Upregulation of Human ST8Sia VI (α2,8-Sialyltransferase) Gene Expression by Physcion in SK-N-BE(2)-C Human Neuroblastoma Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
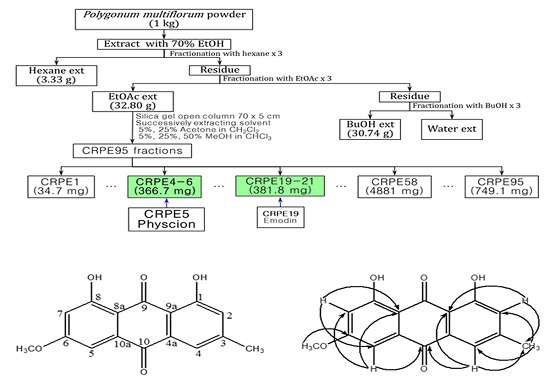
2.1. Isolation and Identification of Physcion
2.2. Effect of Physcion on Gene Expression of hST8Sia VI and Cell Proliferation
2.3. Isolation and Sequence Analysis of the 5′-Flanking Region of the hST8Sia VI Gene
2.4. Promoter Analysis of the 5′-Flanking Region of the hST8Sia VI Gene in Physcion-Induced SK-N-BE(2)-C Cells
2.5. Identification of Physcion-Responsive Element in the Functional −320/−240 Region of hST8Sia VI Promoter
2.6. Transcriptional Activation of hST8Sia VI via ERK and p-38 MAPK Pathways in Physcion-Stimulated SK-N-BE(2)-C Cells
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Extraction, Isolation and Structure Determination of Physcion
4.2. Cell Cultures
4.3. Cell Viability Assay
4.4. Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
4.5. Cloning of the 5′-Flanking Region of the hST8Sia VI Gene and Bioinformatics Analysis
4.6. Construction of Luciferase Reporter Plasmids and Mutagenesis
4.7. Transfection and Luciferase Assay
4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) Assay
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schauer, A. Sialic acids as regulators of molecular and cellular interactions. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2009, 19, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harduin-Lepers, A.; Mollicone, R.; Delannoy, P.; Oriol, R. The animal sialyltransferases and sialyltransferase-related genes: A phylogenetic approach. Glycobiology 2005, 15, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulson, J.C.; Weistein, J.; Schauer, A. Tissue-specific expression of sialyltransferases. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 10931–10934. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Paulson, J.C.; Colley, K.J. Glycosyltransferases: Structure, localization and control of cell type-specific glycosylation. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 17617–17618. [Google Scholar]
- Harduin-Lepers, A.; Vallejo-Ruiz, V.; Krzewinski-Recchi, M.A.; Samyn-Petit, B.; Julien, S.; Delannoy, P. The human sialyltransferase family. Biochimie 2001, 83, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashima, S. Characterization of mouse sialyltransferase genes: Their evolution and diversity. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2008, 72, 1155–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.Y.; Kang, N.Y.; Dae, H.M.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, C.H.; Do, S.I.; Lee, Y.C. Valproic acid-mediated transcriptional regulation of human GM3 synthase (hST3Gal V) in SK-N-BE(2)-C human neuroblastoma cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2008, 29, 999–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.Y.; Dae, H.M.; Song, N.R.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, Y.C. Valproic acid induces transcriptional activation of human GD3 synthase (hST8Sia I) in SK-N-BE(2)-C human neuroblastoma cells. Mol. Cells 2009, 27, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baik, J.S.; Kim, K.S.; Moon, H.I.; An, H.K.; Park, S.J.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, Y.C. Cordycepin-mediated transcriptional regulation of human GD3 synthase (hST8Sia I) in human neuroblastoma SK-N-BE(2)-C cells. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2014, 46, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, C.H.; Son, S.W.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, J.H.; Do, S.I.; Lee, Y.C. Triptolide downregulates human GD3 synthase (hST8Sia I) gene expression in SK-MEL-2 human melanoma cells. Exp. Mol. Med. 2010, 42, 849–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, N.R.; Kim, S.J.; Kwon, H.Y.; Son, S.W.; Kim, K.S.; An, H.B.; Lee, Y.C. Transcriptional activation of human GM3 synthase (hST3Gal V) gene by valproic acid in ARPE-19 human retinal pigment epithelial cells. BMB Rep. 2011, 44, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Lu, G.; Shen, H.M.; Chung, M.C.; Ong, C.N. Anti-cancer properties of anthraquinones from rhubarb. Med. Res. Rev. 2007, 27, 609–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijesekara, I.; Zhang, C.; Ta, Q.V.; Vo, T.S.; Li, Y.X.; Kim, S.K. Physcion from marine-derived fungus Microsporum sp. Induces apoptosis in human cervical carcinoma HeLa cells. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 169, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.L.; Wang, J.B.; Zhou, G.D.; Shan, L.M.; Xiao, X.H. Investigations of free anthraquinones from rhubarb against alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate-induced cholestatic liver injury in rats. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2009, 104, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamokou Jde, D.; Tala, M.F.; Wabo, H.K.; Kuiate, J.R.; Tane, P. Antimicrobial activities of methanol extract and compounds from stem bark of Vismia rubescens. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 124, 571–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Das Sarma, M.; Patra, A.; Hazra, B. Anti-inflammatory and anticancer compounds isolated from Ventilago madraspatana Gaertn., Rubia cordifolia Linn. and Lantana camara Linn. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 62, 1158–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.Y.; Chung, H.J.; Bae, S.Y.; Trung, T.N.; Bae, K.; Lee, S.K. Induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by physcion, an anthraquinone isolated from rhubarb (rhizomes of Rheum tanguticum), in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 19, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Gao, H.; Han, Y.; Ye, J.; Xie, J.; Wang, C. Physcion induces mitochondria-driven apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells via downregulating EMMPRIN. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 764, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.T.; Chen, X.H.; Gao, H.; Ye, J.L.; Wang, C.B. Physcion inhibits the metastatic potential of human colorectal cancer SW620 cells in vitro by suppressing the transcription factor SOX2. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2016, 37, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messeguer, X.; Escudero, R.; Farre, D.; Nunez, O.; Martinez, J.; Alba, M.M. PROMO: Detection of known transcription regulatory elements using species-tailored searches. Bioinformatics 2002, 18, 333–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farré, D.; Roset, R.; Huerta, M.; Adsuara, J.E.; Roselló, L.; Albà, M.M.; Messeguer, X. Identification of patterns in biological sequences at the ALGGEN server: PROMO and MALGEN. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3651–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teintenier-Lelievre, M.; Julien, S.; Juliant, S.; Guerardel, Y.; Duonor-Cerutti, M.; Delannoy, P.; Harduin-Lepers, A. Molecular cloning and expression of a human hST8Sia VI (α2,8-sialyltransferase) responsible for the synthesis of the diSia motif on O-glycosylproteins. Biochem. J. 2005, 393, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, M.L.; Pridans, C.; Nutt, S.L. The regulation of the B-cell gene expression programme by Pax5. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2008, 86, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Brien, P.; Morin, P., Jr.; Ouellette, R.J.; Robichaud, G.A. The Pax-5 gene: A pluripotent regulator of B-cell differentiation and cancer disease. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 7345–7350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, M.; Gruss, P. Pax-5 is expressed at the midbrain-hindbrain boundary during mouse development. Mech. Dev. 1992, 39, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozmik, Z.; Sure, U.; Ruedi, D.; Busslinger, M.; Aguzzi, A. Deregulated expression of PAX5 in medulloblastoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 5709–5713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balasenthil, S.; Gururaj, A.E.; TalUKder, A.H.; Bagheri-Yarmand, R.; Arrington, T.; Haas, B.J.; Braisted, J.C.; Kim, I.; Lee, N.H.; Kumar, R. Identification of Pax5 as a target of MTA1 in B-cell lymphomas. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 7132–7138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanteti, R.; Nallasura, V.; Loganathan, S.; Tretiakova, M.; Kroll, T.; Krishnaswamy, S.; Faoro, L.; Cagle, P.; HUSAin, A.N.; Vokes, E.E.; et al. PAX5 is expressed in small-cell lung cancer and positively regulates c-Met transcription. Lab. Investig. 2009, 89, 301–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagergren, A.; Manetopoulos, C.; Axelson, H.; Sigvardsson, M. Neuroblastoma and pre-B lymphoma cells share expression of key transcription factors but display tissue restricted target gene expression. BMC Cancer 2004, 4, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baumann Kubetzko, F.B.; Di Paolo, C.; Maag, C.; Meier, R.; Schafer, B.W.; Betts, D.R.; Stahel, R.A.; Himmelmann, A. The PAX5 oncogene is expressed in N-type neuroblastoma cells and increases tumorigenicity of a S-type cell line. Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 1839–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.H.; Tsai, C.M.; Lin, K.I.; Khoo, K.H. Advanced mass spectRometry and chemical analyses reveal the presence of terminal disialyl motif on mouse B-cell glycoproteins. Glycobiology 2013, 23, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.J.; Jin, M.L.; An, H.K.; Kim, K.S.; Ko, M.J.; Kim, C.M.; Choi, Y.W.; Lee, Y.C. Emodin induces neurite outgrowth through PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β-mediated signaling pathways in Neuro2a cells. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 588, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, X.; Sun, A.; Liu, R. Preparative isolation and purification of five compounds from the Chinese medicinal herb Polygonum cuspidatum Sieb. et Zucc by high-speed counter-current chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1097, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Li, A.; Sun, A. Preparative isolation and purification of hydroxyanthraquinones and cinnamic acid from the Chinese medicinal herb Rheum officinale Baill. by high-speed counter-current chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1052, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, H.K.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, K.S.; Mun, S.W.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, Y.C. Serum deprivation-induced human GM3 synthase (hST3Gal V) gene expression is mediated by Runx2 in human osteoblastic MG-63 cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 17, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Primer | Sequence | Strand | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| hST8Sia VI | 5′-CCCTATTTCTGGAGGACATTGCAACCTA-3′ | Sense | RT-PCR |
| hST8Sia VI | 5′-GTTGGAGGATCTGGCTGTATTCTTTG-3′ | Antisense | RT-PCR |
| β-actin | 5′-CAAGAGATGGCCACGGCTGCT-3′ | Sense | RT-PCR |
| β-actin | 5′-TCCTTCTGCATCCTGTCGGCA-3′ | Antisense | RT-PCR |
| GAPDH | 5′-AGCCTCAAGATCATCAGCAATGTCCT-3′ | Sense | RT-PCR |
| GAPDH | 5′-AAATTCGTTGTCATACCAGGAAATGAG-3′ | Antisense | RT-PCR |
| P-2660 | 5′-ATGGTACCCTTCTGCTGTTGCCTTGAGCCCAGC-3′ | Sense | Deletion |
| P-2660 | 5′-ATCTCGAGACAGCGTTCACAGGCGGCAGCGAG-3′ | Antisense | Deletion |
| P-1982 | 5′-ATGGTACCGGCTGTCTGGCCTGGTTGCTCCCA-3′ | Sense | Deletion |
| P-1503 | 5′-ATGGTACCAAGGATACCATAGGCTGGGTGACCG-3′ | Sense | Deletion |
| P-968 | 5′-ATGGTACCAGGCTGCCTTGTGGGGCCTGGTATA-3′ | Sense | Deletion |
| P-574 | 5′-ATGGTACCGCCCCTCATACCAGTTCGCTGTCCC-3′ | Sense | Deletion |
| P-240 | 5′-ATGGTACCCGCGCGGCGGCGGCGGCAGCAGC-3′ | Sense | Deletion |
| P-320A | 5′-ATCTCGAGTTCTGCGCCCTCGCCTCGTCCCGA-3′ | Antisense | Deletion |
| P-630A | 5′-ATCTCGAGCCTGGAGACCCGTTTAGCCCCTG-3′ | Antisense | Deletion |
| P-1066A | 5′-ATCTCGAGGGGTGGACCTCATGGACCTCCTC-3′ | Antisense | Deletion |
| Pax-5 Mut | 5′-GGAGTTGAGCTTCCGCATTCCAACCTTCAGGTGACC-3′ | Sense | Mutagenesis |
| Pax-5 Mut | 5′-GGTCACCTGAAGGTTGGAATGCGGAAGCTCAACTCC-3′ | Antisense | Mutagenesis |
| NF-Y Mut | 5′-GCAGAAAACTTGGAGCAATCAGCACGGAGTTGAGC-3′ | Sense | Mutagenesis |
| NF-Y Mut | 5′-GCTCAACTCCGTGCTGATTGCTCCAAGTTTTCTGC-3′ | Antisense | Mutagenesis |
| hST8Sia VI | 5′-AGGCAGAGTTGTGGTGTGGC-3′ | Sense | ChIP |
| hST8Sia VI | 5′-TGGCAGATGACGATTCGCCGA-3′ | Antisense | ChIP |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoon, H.-K.; An, H.-K.; Ko, M.J.; Kim, K.-S.; Mun, S.-W.; Kim, D.-H.; Kim, C.M.; Kim, C.-H.; Choi, Y.W.; Lee, Y.-C. Upregulation of Human ST8Sia VI (α2,8-Sialyltransferase) Gene Expression by Physcion in SK-N-BE(2)-C Human Neuroblastoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081246
Yoon H-K, An H-K, Ko MJ, Kim K-S, Mun S-W, Kim D-H, Kim CM, Kim C-H, Choi YW, Lee Y-C. Upregulation of Human ST8Sia VI (α2,8-Sialyltransferase) Gene Expression by Physcion in SK-N-BE(2)-C Human Neuroblastoma Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(8):1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081246
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoon, Hyun-Kyoung, Hyun-Kyu An, Min Jung Ko, Kyoung-Sook Kim, Seo-Won Mun, Dong-Hyun Kim, Cheol Min Kim, Cheorl-Ho Kim, Young Whan Choi, and Young-Choon Lee. 2016. "Upregulation of Human ST8Sia VI (α2,8-Sialyltransferase) Gene Expression by Physcion in SK-N-BE(2)-C Human Neuroblastoma Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 8: 1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081246
APA StyleYoon, H.-K., An, H.-K., Ko, M. J., Kim, K.-S., Mun, S.-W., Kim, D.-H., Kim, C. M., Kim, C.-H., Choi, Y. W., & Lee, Y.-C. (2016). Upregulation of Human ST8Sia VI (α2,8-Sialyltransferase) Gene Expression by Physcion in SK-N-BE(2)-C Human Neuroblastoma Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(8), 1246. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17081246