The Effect and Action Mechanisms of Oligochitosan on Control of Stem Dry Rot of Zanthoxylum bungeanum
Abstract
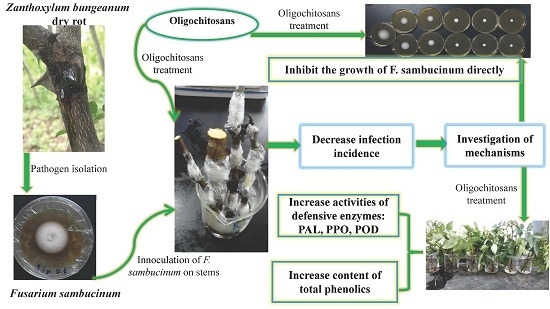
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Protective Effects of Oligochitosan on the Stem of Z. bungeanum against Dry Rot
2.2. Effects of Oligochitosan A (OCHA) and Oligochitosan B (OCHB) on Radial and Submerged Growth of F. sambucinum
2.3. Elicitation of Phenylalanine Ammonia Lyase (PAL), Polyphenoloxidase (PPO) and Peroxidase (POD) Activities in Z. bungeanum by Oligochitosan
2.4. Effects of Oligochitosan on Content of Total Phenolics in Z. bungeanum
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Plant and Fungal Materials
3.3. Evaluation of Protective Effects of Oligochitosan on Stems of Z. bungeanum against Dry Rot
3.4. Determination of the Effect of Oligochitosan on Growth of F. sambucinum
3.5. Assays of PAL, PPO and POD Activities in Z. bungeanum Twigs
3.6. Detection of Total Phenolics Changes in Z. bungeanum Twigs
3.7. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OCHA | Oligochitosan A |
| OCHB | Oligochitosan B |
| Mw | Molecular weight |
| DA | Degree of acetylation |
| DP | Degree of polymerization |
| PAL | Phenylalanine Ammonia Lyase |
| PPO | Polyphenoloxidase |
| POD | Pperoxidase |
| RGI | Radial Growth Inhibition |
| BGI | Biomass Growth Inhibition |
References
- Paik, S.K.; Koh, K.H.; Beak, S.M.; Paek, S.H.; Kim, J.A. The essential oils from Zanthoxylum schinifolium pericarp induce apoptosis of HepG2 human hepatoma cells through increased production of reactive oxygen species. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 28, 802–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.H.; Zhang, Y.H.; Kong, L.H. Research progress of Zanthoxylum bungeanum. China Condiments 2009, 34, 28–35. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.M.; Tian, C.M.; Liang, Y.M.; Wang, P.X. Diseases investigation of Zanthoxylum bungeanum in Shaanxi and Gansu provinces. J. N. W. For. Univ. 1994, 9, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Z.M.; Ming, Y.L.; Chen, D.; Zhang, H. Resistance of prickly ash to stem rot and pathogenicity differentiation of Fusarium sambucinum. J. N. W. For. Univ. 2010, 25, 115–118. [Google Scholar]
- He, M.F.; Li, E.C. The occurrence regularity and control technology of main diseases and pests of Zanthoxylum bungeanum. Shaanxi J. Agric. Sci. 2009, 2009, 218–220. [Google Scholar]
- Yacoub, A.; Gerbore, J.; Magnin, N.; Chambon, P.; Dufour, M.C.; Corio-Costet, M.F.; Guyoneaud, R.; Rey, P. Ability of Pythium oligandrum strains to protect Vitis vinifera L., by inducing plant resistance against Phaeomoniella chlamydospora, a pathogen involved in Esca, a grapevine trunk disease. Biol. Control 2016, 92, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista-Baños, S.; Hernandez-Lauzardoa, A.N.; Velazquez-del Vallea, M.G.; Hernandez-Lópeza, M.; Ait Barka, E.; Bosquez-Molinac, E.; Wilsond, C.L. Chitosan as a potential natural compound to control pre and postharvest diseases of horticultural commodities. Crop Prot. 2006, 25, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, L.A.; Joyce, D.C. Elicitors of induced disease resistance in postharvest horticultural crops: A brief review. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2004, 32, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AitBarka, E.; Eullaffroy, P.; Clément, C.; Vernet, G. Chitosan improves development, and protects Vitis vinifera L. against Botrytis cinerea. Plant Cell Rep. 2004, 22, 608–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilnicka, A.; Walczyk, M.; Lukaszewicz, J.P. The fungicidal properties of the carbon materials obtained from chitin and chitosan promoted by copper salts. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 52, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendra, D.F.; Hadwiger, L.A. Characterization of the smallest chitosan oligomer that is maximally antifungal to Fusarium solani and elicits pisatin formation by Pisum sativum. Exp. Mycol. 