Diverse Effects of an Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitor, Donepezil, on Hippocampal Neuronal Death after Pilocarpine-Induced Seizure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
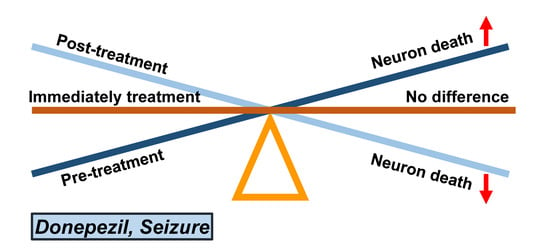
2.1. Pre-Treatment of Donepezil for Three Days before Seizure Increases Neuronal Death, Oxidative Injury, and Microglia Activation
2.2. Post-Treatment of Donepezil for One Week Had No Effects on Seizure-Induced Neuronal Death, Oxidative Injury, and Microglia Activation
2.3. Post-Treatment of Donepezil for Three Weeks from Three Weeks after Seizure Reduced Neuronal Death, Oxidative Injury and Microglia Activation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Experimental Animals
4.3. Seizure Induction
4.4. Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitor (Donepezil) Treatment
4.5. Brain Sample Preparation
4.6. Detection of Neuronal Death
4.7. Detection of Oxidative Injury
4.8. Detection of Microglia Activation
4.9. Detection of Live Neurons
4.10. Data Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Delgado-Escueta, A.V.; Wilson, W.A.; Olsen, R.W.; Porter, R.J. New waves of research in the epilepsies: Crossing into the third millennium. Adv. Neurol. 1999, 79, 3–58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Holmes, G.L.; Gairsa, J.L.; Chevassus-Au-Louis, N.; Ben-Ari, Y. Consequences of neonatal seizures in the rat: Morphological and behavioral effects. Ann. Neurol. 1998, 44, 845–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurman, D.J.; Beghi, E.; Begley, C.E.; Berg, A.T.; Buchhalter, J.R.; Ding, D.; Hesdorffer, D.C.; Hauser, W.A.; Kazis, L.; Kobau, R.; et al. Standards for epidemiologic studies and surveillance of epilepsy. Epilepsia 2011, 52 (Suppl. 7), 2–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, R.S.; Acevedo, C.; Arzimanoglou, A.; Bogacz, A.; Cross, J.H.; Elger, C.E.; Engel, J., Jr.; Forsgren, L.; French, J.A.; Glynn, M.; et al. ILAE official report: A practical clinical definition of epilepsy. Epilepsia 2014, 55, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.C.; Huang, A.M.; Kuo, Y.M.; Wang, S.T.; Chang, Y.Y.; Huang, C.C. Febrile seizures impair memory and cAMP response-element binding protein activation. Ann. Neurol. 2003, 54, 706–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, E.M.; Coulter, D.A. Mechanisms of epileptogenesis: A convergence on neural circuit dysfunction. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, T.; Evans, M.C.; Meldrum, B.S. Intracellular calcium accumulation in rat hippocampus during seizures induced by bicuculline or L-allylglycine. Neuroscience 1983, 10, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mufti, F.; Claassen, J. Neurocritical care: Status epilepticus review. Crit. Care Clin. 2014, 30, 751–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vingerhoets, G. Cognitive effects of seizures. Seizure 2006, 15, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogawski, M.A.; Loscher, W. The neurobiology of antiepileptic drugs. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2004, 5, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akasofu, S.; Kimura, M.; Kosasa, T.; Sawada, K.; Ogura, H. Study of neuroprotection of donepezil, a therapy for Alzheimer’s disease. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2008, 175, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naik, R.S.; Hartmann, J.; Kiewert, C.; Duysen, E.G.; Lockridge, O.; Klein, J. Effects of rivastigmine and donepezil on brain acetylcholine levels in acetylcholinesterase-deficient mice. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 12, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atukeren, P.; Cengiz, M.; Yavuzer, H.; Gelisgen, R.; Altunoglu, E.; Oner, S.; Erdenen, F.; Yuceakin, D.; Derici, H.; Cakatay, U.; et al. The efficacy of donepezil administration on acetylcholinesterase activity and altered redox homeostasis in Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 90, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebell, M.H. Donepezil in the treatment of vascular dementia. Am. Fam. Physician 2004, 70, 1681–1682. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Di, X.; Liu, Y. Protective effects of Donepezil against endothelial permeability. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 811, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, A.D.; Owens, I.J.; Bansal, A.T.; McTighe, S.M.; Bussey, T.J.; Saksida, L.M. FK962 and donepezil act synergistically to improve cognition in rats: Potential as an add-on therapy for Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2011, 98, 76–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, R.; McShane, R.; Lindesay, J.; Ritchie, C.; Baldwin, A.; Barber, R.; Burns, A.; Dening, T.; Findlay, D.; Holmes, C.; et al. Donepezil and memantine for moderate-to-severe Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eleti, S. Drugs in Alzheimer’s disease Dementia: An overview of current pharmacological management and future directions. Psychiatr. Danub. 