Goor, H.; Hofstra, R.M.; van den Berg, E.; Kok, K. The entire miR-200 seed family is strongly deregulated in clear cell renal cell cancer compared to the proximal tubular epithelial cells of the kidney. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2013, 52, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamagawa, S.; Beder, L.B.; Hotomi, M.; Gunduz, M.; Yata, K.; Grenman, R.; Yamanaka, N. Role of miR-200c/miR-141 in the regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and migration in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 33, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoshino, H.; Enokida, H.; Itesako, T.; Tatarano, S.; Kinoshita, T.; Fuse, M.; Kojima, S.; Nakagawa, M.; Seki, N. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related microRNA-200s regulate molecular targets and pathways in renal cell carcinoma. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 58, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.G.; Zhang, S.M.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Wu, H.B.; Xu, X.P. Aberrant expression of microRNAs involved in epithelial-mesenchymal transition of ht-29 cell line. Cell Biol. Int. 2013, 37, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Pan, Q.; Shang, Y.; Zhu, R.; Ye, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, X.; Li, S.; He, Y.; Chen, L.; et al. MicroRNA-200 (miR-200) cluster regulation by achaete scute-like 2 (ascl2): Impact on the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colon cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 36101–36115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Liu, Y.; Deng, X.; Qi, S.; Sun, X.; Liu, G.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, M. Down-regulation of mir-200b-3p by low p73 contributes to the androgen-independence of prostate cancer cells. Prostate 2013, 73, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Banerjee, S.; Ahmad, A.; Kim, H.R.; Sarkar, F.H. MiR-200 regulates PDGF-D-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition, adhesion, and invasion of prostate cancer cells. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 1712–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, L.V.; Veliceasa, D.; Vinokour, E.; Volpert, O.V. MiR-200b inhibits prostate cancer emt, growth and metastasis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacurari, M.; Addison, J.B.; Bondalapati, N.; Wan, Y.W.; Luo, D.; Qian, Y.; Castranova, V.; Ivanov, A.V.; Guo, N.L. The microRNA-200 family targets multiple non-small cell lung cancer prognostic markers in h1299 cells and beas-2b cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 43, 548–560. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schliekelman, M.J.; Gibbons, D.L.; Faca, V.M.; Creighton, C.J.; Rizvi, Z.H.; Zhang, Q.; Wong, C.H.; Wang, H.; Ungewiss, C.; Ahn, Y.H.; et al. Targets of the tumor suppressor miR-200 in regulation of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 7670–7682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; VandenBoom, T.G., 2nd; Kong, D.; Wang, Z.; Ali, S.; Philip, P.A.; Sarkar, F.H. Up-regulation of miR-200 and let-7 by natural agents leads to the reversal of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 6704–6712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Lu, J.; Li, X.; Zhu, H.; Fan, X.; Zhu, S.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Q.; Wang, L.; Huang, Y.; et al. MiR-200a inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition of pancreatic cancer stem cell. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soubani, O.; Ali, A.S.; Logna, F.; Ali, S.; Philip, P.A.; Sarkar, F.H. Re-expression of miR-200 by novel approaches regulates the expression of pten and mt1-mmp in pancreatic cancer. