Anti-Diabetic Effect of Organo-Chalcogen (Sulfur and Selenium) Zinc Complexes with Hydroxy-Pyrone Derivatives on Leptin-Deficient Type 2 Diabetes Model ob/ob Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Syntheses of [Zn(hmpt)2] and [Zn(hmps)2]
2.2. In Vitro Insulin-Mimetic Activity Assay
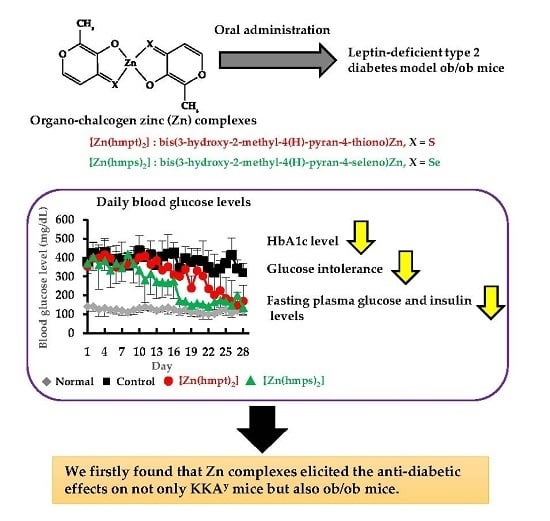
2.3. In Vivo Oral Administration of [Zn(hmpt)2] and [Zn(hmps)2] to ob/ob Mice
2.4. Determination of Zn and Se Concentrations in the Organs of ob/ob Mice
2.5. Histopathological Changes in the Pancreas and Liver Following Treatment with Zn Complexes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Analytical Instrumentation
4.3. Experimental Animals
4.4. Syntheses of [Zn(hmpt)2] and [Zn(hmps)2]
4.4.1. HMPT: 3-Hydroxy-2-Methyl-4(H)-Pyran-4-Thione
4.4.2. HMPS: 3-Hydroxy-2-Methyl-4(H)-Pyran-4-Selenone [17]
4.4.3. [Zn(hmpt)2]: bis(3-Hydroxy-2-Methyl-4(H)-Pyran-4-Thiono)Zn
4.4.4. [Zn(hmps)2]: bis(3-Hydroxy-2-Methyl-4(H)-Pyran-4-Seleno)Zn [17]
4.5. In Vitro Insulin Mimetic Activity Assay
4.6. In Vivo Oral Treatment with both [Zn(hmpt)2] and [Zn(hmps)2] of ob/ob Mice
4.7. OGTT to ob/ob Mice after Treatment with Zn Complexes
4.8. Determination of Blood Parameters and Organ Distributions of Zn and Se in ob/ob Mice after Treatment with Zn Complexes
4.9. Histopathology and Morphometric Analysis
4.10. Detection of Glycogen and TG in the Liver
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALP | alkaline phosphatase |
| AST | aspartate aminotransferase |
| ALT | alanine aminotransferase |
| BUN | blood urea nitrogen |
| G6Pase | glucose-6-phosphatase |
| GK | glucokinase |
| GLUT2 | glucose transporter type 2 |
| HE | hematoxylin and eosin |
| hmps | 3-hydroxy-2-methyl-4(H)-pyran-4-selenone |
| hmpt | 3-hydroxy-2-methyl-4(H)-pyran-4-thione |
| ICP-MS | inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry |
| OGTT | oral glucose tolerance test |
| PDX-1 | pancreatic duodenal homeobox-1 |
| PEPCK | phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase |
| PTEN | phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted from chromosome 10 |
| PTP-1B | protein tyrosine phosphatase 1b |
| T-CHO | total cholesterol |
| TG | triglyceride |
| [Zn(hmps)2] | bis(3-hydroxy-2-methyl-4(H)-pyran-4-seleno)Zn |
| [Zn(hmpt)2] | bis(3-hydroxy-2-methyl-4(H)-pyran-4-thiono)Zn |
References
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 7th ed.; International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2016; Available online: http://www.diabetesatlas.org (accessed on 1 August 2017).
