Treatment with Synthetic Glucocorticoids and the Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
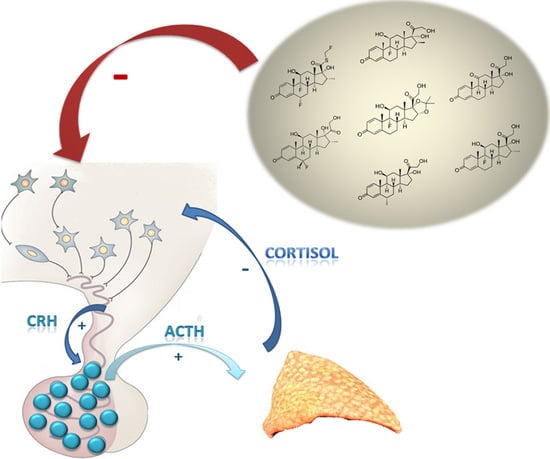
2. Normal Physiology of HPA Axis
3. Effects of Glucocorticoids Therapy on the Hypothalamus–Pituitary–Adrenal Axis
3.1. Synthetic Glucocorticoids
3.1.1. Inhaled Glucocorticoids
3.1.2. Intra-Articular Glucocorticoids
3.1.3. Topical Corticosteroids
3.2. Negative Feedback Loop and Glucocorticoid Receptors
3.3. Clinical Consequence: Tertiary Hypoadrenalism and Adrenal Crisis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 11β-HSD2 | 11-β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 |
| ACTH | Adrenocorticotropic hormone |
| AVP | Arginine vasopressin |
| CBG | Corticosteroid binding globulin |
| CRH | Corticotropin-release hormone |
| cAMP | Cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| GABA | Gamma-aminobutyric acid |
| GC | Glucocorticoid |
| GR | Glucocorticoid receptor |
| HPA | Hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal |
| KO | Knockout |
| MC2R | Melanocyte type-2 receptor |
| MC2R | Mineralocorticoid |
| MR | Mineralocorticoid receptor |
| VO | Nitric oxide |
| PVN | Paraventricular nucleus |
| PY | Patients-year |
| POMC | Proopiomelanocortin |
| RTV | Ritonavir |
| SEGRAs | Selective GC receptor agonists |
| SNPs | Single nucleotide polymorphisms |
| StAR | Steroidogenic acute regulatory |
| SCN | Suprachiasmatic nucleus |
References
- Rhen, T.; Cidlowski, J.A. Antiinflammatory action of glucocorticoids-new mechanisms for old drugs. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1711–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cain, D.W.; Cidlowski, J.A. Immune regulation by glucocorticoids. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, J.P.; McKlveen, J.M.; Ghosal, S.; Kopp, B.; Wulsin, A.; Makinson, R.; Scheimann, J.; Myers, B. Regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical stress response. Compr. Physiol. 2016, 6, 603–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, G.M.; Kalafatakis, K.; Lightman, S.L. The importance of biological oscillators for hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal activity and tissue glucocorticoid response: Coordinating stress and neurobehavioural adaptation. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2015, 27, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adcock, I.M.; Mumby, S. Glucocorticoids. Handb. Exp Pharmacol. 2017, 237, 171–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazso, A.; Szappanos, A.; Patocs, A.; Poor, G.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Kiss, E. The importance of glucocorticoid receptors in systemic lupus erythaematosus. A systematic review. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 349–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busillo, J.M.; Cidlowski, J.A. The five rs of glucocorticoid action during inflammation: Ready, reinforce, repress, resolve, and restore. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 24, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schacke, H.; Docke, W.D.; Asadullah, K. Mechanisms involved in the side effects of glucocorticoids. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 96, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dibas, A.; Yorio, T. Glucocorticoid therapy and ocular hypertension. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 787, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabre, O. Cushing syndrome: Physiopathology, etiology and principles of therapy. Presse Med. 2014, 43, 376–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, R.L.; Leinung, M.C. Exogenous cushing’s syndrome and glucocorticoid withdrawal. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2005, 34, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrousos, G.P.; Pavlaki, A.N.; Magiakou, M.A. Glucocorticoid Therapy and Adrenal Suppression. Endotext [Internet]. 2011. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK279156/ (accessed on 1 September 2017).
