Recipient HLA-G +3142 CC Genotype and Concentrations of Soluble HLA-G Impact on Occurrence of CMV Infection after Living-Donor Kidney Transplantation
Abstract
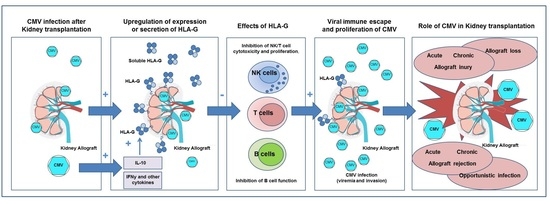
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Population and Outcome Parameters
4.2. HLA-G +3142 C>G SNP Typing and Soluble HLA-G Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.3. Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HLA | Human leukocyte antigen |
| sHLA-G | (Soluble) Human leukocyte antigen-G |
| CMV | Cytomegalovirus |
| SNP | Single Nucleotid Polymorphism |
| 3′UTR | 3′ untranslated region |
| NK cell | Natural killer cell |
| ILT | Immunoglobulin-like transcript |
| KIR | Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor |
| 5′URR | 5′ upstream regulatory region |
| HR | Hazard Ratio |
| 95% CI | 95% Confidence interval |
| R | Recipient |
| D | Donor |
| US | Ultra short |
| eGFR | Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
References
- Asberg, A.; Jardine, A.G.; Bignamini, A.A.; Rollag, H.; Pescovitz, M.D.; Gahlemann, C.C.; Humar, A.; Hartmann, A.; VICTOR Study Group. Effects of the intensity of immunosuppressive therapy on outcome of treatment for CMV disease in organ transplant recipients. Am. J. Transplant. 2010, 10, 1881–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fishman, J.A. Infection in Organ Transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2017, 17, 856–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcami, A.; Koszinowski, U.H. Viral mechanisms of immune evasion. Trends Microbiol. 2000, 8, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploegh, H.L. Viral strategies of immune evasion. Science 1998, 280, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halenius, A.; Gerke, C.; Hengel, H. Classical and non-classical MHC I molecule manipulation by human cytomegalovirus: So many targets-but how many arrows in the quiver? Cell Mol. Immunol. 2015, 12, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schust, D.J.; Tortorella, D.; Seebach, J.; Phan, C.; Ploegh, H.L. Trophoblast class I major histocompatibility complex (MHC) products are resistant to rapid degradation imposed by the human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) gene products US2 and US11. J. Exp. Med. 1998, 188, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, B.; Spooner, E.; Houser, B.L.; Strominger, J.L.; Ploegh, H.L. The HCMV membrane glycoprotein US10 selectively targets HLA-G for degradation. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 2033–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, Y.; Kim, E.; Jin, M.; Sung, H.C.; Han, H.; Geraghty, D.E.; Ahn, K. Human cytomegalovirus gene products US3 and US6 down-regulate trophoblast class I MHC molecules. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onno, M.; Pangault, C.; Le Friec, G.; Guilloux, V.; André, P.; Fauchet, R. Modulation of HLA-G antigens expression by human cytomegalovirus: Specific induction in activated macrophages harboring human cytomegalovirus infection. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 6426–6434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, R.; Gabrielli, L.; Bortolotti, D.; Gentili, V.; Piccirilli, G.; Chiereghin, A.; Pavia, C.; Bolzani, S.; Guerra, B.; Simonazzi, G. Study of Soluble HLA-G in Congenital Human Cytomegalovirus Infection. J. Immunol. Res. 2016, 2016, 3890306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebmann, V.; da Silva Nardi, F.; Wagner, B.; Horn, P.A. HLA-G as a tolerogenic molecule in transplantation and pregnancy. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 297073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carosella, E.D.; Moreau, P.; Le Maoult, J.; Le Discorde, M.; Dausset, J.; Rouas-Freiss, N. HLA-G molecules: from maternal-fetal tolerance to tissue acceptance. Adv. Immunol. 2003, 81, 199–252. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carosella, E.D.; Moreau, P.; Lemaoult, J.; Rouas-Freiss, N. HLA-G: From biology to clinical benefits. Trends Immunol. 2008, 29, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, L.C.; Hoare, H.L.; McCluskey, J.; Rossjohn, J.; Brooks, A.G. A structural perspective on MHC class Ib molecules in adaptive immunity. Trends Immunol. 2006, 27, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morandi, F.; Pistoia, V. Soluble HLA-G modulates miRNA-210 and miRNA-451 expression in activated CD4+ T lymphocytes. Int. Immunol. 2013, 25, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiroishi, M.; Kuroki, K.; Rasubala, L.; Tsumoto, K.; Kumagai, I.; Kurimoto, E.; Kato, K.; Kohda, D.; Maenaka, K. Structural basis for recognition of the nonclassical MHC molecule HLA-G by the leukocyte Ig-like receptor B2 (LILRB2/LIR2/ILT4/CD85d). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 16412–16417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pistoia, V.; Morandi, F.; Wang, X.; Ferrone, S. Soluble HLA-G: Are they clinically relevant? Semin. Cancer Biol. 2007, 17, 469–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castelli, E.C.; Veiga-Castelli, L.C.; Yaghi, L.; Moreau, P.; Donadi, E.A. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulations of the HLA-G gene. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 734068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Z.; Randall, G.; Fan, J.; Camoretti-Mercado, B.; Brockman-Schneider, R.; Pan, L.; Solway, J.; Gern, J.E.; Lemanske, R.F.; Nicolae, D.; et al. Allele-specific targeting of microRNAs to HLA-G and risk of asthma. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 829–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veit, T.D.; Chies, J.A. Tolerance versus immune response—microRNAs as important elements in the regulation of the HLA-G gene expression. Transpl. Immunol. 2009, 20, 229–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.K.; Xu, C.X.; Tian, P.X.; Xue, W.J.; Ding, X.M.; Zheng, J.; Ding, C.G.; Ge, G.Q.; Mao, T.C.; Lin, Y. Impact of HLA-G 14-bp polymorphism on acute rejection and cytomegalovirus infection in kidney transplant recipients from northwestern China. Transpl. Immunol. 2012, 27, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, M.K.; Prakash, S.; Kapoor, R.; Pandey, S.K.; Sharma, R.K.; Agrawal, S. Association of HLA-G promoter and 14-bp insertion-deletion variants with acute allograft rejection and end-stage renal disease. Tissue Antigens 2013, 82, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carosella, E.D.; Rouas-Freiss, N.; Tronik-Le Roux, D.; Moreau, P.; LeMaoult, J. HLA-G: An Immune Checkpoint Molecule. Adv. Immunol. 2015, 127, 33–144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rebmann, V.; Pfeiffer, K.; Pässler, M.; Ferrone, S.; Maier, S.; Weiss, E.; Grosse-Wilde, H. Detection of soluble HLA-G molecules in plasma and amniotic fluid. Tissue Antigens 1999, 53, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baricordi, O.R.; Stignani, M.; Melchiorri, L.; Rizzo, R. HLA-G and inflammatory diseases. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Targets 2008, 7, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, P.J.; Fu, Y.M.; Ding, S.X.; Xu, D.P.; Lin, A.; Yan, W.H. Elevation of plasma soluble human leukocyte antigen-G in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Hum. Immunol. 2011, 72, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murdaca, G.; Contini, P.; Setti, M.; Cagnati, P.; Lantieri, F.; Indiveri, F.; Puppo, F. Behavior of non-classical soluble HLA class G antigens in human immunodeficiency virus 1-infected patients before and after HAART: Comparison with classical soluble HLA-A, -B, -C antigens and potential role in immune-reconstitution. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 133, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordero, E.A.; Veit, T.D.; da Silva, M.A.; Jacques, S.M.; Silla, L.M.; Chies, J.A. HLA-G polymorphism influences the susceptibility to HCV infection in sickle cell disease patients. Tissue Antigens 2009, 74, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebmann, V.; Bartsch, D.; Wunsch, A.; Möllenbeck, P.; Golda, T.; Viebahn, R.; Grosse-Wilde, H. Soluble total human leukocyte antigen class I and human leukocyte antigen-G molecules in kidney and kidney/pancreas transplantation. Hum. Immunol. 2009, 70, 995–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thude, H.; Janssen, M.; Sterneck, M.; Nashan, B.; Koch, M. 14-bp ins/del polymorphism and +3142 C>G SNP of the HLA-G gene have a significant impact on acute rejection after liver transplantation. Hum. Immunol. 2016, 77, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubin, R.H. The pathogenesis and clinical management of cytomegalovirus infection in the organ transplant recipient: The end of the “silo hypothesis”. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 20, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kas-Deelen, A.M.; de Maar, E.F.; Harmsen, M.C.; Driessen, C.; van Son, W.J.; The, T.H. Uninfected and cytomegalic endothelial cells in blood during cytomegalovirus infection: Effect of acute rejection. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 181, 721–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humar, A.; Gillingham, K.J.; Payne, W.D.; Dunn, D.L.; Sutherland, D.E.; Matas, A.J. Association between cytomegalovirus disease and chronic rejection in kidney transplant recipients. Transplantation 1999, 68, 1879–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weill, D. Role of cytomegalovirus in cardiac allograft vasculopathy. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2001, 3, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humar, A.; Limaye, A.P.; Blumberg, E.A.; Hauser, I.A.; Vincenti, F.; Jardine, A.G.; Abramowicz, D.; Ives, J.A.; Farhan, M.; Peeters, P. Extended valganciclovir prophylaxis in D+/R- kidney transplant recipients is associated with long-term reduction in cytomegalovirus disease: Two-year results of the IMPACT study. Transplantation 2010, 90, 1427–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotton, C.N.; Kumar, D.; Caliendo, A.M.; Asberg, A.; Chou, S.; Danziger-Isakov, L.; Humar, A.; Transplantation Society International CMV Consensus Group. Updated international consensus guidelines on the management of cytomegalovirus in solid-organ transplantation. Transplantation 2013, 96, 333–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castelli, E.C.; Mendes-Junior, C.T.; Deghaide, N.H.; de Albuquerque, R.S.; Muniz, Y.C.; Simões, R.T.; Carosella, E.D.; Moreau, P.; Donadi, E.A. The genetic structure of 3′ untranslated region of the HLA-G gene: polymorphisms and haplotypes. Genes Immun. 2010, 11, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebmann, V.; LeMaoult, J.; Rouas-Freiss, N.; Carosella, E.D.; Grosse-Wilde, H. Quantification and identification of soluble HLA-G isoforms. Tissue Antigens 2007, 69, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| (A) Recipient | CMV Infection N = 18 | No CMV Infection N = 160 | p Value | OR | CI (95%) |
| C/C | 8 (44.4%) | 34 (21.3%) | 0.0394 | 2.965 | 1.082–8.092 |
| C/G | 5 (27.8%) | 80 (50%) | 0.0855 | 0.384 | 0.131–1.129 |
| G/G | 5 (27.8%) | 46 (28.7%) | 1 | 1.037 | 0.35–3.07 |
| Allele | |||||
| C | 26 | 148 | 0.0462 | 2.01 | 1.028–3.947 |
| G | 15 | 172 | |||
| (B) Donor | CMV Infection N = 18 | No CMV Infection N = 160 | p Value | OR | CI (95%) |
| C/C | 4 (22.2%) | 41 (25.6%) | 1 | 0.82 | 0.26–2.66 |
| C/G | 8 (44.4%) | 85 (53.1%) | 0.62 | 0.7059 | 0.26–1.882 |
| G/G | 6 (33.3%) | 34 (21.3%) | 0.24 | 1.85 | 0.64–5.3 |
| Allele | |||||
| C | 16 | 167 | 0.386 | 0.732 | 0.366–1.46 |
| G | 20 | 153 | |||
| (A) Recipient | Graft Loss N = 11 | No Allograft Loss N = 167 | p Value | OR | CI (95%) |