- American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, S81–S90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olokoba, A.B.; Obateru, O.A.; Olokoba, L.B. Type 2 diabetes mellitus: A review of current trends. Oman Med. J. 2012, 27, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meunier, N.; O’Connor, J.M.; Maiani, G.; Cashman, K.D.; Secker, D.L.; Ferry, M.; Roussel, A.M.; Coudray, C. Importance of zinc the elderly: The ZENITH study. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 59, S1–S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulston, L.; Dandona, P. Insulin-like effect of zinc on adipocytes. Diabetes 1980, 29, 665–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, J.M.; Contoreggi, C.S. The mechanism of the insulin-like effects of ionic zinc. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 4362–4368. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shisheva, A.; Gefel, D.; Shechter, Y. Insulin-like effect of zinc ion In Vitro and In Vivo: Preferential effects on desensitized adipocytes and induction of normoglycemia in streptozotocin-induced rats. Diabetes 1992, 41, 982–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.D.; Liou, S.J.; Lin, P.Y.; Yang, V.C.; Alexander, P.S.; Lin, W.H. Effects of zinc supplementation on the plasma glucose level and insulin activity in genetically obese (ob/ob) mice. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 1998, 61, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, Y.; Ueda, E.; Kawabe, K.; Miyake, H.; Sakurai, H.; Kojima, Y. New insulin-mimetic zinc(II) complexes; bis-maltolato Zinc(II) and bis-2-hydroxypyridine-N-oxido Zinc(II) with Zn(O4) coordination mode. Chem. Lett. 2000, 29, 874–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, Y.; Ueda, E.; Kawabe, K.; Miyake, H.; Takino, T.; Sakurai, H.; Kojima, Y. Development of new insulinomimetic Zinc(II) picolinate complexes with a Zn(N2O2) coordination mode: Structure characterization, In Vitro, and In Vivo studies. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2002, 7, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, Y.; Ueda, E.; Sakurai, H.; Kojima, Y. Anti-diabetes effect of Zn(II)/carnitine complex by oral administration. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2003, 51, 230–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, E.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Kishimoto, N.; Tadokoro, M.; Yanagihara, N.; Sakurai, H.; Kojima, Y. New insulinomimetic Zinc(II) complexes of nicotinamide and its derivatives: X-ray structure and biochemical activity. Chem. Lett. 2001, 30, 1184–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, H.; Yasui, H.; Yoshikawa, Y. Pharmacological and pharmacokinetic studies of anti-diabetic tropolonato-Zn(II) complexes with Zn(S2O2) coordination mode. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 60, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, S.; Yasui, H.; Yoshikawa, Y. Development of a novel antidiabetic zinc complex with an organoselenium ligand at the lowest dosage in KK-Ay mice. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2013, 121, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwatsuka, H.; Shino, A.; Suzuki, Z. General survey of diabetic features of yellow KK mice. Endocrinol. Jpn. 1970, 17, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernándex-Formoso, G.; Pérez-Sieira, S.; González-Touceda, D.; Dieguez, C.; Tovar, S. Leptin, 20 years of searching for glucose homeostasis. Life Sci. 2015, 140, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishiguchi, T.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Yasui, H. Investigating the target organs of novel anti-diabetic zinc complexes with organo-selenium ligands. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2007. in print. [Google Scholar]
- Gutmann, V. The Donor-Acceptor Approach to Molecular Interactions; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1978; pp. 35–56. ISBN 978-1-4615-8827-6. [Google Scholar]
- Quentin, M.A.; Goldin, R.D. Mouse models in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and steatohepatitis research. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2006, 87, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, I.K.; Go, V.L.; Harris, D.M.; Yip, I.; Kang, K.W.; Song, M.K. Effects of cyclo (his-pro) plus zinc on glucose metabolism in genetically diabetic obese mice. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2003, 5, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, Y.; Ueda, E.; Miyake, H.; Sakurai, H.; Kojima, Y. Insulinomimetic bis(maltolato)Zinc(II) complex: Blood glucose normalizing effect in KK-Ay mice with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 281, 1190–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Environmental Health Criteria 221: Zinc; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2001; Available online: http://www.who.int/ipcs/publications/ehc/ehc_221/en/ (accessed on 1 November 2017).