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 1563–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellner, U.; Brabletz, T.; Keck, T. Zeb1 in pancreatic cancer. Cancers 2010, 2, 1617–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berx, G.; Raspe, E.; Christofori, G.; Thiery, J.P.; Sleeman, J.P. Pre-emting metastasis? Recapitulation of morphogenetic processes in cancer. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2007, 24, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spaderna, S.; Schmalhofer, O.; Hlubek, F.; Berx, G.; Eger, A.; Merkel, S.; Jung, A.; Kirchner, T.; Brabletz, T. A transient, emt-linked loss of basement membranes indicates metastasis and poor survival in colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology 2006, 131, 830–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tavazoie, S.F.; Alarcon, C.; Oskarsson, T.; Padua, D.; Wang, Q.; Bos, P.D.; Gerald, W.L.; Massague, J. Endogenous human microRNAs that suppress breast cancer metastasis. Nature 2008, 451, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bracken, C.P.; Gregory, P.A.; Kolesnikoff, N.; Bert, A.G.; Wang, J.; Shannon, M.F.; Goodall, G.J. A double-negative feedback loop between zeb1-sip1 and the microRNA-200 family regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 7846–7854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burk, U.; Schubert, J.; Wellner, U.; Schmalhofer, O.; Vincan, E.; Spaderna, S.; Brabletz, T. A reciprocal repression between zeb1 and members of the miR-200 family promotes emt and invasion in cancer cells. EMBO Rep. 2008, 9, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, P.A.; Bert, A.G.; Paterson, E.L.; Barry, S.C.; Tsykin, A.; Farshid, G.; Vadas, M.A.; Khew-Goodall, Y.; Goodall, G.J. The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting zeb1 and sip1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hugo, H.J.; Pereira, L.; Suryadinata, R.; Drabsch, Y.; Gonda, T.J.; Gunasinghe, N.P.; Pinto, C.; Soo, E.T.; van Denderen, B.J.; Hill, P.; et al. Direct repression of myb by zeb1 suppresses proliferation and epithelial gene expression during epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. 2013, 15, R113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banyard, J.; Chung, I.; Wilson, A.M.; Vetter, G.; Le Bechec, A.; Bielenberg, D.R.; Zetter, B.R. Regulation of epithelial plasticity by miR-424 and miR-200 in a new prostate cancer metastasis model. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.C.; Yoon, S.; Jeong, Y.; Yoon, J.; Baek, K. Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor signaling by miR-200b. Mol. Cells 2011, 32, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, N.; Du, P.; Zhang, A.; Shen, F.; Su, J.; Pu, P.; Wang, T.; Zjang, J.; Kang, C.; Zhang, Q. Downregulated microRNA-200a promotes emt and tumor growth through the wnt/β-catenin pathway by targeting the e-cadherin repressors zeb1/zeb2 in gastric adenocarcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 1579–1587. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roybal, J.D.; Zang, Y.; Ahn, Y.H.; Yang, Y.; Gibbons, D.L.; Baird, B.N.; Alvarez, C.; Thilaganathan, N.; Liu, D.D.; Saintigny, P.; et al. MiR-200 inhibits lung adenocarcinoma cell invasion and metastasis by targeting flt1/vegfr1. Mol. Cancer Res. 2011, 9, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saydam, O.; Shen, Y.; Wurdinger, T.; Senol, O.; Boke, E.; James, M.F.; Tannous, B.A.; Stemmer-Rachamimov, A.O.; Yi, M.; Stephens, R.M.; et al. Downregulated microRNA-200a in meningiomas promotes tumor growth by reducing e-cadherin and activating the wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 5923–5940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hicklin, D.J.; Ellis, L.M. Role of the vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumor growth and angiogenesis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 1011–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Sawai, H.; Ochi, N.; Matsuo, Y.; Xu, D.; Yasuda, A.; Takahashi, H.; Wakasugi, T.; Takeyama, H. Pten regulates angiogenesis through PI3K/Akt/VEGF signaling pathway in human pancreatic cancer cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2009, 331, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottaviano, A.J.; Sun, L.; Ananthanarayanan, V.; Munshi, H.G. Extracellular matrix-mediated membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase expression in pancreatic ductal cells is regulated by transforming growth factor-β1. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 7032–7040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Heidt, D.G.; Dalerba, P.; Burant, C.F.; Zhang, L.; Adsay, V.; Wicha, M.; Clarke, M.F.; Simeone, D.M. Identification of pancreatic cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 1030–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermann, P.C.; Huber, S.L.; Herrler, T.; Aicher, A.; Ellwart, J.W.; Guba, M.; Bruns, C.J.; Heeschen, C. Distinct populations of cancer stem cells determine tumor growth and metastatic activity in human pancreatic cancer. Cell Stem Cell 2007, 1, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.P.; Fleming, J.B.; Wang, H.; Abbruzzese, J.L.; Choi, W.; Kopetz, S.; McConkey, D.J.; Evans, D.B.; Gallick, G.E. ALDH activity selectively defines an enhanced tumor-initiating cell population relative to CD133 expression in human pancreatic adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olempska, M.; Eisenach, P.A.; Ammerpohl, O.; Ungefroren, H.; Fandrich, F.; Kalthoff, H. Detection of tumor stem cell markers in pancreatic carcinoma cell lines. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2007, 6, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, A.; Maitah, M.Y.; Ginnebaugh, K.R.; Li, Y.; Bao, B.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Sarkar, F.H. Inhibition of hedgehog signaling sensitizes NSCLC cells to standard therapies through modulation of emt-regulating mirnas. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2013, 6, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.N.; Chen, S.Y.; Hwang, S.M.; Yu, C.C.; Su, M.W.; Mai, W.; Wang, H.W.; Cheng, W.C.; Schuyler, S.C.; Ma, N.; et al. MiR-200c and gata binding protein 4 regulate human embryonic stem cell renewal and differentiation. Stem Cell Res. 2014, 12, 338–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimono, Y.; Zabala, M.; Cho, R.W.; Lobo, N.; Dalerba, P.; Qian, D.; Diehn, M.; Liu, H.; Panula, S.P.; Chiao, E.; et al. Downregulation of miRNA-200c links breast cancer stem cells with normal stem cells. Cell 2009, 138, 592–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagman, Z.; Larne, O.; Edsjo, A.; Bjartell, A.; Ehrnstrom, R.A.; Ulmert, D.; Lilja, H.; Ceder, Y. MiR-34c is downregulated in prostate cancer and exerts tumor suppressive functions. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 2768–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Q.; Hao, X.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, M.; Desano, J.; Fan, D.; Xu, L. Restoration of tumor suppressor miR-34 inhibits human p53-mutant gastric cancer tumorspheres. BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalimutho, M.; Minutolo, A.; Grelli, S.; Formosa, A.; Sancesario, G.; Valentini, A.; Federici, G.; Bernardini, S. Satraplatin (jm-216) mediates g2/m cell cycle arrest and potentiates apoptosis via multiple death pathways in colorectal cancer cells thus overcoming platinum chemo-resistance. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2011, 67, 1299–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Yuan, L.; Luo, J.; Gao, J.; Guo, J.; Xie, X. MiR-34a inhibits proliferation and migration of breast cancer through down-regulation of bcl-2 and sirt1. Clin. Exp. Med. 2013, 13, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Li, Y.; Gao, J.; Zhang, T.; Li, S.; Luo, A.; Chen, H.; Ding, F.