2016, 28 (Suppl. 1), 136–140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khateb, A.; Ammann, J.; Annoni, J.M.; Diserens, K. Cognition-enhancing effects of donepezil in traumatic brain injury. Eur. Neurol. 2005, 54, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Young Choi, B.; Suh, S.W. Unexpected effects of acetylcholine precursors on pilocarpine seizure-induced neuronal death. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Choi, B.Y.; Kim, J.H.; Kho, A.R.; Sohn, M.; Song, H.K.; Choi, H.C.; Suh, S.W. Late treatment with choline alfoscerate (l-alpha glycerylphosphorylcholine, alpha-GPC) increases hippocampal neurogenesis and provides protection against seizure-induced neuronal death and cognitive impairment. Brain Res. 2017, 1654 Pt A, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, D.W.; Choi, B.Y.; Sohn, M.; Lee, S.H.; Choi, H.C.; Song, H.K.; Suh, S.W. Cytidine 5′-diphosphocholine (CDP-choline) adversely effects on pilocarpine seizure-induced hippocampal neuronal death. Brain Res. 2015, 1595, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Croda, D.M.; Santiago-Garcia, J.; Medel-Matus, J.S.; Martinez-Quiroz, J.; Puig-Lagunes, A.A.; Beltran-Parrazal, L.; Lopez-Meraz, M.L. Hippocampal distribution of IL-1beta and IL-1RI following lithium-pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus in the developing rat. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências 2016, 88 (Suppl. 1), 653–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauppinen, T.M.; Swanson, R.A. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 promotes microglial activation, proliferation, and matrix metalloproteinase-9-mediated neuron death. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 2288–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauppinen, T.M.; Higashi, Y.; Suh, S.W.; Escartin, C.; Nagasawa, K.; Swanson, R.A. Zinc triggers microglial activation. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 5827–5835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, P.B.; Ramsay, L.A.; MacDonald, D.S.; Tasker, R.A. Progressive changes in hippocampal cytoarchitecture in a neurodevelopmental rat model of epilepsy: Implications for understanding presymptomatic epileptogenesis, predictive diagnosis, and targeted treatments. EPMA J. 2017, 8, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Ido, K.; Osada, Y.; Kotani, S.; Tamaoka, A.; Hanada, T. The neuroprotective effect of perampanel in lithium-pilocarpine rat seizure model. Epilepsy Res. 2017, 137, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oboh, G.; Ogunsuyi, O.B.; Olonisola, O.E. Does caffeine influence the anticholinesterase and antioxidant properties of donepezil? Evidence from in vitro and in vivo studies. Metab. Brain Dis. 2017, 32, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turski, L.; Ikonomidou, C.; Turski, W.A.; Bortolotto, Z.A.; Cavalheiro, E.A. Review: Cholinergic mechanisms and epileptogenesis. The seizures induced by pilocarpine: A novel experimental model of intractable epilepsy. Synapse 1989, 3, 154–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, D.; Mao, X.; Wu, K.; Cao, Y.; Guo, F.; Zhu, S.; Xie, N.; Wang, L.; Chen, T.; Shaw, C.; et al. Donepezil attenuates hippocampal neuronal damage and cognitive deficits after global cerebral ischemia in gerbils. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 510, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiki, M.; Kubo, T.; Kamida, T.; Sugita, K.; Hikawa, T.; Abe, T.; Ishii, K.; Kobayashi, H. Neuroprotective and antiamnesic effect of donepezil, a nicotinic acetylcholine-receptor activator, on rats with concussive mild traumatic brain injury. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2008, 15, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jope, R.S.; Simonato, M.; Lally, K. Acetylcholine content in rat brain is elevated by status epilepticus induced by lithium and pilocarpine. J. Neurochem. 1987, 49, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerman, G.; Njunting, M.; Ivens, S.; Tolner, E.A.; Behrens, C.J.; Gross, M.; Soreq, H.; Heinemann, U.; Friedman, A. Acetylcholine-induced seizure-like activity and modified cholinergic gene expression in chronically epileptic rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 27, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teitelbaum, H.; Lee, J.F.; Johannessen, J.N. Behaviorally evoked hippocampal theta waves: A cholinergic response. Science 1975, 188, 1114–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Rijckevorsel, K. Cognitive problems related to epilepsy syndromes, especially malignant epilepsies. Seizure 2006, 15, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persinger, M.A.; Makarec, K.; Bradley, J.C. Characteristics of limbic seizures evoked by peripheral injections of lithium and pilocarpine. Physiol. Behav. 