Astrocyte Aquaporin Dynamics in Health and Disease
Abstract
:1. Water Homeostasis, Brain Edema, and Astrocytes
2. Aquaporin Types and Their Isoforms in Astrocytes
2.1. Aquaporin 1
2.1.1. Aquaporin 1 (AQP1) in the Central Nervous System (CNS): Expression in Physiological and Pathological Conditions
2.1.2. Water Permeability of AQP1
2.2. Aquaporin 4
2.2.1. AQP4 in the CNS: Expression in Physiological Conditions
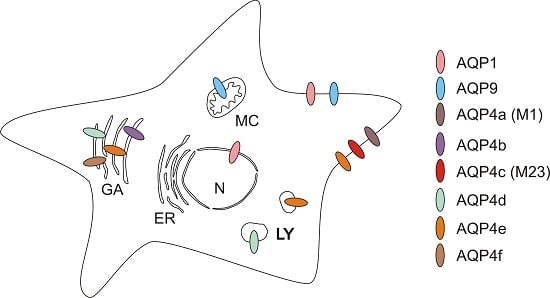
2.2.2. Intracellular Distribution of AQP4
2.2.3. Orthogonal Arrays of Particles
2.2.4. AQP4 Water Permeability Regulation in Astrocytes
2.2.5. Altered Expression of Astrocytic AQP4 in Pathologic Conditions
2.3. Aquaglyceroporin 9
2.3.1. AQP9 in the CNS: Expression in Physiological Conditions
2.3.2. Intracellular Distribution of AQP9
2.3.3. The Role of AQP9 in the CNS
2.3.4. Permeability Regulation and Expression of AQP9 in Pathological Conditions
3. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AQP | aquaporin |
| OAP | orthogonal array of particles |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| CPE | choroid plexus epithelium |
| CSF | cerebrospinal fluid |
| MS | multiple sclerosis |
| AD | Alzheimer disease |
| PD | Parkinson disease |
| CJD | Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease |
| CAA | cerebral amyloid angiopathy |
| PKA | protein kinase A |
| PKC | protein kinase C |
References
- Amiry-Moghaddam, M.; Ottersen, O.P. The molecular basis of water transport in the brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadoun, S.; Papadopoulos, M.C. Aquaporin-4 in brain and spinal cord oedema. Neuroscience 2010, 168, 1036–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokum, J.A.; Gerzanich, V.; Simard, J.M. Molecular pathophysiology of cerebral edema. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2016, 36, 513–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harukuni, I.; Kirsch, J.R.; Bhardwaj, A. Cerebral resuscitation: Role of osmotherapy. J. Anesth. 2002, 16, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardjan, N.; Horvat, A.; Anderson, J.E.; Yu, D.; Croom, D.; Zeng, X.; Luznik, Z.; Kreft, M.; Teng, Y.D.; Kirov, S.A.; et al. Adrenergic activation attenuates astrocyte swelling induced by hypotonicity and neurotrauma. Glia 2016, 64, 1034–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pangrsic, T.; Potokar, M.; Haydon, P.; Zorec, R.; Kreft, M. Astrocyte swelling leads to membrane unfolding, not membrane insertion. J. Neurochem. 2006, 99, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thrane, A.S.; Rappold, P.M.; Fujita, T.; Torres, A.; Bekar, L.K.; Takano, T.; Peng, W.; Wang, F.; Thrane, V.R.; Enger, R.; et al. Critical role of aquaporin-4 (AQP4) in astrocytic Ca2+ signaling events elicited by cerebral edema. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 846–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risher, W.C.; Andrew, R.D.; Kirov, S.A. Real-time passive volume responses of astrocytes to acute osmotic and ischemic stress in cortical slices and in vivo revealed by two-photon microscopy. Glia 2009, 57, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verkhratsky, A.; Butt, A.M. Glial Physiology and Pathophysiology; Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, UK, 2013; p. 560. [Google Scholar]
- Pekny, M.; Pekna, M. Astrocyte reactivity and reactive astrogliosis: Costs and benefits. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 1077–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedergaard, M.; Ransom, B.; Goldman, S. New roles for astrocytes: Redefining the functional architecture of the brain. Trends Neurosci. 2003, 26, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, B. Neuron-astrocyte signaling in the development and plasticity of neural circuits. Neurosignals 2008, 16, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haydon, P. Glia: Listening and talking to the synapse. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 2, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, C.; Nedergaard, M. Astrocyte-mediated control of cerebral microcirculation. Trends Neurosci. 2003, 26, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonta, M.; Angulo, M.; Gobbo, S.; Rosengarten, B.; Hossmann, K.; Pozzan, T.; Carmignoto, G. Neuron-to-astrocyte signaling is central to the dynamic control of brain microcirculation. Nat. Neurosci. 2003, 6, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, G.; Mulligan, S.; MacVicar, B. Astrocyte control of the cerebrovasculature. Glia 2007, 55, 1214–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Benveniste, E. Immune function of astrocytes. Glia 2001, 36, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Keyser, J.; Zeinstra, E.; Frohman, E. Are astrocytes central players in the pathophysiology of multiple sclerosis? Arch. Neurol. 2003, 60, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, N.; Rönnbäck, L.; Hansson, E. Astrocyte–endothelial interactions at the blood–brain barrier. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, C.; Poon, W.S.; Ng, H.K.; Pang, J.C.; Chan, Y. Heterogeneous responses of aquaporin-4 in oedema formation in a replicated severe traumatic brain injury model in rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2001, 301, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nase, G.; Helm, P.J.; Enger, R.; Ottersen, O.P. Water entry into astrocytes during brain edema formation. Glia 2008, 56, 895–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedergaard, M.; Verkhratsky, A. Artifact versus reality—How astrocytes contribute to synaptic events. Glia 2012, 60, 1013–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verkhratsky, A.; Nedergaard, M. Astroglial cradle in the life of the synapse. Philos. Trans. R Soc. Lond. B 2014, 369, 20130595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parpura, V.; Zorec, R. Gliotransmission: Exocytotic release from astrocytes. Brain Res. Rev. 2010, 63, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborne, K.D.; Lee, W.; Malarkey, E.B.; Irving, A.J.; Parpura, V. Dynamic imaging of cannabinoid receptor 1 vesicular trafficking in cultured astrocytes. ASN Neuro 2009, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreft, M.; Stenovec, M.; Rupnik, M.; Grilc, S.; Krzan, M.; Potokar, M.; Pangrsic, T.; Haydon, P.; Zorec, R. Properties of Ca2+-dependent exocytosis in cultured astrocytes. Glia 2004, 46, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorec, R.; Araque, A.; Carmignoto, G.; Haydon, P.G.; Verkhratsky, A.; Parpura, V. Astroglial excitability and gliotransmission: An appraisal of Ca2+ as a signalling route. ASN Neuro 2012, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parpura, V.; Heneka, M.T.; Montana, V.; Oliet, S.H.; Schousboe, A.; Haydon, P.G.; Stout, R.F.; Spray, D.C.; Reichenbach, A.; Pannicke, T.; et al. Glial cells in (patho)physiology. J. Neurochem. 2012, 121, 4–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parpura, V.; Grubišić, V.; Verkhratsky, A. Ca2+ sources for the exocytotic release of glutamate from astrocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 984–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gucek, A.; Vardjan, N.; Zorec, R. Exocytosis in astrocytes: Transmitter release and membrane signal regulation. Neurochem. Res. 2012, 37, 2351–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potokar, M.; Kreft, M.; Pangrsic, T.; Zorec, R. Vesicle mobility studied in cultured astrocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 329, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potokar, M.; Kreft, M.; Li, L.; Daniel Andersson, J.; Pangrsic, T.; Chowdhury, H.; Pekny, M.; Zorec, R. Cytoskeleton and vesicle mobility in astrocytes. Traffic 2007, 8, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardjan, N.; Verkhratsky, A.; Zorec, R. Pathologic potential of astrocytic vesicle traffic: New targets to treat neurologic diseases? Cell Transplant. 2015, 24, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potokar, M.; Vardjan, N.; Stenovec, M.; Gabrijel, M.; Trkov, S.; Jorgačevski, J.; Kreft, M.; Zorec, R. Astrocytic vesicle mobility in health and disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 11238–11258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azevedo, F.A.; Carvalho, L.R.; Grinberg, L.T.; Farfel, J.M.; Ferretti, R.E.; Leite, R.E.; Jacob Filho, W.; Lent, R.; Herculano-Houzel, S. Equal numbers of neuronal and nonneuronal cells make the human brain an isometrically scaled-up primate brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 2009, 513, 532–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bushong, E.A.; Martone, M.E.; Jones, Y.Z.; Ellisman, M.H. Protoplasmic astrocytes in CA1 stratum radiatum occupy separate anatomical domains. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Halassa, M.M.; Fellin, T.; Haydon, P.G. The tripartite synapse: Roles for gliotransmission in health and disease. Trends Mol. Med. 2007, 13, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agre, P.; Preston, G.M.; Smith, B.L.; Jung, J.S.; Raina, S.; Moon, C.; Guggino, W.B.; Nielsen, S. Aquaporin CHIP: The archetypal molecular water channel. Am. J. Physiol. 1993, 265, F463–F476. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nagelhus, E.A.; Ottersen, O.P. Physiological roles of aquaporin-4 in brain. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 1543–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, S.; Nagelhus, E.A.; Amiry-Moghaddam, M.; Bourque, C.; Agre, P.; Ottersen, O.P. Specialized membrane domains for water transport in glial cells: High-resolution immunogold cytochemistry of aquaporin-4 in rat brain. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Agre, P.; Bonhivers, M.; Borgnia, M.J. The aquaporins, blueprints for cellular plumbing systems. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 14659–14662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.S.; Bhat, R.V.; Preston, G.M.; Guggino, W.B.; Baraban, J.M.; Agre, P. Molecular characterization of an aquaporin cDNA from brain: Candidate osmoreceptor and regulator of water balance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 13052–13056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulders, S.M.; Preston, G.M.; Deen, P.M.; Guggino, W.B.; van Os, C.H.; Agre, P. Water channel properties of major intrinsic protein of lens. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 9010–9016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulders, S.M.; van der Kemp, A.J.; Terlouw, S.A.; van Boxtel, H.A.; van Os, C.H.; Deen, P.M. The exchange of functional domains among aquaporins with different transport characteristics. Pflugers. Arch. 1998, 436, 599–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badaut, J.; Fukuda, A.M.; Jullienne, A.; Petry, K.G. Aquaporin and brain diseases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1840, 1554–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondy, C.; Chin, E.; Smith, B.L.; Preston, G.M.; Agre, P. Developmental gene expression and tissue distribution of the CHIP28 water-channel protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 4500–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh, J.; Tabunoki, H.; Yamamura, T.; Arima, K.; Konno, H. Human astrocytes express aquaporin-1 and aquaporin-4 in vitro and in vivo. Neuropathology 2007, 27, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badaut, J.; Hirt, L.; Granziera, C.; Bogousslavsky, J.; Magistretti, P.J.; Regli, L. Astrocyte-specific expression of aquaporin-9 in mouse brain is increased after transient focal cerebral ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2001, 21, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badaut, J.; Petit, J.M.; Brunet, J.F.; Magistretti, P.J.; Charriaut-Marlangue, C.; Regli, L. Distribution of aquaporin 9 in the adult rat brain: Preferential expression in catecholaminergic neurons and in glial cells. Neuroscience 2004, 128, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkjaer, M.; Vajda, Z.; Nejsum, L.N.; Kwon, T.; Jensen, U.B.; Amiry-Moghaddam, M.; Frøkiaer, J.; Nielsen, S. Immunolocalization of AQP9 in liver, epididymis, testis, spleen, and brain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 276, 1118–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshio, K.; Watanabe, H.; Song, Y.; Verkman, A.S.; Manley, G.T. Reduced cerebrospinal fluid production and intracranial pressure in mice lacking choroid plexus water channel aquaporin-1. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 76–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agre, P.; Brown, D.; Nielsen, S. Aquaporin water channels: Unanswered questions and unresolved controversies. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1995, 7, 472–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, G.M.; Agre, P. Isolation of the cDNA for erythrocyte integral membrane protein of 28 kilodaltons: Member of an ancient channel family. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 11110–11114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hoek, A.N.; Verkman, A.S. Functional reconstitution of the isolated erythrocyte water channel CHIP28. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 18267–18269. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, S.; Smith, B.L.; Christensen, E.I.; Agre, P. Distribution of the aquaporin CHIP in secretory and resorptive epithelia and capillary endothelia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 7275–7279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthony, T.L.; Brooks, H.L.; Boassa, D.; Leonov, S.; Yanochko, G.M.; Regan, J.W.; Yool, A.J. Cloned human aquaporin-1 is a cyclic GMP-gated ion channel. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000, 57, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boassa, D.; Stamer, W.D.; Yool, A.J. Ion channel function of aquaporin-1 natively expressed in choroid plexus. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 7811–7819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saparov, S.M.; Kozono, D.; Rothe, U.; Agre, P.; Pohl, P. Water and ion permeation of aquaporin-1 in planar lipid bilayers. Major differences in structural determinants and stoichiometry. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 31515–31520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, H.; Lian, S.C.; Finkbeiner, W.E.; Verkman, A.S. Extrarenal tissue distribution of CHIP28 water channels by in situ hybridization and antibody staining. Am. J. Physiol. 1994, 266, C893–C903. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nandasena, B.G.; Suzuki, A.; Aita, M.; Kawano, Y.; Nozawa-Inoue, K.; Maeda, T. Immunolocalization of aquaporin-1 in the mechanoreceptive Ruffini endings in the periodontal ligament. Brain Res. 2007, 1157, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oshio, K.; Watanabe, H.; Yan, D.; Verkman, A.S.; Manley, G.T. Impaired pain sensation in mice lacking Aquaporin-1 water channels. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 341, 1022–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misawa, T.; Arima, K.; Mizusawa, H.; Satoh, J. Close association of water channel AQP1 with amyloid-β deposition in Alzheimer disease brains. Acta Neuropathol. 