| C/C | 6 (54.5%) | 36 (21.6%) | 0.022 | 4.37 | 1.26–15.14 |
| C/G | 4 (36.4%) | 81 (48.5%) | 0.54 | 0.61 | 0.17–2.15 |
| G/G | 1 (9.1%) | 50 (29.9%) | 0.29 | 0.25 | 0.03–2.03 |
| Allele | |||||
| C | 16 | 153 | 0.0158 | 3.155 | 1.204–8.263 |
| G | 6 | 181 | |||
| (B) Donor | Graft Loss N = 11 | No Allograft Loss N = 167 | p Value | OR | CI (95%) |
| C/C | 5 | 40 | 0.125 | 3.175 | 0.87–11.5 |
| C/G | 5 | 88 | 0.76 | 0.75 | 0.22–2.54 |
| G/G | 1 | 39 | 0.46 | 0.33 | 0.04–2.65 |
| Allele | |||||
| C | 15 | 168 | 0.125 | 2.11 | 0.84–5.33 |
| G | 7 | 166 | |||
| Total | HLA-G +3142 GG or GC carrier | HLA-G +3142 CC carrier | p Value HLA-G +3142 GG/GC vs. CC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recipient | N = 178 | N = 136 | N = 42 | |
| Gender (men/women) | 106/72 | 85/51 | 21/21 | 0.15 |
| Age (y ± SD) | 41.9 ± 15.9 | 41.1 ± 15.6 | 44.6 ± 9.5 | 0.96 |
| CMV positive recipient (R+) | 91 | 73 | 18 | 0.22 |
| Donor | N = 178 | N = 133 | N = 45 | |
| Gender (men/women) | 71/107 | 56/77 | 15/30 | 0.29 |
| Age (y ± SD) | 51.4 ± 9.7 | 50.8 ± 9.6 | 53.0 ± 9.9 | 0.19 |
| CMV positive donor (D+) | 97 | 70 | 27 | 0.39 |
| Cause of end-stage renal disease | ||||
| Diabetes mellitus | 9 | 6 | 3 | 0.44 |
| Chronic glomerulonephritis | 56 | 42 | 14 | 0.85 |
| Polycystic kidney disease | 24 | 18 | 6 | 0.80 |
| Other or unknown | 89 | 70 | 19 | 0.60 |
| Transplant related characteristics | ||||
| Mean cold ischemia time (minutes ± SD) | 133.5 ± 49.4 | 131 ± 51.2 | 140.6 ± 42.9 | 0.67 |
| Lymphocyte-depleting induction therapy (yes/no) | 12/166 | 8/128 | 4/38 | 0.41 |
| AB0 incompatible transplant (yes/no) | 20/158 | 14/122 | 6/36 | 0.47 |
| HLA A, B mismatches (mean ± SD) | 2.0 ± 1.2 | 2.01 ± 1.15 | 2.0 ± 1.1 | 0.78 |
| HLA-DR mismatch (mean ± SD) | 1.1 ± 0.7 | 1.1 ± 0.7 | 1.2 ± 0.6 | 0.85 |
| Transplantation outcome parameters | ||||
| CMV infection first year after KTx total group (yes/no) | 21/157 | 12/124 | 9/33 | 0.027 |
| 5 year Allograft loss (yes/no) | 11/167 | 5/131 | 6/36 | 0.013 |
| Acute cellular rejection (yes/no) | 36/142 | 28/108 | 8/34 | 0.82 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guberina, H.; Tomoya Michita, R.; Dolff, S.; Bienholz, A.; Trilling, M.; Heinemann, F.M.; Horn, P.A.; Kribben, A.; Witzke, O.; Rebmann, V. Recipient HLA-G +3142 CC Genotype and Concentrations of Soluble HLA-G Impact on Occurrence of CMV Infection after Living-Donor Kidney Transplantation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2338. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112338
Guberina H, Tomoya Michita R, Dolff S, Bienholz A, Trilling M, Heinemann FM, Horn PA, Kribben A, Witzke O, Rebmann V. Recipient HLA-G +3142 CC Genotype and Concentrations of Soluble HLA-G Impact on Occurrence of CMV Infection after Living-Donor Kidney Transplantation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(11):2338. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112338
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuberina, Hana, Rafael Tomoya Michita, Sebastian Dolff, Anja Bienholz, Mirko Trilling, Falko M. Heinemann, Peter A. Horn, Andreas Kribben, Oliver Witzke, and Vera Rebmann. 2017. "Recipient HLA-G +3142 CC Genotype and Concentrations of Soluble HLA-G Impact on Occurrence of CMV Infection after Living-Donor Kidney Transplantation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 11: 2338. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112338
APA StyleGuberina, H., Tomoya Michita, R., Dolff, S., Bienholz, A., Trilling, M., Heinemann, F. M., Horn, P. A., Kribben, A., Witzke, O., & Rebmann, V. (2017). Recipient HLA-G +3142 CC Genotype and Concentrations of Soluble HLA-G Impact on Occurrence of CMV Infection after Living-Donor Kidney Transplantation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(11), 2338. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112338