1984, 8, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathiyabama, M.; Balasubramanian, R. Chitosan induces resistance components in Arachis hypogaea against leaf rust caused by Puccinia arachidis. Speg. Crop Prot. 1998, 17, 307–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, M.V.B.; Arul, J.; Ait-Barka, E.; Angers, P.; Richard, C.; Castaigne, F. EVect of chitosan on growth and toxin production by Alternaria alternata f. sp. lycopersici. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 1998, 8, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plascencia-Jatomea, M.; Viniegra, G.; Olayo, R.; Castillo-Ortega, M.M.; Shirai, K. Effect of chitosan and temperature on spore germination of Aspergillus niger. Macromol. Biosci. 2003, 3, 582–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.T.; Huang, K.L.; Guo, F.; Qu, W.; Yang, J.J.; Liang, Z.H.; Luo, Y.B. Postharvest grapefruit seed extract and chitosan treatments of table grapes to control Botrytis cinerea. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2007, 46, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ghaouth, A.; Arul, J.; Asselin, A.; Benhamou, N. Antifungal activity of chitosan on post-harvest pathogens: Induction of morphological and cytological alterations in Rhizopus stolonifer. Mycol. Res. 1992, 96, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.Y.; Zhang, J.L.; Bassett, C.L.; Meng, X.H. Difference between chitosan and oligochitosan in growth of Monilinia fructicola and control of brown rot in peach fruit. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, J.K.; Valent, B.; Albersheim, P. Purification and partial characterization of a β-glucan fragment that elicits phytoalexin accumulation in soybean. J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 11312–11320. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khan, W.; Prithiviraj, B.; Smith, D. Chitosan and chitin oligomers increase phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and tyrosine ammonia-lyase activities in soybean leaves. J. Plant Physiol. 2003, 160, 859–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prapagdee, B.; Kotchadat, K.; Kumsopa, A.; Visarathanonth, N. The role of chitosan in protection of soybean from sudden death syndrome caused by Fusarium solani f. sp. glycines. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 1353–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Tian, S.; Meng, X.; Xu, Y. Effects of chitosan on control of postharvest diseases and physiological responses of tomato fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2007, 44, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhanova, G.F.; Yarullina, L.G.; Maksimov, I.V. The control of wheat defense responses during infection with Bipolaris sorokiniana by chitooligosaccharides. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2007, 54, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairullin, R.M.; Akhmetova, I.E. Luminol-dependent chemiluminescence analysis of chitooligosaccharide-induced rapid production of hydrogen peroxide by intact wheat seedlings. Biochemistry (Mosc.) 2001, 66, 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozeretskovskaya, O.L.; Vasyukova, N.I.; Panina, Y.S.; Chalenko, G.I. Effect of immunomodulators on potato resistance and susceptibility to Phytophthora infestans. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2006, 53, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonni, F.; Moreira, M.T.; Fasoli, H.; Grandi, L.; Cabral, D. Simple and easy method for the determination of fungal growth and decolourative capacity in solid media. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2004, 54, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Luo, H.; Meng, J.; Sun, W.; Wang, X.; Lu, S.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, L. Effects of oligosaccharides from endophytic Fusarium oxysporum Dzf17 on activities of defense-related enzymes in Dioscorea zingiberensis suspension cell and seedling cultures. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 17, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, M.K.; Ward, E.W.B. Phenylalanine ammonia lyase activity in soybean hypocotyls and leaves following infection with Phytophthora megasperma f. sp. glycinea. Can. J. Bot. 1988, 66, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, K.; Ćirić, A.; Glamočlija, J.; Soković, M. Antibacterial and antifungal activities of methanol extract and phenolic compounds from Diospyros virginiana L. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 59, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Q.; Shi, D.; Mizuno, M. Flavonol glucosides in pericarps of Zanthoxylum bungeanum. Phytochemistry 1995, 39, 723–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkis, J.R.; Michel, I.; Tessaro, I.C.; Marczak, L.D.F. Optimization of phenolics extraction from sesame seed cake. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 122, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Cheng, C.; Liang, J. Effect of esterification condensation on the Folin–Ciocalteu method for the quantitative measurement of total phenols. Food Chem. 2015, 170, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magalhães, L.M.; Santos, F.; Segundo, M.A.; Reis, S.; Lima, J.L.F.C. Rapid microplate high-throughput methodology for assessment of Folin–Ciocalteu reducing capacity. Talanta 2010, 83, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Guo, P.; An, H.; Du, Y.; Han, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y. Functions of oligochitosan induced protein kinase in tobacco mosaic virus resistance and pathogenesis related proteins in tobacco. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 47, 724–731. [Google Scholar]
- Hadwiger, L.A.; Kendra, D.F.; Fristensky, B.W.; Wagoner, W. Chitosan both activates genes in plants and inhibits RNA synthesis in fungi. In Chitin in Nature and Technology; Muzarelli, G., Jeuniaus, C., Graham, G.W., Eds.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1986; pp. 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Hadwiger, L.A.; Beckman, J.M.; Adams, M.J. Localization of fungal components in the pea-Fusarium interaction detected immunochemically with anti-chitosan and antifungal cell wall antisera. Plant Physiol. 1981, 67, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Shalom, N.; Ardi, R.; Pinto, R.; Aki, C.; Fallik, E. Controlling gray mould caused by Botrytis cinerea in cucumber plants by means of chitosan. Crop Prot. 2003, 22, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, D.J.; Nguyen, D.M.C.; Park, R.D.; Jung, W.J. Chitosan–cinnamon beads enhance suppressive activity against Rhizoctonia solani and Meloidogyne incognita in vitro. Microb. Pathog. 2014, 66, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, A.; Nagao, N. Effects of chitosan, pectic acid, lysozyme, and chitinase on the growth of several phytopathogens. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1989, 53, 3065–3066. [Google Scholar]
- Kiirika, L.M.; Stahl, F.; Wydra, K. Phenotypic and molecular characterization of resistance induction by single and combined application of chitosan and silicon in tomato against Ralstonia solanacearum. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2013, 81, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakrzewska, A.; Boorsma, A.; Brul, S.; Hellingwerf, K.J.; Klis, F.M. Transcriptional response of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to the plasma membrance-perturbing compound chitosan. Eukaryot. Cell 2005, 4, 703–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benhamou, N.; Thériault, G. Treatment with chitosan enhances resistance of tomato plants to the crown and root rot pathogen Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. radicis-lycopersici. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 1992, 41, 33–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopoulos, M.V.; Tsantili, E. Participation of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) in increased phenolic compounds in fresh cold stressed walnut (Juglans regia L.) kernels. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2015, 104, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughn, K.C.; Duke, S.O. Function of polyphenol oxidase in higher plants. Physiol. Plant. 1984, 60, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, M.Y.; Graham, T.L. Rapid accumulation of anionic peroxidases and phenolic polymers in soybean cotyledon tissues following treatment with Phytophthora megasperma f. sp. Glycinea wall glucan. Plant Physiol. 1991, 97, 1445–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadwiger, L.A.; Beckman, J.M. Chitosan as a component of pea-Fusarium solani interactions. Plant Physiol. 1980, 66, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, H.; Zhao, X.; Du, Y. Oligochitosan: A plant diseases vaccine—A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 82, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Oligochitosan Concentration (mg/mL) | Detection Time (day) | RGI (%) | BGI (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OCHA | OCHB | OCHA | OCHB | ||
| 0.2 | 2 | 26.78 ± 1.13 y | 26.47 ± 1.01 y | 37.11 ± 4.27 t | 42.37 ± 6.11 r |
| 4 | 32.14 ± 1.27 x | 39.06 ± 3.36 v | 39.74 ± 3.36 s | 44.12 ± 4.08 q | |
| 6 | 40.64 ± 1.58 uv | 32.70 ± 1.82 x | 34.84 ± 1.91 u | 39.93 ± 5.10 s | |
| 8 | 42.74 ± 1.77 t | 35.18 ± 2.31 w | 31.63 ± 3.60 v | 38.30 ± 3.97 st | |
| 10 | 42.65 ± 1.08 t | 36.06 ± 1.42 w | 25.33 ± 2.37 w | 25.21 ± 1.87 w | |
| 0.4 | 2 | 41.83 ± 1.13 tu | 36.49 ± 1.70 w | 54.19 ± 2.59 mn | 59.15 ± 4.48 kl |
| 4 | 55.51 ± 0.76 p | 53.74 ± 2.20 q | 53.47 ± 3.44 n | 60.81 ± 6.89 k | |
| 6 | 51.10 ± 3.15 qr | 46.37 ± 3.15 s | 55.61 ± 2.24 m | 63.98 ± 6.19 j | |
| 8 | 40.07 ± 2.31 uv | 43.06 ± 2.91 t | 50.12 ± 2.24 o | 58.75 ± 4.21 l | |
| 10 | 39.17 ± 1.42 v | 41.89 ± 3.88 tu | 49.03 ± 1.87 op | 48.18 ± 3.58 p | |
| 0.6 | 2 | 51.00 ± 1.70 r | 56.71 ± 3.44 p | 60.84 ± 5.95 k | 64.78 ± 5.95 j |
| 4 | 64.02 ± 1.27 lm | 66.25 ± 2.26 k | 63.27 ± 3.00 j | 67.65 ± 5.19 i | |
| 6 | 65.25 ± 1.82 kl | 72.03 ± 0.00 g | 66.90 ± 5.30 i | 70.52 ± 1.27 h | |
| 8 | 68.10 ± 1.34 j | 75.59 ± 1.92 f | 63.50 ± 3.25 j | 77.05 ± 3.05 f | |
| 10 | 71.55 ± 1.08 gh | 78.38 ± 1.08 d | 58.67 ± 1.64 l | 74.18 ± 2.18 g | |
| 0.8 | 2 | 61.78 ± 0.92 no | 60.63 ± 3.96 o | 67.45 ± 5.18 i | 71.49 ± 6.11 h |
| 4 | 69.60 ± 0.76 ij | 69.16 ± 1.02 ij | 71.18 ± 4.93 h | 75.95 ± 3.00 f | |
| 6 | 71.56 ± 1.11 gh | 75.76 ± 1.27 ef | 74.09 ± 1.95 g | 81.37 ± 3.21 d | |
| 8 | 75.52 ± 3.18 f | 82.47 ± 0.67 c | 80.95 ± 2.72 d | 85.53 ± 2.20 c | |
| 10 | 80.95 ± 1.52 c | 88.86 ± 4.27 b | 85.94 ± 3.30 c | 88.82 ± 1.09 b | |
| 1.0 | 2 | 62.78 ± 1.23 mn | 65.35 ± 4.08 kl | 70.23 ± 5.18 h | 76.84 ± 6.42 f |
| 4 | 70.04 ± 0.76 hi | 73.19 ± 2.31 g | 75.62 ± 2.04 fg | 79.14 ± 5.99 e | |
| 6 | 77.41 ± 3.80 de | 80.76 ± 2.45 c | 80.93 ± 2.41 d | 86.22 ± 2.57 c | |
| 8 | 82.41 ± 3.68 c | 88.85 ± 1.57 b | 81.95 ± 2.58 d | 88.78 ± 2.24 b | |
| 10 | 89.73 ± 1.86 b | 95.69 ± 1.08 a | 84.64 ± 1.82 c | 92.34 ± 2.07 a | |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, P.; Cao, Z.; Wu, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, X. The Effect and Action Mechanisms of Oligochitosan on Control of Stem Dry Rot of Zanthoxylum bungeanum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071044
Li P, Cao Z, Wu Z, Wang X, Li X. The Effect and Action Mechanisms of Oligochitosan on Control of Stem Dry Rot of Zanthoxylum bungeanum. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(7):1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071044
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Peiqin, Zhimin Cao, Zhou Wu, Xing Wang, and Xiuhong Li. 2016. "The Effect and Action Mechanisms of Oligochitosan on Control of Stem Dry Rot of Zanthoxylum bungeanum" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 7: 1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071044
APA StyleLi, P., Cao, Z., Wu, Z., Wang, X., & Li, X. (2016). The Effect and Action Mechanisms of Oligochitosan on Control of Stem Dry Rot of Zanthoxylum bungeanum. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(7), 1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071044