- Kolodziejczyk, L.; Put, A.; Szczecin, P.G. Liver morphology and histochemistry in rats resulting from ingestion of sodium selenite and sodium fluoride. Fluoride 2000, 33, 6–16. [Google Scholar]
- Sayato, Y.; Hasegawa, Y.; Taniguchi, S.; Maeda, H.; Ozaki, K.; Narama, I.; Nakamuro, K. Acute and subacute oral toxicity of selenocystine in Mice. Eisei Kagaku 1993, 39, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreutner, W.; Springer, S.C.; Sherwood, J.E. Resistance of gluconeogenic and glycogenic pathways in obese-hyperglycemic mice. Am. J. Physiol. 1975, 228, 663–671. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sajan, M.P.; Ivey, R.A.; Lee, M.C.; Farese, R.V. Hepatic insulin resistance in ob/ob mice involves increases in ceramide, aPKC activity, and selective impairment of Akt-dependent FoxO1 phosphorylation. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellomo, E.; Singh, K.B.; Massarotti, A.; Hogstrand, C.; Maret, W. The metal face of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 327–328, 70–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naito, Y.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Masuda, K.; Yasui, H. Bis(hinokitiolato)zinc complex ([Zn(hkt)2]) activates Akt/protein kinase B independent of insulin signal transduction. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 21, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naito, Y.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Shintani, M.; Kamoshida, S.; Kajiwara, N.; Yasui, H. Anti-hyperglycemic effect of Long-term bis(hinokitiolato)zinc complex ([Zn(hkt)2]) ingestion on insulin resistance and pancreatic islet cells protection in type 2 diabetic KK-Ay mice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 40, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barthel, A.; Ostrakhovitch, E.A.; Walter, P.L.; Kamplötter, A.; Klotz, L.O. Stimulation of phosphoionositide 3-kinase/Akt signaling by copper and zinc ions: Mechanisms and consequences. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 463, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamaki, M.; Fujitani, Y.; Hara, A.; Uchida, T.; Tamura, Y.; Takeno, K.; Kawaguchi, M.; Watanabe, T.; Ogihara, T.; Fukunaka, A.; et al. The diabetes-susceptible gene SLC 30A8/ZnT8 regulates hepatic insulin clearance. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 4513–4524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herberg, L.; Coleman, D.L. Laboratory animals exhibiting obesity and diabetes syndromes. Metabolism 1977, 26, 59–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, K.; Liu, Z.; Patel, S.; Doble, B.W.; Li, L.; Cras-Méneur, C.; Martinez, S.C.; Welling, C.M.; White, M.F.; Bernal-Mizrachi, E.; et al. Genetic deficiency of glycogen synthase kinase-3b corrects diabetes in mouse models of insulin resistance. PLoS Biol. 2008, 6, e37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kitamura, T.; Nakae, J.; Kitamura, Y.; Kido, Y.; Biggs, W.H., III; Wright, C.V.; White, M.F.; Arden, K.C.; Accili, D. The forkhead transcription factor Foxo1 links insulin signaling to pdx1 regulation of pancreatic β cell growth. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 1839–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, H.; Perfetti, R. Pancreas duodenum homeobox-1 regulates pancreas development during embryogenesis and islet cell function in adulthood. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2002, 146, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, H.; Yamamoto, E.; Tashiro, F.; Ikegami, H.; Ogihara, T.; Miyazaki, J. β-cell neogenesis induced by adenovirus-mediated gene delivery of transcription factor pdx-1 into mouse pancreas. Gene Ther. 2003, 10, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakai, M.; Watanabe, H.; Fujiwara, C.; Kakegawa, H.; Satoh, T.; Takada, J.; Matsushita, R.; Sakurai, H. Mechanism on insulin-like action of vanadyl sulfate: Studies on interaction between rat adipocytes and vanadium compounds. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 1995, 18, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folch, J.; Ascoli, I.; Lees, M.; Meath, J.A.; LeBaroon, R.N. Preparation of lipid extracts from brain tissue. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 191, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]