1988, 44, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racine, R.J.; Gartner, J.G.; Burnham, W.M. Epileptiform activity and neural plasticity in limbic structures. Brain Res. 1972, 47, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.E.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Kang, T.C. PARP1 activation/expression modulates regional-specific neuronal and glial responses to seizure in a hemodynamic-independent manner. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Jang, B.G.; Choi, B.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Sohn, M.; Chung, T.N.; Choi, H.C.; Song, H.K.; Suh, S.W. Post-treatment of an NADPH oxidase inhibitor prevents seizure-induced neuronal death. Brain Res. 2013, 1499, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattanashetti, L.A.; Taranalli, A.D.; Parvatrao, V.; Malabade, R.H.; Kumar, D. Evaluation of neuroprotective effect of quercetin with donepezil in scopolamine-induced amnesia in rats. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2017, 49, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Akinyemi, A.J.; Oboh, G.; Oyeleye, S.I.; Ogunsuyi, O. Anti-amnestic Effect of Curcumin in Combination with Donepezil, an Anticholinesterase Drug: Involvement of Cholinergic System. Neurotox. Res. 2017, 31, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-El-Fattah, M.A.; Abdelakader, N.F.; Zaki, H.F. Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate protects against scopolamine-induced cognitive impairment in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 723, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmued, L.C.; Hopkins, K.J. Fluoro-Jade B: A high affinity fluorescent marker for the localization of neuronal degeneration. Brain Res. 2000, 874, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, S.W.; Aoyama, K.; Chen, Y.; Garnier, P.; Matsumori, Y.; Gum, E.; Liu, J.; Swanson, R.A. Hypoglycemic neuronal death and cognitive impairment are prevented by poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors administered after hypoglycemia. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 10681–10690. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Suh, S.W.; Gum, E.T.; Hamby, A.M.; Chan, P.H.; Swanson, R.A. Hypoglycemic neuronal death is triggered by glucose reperfusion and activation of neuronal NADPH oxidase. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 910–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, B.Y.; Jang, B.G.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, B.E.; Sohn, M.; Song, H.K.; Suh, S.W. Prevention of traumatic brain injury-induced neuronal death by inhibition of NADPH oxidase activation. Brain Res. 2012, 1481, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, J.H.; Choi, B.Y.; Kho, A.R.; Lee, S.H.; Hong, D.K.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Song, H.K.; Choi, H.C.; Suh, S.W. Diverse Effects of an Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitor, Donepezil, on Hippocampal Neuronal Death after Pilocarpine-Induced Seizure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2311. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112311
Jeong JH, Choi BY, Kho AR, Lee SH, Hong DK, Lee SH, Lee SY, Song HK, Choi HC, Suh SW. Diverse Effects of an Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitor, Donepezil, on Hippocampal Neuronal Death after Pilocarpine-Induced Seizure. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(11):2311. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112311
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Jeong Hyun, Bo Young Choi, A Ra Kho, Song Hee Lee, Dae Ki Hong, Sang Hwon Lee, Sang Yup Lee, Hong Ki Song, Hui Chul Choi, and Sang Won Suh. 2017. "Diverse Effects of an Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitor, Donepezil, on Hippocampal Neuronal Death after Pilocarpine-Induced Seizure" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 11: 2311. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112311
APA StyleJeong, J. H., Choi, B. Y., Kho, A. R., Lee, S. H., Hong, D. K., Lee, S. H., Lee, S. Y., Song, H. K., Choi, H. C., & Suh, S. W. (2017). Diverse Effects of an Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitor, Donepezil, on Hippocampal Neuronal Death after Pilocarpine-Induced Seizure. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(11), 2311. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112311