- Schlaghecke, R.; Kornely, E.; Santen, R.T.; Ridderskamp, P. The effect of long-term glucocorticoid therapy on pituitary-adrenal responses to exogenous corticotropin-releasing hormone. N. Engl. J. Med. 1992, 326, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinsen, S.; Baslund, B.; Klose, M.; Rasmussen, A.K.; Friis-Hansen, L.; Hilsted, L.; Feldt-Rasmussen, U. Why glucocorticoid withdrawal may sometimes be as dangerous as the treatment itself. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 24, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streck, W.F.; Lockwood, D.H. Pituitary adrenal recovery following short-term suppression with corticosteroids. Am. J. Med. 1979, 66, 910–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Cruz, A.C.; Wargon, O.; Adams, S.; Tran, H.; Verge, C.F. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis recovery following prolonged prednisolone therapy in infants. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, E1936–E1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, R.M.; Hunter, A.L.; Ray, D.W.; Dixon, W.G. Systemic glucocorticoid therapy and adrenal insufficiency in adults: A systematic review. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2016, 46, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, W.L.; Auchus, R.J. The molecular biology, biochemistry, and physiology of human steroidogenesis and its disorders. Endocr. Rev. 2011, 32, 81–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, S.; Debono, M. Replication of cortisol circadian rhythm: New advances in hydrocortisone replacement therapy. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 1, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.V.; Accili, D. Hormonal regulation of hepatic glucose production in health and disease. Cell Metab. 2011, 14, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Cauter, E.; Leproult, R.; Kupfer, D.J. Effects of gender and age on the levels and circadian rhythmicity of plasma cortisol. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1996, 81, 2468–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.; Palacios-Bois, J.; Schwartz, G.; Iskandar, H.; Thakur, M.; Quirion, R.; Nair, N.P. Circadian rhythms of melatonin and cortisol in aging. Biol. Psychiatry 1989, 25, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debono, M.; Ghobadi, C.; Rostami-Hodjegan, A.; Huatan, H.; Campbell, M.J.; Newell-Price, J.; Darzy, K.; Merke, D.P.; Arlt, W.; Ross, R.J. Modified-release hydrocortisone to provide circadian cortisol profiles. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 1548–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paragliola, R.M.; Corsello, S.M. Secondary adrenal insufficiency: From the physiopathology to the possible role of modified-release hydrocortisone treatment. Minerva Endocrinol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locatelli, V.; Bresciani, E.; Tamiazzo, L.; Torsello, A. Central nervous system-acting drugs influencing hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis function. Endocr. Dev. 2010, 17, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hastings, M.H.; Herzog, E.D. Clock genes, oscillators, and cellular networks in the suprachiasmatic nuclei. J. Biol. Rhythms 2004, 19, 400–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vries, M.J.; Nunes Cardozo, B.; van der Want, J.; de Wolf, A.; Meijer, J.H. Glutamate immunoreactivity in terminals of the retinohypothalamic tract of the brown norwegian rat. Brain Res. 1993, 612, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calogero, A.E. Neurotransmitter regulation of the hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing hormone neuron. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1995, 771, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raff, H.; Sharma, S.T.; Nieman, L.K. Physiological basis for the etiology, diagnosis, and treatment of adrenal disorders: Cushing’s syndrome, adrenal insufficiency, and congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Compr. Physiol. 2014, 4, 739–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cone, R.D.; Mountjoy, K.G. Molecular genetics of the acth and melanocyte-stimulating hormone receptors. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 1993, 4, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oster, H.; Damerow, S.; Kiessling, S.; Jakubcakova, V.; Abraham, D.; Tian, J.; Hoffmann, M.W.; Eichele, G. The circadian rhythm of glucocorticoids is regulated by a gating mechanism residing in the adrenal cortical clock. Cell Metab. 