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z. MicroRNA-34 suppresses breast cancer invasion and metastasis by directly targeting FRA-1. Oncogene 2013, 32, 4294–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misso, G.; Di Martino, M.T.; De Rosa, G.; Farooqi, A.A.; Lombardi, A.; Campani, V.; Zarone, M.R.; Gulla, A.; Tagliaferri, P.; Tassone, P.; et al. MiR-34: A new weapon against cancer? Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2014, 3, e194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Jazdzewski, K.; Li, W.; Liyanarachchi, S.; Nagy, R.; Volinia, S.; Calin, G.A.; Liu, C.G.; Franssila, K.; Suster, S.; et al. The role of microRNA genes in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 19075–19080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacifico, F.; Crescenzi, E.; Mellone, S.; Iannetti, A.; Porrino, N.; Liguoro, D.; Moscato, F.; Grieco, M.; Formisano, S.; Leonardi, A. Nuclear factor-κb contributes to anaplastic thyroid carcinomas through up-regulation of miR-146a. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Zhong, H.; Wan, H.; Chen, F.Y.; Zhong, J.; Xiao, F.; Liu, J.; Shen, L. MiR-146a expression level as a novel putative prognostic marker for acute promyelocytic leukemia. Dis. Markers 2014, 2014, 150604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Tang, S.; Le, S.Y.; Lu, R.; Rader, J.S.; Meyers, C.; Zheng, Z.M. Aberrant expression of oncogenic and tumor-suppressive microRNAs in cervical cancer is required for cancer cell growth. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.L.; Chiang, A.; Chang, D.; Ying, S.Y. Loss of miR-146a function in hormone-refractory prostate cancer. RNA 2008, 14, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Z.; Xie, L.; Yu, L.; Qian, X.; Liu, B. MicroRNA-146a is down-regulated in gastric cancer and regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis. Med. Oncol. 2012, 29, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kogo, R.; Mimori, K.; Tanaka, F.; Komune, S.; Mori, M. Clinical significance of miR-146a in gastric cancer cases. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 4277–4284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhaumik, D.; Scott, G.K.; Schokrpur, S.; Patil, C.K.; Campisi, J.; Benz, C.C. Expression of microRNA-146 suppresses NF-κb activity with reduction of metastatic potential in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5643–5647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumaraswamy, E.; Wendt, K.L.; Augustine, L.A.; Stecklein, S.R.; Sibala, E.C.; Li, D.; Gunewardena, S.; Jensen, R.A. Brca1 regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) expression in human breast cancer cells involves microRNA-146a and is critical for its tumor suppressor function. Oncogene 2014, 34, 4333–4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Umelo, I.A.; Lv, S.; Teugels, E.; Fostier, K.; Kronenberger, P.; Dewaele, A.; Sadones, J.; Geers, C.; De Greve, J. MiR-146a inhibits cell growth, cell migration and induces apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Ahmad, A.; Aboukameel, A.; Ahmed, A.; Bao, B.; Banerjee, S.; Philip, P.A.; Sarkar, F.H. Deregulation of miR-146a expression in a mouse model of pancreatic cancer affecting egfr signaling. Cancer Lett. 2014, 351, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.J.; Wang, Q.Y.; Zhou, C.X.; Yin, Q.Q.; He, M.; Yu, X.T.; Cao, D.X.; Chen, G.Q.; He, J.R.; Zhao, Q. MiR-124 targets slug to regulate epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of breast cancer. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.H.; Jiang, X.J.; Xiao, G.L.; Liu, D.Y.; Yuan, X.R. MiR-124a restoration inhibits glioma cell proliferation and invasion by suppressing iqgap1 and β-catenin. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 2104–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.H.; Huang, H.R.; Lu, J.; Liu, X.; Zhao, F.P.; Zhang, B.; Lin, S.X.; Wang, L.; Chen, H.H.; Xu, X.; et al. MiR-124 suppresses tumor growth and metastasis by targeting foxq1 in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, J.; Zhai, X.; Li, H.; Li, C.; Chang, J. MiR-124 retards bladder cancer growth by directly targeting CDK4. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2014, 46, 1072–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agirre, X.; Vilas-Zornoza, A.; Jimenez-Velasco, A.; Martin-Subero, J.I.; Cordeu, L.; Garate, L.; San Jose-Eneriz, E.; Abizanda, G.; Rodriguez-Otero, P.; Fortes, P.; et al. Epigenetic silencing of the tumor suppressor microRNA hsa-miR-124a regulates CDK6 expression and confers a poor prognosis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 4443–4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lujambio, A.; Ropero, S.; Ballestar, E.; Fraga, M.F.; Cerrato, C.; Setien, F.; Casado, S.; Suarez-Gauthier, A.; Sanchez-Cespedes, M.; Git, A.; et al. Genetic unmasking of an epigenetically silenced microRNA in human cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 1424–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, E.; Jana, N.R.; Bhattacharyya, N.P. MicroRNA-124 targets CCNA2 and regulates cell cycle in STHdh(Q111)/Hdh(Q111) cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 437, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baroukh, N.; Ravier, M.A.; Loder, M.K.; Hill, E.V.; Bounacer, A.; Scharfmann, R.; Rutter, G.A.; Van Obberghen, E. MicroRNA-124a regulates foxa2 expression and intracellular signaling in pancreatic beta-cell lines. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 19575–19588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asuthkar, S.; Stepanova, V.; Lebedeva, T.; Holterman, A.L.; Estes, N.; Cines, D.B.; Rao, J.S.; Gondi, C.S. Multifunctional roles of urokinase plasminogen activator (upa) in cancer stemness and chemoresistance of pancreatic cancer. Mol. Biol. Cell 2013, 24, 2620–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikenaga, N.; Ohuchida, K.; Mizumoto, K.; Yu, J.; Kayashima, T.; Sakai, H.; Fujita, H.; Nakata, K.; Tanaka, M. MicroRNA-203 expression as a new prognostic marker of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 17, 3120–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.; Wang, Q.; An, Y.; Xu, L. MiR203 regulates the proliferation, apoptosis and cell cycle progression of pancreatic cancer cells by targeting survivin. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 8, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chitkara, D.; Mittal, A.; Mahato, R.I. MiRNAs in pancreatic cancer: Therapeutic potential, delivery challenges and strategies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 81, 34–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naidu, S.; Magee, P.; Garofalo, M. MiRNA-based therapeutic intervention of cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 8, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothschild, S.I. MicroRNA therapies in cancer. Mol. Cell. Ther. 2014, 2, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zang, W.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Du, Y.; Chen, X.; Deng, M.; Sun, W.; Wang, L.; Zhao, G.; et al. MicroRNA-124 inhibits cellular proliferation and invasion by targeting ets-1 in breast cancer. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 10897–10904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pramanik, D.; Campbell, N.R.; Karikari, C.; Chivukula, R.; Kent, O.A.; Mendell, J.T.; Maitra, A. Restitution of tumor suppressor microRNAs using a systemic nanovector inhibits pancreatic cancer growth in mice. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 1470–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soifer, H.S.; Rossi, J.J.; Saetrom, P. MicroRNAs in disease and potential therapeutic applications. Mol. Ther. 2007, 15, 2070–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vychytilova-Faltejskova, P.; Kiss, I.; Klusova, S.; Hlavsa, J.; Prochazka, V.; Kala, Z.; Mazanec, J.; Hausnerova, J.; Kren, L.; Hermanova, M.; et al. MiR-21, miR-34a, miR-198 and miR-217 as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Diagn. Pathol. 2015, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sicard, F.; Gayral, M.; Lulka, H.; Buscail, L.; Cordelier, P. Targeting miR-21 for the therapy of pancreatic cancer. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rooij, E.; Purcell, A.L.; Levin, A.A. Developing microRNA therapeutics. Circ. Res. 2012, 110, 496–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



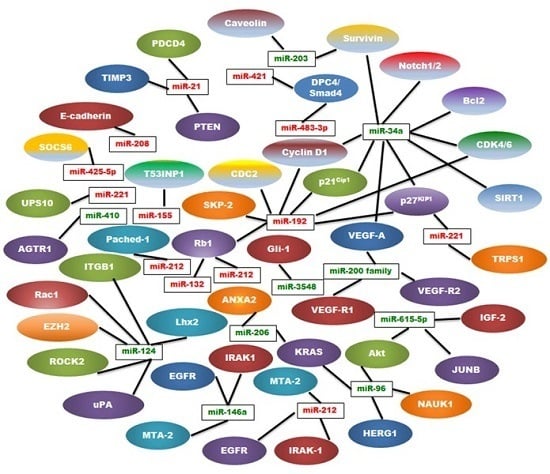
| MiRNA | Type | Regulation | Location | Targets | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-21 | Oncogenic | Up | 17q23.2 | PTEN, PDCD4, TIMP3 | [9,25,26,27] |
| miR-221 | Oncogenic | Up | Xp11.3 | TRPS1, p27kip1 | [28,29,30,31] |
| miR-155 | Oncogenic | Up | 21q21 | TP53INP1, SOCS1 | [24,32,33,34] |
| miR-10b | Oncogenic | Up | 2q31.1 | TIP30 | [35,36,37] |
| miR-208 | Oncogenic | Up | 14q11 | E-cadherin | [38,39] |
| miR-192 | Oncogenic | Up | 11q13.1 | Rb1, p27Kip1, p21Cip1, CyclinD1/2, SKP-2,CDK4, CDC2 | [40,41] |
| miR-425-5p | Oncogenic | Up | 3p21.31 | SOCS6 | [42] |
| miR-483-3p | Oncogenic | Up | 11p15.5 | DPC4/Smad4 | [43] |
| miR-421 | Oncogenic | Up | Xq13.2 | DPC4/Smad4 | [44] |
| miR-132 | Oncogenic | Up | 17p13 | Rb1 | [45] |
| miR-212 | Oncogenic | Up | 17p13 | Rb1 | [45] |
| miR-191 | Oncogenic | Up | 3p21.31 | UPS10 | [46] |
| miR-212 | Oncogenic | Up | 17p13.3 | Patched-1 | [47] |
| MiRNA | Type | Regulation | Location | Targets | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-200 Family | Tumor Suppressor | Down | 1p36, 12p12 | VEGF-A, FLT1/VEGFR1 KDR/VEGFR2 | [48,49,50,51,52,53,54] |
| miR-34a | Tumor Suppressor | Down | 1p36.22 | Notch1/2, Bcl-2, Cyclin D1, Survivin, SIRT1,VEGF, CDK4/6, p27KIP1 | [55,56,57,58,59] |
| miR-146a | Tumor Suppressor | Down | 5q33.3 | EGFR, IRAK-1, MTA-2 | [60,61,62] |
| miR-124 | Tumor Suppressor | Down | 8p23.1, 8q12.3, 20q13.33 | Rac1, ITGB1, EZH2, ROCK2, uPA, Lhx2 | [63,64,65,66,67] |
| miR-203 | Tumor Suppressor | Down | 14q32-33 | Survivin, Caveolin‑1 | [68,69] |
| miR-615-5p | Tumor Suppressor | Down | 12q13.13 | Akt2, IGF2, JUNB | [70,71,72,73] |
| miR-206 | Tumor suppressor | Down | 6p12.2 | K-Ras, ANXA2 | [74] |
| miR-96 | Tumor Suppressor | Down | 7q32.2 | NUAK1, Akt, HERG1, K-Ras | [75,76,77] |
| miR-410 | Tumor Suppressor | Down | 14q32.31 | AGTR1 | [78] |
| miR-3548 | Tumor Suppressor | Down | - | Gli-1 | [79] |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hawa, Z.; Haque, I.; Ghosh, A.; Banerjee, S.; Harris, L.; Banerjee, S.K. The miRacle in Pancreatic Cancer by miRNAs: Tiny Angels or Devils in Disease Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 809. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060809
Hawa Z, Haque I, Ghosh A, Banerjee S, Harris L, Banerjee SK. The miRacle in Pancreatic Cancer by miRNAs: Tiny Angels or Devils in Disease Progression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(6):809. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060809
Chicago/Turabian StyleHawa, Zuhair, Inamul Haque, Arnab Ghosh, Snigdha Banerjee, LaCoiya Harris, and Sushanta K. Banerjee. 2016. "The miRacle in Pancreatic Cancer by miRNAs: Tiny Angels or Devils in Disease Progression" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 6: 809. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060809
APA StyleHawa, Z., Haque, I., Ghosh, A., Banerjee, S., Harris, L., & Banerjee, S. K. (2016). The miRacle in Pancreatic Cancer by miRNAs: Tiny Angels or Devils in Disease Progression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(6), 809. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17060809