| Zn Complex | IC50 (μM) | Glucose Uptake (µg/106 Cells) |
|---|---|---|
| [Zn(hmpt)2] | 2 ± 1 | 79 ± 26 |
| [Zn(hmps)2] [17] | 8 ± 1 | 138 ± 6 |
| ZnSO4 [17] | 585 ± 305 | none |
| Normal | Control | [Zn(hmpt)2] | [Zn(hmps)2] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HbA1c (%) | 4.1 ± 0.3 | 7.9 ± 0.8 ** | 6.5 ± 0.7 **,## | 6.7 ± 0.4 **,## |
| Insulin (ng/mL) | 0.3 ± 0.0 | 2.2 ± 1.0 ** | 0.9 ± 0.3 ## | 1.4 ± 0.6 ** |
| Adiponectin (µg/mL) | 12.8 ± 2.7 | 8.2 ± 1.1 ** | 9.4 ± 0.8 ** | 9.0 ± 0.8 ** |
| AST (U/L) | 34 ± 6 | 93 ± 19 * | 103 ± 25 ** | 200 ± 55 **,##,†† |
| ALT (U/L) | 13 ± 2 | 164 ± 64 * | 118 ± 68 | 355 ± 138 **,##,†† |
| BUN (mg/dL) | 16 ± 1 | 17 ± 4 | 23 ± 2 **,## | 24 ± 3 **,## |
| TG (mg/dL) | 30 ± 3 | 83 ± 16 ** | 76 ± 25 ** | 87 ± 11 ** |
| T-CHO (mg/dL) | 76 ± 12 | 195 ± 16 ** | 189 ± 42 ** | 186 ± 16 ** |
| ALP (U/L) | 257 ± 28 | 723 ± 126 ** | 360 ± 88 ## | 550 ± 89 **,##,†† |
| Organ | Zn | Se | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | Control | [Zn(hmpt)2] | [Zn(hmps)2] | Normal | Control | [Zn(hmpt)2] | [Zn(hmps)2] | |
| Plasma | 1.8 ± 0.2 | 2.1 ± 0.1 | 2.3 ± 0.2 ** | 2.5 ± 0.2 **,## | 0.4 ± 0.1 | 0.6 ± 0.1 * | 0.5 ± 0.1 | 1.1 ± 0.2 **,##,†† |
| Liver | 99 ± 10 | 44 ± 5 ** | 74 ± 30 # | 46 ± 6 ##,† | 5.4 ± 0.6 | 2.1 ± 0.3 ** | 2.4 ± 0.7 ** | 5.1 ± 0.6 ##,†† |
| Kidney | 77 ± 6 | 67 ± 3 ** | 73 ± 4 | 68 ± 4 ** | 6.6 ± 0.2 | 6.4 ± 0.2 | 5.8 ± 0.5 | 12.7 ± 2.0 **,##,†† |
| Muscle | 44 ± 6 | 47 ±10 | 45 ± 8 | 41 ± 2 | 1.2 ± 0.4 | 1.3 ± 0.4 | 1.2 ± 0.2 | 2.5 ± 0.4 **,#,†† |
| Pancreas | 121 ± 14 | 133 ± 19 | 153 ± 18 | 158 ± 28 * | 1.7 ± 0.5 | 2.3 ± 0.6 | 1.6 ± 0.9 | 3.4 ± 0.8 **,##,†† |
| Spleen | 87 ± 9 | 100 ± 17 | 95 ± 11 | 95 ± 12 | 2.4 ± 0.9 | 2.7 ± 0.8 | 2.2 ± 0.3 | 9.1 ± 2.4 **,##,†† |
| Bone | 177 ± 8 | 154 ± 7 ** | 188 ± 8 ## | 162 ± 10 *,†† | 0.6 ± 0.3 | 0.5 ± 0.2 | 0.5 ± 0.2 | 1.9 ± 0.6 |
| (A) | |||||
| Plasma | Liver | Kidney | Bone | Pancreas | |
| Δ[Zn] (nmol/g) | 3 | 453 | 86 | 517 | 302 |
| (B) | |||||
| Plasma | Liver | Kidney | Bone | Pancreas | |
| Δ[Zn] (nmol/g) | 6 | 23 | 20 | 124 | 375 |
| Δ[Se] (nmol/g) | 6 | 38 | 81 | 18 | 14 |
| Δ[Zn]/Δ[Se] | 1.0 | 0.61 | 0.25 | 6.9 | 27 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nishiguchi, T.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Yasui, H. Anti-Diabetic Effect of Organo-Chalcogen (Sulfur and Selenium) Zinc Complexes with Hydroxy-Pyrone Derivatives on Leptin-Deficient Type 2 Diabetes Model ob/ob Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2647. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122647
Nishiguchi T, Yoshikawa Y, Yasui H. Anti-Diabetic Effect of Organo-Chalcogen (Sulfur and Selenium) Zinc Complexes with Hydroxy-Pyrone Derivatives on Leptin-Deficient Type 2 Diabetes Model ob/ob Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(12):2647. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122647
Chicago/Turabian StyleNishiguchi, Takayuki, Yutaka Yoshikawa, and Hiroyuki Yasui. 2017. "Anti-Diabetic Effect of Organo-Chalcogen (Sulfur and Selenium) Zinc Complexes with Hydroxy-Pyrone Derivatives on Leptin-Deficient Type 2 Diabetes Model ob/ob Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 12: 2647. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122647
APA StyleNishiguchi, T., Yoshikawa, Y., & Yasui, H. (2017). Anti-Diabetic Effect of Organo-Chalcogen (Sulfur and Selenium) Zinc Complexes with Hydroxy-Pyrone Derivatives on Leptin-Deficient Type 2 Diabetes Model ob/ob Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(12), 2647. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122647