2006, 4, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, S.; Son, G.H.; Kim, K. Circadian rhythm of adrenal glucocorticoid: Its regulation and clinical implications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1812, 581–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fardet, L.; Petersen, I.; Nazareth, I. Description of oral glucocorticoid prescriptions in general population. Rev. Med. Interne 2011, 32, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fardet, L.; Petersen, I.; Nazareth, I. Prevalence of long-term oral glucocorticoid prescriptions in the uk over the past 20 years. Rheumatol. Oxf. 2011, 50, 1982–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smans, L.C.; Van der Valk, E.S.; Hermus, A.R.; Zelissen, P.M. Incidence of adrenal crisis in patients with adrenal insufficiency. Clin. Endocrinol. Oxf. 2016, 84, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schacke, H.; Schottelius, A.; Docke, W.D.; Strehlke, P.; Jaroch, S.; Schmees, N.; Rehwinkel, H.; Hennekes, H.; Asadullah, K. Dissociation of transactivation from transrepression by a selective glucocorticoid receptor agonist leads to separation of therapeutic effects from side effects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulliver, T.; Morton, R.; Eid, N. Inhaled corticosteroids in children with asthma: Pharmacologic determinants of safety and efficacy and other clinical considerations. Paediatr. Drugs 2007, 9, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalski, M.L.; Wojciechowski, P.; Dziewonska, M.; Rys, P. Adrenal suppression by inhaled corticosteroids in patients with asthma: A systematic review and quantitative analysis. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2016, 37, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, H.W. Comparison of inhaled corticosteroids: An update. Ann. Pharmacother. 2009, 43, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldwell, J.R. Intra-articular corticosteroids. Guide for selection and indications for use. Drugs 1996, 52, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habib, G.S. Systemic effects of intra-articular corticosteroids. Clin. Rheumatol. 2009, 28, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, P.C.; Lansang, M.C.; Chatterjee, S.; Kennedy, L. Intra-articular glucocorticoid injections and their effect on hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (hpa)-axis function. Endocrine 2015, 48, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arroll, B.; Goodyear-Smith, F. Corticosteroid injections for osteoarthritis of the knee: Meta-analysis. BMJ 2004, 328, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duclos, M.; Guinot, M.; Colsy, M.; Merle, F.; Baudot, C.; Corcuff, J.B.; Lebouc, Y. High risk of adrenal insufficiency after a single articular steroid injection in athletes. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tempark, T.; Phatarakijnirund, V.; Chatproedprai, S.; Watcharasindhu, S.; Supornsilchai, V.; Wananukul, S. Exogenous cushing’s syndrome due to topical corticosteroid application: Case report and review literature. Endocrine 2010, 38, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turpeinen, M.; Salo, O.P.; Leisti, S. Effect of percutaneous absorption of hydrocortisone on adrenocortical responsiveness in infants with severe skin disease. Br. J. Dermatol. 1986, 115, 475–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, A.; Nelson, K.; Goodwin, M.; McCluggage, J. Iatrogenic cushing’s syndrome. Br. Med. J. 1972, 4, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decani, S.; Federighi, V.; Baruzzi, E.; Sardella, A.; Lodi, G. Iatrogenic cushing’s syndrome and topical steroid therapy: Case series and review of the literature. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2014, 25, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousseau, G.G. Fifty years ago: The quest for steroid hormone receptors. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2013, 375, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, L. Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical axis regulation. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2005, 34, 271–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, R.L.; Young, E.A.; Choo, P.H.; McEwen, B.S. Adrenal steroid type i and type ii receptor binding estimates of in vivo receptor number, occupancy, and activation with varying level of steroid. Brain Res. 1990, 514, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, K.; Holmes, M.; Seckl, J. 