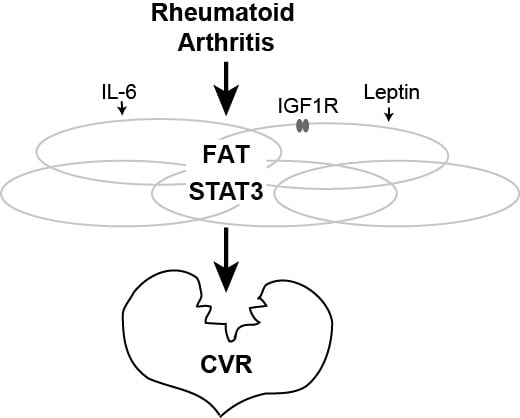
High Expression of STAT3 in Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Associates with Cardiovascular Risk in Women with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Frequency of CVR Factors in the Study Cohort
2.2. Expression of STAT3 is Enriched in WAT
2.3. Metabolic Axis IGF1R–AKT1 in CVR
2.4. Inflammatory Axis TLR4–NF-κB in CVR
2.5. Multivariate Regression Analysis of Parameters Associated with CVR in WAT
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. Modified Systematic Coronary Risk Evaluation (mSCORE)
4.3. Collection and Preparation of Blood and Adipose Tissue Samples
4.4. Preparation of mRNA
4.5. Gene Expression Analysis
4.6. Adipokine Measurement
4.7. Other Serological Measures
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RA | rheumatoid arthritis |
| mSCORE | modified Systemic Coronary Risk Evaluation |
| IQR | interquartile range |
| RF | rheumatoid factor |
| ACPA | antibodies against citrullinated peptides |
| DAS28 | 28 joint count Disease Activity Score |
| BMI | body mass index |
| CVR | cardiovascular risk |
| STAT | signal transducer and activator of transcription |
| RELA | transcription factor p65 |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor kappa B |
| IGF1 | insulin-like growth factor 1 |
| IGF1R | insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor |
| AKT1 | serine-threonine kinase 1 |
| WAT | white adipose tissue |
| WBC | white blood cells |
| TLR | Toll-like receptor |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| CI | Confidence interval |
References
- Gabriel, S.E.; Crowson, C.S.; Kremers, H.M.; Doran, M.F.; Turesson, C.; O’Fallon, W.M.; Matteson, E.L. Survival in rheumatoid arthritis: A population-based analysis of trends over 40 years. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maradit-Kremers, H.; Nicola, P.J.; Crowson, C.S.; Ballman, K.V.; Gabriel, S.E. Cardiovascular death in rheumatoid arthritis: A population-based study. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avina-Zubieta, J.A.; Choi, H.K.; Sadatsafavi, M.; Etminan, M.; Esdaile, J.M.; Lacaille, D. Risk of cardiovascular mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 59, 1690–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabriel, S.E.; Crowson, C.S.; O’Fallon, W.M. Mortality in rheumatoid arthritis: Have we made an impact in 4 decades? J. Rheumatol. 1999, 26, 2529–2533. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ljung, L.; Rantapaa-Dahlqvist, S.; Jacobsson, L.T.; Askling, J. Response to biological treatment and subsequent risk of coronary events in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 2087–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symmons, D.P.; Bankhead, C.R.; Harrison, B.J.; Brennan, P.; Barrett, E.M.; Scott, D.G.; Silman, A.J. Blood transfusion, smoking, and obesity as risk factors for the development of rheumatoid arthritis: Results from a primary care-based incident case-control study in norfolk, england. Arthritis Rheum. 1997, 40, 1955–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolt, P.; Bengtsson, C.; Nordmark, B.; Lindblad, S.; Lundberg, I.; Klareskog, L.; Alfredsson, L. Quantification of the influence of cigarette smoking on rheumatoid arthritis: Results from a population based case-control study, using incident cases. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2003, 62, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Gonzalez-Juanatey, C.; Martin, J. Rheumatoid arthritis: A disease associated with accelerated atherogenesis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 35, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Juanatey, C.; Testa, A.; Garcia-Castelo, A.; Garcia-Porrua, C.; Llorca, J.; Vidan, J.; Hajeer, A.H.; Ollier, W.E.; Mattey, D.L.; Gonzalez-Gay, M.A. Hla-drb1 status affects endothelial function in treated patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Am. J. Med. 2003, 114, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaudo, G.; Marchesi, S.; Gerli, R.; Allegrucci, R.; Giordano, A.; Siepi, D.; Pirro, M.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Schillaci, G.; Mannarino, E. Endothelial dysfunction in young patients with rheumatoid arthritis and low disease activity. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2004, 63, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, A.D.; Manson, J.E.; Rifai, N.; Buring, J.E.; Ridker, P.M. C-reactive protein, interleukin 6, and risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus. JAMA 2001, 286, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solomon, D.H.; Karlson, E.W.; Rimm, E.B.; Cannuscio, C.C.; Mandl, L.A.; Manson, J.E.; Stampfer, M.J.; Curhan, G.C. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in women diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis. Circulation 2003, 107, 1303–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maradit-Kremers, H.; Crowson, C.S.; Nicola, P.J.; Ballman, K.V.; Roger, V.L.; Jacobsen, S.J.; Gabriel, S.E. Increased unrecognized coronary heart disease and sudden deaths in rheumatoid arthritis: A population-based cohort study. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 402–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steingart, R.M.; Packer, M.; Hamm, P.; Coglianese, M.E.; Gersh, B.; Geltman, E.M.; Sollano, J.; Katz, S.; Moye, L.; Basta, L.L.; et al. Sex differences in the management of coronary artery disease. Survival and ventricular enlargement investigators. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 325, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, E.; Frommer, K.W.; Vasile, M.; Muller-Ladner, U. Adipocytokines as driving forces in rheumatoid arthritis and related inflammatory diseases? Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierra-Johnson, J.; Romero-Corral, A.; Lopez-Jimenez, F.; Gami, A.S.; Sert Kuniyoshi, F.H.; Wolk, R.; Somers, V.K. Relation of increased leptin concentrations to history of myocardial infarction and stroke in the united states population. Am. J. Cardiol. 2007, 100, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinan, U.Y.; Canbolat, I.P.; Baydar, O.; Oktay, V.; Imre, G.; Kocas, C.; Abaci, O.; Coskun, U.; Bostan, C.; Kilickesmez, K.O.; et al. Relationship between increased serum resistin level and severity of coronary artery disease. Angiology 2014, 65, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bostrom, E.A.; Svensson, M.; Andersson, S.; Jonsson, I.M.; Ekwall, A.K.; Eisler, T.; Dahlberg, L.E.; Smith, U.; Bokarewa, M.I. Resistin and insulin/insulin-like growth factor signaling in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 2894–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarkowski, A.; Bjersing, J.; Shestakov, A.; Bokarewa, M.I. Resistin competes with lipopolysaccharide for binding to toll-like receptor 4. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2010, 14, 1419–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batra, A.; Pietsch, J.; Fedke, I.; Glauben, R.; Okur, B.; Stroh, T.; Zeitz, M.; Siegmund, B. Leptin-dependent toll-like receptor expression and responsiveness in preadipocytes and adipocytes. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 170, 1931–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panduro, M.; Benoist, C.; Mathis, D. Tissue tregs. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 34, 609–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hursting, S.D.; Hursting, M.J. Growth signals, inflammation, and vascular perturbations: Mechanistic links between obesity, metabolic syndrome, and cancer. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 1766–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erlandsson, M.C.; Toyra Silfversward, S.; Nadali, M.; Turkkila, M.; Svensson, M.N.D.; Jonsson, I.M.; Andersson, K.M.E.; Bokarewa, M.I. IGF-1R signalling contributes to IL-6 production and t cell dependent inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2017, 1863, 2158–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erlandsson, M.C.; Doria Medina, R.; Toyra Silfversward, S.; Bokarewa, M.I. Smoking functions as a negative regulator of IGF1 and impairs adipokine network in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 3082820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Littlewood, T.; Bennett, M. Akt isoforms in vascular disease. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2015, 71, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boucher, J.; Softic, S.; El Ouaamari, A.; Krumpoch, M.T.; Kleinridders, A.; Kulkarni, R.N.; O’Neill, B.T.; Kahn, C.R. Differential roles of insulin and IGF-1 receptors in adipose tissue development and function. Diabetes 2016, 65, 2201–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, P.T.; Smith, L.M.; O’Connor, R. Insulin-like growth factor-1 activates Akt and Jun N-terminal kinases (JNKs) in promoting the survival of T lymphocytes. Immunology 2002, 107, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bluher, S.; Kratzsch, J.; Kiess, W. Insulin-like growth factor I, growth hormone and insulin in white adipose tissue. Best practice & research. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 19, 577–587. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, L.A. Targeting signal transduction as a strategy to treat inflammatory diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 549–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Scherer, P.E. Adipokines as novel biomarkers and regulators of the metabolic syndrome. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1212, E1–E19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cernkovich, E.R.; Deng, J.; Bond, M.C.; Combs, T.P.; Harp, J.B. Adipose-specific disruption of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 increases body weight and adiposity. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 1581–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.; McLeod, L.; Alhayyani, S.; Szczepny, A.; Watkins, D.N.; Chen, W.; Enriori, P.; Ferlin, W.; Ruwanpura, S.; Jenkins, B.J. Blockade of the IL-6 trans-signalling/STAT3 axis suppresses cachexia in Kras-induced lung adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 2017, 36, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.B.; Tanaka, Y.; Mariette, X.; Curtis, J.R.; Lee, E.B.; Nash, P.; Winthrop, K.L.; Charles-Schoeman, C.; Thirunavukkarasu, K.; DeMasi, R.; et al. Long-term safety of tofacitinib for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis up to 8.5 years: Integrated analysis of data from the global clinical trials. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saremi, A.; Anderson, R.J.; Luo, P.; Moritz, T.E.; Schwenke, D.C.; Allison, M.; Reaven, P.D. Association between IL-6 and the extent of coronary atherosclerosis in the veterans affairs diabetes trial (vadt). Atherosclerosis 2009, 203, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tehrani, D.M.; Gardin, J.M.; Yanez, D.; Hirsch, C.H.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Stein, P.K.; Wong, N.D. Impact of inflammatory biomarkers on relation of high density lipoprotein-cholesterol with incident coronary heart disease: Cardiovascular health study. Atherosclerosis 2013, 231, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bermudez, E.A.; Rifai, N.; Buring, J.; Manson, J.E.; Ridker, P.M. Interrelationships among circulating interleukin-6, c-reactive protein, and traditional cardiovascular risk factors in women. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2002, 22, 1668–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpato, S.; Guralnik, J.M.; Ferrucci, L.; Balfour, J.; Chaves, P.; Fried, L.P.; Harris, T.B. Cardiovascular disease, interleukin-6, and risk of mortality in older women: The women’s health and aging study. Circulation 2001, 103, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naerr, G.W.; Rein, P.; Saely, C.H.; Drexel, H. Effects of synthetic and biological disease modifying antirheumatic drugs on lipid and lipoprotein parameters in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2016, 81, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.C.; Solomon, D.H.; Rogers, J.R.; Gale, S.; Klearman, M.; Sarsour, K.; Schneeweiss, S. Cardiovascular safety of tocilizumab versus tumor necrosis factor inhibitors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A multi-database cohort study. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017, 69, 1154–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabe, B.; Chalaris, A.; May, U.; Waetzig, G.H.; Seegert, D.; Williams, A.S.; Jones, S.A.; Rose-John, S.; Scheller, J. Transgenic blockade of interleukin 6 transsignaling abrogates inflammation. Blood 2008, 111, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose-John, S. IL-6 trans-signaling via the soluble IL-6 receptor: Importance for the pro-inflammatory activities of IL-6. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2012, 8, 1237–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taube, A.; Schlich, R.; Sell, H.; Eckardt, K.; Eckel, J. Inflammation and metabolic dysfunction: Links to cardiovascular diseases. American journal of physiology. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2012, 302, H2148–H2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sattar, N.; Wannamethee, G.; Sarwar, N.; Chernova, J.; Lawlor, D.A.; Kelly, A.; Wallace, A.M.; Danesh, J.; Whincup, P.H. Leptin and coronary heart disease: Prospective study and systematic review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 53, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolk, R.; Bertolet, M.; Singh, P.; Brooks, M.M.; Pratley, R.E.; Frye, R.L.; Mooradian, A.D.; Rutter, M.K.; Calvin, A.D.; Chaitman, B.R.; et al. Prognostic value of adipokines in predicting cardiovascular outcome: Explaining the obesity paradox. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2016, 91, 858–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMahon, M.; Skaggs, B.J.; Sahakian, L.; Grossman, J.; FitzGerald, J.; Ragavendra, N.; Charles-Schoeman, C.; Chernishof, M.; Gorn, A.; Witztum, J.L.; et al. High plasma leptin levels confer increased risk of atherosclerosis in women with systemic lupus erythematosus, and are associated with inflammatory oxidised lipids. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 1619–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charles-Schoeman, C.; Fleischmann, R.; Davignon, J.; Schwartz, H.; Turner, S.M.; Beysen, C.; Milad, M.; Hellerstein, M.K.; Luo, Z.; Kaplan, I.V.; et al. Potential mechanisms leading to the abnormal lipid profile in patients with rheumatoid arthritis versus healthy volunteers and reversal by tofacitinib. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnett, F.C.; Edworthy, S.M.; Bloch, D.A.; McShane, D.J.; Fries, J.F.; Cooper, N.S.; Healey, L.A.; Kaplan, S.R.; Liang, M.H.; Luthra, H.S.; et al. The american rheumatism association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1988, 31, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deurenberg, P.; Weststrate, J.A.; Seidell, J.C. Body mass index as a measure of body fatness: Age- and sex-specific prediction formulas. Br. J. Nutr. 1991, 65, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arts, E.E.; Popa, C.D.; Den Broeder, A.A.; Donders, R.; Sandoo, A.; Toms, T.; Rollefstad, S.; Ikdahl, E.; Semb, A.G.; Kitas, G.D.; et al. Prediction of cardiovascular risk in rheumatoid arthritis: Performance of original and adapted score algorithms. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conroy, R.M.; Pyorala, K.; Fitzgerald, A.P.; Sans, S.; Menotti, A.; De Backer, G.; De Bacquer, D.; Ducimetiere, P.; Jousilahti, P.; Keil, U.; et al. Estimation of ten-year risk of fatal cardiovascular disease in europe: The score project. Eur. Heart J. 2003, 24, 987–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.J.; Symmons, D.P.; McCarey, D.; Dijkmans, B.A.; Nicola, P.; Kvien, T.K.; McInnes, I.B.; Haentzschel, H.; Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Provan, S.; et al. Eular evidence-based recommendations for cardiovascular risk management in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other forms of inflammatory arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| No CVR n = 89 | CVR n = 93 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 44 (35–59) | 62 (58–64) | <0.0001 |
| Total cholesterol, mmol/L, >5 mmol/L, n (%) | 4.8 (4.1–5.5) | 5.7 (5.2–6.5) | <0.0001 |
| 31 (35) | 74 (80) | <0.0001 | |
| Systolic blood pressure, >140 mmHg, n (%) | 2 (2) | 26 (28) | <0.0001 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 1 | 6 | 0.1 |
| Disease duration, years, >10 years, n (%) | 6 (3–10) | 10 (6–18) | 0.0002 |
| 20 (22) | 42 (45) | 0.0013 | |
| RF and/or ACPA positive, n (%) | 78/89 (88) | 86/95 (92) | 0.54 |
| DAS28 > 3.2, n (%) | 38/84 (45) | 42/88 (48) | 1 |
| Body fat content, % | 33 (30–37) | 40 (36–43) | 0.005 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 23.6 (21–26) | 26.3 (23–29) | 0.0005 |
| BMI > 25 kg/m2, n (%) | 33/88 (37) | 58/93 (62) | 0.0007 |
| ESR, mm/h | 7 (4.2–13.0) | 11 (6.0–17.0) | 0.002 |
| Methotrexate, mg/week | 17.5 (13–20) | 17.5 (15–20) | 0.74 |
| Current/former smoker, n (%) | 41/89 (46) | 74/93 (80) | <0.0001 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nadali, M.; Pullerits, R.; Andersson, K.M.E.; Töyrä Silfverswärd, S.; Erlandsson, M.C.; Bokarewa, M.I. High Expression of STAT3 in Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Associates with Cardiovascular Risk in Women with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2410. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112410
Nadali M, Pullerits R, Andersson KME, Töyrä Silfverswärd S, Erlandsson MC, Bokarewa MI. High Expression of STAT3 in Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Associates with Cardiovascular Risk in Women with Rheumatoid Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(11):2410. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112410
Chicago/Turabian StyleNadali, Mitra, Rille Pullerits, Karin M. E. Andersson, Sofia Töyrä Silfverswärd, Malin C. Erlandsson, and Maria I. Bokarewa. 2017. "High Expression of STAT3 in Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Associates with Cardiovascular Risk in Women with Rheumatoid Arthritis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 11: 2410. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112410
APA StyleNadali, M., Pullerits, R., Andersson, K. M. E., Töyrä Silfverswärd, S., Erlandsson, M. C., & Bokarewa, M. I. (2017). High Expression of STAT3 in Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue Associates with Cardiovascular Risk in Women with Rheumatoid Arthritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(11), 2410. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112410