2008, 116, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arciénega, I.I.; Brunet, J.F.; Bloch, J.; Badaut, J. Cell locations for AQP1, AQP4 and 9 in the non-human primate brain. Neuroscience 2010, 167, 1103–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanahan, C.M.; Connolly, D.L.; Tyson, K.L.; Cary, N.R.; Osbourn, J.K.; Agre, P.; Weissberg, P.L. Aquaporin-1 is expressed by vascular smooth muscle cells and mediates rapid water transport across vascular cell membranes. J. Vasc. Res. 1999, 36, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, E.; Barrachina, M.; Rodríguez, A.; Torrejón-Escribano, B.; Boada, M.; Hernández, I.; Sánchez, M.; Ferrer, I. Aquaporin expression in the cerebral cortex is increased at early stages of Alzheimer disease. Brain Res. 2007, 1128, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badaut, J.; Brunet, J.F.; Grollimund, L.; Hamou, M.F.; Magistretti, P.J.; Villemure, J.G.; Regli, L. Aquaporin 1 and aquaporin 4 expression in human brain after subarachnoid hemorrhage and in peritumoral tissue. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2003, 86, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Costa, C.; Tortosa, R.; Rodríguez, A.; Ferrer, I.; Torres, J.M.; Bassols, A.; Pumarola, M. Aquaporin 1 and aquaporin 4 overexpression in bovine spongiform encephalopathy in a transgenic murine model and in cattle field cases. Brain Res. 2007, 1175, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.E.; Ryu, H.J.; Yeo, S.I.; Seo, C.H.; Lee, B.C.; Choi, I.G.; Kim, D.S.; Kang, T.C. Differential expressions of aquaporin subtypes in astroglia in the hippocampus of chronic epileptic rats. Neuroscience 2009, 163, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, A.; Pérez-Gracia, E.; Espinosa, J.C.; Pumarola, M.; Torres, J.M.; Ferrer, I. Increased expression of water channel aquaporin 1 and aquaporin 4 in Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease and in bovine spongiform encephalopathy-infected bovine-PrP transgenic mice. Acta Neuropathol. 2006, 112, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadoun, S.; Papadopoulos, M.C.; Davies, D.C.; Bell, B.A.; Krishna, S. Increased aquaporin 1 water channel expression in human brain tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 87, 621–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicchia, G.P.; Rossi, A.; Mola, M.G.; Procino, G.; Frigeri, A.; Svelto, M. Actin cytoskeleton remodeling governs aquaporin-4 localization in astrocytes. Glia 2008, 56, 1755–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potokar, M.; Stenovec, M.; Jorgačevski, J.; Holen, T.; Kreft, M.; Ottersen, O.P.; Zorec, R. Regulation of AQP4 surface expression via vesicle mobility in astrocytes. Glia 2013, 61, 917–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelenina, M. Regulation of brain aquaporins. Neurochem. Int. 2010, 57, 468–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; Patil, R.V. Protein kinase A-dependent phosphorylation of aquaporin-1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 273, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zitron, E.; Hömme, M.; Kihm, L.; Morath, C.; Scherer, D.; Hegge, S.; Thomas, D.; Schmitt, C.P.; Zeier, M.; et al. Aquaporin-1 channel function is positively regulated by protein kinase C. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 20933–20940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Verkman, A.S. Water and glycerol permeabilities of aquaporins 1–5 and MIP determined quantitatively by expression of epitope-tagged constructs in Xenopus oocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 16140–16146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, R.V.; Han, Z.; Wax, M.B. Regulation of water channel activity of aquaporin 1 by arginine vasopressin and atrial natriuretic peptide. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 238, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marinelli, R.A.; Tietz, P.S.; Pham, L.D.; Rueckert, L.; Agre, P.; LaRusso, N.F. Secretin induces the apical insertion of aquaporin-1 water channels in rat cholangiocytes. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 276, G280–G286. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, H.; Ma, T.; Skach, W.; Matthay, M.A.; Verkman, A.S. Molecular cloning of a mercurial-insensitive water channel expressed in selected water-transporting tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 5497–5500. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frigeri, A.; Gropper, M.A.; Umenishi, F.; Kawashima, M.; Brown, D.; Verkman, A.S. Localization of MIWC and GLIP water channel homologs in neuromuscular, epithelial and glandular tissues. J. Cell Sci. 1995, 108, 2993–3002. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frigeri, A.; Gropper, M.A.; Turck, C.W.; Verkman, A.S. Immunolocalization of the mercurial-insensitive water channel and glycerol intrinsic protein in epithelial cell plasma membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 4328–4331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagelhus, E.A.; Veruki, M.L.; Torp, R.; Haug, F.M.; Laake, J.H.; Nielsen, S.; Agre, P.; Ottersen, O.P. Aquaporin-4 water channel protein in the rat retina and optic nerve: Polarized expression in Müller cells and fibrous astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 2506–2519. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Badaut, J.; Nehlig, A.; Verbavatz, J.; Stoeckel, M.; Freund-Mercier, M.J.; Lasbennes, F. Hypervascularization in the magnocellular nuclei of the rat hypothalamus: Relationship with the distribution of aquaporin-4 and markers of energy metabolism. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2000, 12, 960–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badaut, J.; Verbavatz, J.M.; Freund-Mercier, M.J.; Lasbennes, F. Presence of aquaporin-4 and muscarinic receptors in astrocytes and ependymal cells in rat brain: A clue to a common function? Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 292, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rash, J.E.; Yasumura, T.; Hudson, C.S.; Agre, P.; Nielsen, S. Direct immunogold labeling of aquaporin-4 in square arrays of astrocyte and ependymocyte plasma membranes in rat brain and spinal cord. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 11981–11986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirt, B.; Gleiser, C.; Eckhard, A.; Mack, A.F.; Müller, M.; Wolburg, H.; Löwenheim, H. All functional aquaporin-4 isoforms are expressed in the rat cochlea and contribute to the formation of orthogonal arrays of particles. Neuroscience 2011, 189, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takumi, Y.; Nagelhus, E.A.; Eidet, J.; Matsubara, A.; Usami, S.; Shinkawa, H.; Nielsen, S.; Ottersen, O.P. Select types of supporting cell in the inner ear express aquaporin-4 water channel protein. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1998, 10, 3584–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frigeri, A.; Nicchia, G.P.; Verbavatz, J.M.; Valenti, G.; Svelto, M. Expression of aquaporin-4 in fast-twitch fibers of mammalian skeletal muscle. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 102, 695–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moe, S.E.; Sorbo, J.G.; Sogaard, R.; Zeuthen, T.; Petter Ottersen, O.; Holen, T. New isoforms of rat aquaporin-4. Genomics 2008, 91, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neely, J.D.; Christensen, B.M.; Nielsen, S.; Agre, P. Heterotetrameric composition of aquaporin-4 water channels. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 11156–11163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Bellis, M.; Pisani, F.; Mola, M.G.; Basco, D.; Catalano, F.; Nicchia, G.P.; Svelto, M.; Frigeri, A. A novel human aquaporin-4 splice variant exhibits a dominant-negative activity: A new mechanism to regulate water permeability. Mol. Biol. Cell 2014, 25, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Lee, M.D.; Smith, B.L.; Jung, J.S.; Agre, P.; Verdijk, M.A.; Merkx, G.; Rijss, J.P.; Deen, P.M. The human AQP4 gene: Definition of the locus encoding two water channel polypeptides in brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 10908–10912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Ma, T.; Verkman, A.S. cDNA cloning, gene organization, and chromosomal localization of a human mercurial insensitive water channel. Evidence for distinct transcriptional units. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 22907–22913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furman, C.S.; Gorelick-Feldman, D.A.; Davidson, K.G.; Yasumura, T.; Neely, J.D.; Agre, P.; Rash, J.E. Aquaporin-4 square array assembly: Opposing actions of M1 and M23 isoforms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13609–13614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crane, J.M.; van Hoek, A.N.; Skach, W.R.; Verkman, A.S. Aquaporin-4 dynamics in orthogonal arrays in live cells visualized by quantum dot single particle tracking. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 3369–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, A.; Crane, J.M.; Verkman, A.S. Aquaporin-4 Mz isoform: Brain expression, supramolecular assembly and neuromyelitis optica antibody binding. Glia 2011, 59, 1056–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørbø, J.G.; Fleckenstein, B.; Ottersen, O.P.; Holen, T. Small-scale purification and mass spectrometry analysis reveal a third aquaporin-4 protein isoform of 36 kDa in rat brain. J. Neurosci. Methods 2012, 211, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorbo, J.G.; Moe, S.E.; Ottersen, O.P.; Holen, T. The molecular composition of square arrays. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 2631–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madrid, R.; Le Maout, S.; Barrault, M.B.; Janvier, K.; Benichou, S.; Mérot, J. Polarized trafficking and surface expression of the AQP4 water channel are coordinated by serial and regulated interactions with different clathrin-adaptor complexes. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 7008–7021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hub, J.S.; de Groot, B.L.; Grubmüller, H.; Groenhof, G. Quantifying artifacts in Ewald simulations of inhomogeneous systems with a net charge. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2014, 10, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, A.; van Hoek, A.N.; Yeager, M.; Verkman, A.S.; Mitra, A.K. Three-dimensional organization of a human water channel. Nature 1997, 387, 627–630. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marples, D.; Schroer, T.A.; Ahrens, N.; Taylor, A.; Knepper, M.A.; Nielsen, S. Dynein and dynactin colocalize with AQP2 water channels in intracellular vesicles from kidney collecting duct. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 274, F384–F394. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- King, L.S.; Kozono, D.; Agre, P. From structure to disease: The evolving tale of aquaporin biology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasui, M.; Kwon, T.H.; Knepper, M.A.; Nielsen, S.; Agre, P. Aquaporin-6: An intracellular vesicle water channel protein in renal epithelia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 5808–5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasui, M.; Hazama, A.; Kwon, T.H.; Nielsen, S.; Guggino, W.B.; Agre, P. Rapid gating and anion permeability of an intracellular aquaporin. Nature 1999, 402, 184–187. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gorelick, D.A.; Praetorius, J.; Tsunenari, T.; Nielsen, S.; Agre, P. Aquaporin-11: A channel protein lacking apparent transport function expressed in brain. BMC Biochem. 2006, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, S.; Muta, K.; Sonoda, H.; Kato, A.; Abdeen, A.; Ikeda, M. The role of cysteine 227 in subcellular localization, water permeability, and multimerization of aquaporin-11. FEBS Open Bio 2014, 4, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiroaki, Y.; Tani, K.; Kamegawa, A.; Gyobu, N.; Nishikawa, K.; Suzuki, H.; Walz, T.; Sasaki, S.; Mitsuoka, K.; Kimura, K.; et al. Implications of the aquaporin-4 structure on array formation and cell adhesion. J. Mol. Biol. 2006, 355, 628–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verbavatz, J.M.; Ma, T.; Gobin, R.; Verkman, A.S. Absence of orthogonal arrays in kidney, brain and muscle from transgenic knockout mice lacking water channel aquaporin-4. J. Cell Sci. 1997, 110, 2855–2860. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rash, J.E.; Davidson, K.G.; Yasumura, T.; Furman, C.S. Freeze-fracture and immunogold analysis of aquaporin-4 (AQP4) square arrays, with models of AQP4 lattice assembly. Neuroscience 2004, 129, 915–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajima, M.; Crane, J.M.; Verkman, A.S. Aquaporin-4 (AQP4) associations and array dynamics probed by photobleaching and single-molecule analysis of green fluorescent protein-AQP4 chimeras. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 8163–8170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crane, J.M.; Bennett, J.L.; Verkman, A.S. Live cell analysis of aquaporin-4 M1/M23 interactions and regulated orthogonal array assembly in glial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 35850–35860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crane, J.M.; Verkman, A.S. Determinants of aquaporin-4 assembly in orthogonal arrays revealed by live-cell single-molecule fluorescence imaging. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iliff, J.J.; Wang, M.; Liao, Y.; Plogg, B.A.; Peng, W.; Gundersen, G.A.; Benveniste, H.; Vates, G.E.; Deane, R.; Goldman, S.A.; et al. A paravascular pathway facilitates CSF flow through the brain parenchyma and the clearance of interstitial solutes, including amyloid β. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 147ra111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silberstein, C.; Bouley, R.; Huang, Y.; Fang, P.; Pastor-Soler, N.; Brown, D.; van Hoek, A.N. Membrane organization and function of M1 and M23 isoforms of aquaporin-4 in epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2004, 287, F501–F511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, N.; Sobue, K.; Fujita, M.; Katsuya, H.; Asai, K. Differential regulation of aquaporin-5 and -9 expression in astrocytes by protein kinase A. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2002, 104, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assentoft, M.; Kaptan, S.; Fenton, R.A.; Hua, S.Z.; de Groot, B.L.; MacAulay, N. Phosphorylation of rat aquaporin-4 at Ser111 is not required for channel gating. Glia 2013, 61, 1101–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCoy, E.S.; Haas, B.R.; Sontheimer, H. Water permeability through aquaporin-4 is regulated by protein kinase C and becomes rate-limiting for glioma invasion. Neuroscience 2010, 168, 971–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, N.; Sobue, K.; Miyachi, T.; Inagaki, M.; Miura, Y.; Katsuya, H.; Asai, K. Differential regulation of aquaporin expression in astrocytes by protein kinase C. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2001, 95, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenovec, M.; Trkov, S.; Lasič, E.; Terzieva, S.; Kreft, M.; Rodríguez Arellano, J.J.; Parpura, V.; Verkhratsky, A.; Zorec, R. Expression of familial Alzheimer disease presenilin 1 gene attenuates vesicle traffic and reduces peptide secretion in cultured astrocytes devoid of pathologic tissue environment. Glia 2016, 64, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, A.; Baumgart, F.; van Hoek, A.N.; Verkman, A.S. Post-Golgi supramolecular assembly of aquaporin-4 in orthogonal arrays. Traffic 2012, 13, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, A.; Moritz, T.J.; Ratelade, J.; Verkman, A.S. Super-resolution imaging of aquaporin-4 orthogonal arrays of particles in cell membranes. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 4405–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisani, F.; Rossi, A.; Nicchia, G.P.; Svelto, M.; Frigeri, A. Translational regulation mechanisms of aquaporin-4 supramolecular organization in astrocytes. Glia 2011, 59, 1923–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Nishikawa, K.; Hiroaki, Y.; Fujiyoshi, Y. Formation of aquaporin-4 arrays is inhibited by palmitoylation of N-terminal cysteine residues. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1778, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eid, T.; Lee, T.S.; Thomas, M.J.; Amiry-Moghaddam, M.; Bjørnsen, L.P.; Spencer, D.D.; Agre, P.; Ottersen, O.P.; de Lanerolle, N.C. Loss of perivascular aquaporin 4 may underlie deficient water and K+ homeostasis in the human epileptogenic hippocampus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 1193–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.S.; Eid, T.; Mane, S.; Kim, J.H.; Spencer, D.D.; Ottersen, O.P.; de Lanerolle, N.C. Aquaporin-4 is increased in the sclerotic hippocampus in human temporal lobe epilepsy. Acta Neuropathol. 2004, 108, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moftakhar, P.; Lynch, M.D.; Pomakian, J.L.; Vinters, H.V. Aquaporin expression in the brains of patients with or without cerebral amyloid angiopathy. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2010, 69, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshi, A.; Yamamoto, T.; Shimizu, K.; Ugawa, Y.; Nishizawa, M.; Takahashi, H.; Kakita, A. Characteristics of aquaporin expression surrounding senile plaques and cerebral amyloid angiopathy in Alzheimer disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 71, 750–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Lunde, L.K.; Nuntagij, P.; Oguchi, T.; Camassa, L.M.; Nilsson, L.N.; Lannfelt, L.; Xu, Y.; Amiry-Moghaddam, M.; Ottersen, O.P.; et al. Loss of astrocyte polarization in the tg-ArcSwe mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2011, 27, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aoki-Yoshino, K.; Uchihara, T.; Duyckaerts, C.; Nakamura, A.; Hauw, J.J.; Wakayama, Y. Enhanced expression of aquaporin 4 in human brain with inflammatory diseases. Acta Neuropathol. 2005, 110, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadoun, S.; Papadopoulos, M.C.; Davies, D.C.; Krishna, S.; Bell, B.A. Aquaporin-4 expression is increased in oedematous human brain tumours. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2002, 72, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, K.; Uchihara, T.; Tsuchiya, K.; Nakamura, A.; Ikeda, K.; Wakayama, Y. Enhanced expression of aquaporin 4 in human brain with infarction. Acta Neuropathol. 2003, 106, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukaguchi, H.; Shayakul, C.; Berger, U.V.; Mackenzie, B.; Devidas, S.; Guggino, W.B.; van Hoek, A.N.; Hediger, M.A. Molecular characterization of a broad selectivity neutral solute channel. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 24737–24743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukaguchi, H.; Weremowicz, S.; Morton, C.C.; Hediger, M.A. Functional and molecular characterization of the human neutral solute channel aquaporin-9. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 277, F685–F696. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ishibashi, K.; Kuwahara, M.; Gu, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Marumo, F.; Sasaki, S. Cloning and functional expression of a new aquaporin (AQP9) abundantly expressed in the peripheral leukocytes permeable to water and urea, but not to glycerol. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 244, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, G.; Sun, S.Q.; Yuan, D.L. Expression of the water channel protein aquaporin-9 in human astrocytic tumours: Correlation with pathological grade. J. Int. Med. Res. 2008, 36, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jelen, S.; Parm Ulhøi, B.; Larsen, A.; Frøkiær, J.; Nielsen, S.; Rützler, M. AQP9 expression in glioblastoma multiforme tumors is limited to a small population of astrocytic cells and CD15+/CalB+ leukocytes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshio, K.; Binder, D.K.; Yang, B.; Schecter, S.; Verkman, A.S.; Manley, G.T. Expression of aquaporin water channels in mouse spinal cord. Neuroscience 2004, 127, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicchia, G.P.; Frigeri, A.; Nico, B.; Ribatti, D.; Svelto, M. Tissue distribution and membrane localization of aquaporin-9 water channel: Evidence for sex-linked differences in liver. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2001, 49, 1547–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiry-Moghaddam, M.; Lindland, H.; Zelenin, S.; Roberg, B.A.; Gundersen, B.B.; Petersen, P.; Rinvik, E.; Torgner, I.A.; Ottersen, O.P. Brain mitochondria contain aquaporin water channels: Evidence for the expression of a short AQP9 isoform in the inner mitochondrial membrane. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1459–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badaut, J.; Brunet, J.F.; Guérin, C.; Regli, L.; Pellerin, L. Alteration of glucose metabolism in cultured astrocytes after AQP9-small interference RNA application. Brain Res. 2012, 1473, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| AQP Type | AQP Isoforms | Permeability to Water | Permeability to Small Solutes (i.e., Glycerol, Urea, Monocarboxylates) | Ability to Form OAPs in the Plasma Membrane |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AQP1 | AQP1 | Yes | No | No |
| AQP4 | AQP4a (M1) | Yes | No | Only together with AQP4c |
| AQP4c (M23) | Yes | No | Yes | |
| AQP4e | Yes | No | Only together with AQP4c | |
| AQP4b | ? | No | N/A | |
| AQP4d | ? | No | N/A | |
| AQP4f | ? | No | N/A | |
| AQP9 | AQP9 ~32 kDa (is AQP9 ~30 kDa its splicing isoform?) | Yes | Yes | No |
| AQP9 ~25 kDa | Yes | Yes | No |
| Cell Type | Reference |
|---|---|
| Erythrocytes | [53] |
| Renal epithelial cells | [53] |
| Endothelial cells (except central nervous system (CNS)) | [55] |
| Epithelial cells of the choroid plexus | [55,59] |
| Epithelial cells of the iris, ciliary body, lens, trachea, kidney, colonic crypt, sweat glands, pancreatic acini, gallbladder epithelium, placental syncytial trophoblast cells | [55,59] |
| Sensory nerve fibers in the dorsal horn of the spinal cord and the trigeminal sensory ganglia | [60,61] |
| Reactive astrocytes (human CNS) in Alzheimer disease, Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease, multiple sclerosis, and in ischemic lesions | [47,62] |
| Astrocytes (non-human primate CNS, a subpopulation of white matter astrocytes in Macaca fascicularis) | [63] |
| Schwann cells (Macaca fascicularis CNS) | [63] |
| Trigeminal nerve fibers (Macaca fascicularis CNS) | [63] |
| Neurons on the surface of the pial blood vessels (Macaca fascicularis CNS) | [63] |
| Vascular smooth muscle cells | [64] |
| Cell Type | Reference |
|---|---|
| Astrocytes (brain and spinal cord) | [42,79,80,85] |
| A subpopulation of brain ependymal cells | [40,80,81,85] |
| Retina, iris, ciliary body | [79,81,82] |
| Lung epithelial cells | [79,81] |
| Renal basolateral plasma membrane of collecting duct principal cells, renal papillary vasa recta | [79,81] |
| Colon (villus) epithelial cells | [81] |
| Stomach parietal cells | [80] |
| Excretory tubules of salivary and lacrimal glands | [80] |
| Auditory epithelium of the organ of Corti | [86,87] |
| Skeletal muscle; the sarcolemma of fast-twitch fibers | [80,88] |
| AQP4 Isoforms | Cell Type | Intracellular Localization | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| AQP4a (M1) | Astrocytes | PM | [85,90,95] |
| AQP4c (M23) | Astrocytes, skeletal muscle, kidney | PM | [85,90,95] |
| AQP4e (Mz) | Astrocytes (rat), organ of Corti (rat) | PM, intracellular vesicles, GA, EC | [72,89,96] |
| AQP4b | Astrocytes (rat) | GA | [89] |
| AQP4d | Astrocytes (rat) | GA, EC | [72,89] |
| AQP4f | Astrocytes (rat) | GA | [89] |
| AQP4-Δ | Skeletal muscle | ER, faintly in the PM | [91] |
| Cell Type | Reference |
|---|---|
| Spinal cord and brain: Astrocytes, ependymal cells lining the ventricles and tanycytes, catecholaminergic neurons, endothelial cells of pial vessels, Bergmann glia | [49,50,138] |
| Hepatocytes | [50,139] |
| Testis Leydig cells | [50] |
| Epididymis stereocilia | [50] |
| Spleen leukocytes | [50] |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Potokar, M.; Jorgačevski, J.; Zorec, R. Astrocyte Aquaporin Dynamics in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071121
Potokar M, Jorgačevski J, Zorec R. Astrocyte Aquaporin Dynamics in Health and Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(7):1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071121
Chicago/Turabian StylePotokar, Maja, Jernej Jorgačevski, and Robert Zorec. 2016. "Astrocyte Aquaporin Dynamics in Health and Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 7: 1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071121
APA StylePotokar, M., Jorgačevski, J., & Zorec, R. (2016). Astrocyte Aquaporin Dynamics in Health and Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(7), 1121. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071121