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases: Intracellular gate-keepers of tissue glucocorticoid action. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 1139–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arriza, J.L.; Simerly, R.B.; Swanson, L.W.; Evans, R.M. The neuronal mineralocorticoid receptor as a mediator of glucocorticoid response. Neuron 1988, 1, 887–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kloet, R.; Wallach, G.; McEwen, B.S. Differences in corticosterone and dexamethasone binding to rat brain and pituitary. Endocrinology 1975, 96, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallman, M.F.; Levin, N.; Cascio, C.S.; Akana, S.F.; Jacobson, L.; Kuhn, R.W. Pharmacological evidence that inhibition of diurnal adrenocorticotropin secretion by corticosteroids is mediated via type i corticosteronepreferring receptors. Endocrinology 1989, 124, 2844–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, E.A.; Lopez, J.F.; Murphy-Weinberg, V.; Watson, S.J.; Akil, H. The role of mineralocorticoid receptors in hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis regulation in humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 83, 3339–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnett, M.G.; Muglia, L.M.; Laryea, G.; Muglia, L.J. Genetic approaches to hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis regulation. Neuropsychopharmacology 2016, 41, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, N.; Shinsako, J.; Dallman, M.F. Corticosterone acts on the brain to inhibit adrenalectomy-induced adrenocorticotropin secretion. Endocrinology 1988, 122, 694–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muglia, L.J.; Jacobson, L.; Luedke, C.; Vogt, S.K.; Schaefer, M.L.; Dikkes, P.; Fukuda, S.; Sakai, Y.; Suda, T.; Majzoub, J.A. Corticotropin-releasing hormone links pituitary adrenocorticotropin gene expression and release during adrenal insufficiency. J. Clin. Investig. 2000, 105, 1269–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulte, H.M.; Chrousos, G.P.; Avgerinos, P.; Oldfield, E.H.; Gold, P.W.; Cutler, G.B., Jr.; Loriaux, D.L. The corticotropin-releasing hormone stimulation test: A possible aid in the evaluation of patients with adrenal insufficiency. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1984, 58, 1064–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassel, O.; Herrlich, P. Crosstalk between the glucocorticoid receptor and other transcription factors: Molecular aspects. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2007, 275, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller-Wood, M.E.; Dallman, M.F. Corticosteroid inhibition of acth secretion. Endocr. Rev. 1984, 5, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, H.C.; Wood, S.A.; Castrique, E.S.; Kershaw, Y.M.; Wiles, C.C.; Lightman, S.L. Corticosteroids mediate fast feedback of the rat hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis via the mineralocorticoid receptor. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 294, 1011–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fehm, H.L.; Voigt, K.H.; Kummer, G.; Lang, R.; Pfeiffer, E.F. Differential and integral corticosteroid feedback effects on acth secretion in hypoadrenocorticism. J. Clin. Investig. 1979, 63, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossmann, C.; Scholz, T.; Rochel, M.; Bumke-Vogt, C.; Oelkers, W.; Pfeiffer, A.F.; Diederich, S.; Bahr, V. Transactivation via the human glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptor by therapeutically used steroids in cv-1 cells: A comparison of their glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid properties. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2004, 151, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karst, H.; Berger, S.; Turiault, M.; Tronche, F.; Schutz, G.; Joels, M. Mineralocorticoid receptors are indispensable for nongenomic modulation of hippocampal glutamate transmission by corticosterone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 19204–19207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, G.M.; Henley, D.E.; Leendertz, J.; Douthwaite, J.A.; Wood, S.A.; Stevens, A.; Woltersdorf, W.W.; Peeters, B.W.; Ruigt, G.S.; White, A.; et al. Rapid glucocorticoid receptor-mediated inhibition of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal ultradian activity in healthy males. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 6106–6115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayanithi, G.; Antoni, F.A. Rapid as well as delayed inhibitory effects of glucocorticoid hormones on pituitary adrenocorticotropic hormone release are mediated by type ii glucocorticoid receptors and require newly synthesized messenger ribonucleic acid as well as protein. Endocrinology 1989, 125, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raff, H. Glucocorticoid inhibition of neurohypophysial vasopressin secretion. Am. J. Physiol. 1987, 252, R635–R644. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mouri, T.; Itoi, K.; Takahashi, K.; Suda, T.; Murakami, O.; Yoshinaga, K.; Andoh, N.; Ohtani, H.; Masuda, T.; Sasano, N. Colocalization of corticotropin-releasing factor and vasopressin in the paraventricular nucleus of the human hypothalamus. Neuroendocrinology 1993, 57, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitnall, M.H. Regulation of the hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing hormone neurosecretory system. Prog. Neurobiol. 1993, 40, 573–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diederich, S.; Eigendorff, E.; Burkhardt, P.; Quinkler, M.; Bumke-Vogt, C.; Rochel, M.; Seidelmann, D.; Esperling, P.; Oelkers, W.; Bahr, V. 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase types 1 and 2: An important pharmacokinetic determinant for the activity of synthetic mineralo- and glucocorticoids. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 5695–5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funder, J.W. Apparent mineralocorticoid excess. J. Steroid. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2017, 165, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assandri, A.; Buniva, G.; Martinelli, E.; Perazzi, A.; Zerilli, L. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of deflazacort in the rat, dog, monkey and man. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1984, 171, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Schroeder, J.R.; Bush, L.M. Iatrogenic cushing syndrome and secondary adrenal insufficiency related to concomitant triamcinolone and ritonavir administration: A case report and review. J. Int. Assoc. Provid. AIDS Care 2014, 13, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saberi, P.; Phengrasamy, T.; Nguyen, D.P. Inhaled corticosteroid use in hiv-positive individuals taking protease inhibitors: A review of pharmacokinetics, case reports and clinical management. HIV Med. 2013, 14, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wassner, C.; Maiti, S.; Kodroff, K.; Cohen, H. Iatrogenic adrenal insufficiency secondary to combination therapy with elvitegravir/cobicistat/tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine and interlaminar triamcinolone injection in an aids patient. J. Int. Assoc. Provid. AIDS Care 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, M.R.; Szefler, S.J.; Ball, B.D.; Bartoszek, M.; Brenner, a.m. Monitoring glucocorticoid therapy: A pharmacokinetic approach. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1990, 48, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamilloux, Y.; Liozon, E.; Pugnet, G.; Nadalon, S.; Heang Ly, K.; Dumonteil, S.; Gondran, G.; Fauchais, A.L.; Vidal, E. Recovery of adrenal function after long-term glucocorticoid therapy for giant cell arteritis: A cohort study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.; Robazzi, T.C.; Mendonca, M. Withdrawal from glucocorticosteroid therapy: Clinical practice recommendations. J. Pediatr. (Rio. J.) 2008, 84, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guaraldi, F.; Karamouzis, I.; Berardelli, R.; D’Angelo, V.; Rampino, A.; Zichi, C.; Ghigo, E.; Giordano, R. Secondary adrenal insufficiency: Where is it hidden and what does it look like? Front. Horm. Res. 2016, 46, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasner, A.S. Glucocorticoid-induced adrenal insufficiency. JAMA 1999, 282, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henzen, C.; Suter, A.; Lerch, E.; Urbinelli, R.; Schorno, X.H.; Briner, V.A. Suppression and recovery of adrenal response after short-term, high-dose glucocorticoid treatment. Lancet 2000, 355, 542–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neidert, S.; Schuetz, P.; Mueller, B.; Christ-Crain, M. Dexamethasone suppression test predicts later development of an impaired adrenal function after a 14-day course of prednisone in healthy volunteers. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2010, 162, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.Q.; Xie, W.Y.; Tang, Y.J.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J. Genetic variation in the glucocorticoid pathway involved in interindividual differences in the glucocorticoid treatment. Pharmacogenomics 2017, 18, 293–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derijk, R.H. Single nucleotide polymorphisms related to hpa axis reactivity. Neuroimmunomodulation 2009, 16, 340–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manenschijn, L.; van den Akker, E.L.; Lamberts, S.W.; van Rossum, E.F. Clinical features associated with glucocorticoid receptor polymorphisms. An overview. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1179, 179–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, T.L.; Tung, K.; Lim, D.; Leventhal, S.M.; Cho, K.; Greenhalgh, D.G. A novel human glucocorticoid receptor snp results in increased transactivation potential. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2017, 9, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, A.C.; Chew, V.W.; Green, T.L.; Tung, K.; Lim, D.; Cho, K.; Greenhalgh, D.G. Single nucleotide polymorphisms and type of steroid impact the functional response of the human glucocorticoid receptor. J. Surg. Res. 2013, 180, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramamoorthy, S.; Cidlowski, J.A. Corticosteroids: Mechanisms of action in health and disease. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 42, 15–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koper, J.W.; van Rossum, E.F.; van den Akker, E.L. Glucocorticoid receptor polymorphisms and haplotypes and their expression in health and disease. Steroids 2014, 92, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Synthetic Glucocorticoids | Equivalent Dose (mg) | Anti-Inflammatory Activity (Related to Hydrocortisone) | Mineralocorticoid Activity (Related to Hydrocortisone) | Biological Half-Life (hours) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrocortisone | 20 | 1 | 1 | 8–12 |
| Cortisone Acetate | 25 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 8–12 |
| Deflazacort | 5 | 4 | 1 | <12 |
| Prednisone | 5 | 4 | 0.3 | 12–36 |
| Prednisolone | 5 | 4 | 0.3 | 12–36 |
| Triamcinolone | 4 | 5 | 0 | 12–36 |
| Methylprednisolone | 4 | 5 | 0.5 | 12–36 |
| Paramethasone | 2 | 10 | 0 | / |
| Dexamethasone | 0.75 | 30 | 0 | 36–72 |
| Betamethasone | 0.6 | 25 | 0 | 36–72 |
| Fludrocortisone | Not for anti-inflammatory use | 10 | 250 | 18–36 |
| Inhaled synthetic Glucocorticoids | Receptor Binding Affinity (Relative to Dexamethasone = 1) | Oral Bioavailability (%) | Systemic Clearance (L/h) | Half-Life (h) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beclomethasone dipropionate | 0.4 | 20 | 150 | Unknown |
| Beclomethasone 17-monopropionate | 13.5 | 40 | 120 | 2.7 |
| Budesonide | 9.4 | 11 | 84 | 2.0 |
| Ciclesonide | 0.12 | <1 | 152 | 0.5 |
| Flunisolide | 1.8 | 20 | 58 | 1.6 |
| Fluticasone propionate | 18 | ≤1 | 66 | 14.4 |
| Mometasone furoate | 23 | <1 | 53 | Unknown |
| Triamcinolone acetonide | 3.6 | 23 | 45 | 3.6 |
| Potency | Topical Synthetic Glucocorticoids |
|---|---|
| Low | Hydrocortisone acetate 1% Alclometasone dipropionate 0.05% Methylprednisolone acetate 0.25% |
| Medium | Clobetasone butyrate 0.05% Hydrocortisone butyrate 0.1% Fluocortolone pivalate 0.5% |
| High | Beclomethasone dipropionate 0.025% Betamethasone dipropionate 0.05% Betamethasone benzoate 0.025% Betamethasone valerate 0.1% Difluocortolone valerate 0.1% Fluocinolone acetonide 0.025% Fluticasone propionate 0.05% Fluocinonide 0.05% |
| Very High | Clobetasol propionate 0.05% Diflucortolone valerate 0.3% Halcinonide 0.01% |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paragliola, R.M.; Papi, G.; Pontecorvi, A.; Corsello, S.M. Treatment with Synthetic Glucocorticoids and the Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2201. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18102201
Paragliola RM, Papi G, Pontecorvi A, Corsello SM. Treatment with Synthetic Glucocorticoids and the Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(10):2201. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18102201
Chicago/Turabian StyleParagliola, Rosa Maria, Giampaolo Papi, Alfredo Pontecorvi, and Salvatore Maria Corsello. 2017. "Treatment with Synthetic Glucocorticoids and the Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 10: 2201. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18102201
APA StyleParagliola, R. M., Papi, G., Pontecorvi, A., & Corsello, S. M. (2017). Treatment with Synthetic Glucocorticoids and the Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(10), 2201. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18102201