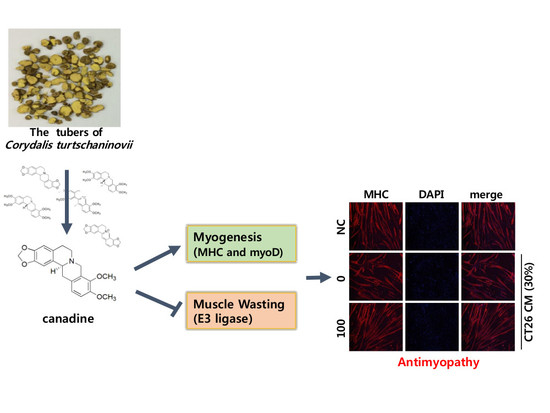
Canadine from Corydalis turtschaninovii Stimulates Myoblast Differentiation and Protects against Myotube Atrophy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Purification of Compounds from Corydalis turtschaninovii
2.2. Evaluation of Myogenic Activity of CT Compounds
2.3. Canadine Stimulates Myoblast Differentiation
2.4. Canadine Activates p38 MAPK and Akt Signaling Pathway
2.5. Canadine Prevents Muscle Wasting In Vitro
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Isolation of Canadine from the Tuber of Corydalis turtschaninovii
4.2. Cell Culture, Myoblast Differentiation and Preparation of Conditioned Medium of Cancer Cells
4.3. MyoD-Reporter Gene Assay
4.4. Immunostaining for MHC
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. RNA Extraction and RT-qPCR
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cohen, S.; Nathan, J.A.; Goldberg, A.L. Muscle wasting in disease: Molecular mechanisms and promising therapies. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 58–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fearon, K.C.; Glass, D.J.; Guttridge, D.C. Cancer cachexia: Mediators, signaling, and metabolic pathways. Cell Metab. 2012, 16, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.; Ji, L.L. Role of PGC-1alpha in muslce function and aging. J. Sport Health Sci. 2013, 2, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanzani, A.; Conraads, V.M.; Penna, F.; Martinet, W. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of skeletal muscle atrophy: An update. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2012, 3, 163–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutt, V.; Gupta, S.; Dabur, R.; Injeti, E.; Mittal, A. Skeletal muscle atrophy: Potential therapeutic agents and their mechanisms of action. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 99, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, X.H.; Wang, H.; Du, J.; Mitch, W.E. Satellite cell dysfunction and impaired IGF-1 signaling cause CKD-induced muscle atrophy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.; Im, M.; Gu, M.J.; Ma, J.Y. Citrus unshiu peel extract alleviates cancer-induced weight loss in mice bearing CT-26 adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wu, Y.; Yang, T.; Wei, M.; Wang, Y.; Deng, X.; Shen, C.; Li, W.; Zhang, H.; Xu, W.; et al. Salidroside alleviates cachexia symptoms in mouse models of cancer cachexia via activating mTOR signalling. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2016, 7, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Wan, L.; Li, Y.; Yu, Q.; Chen, P.; Gan, R.; Yang, Q.; Han, Y.; Guo, C. Baicalin, a component of Scutellaria baicalensis, alleviates anorexia and inhibits skeletal muscle atrophy in experimental cancer cachexia. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 12415–12425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Sung, B.; Kang, Y.J.; Kim, D.H.; Lee, Y.; Hwang, S.Y.; Yoon, J.H.; Yoo, M.A.; Kim, C.M.; Chung, H.Y.; et al. The combination of ursolic acid and leucine potentiates the differentiation of C2C12 murine myoblasts through the mTOR signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 35, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyle, M.C.; Ebert, S.M.; Cook, D.P.; Kunkel, S.D.; Fox, D.K.; Bongers, K.S.; Bullard, S.A.; Dierdorff, J.M.; Adams, C.M. Systems-based discovery of tomatidine as a natural small molecule inhibitor of skeletal muscle atrophy. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 14913–14924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Yoo, M.; Go, G.Y.; Hwang, J.; Lee, H.G.; Kim, Y.K.; Seo, D.W.; Baek, N.I.; Ryu, J.H.; Kang, J.S.; et al. Tetrahydropalmatine promotes myoblast differentiation through activation of p38MAPK and MyoD. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 455, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Yoo, M.; Go, G.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Choi, H.; Leem, Y.E.; Kim, Y.K.; Seo, D.W.; Ryu, J.H.; Kang, J.S.; et al. Bakuchiol augments MyoD activation leading to enhanced myoblast differentiation. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2016, 248, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, M.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, Y.K.; Seo, D.W.; Baek, N.I.; Ryu, J.H.; Kang, J.S.; Bae, G.U. Dehydrocorydaline promotes myogenic differentiation via p38 MAPK activation. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 3029–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.K.; Cho, J.G.; Song, M.C.; Yoo, J.S.; Lee, D.Y.; Yang, H.J.; Han, K.M.; Kim, D.H.; Oh, Y.J.; Jeong, T.S.; et al. Isolation of isoquinoline alkaloids from the tuber of Corydalis turtschaninovii and their inhibition activity on low density lipoprotein oxidation. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2009, 52, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrzanowska, M. Synthesis of Isoquinoline Alkaloids. Total Synthesis of (±)-Stylopine. J. Nat. Prod. 1995, 58, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushman, M.; Dekow, F.W. A Total Synthesis of Corydaline. Tetrahedron 1997, 34, 1435–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentry, E.J.; Jampani, H.B.; Keshavarz-Shokri, A.; Morton, M.D.; Velde, D.V.; Telikepalli, H.; Mitscher, L.A.; Shawar, R.; Humble, D.; Baker, W. Antitubercular Natural Products: Berberine from the Roots of Commercial Hydrastis canadensis Powder. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cutter, P.S.; Miller, R.B.; Schore, L.E. Synthesis of protoberberines using a silyl-directed Pictet–Spengler cyclization. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Hu, S.; Zhang, M.; Li, L.; Lin, Y. Simultaneous determination of four alkaloids in mice plasma and brain by LC-MS/MS for pharmacokinetic studies after administration of Corydalis Rhizoma and Yuanhu Zhitong extracts. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 92, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, R.B.; Stevenson, E.; Koncarevic, A.; Mitchell-Felton, H.; Essig, D.A.; Kandarian, S.C. Activation of an alternative NF-κB pathway in skeletal muscle during disuse atrophy. FASEB J. 2002, 16, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Woodring, P.J.; Bhakta, K.S.; Tamura, K.; Wen, F.; Feramisco, J.R.; Karin, M.; Wang, J.Y.; Puri, P.L. p38 and extracellular signal-regulated kinases regulate the myogenic program at multiple steps. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 3951–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandromme, M.; Rochat, A.; Meier, R.; Carnac, G.; Besser, D.; Hemmings, B.A.; Fernandez, A.; Lamb, N.J. Protein kinase B beta/Akt2 plays a specific role in muscle differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 8173–8179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuenda, A.; Rousseau, S. p38 MAP-kinases pathway regulation, function and role in human diseases. Biochim, Biophys. Acta 2007, 1773, 1358–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassar, A.B. The p38 MAPK family, a pushmi-pullyu of skeletal muscle differentiation. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 187, 941–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bae, G.U.; Lee, J.R.; Kim, B.G.; Han, J.W.; Leem, Y.E.; Lee, H.J.; Ho, S.M.; Hahn, M.J.; Kang, J.S. Cdo interacts with APPL1 and activates Akt in myoblast differentiation. Mol. Biol. Cell 2010, 21, 2399–2411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porporato, P.E. Understanding cachexia as a cancer metabolism syndrome (Review). Oncogenesis 2016, 5, e200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiota, C.; Abe, T.; Kawai, N.; Ohno, A.; Teshima-Kondo, S.; Mori, H.; Terao, J.; Tanaka, E.; Nikawa, T. Flavones Inhibit LPS-Induced Atrogin-1/MAFbx Expression in Mouse C2C12 Skeletal Myotubes. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2015, 61, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laumonier, T.; Menetrey, J. Muscle injuries and strategies for improving their repair. J. Exp. Orthop. 2016, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, S.; Yakabe, M.; Akishita, M. Age-related sarcopenia and its pathophysiological bases. Inflamm. Regen. 2016, 36, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Jentoft, A.J.; Landi, F.; Topinkova, E.; Michel, J.P. Understanding sarcopenia as a geriatric syndrome. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2010, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avula, B.; Wang, Y.H.; Khan, I.A. Quantitative determination of alkaloids from roots of Hydrastis canadensis L. and dietary supplements using ultra-performance liquid chromatography with UV detection. J. AOAC Int. 2012, 95, 1398–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, K.; Wen, J.; Fan, G.; Chai, Y.; Hong, Z. Chiral HPLC determination and stereoselective pharmacokinetics of tetrahydroberberine enantiomers in rats. Chirality 2012, 24, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Haq, H.; Cometa, M.F.; Palmery, M.; Leone, M.G.; Silvestrini, B.; Saso, L. Relaxant effects of Hydrastis canadensis L. and its major alkaloids on guinea pig isolated trachea. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2000, 87, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correché, E.R.; Andujar, S.A.; Kurdelas, R.R.; Lechón, M.J.G.; Freile, M.L.; Enriz, R.D. Antioxidant and cytotoxic activities of canadine: Biological effects and structural aspects. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2008, 16, 3641–3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, C.; Wang, F.Q.; Li, C.H.; Zhang, Q.H.; Hu, Y.J.; Xia, Z.N.; Yang, F.Q. Simultaneous screening and analysis of antiplatelet aggregation active alkaloids from Rhizoma Corydalis. Pharm. Biol. 2016, 54, 3113–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chlebek, J.; de Simone, A.; Hostalkova, A.; Opletal, L.; Perez, C.; Perez, D.I.; Havlikova, L.; Cahlikova, L.; Andrisano, V. Application of BACE1 immobilized enzyme reactor for the characterization of multifunctional alkaloids from Corydalis cava (Fumariaceae) as Alzheimer’s disease targets. Fitoterapia 2016, 109, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietra, D.; Borghini, A.; Bianucci, A.M. In vitro studies of antifibrotic and cytoprotective effects elicited by proto-berberine alkaloids in human dermal fibroblasts. Pharmacol. Rep. 2015, 67, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; MacQuarrie, K.L.; Analau, E.; Tyler, A.E.; Dilworth, F.J.; Cao, Y.; Diede, S.J.; Tapscott, S.J. MyoD and E-protein heterodimers switch rhabdomyosarcoma cells from an arrested myoblast phase to a differentiated state. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 694–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabane, C.; Coldefy, A.S.; Yeow, K.; Dérijard, B.T. The p38 pathway regulates Akt both at the protein and transcriptional activation levels during myogenesis. Cell. Signal. 2004, 16, 1405–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, B.A.; Drujan, D.; Willis, M.S.; Murphy, L.O.; Corpina, R.A.; Burova, E.; Rakhilin, S.V.; Stitt, T.N.; Patterson, C.; Latres, E.; et al. The E3 Ligase MuRF1 degrades myosin heavy chain protein in dexamethasone-treated skeletal muscle. Cell Metab. 2007, 6, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagirand-Cantaloube, J.; Cornille, K.; Csibi, A.; Batonnet-Pichon, S.; Leibovitch, M.P.; Leibovitch, S.A. Inhibition of atrogin-1/MAFbx mediated MyoD proteolysis prevents skeletal muscle atrophy in vivo. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, H.; Zhang, G.; Sin, K.W.; Liu, Z.; Lin, R.K.; Li, M.; Li, Y.P. Activin A induces skeletal muscle catabolism via p38β mitogen-activated protein kinase. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2017, 8, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bongers, K.S.; Fox, D.K.; Ebert, S.M.; Kunkel, S.D.; Dyle, M.C.; Bullard, S.A.; Dierdorff, J.M.; Adams, C.M. Skeletal muscle denervation causes skeletal muscle atrophy through a pathway that involves both Gadd45a and HDAC4. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 305, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Chan, Y.L.; Li, T.L.; Wu, C.J. Improving cachectic symptoms and immune strength of tumour-bearing mice in chemotherapy by a combination of Scutellaria baicalensis and Qing-Shu-Yi-Qi-Tang. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 1074–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yae, S.; Takahashi, F.; Yae, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Tsukada, R.; Koike, K.; Minakata, K.; Murakami, A.; Nurwidya, F.; Kato, M.; et al. Hochuekkito (TJ-41), a Kampo Formula, Ameliorates Cachexia Induced by Colon 26 Adenocarcinoma in Mice. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 976926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iizuka, N.; Hazama, S.; Yoshimura, K.; Yoshino, S.; Tangoku, A.; Miyamoto, K.; Okita, K.; Oka, M. Anticachectic effects of the natural herb Coptidis rhizoma and berberine on mice bearing colon 26/clone 20 adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 99, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shadfar, S.; Couch, M.E.; McKinney, K.A.; Weinstein, L.J.; Yin, X.; Rodriguez, J.E.; Guttridge, D.C.; Willis, M. Oral resveratrol therapy inhibits cancer-induced skeletal muscle and cardiac atrophy in vivo. Nutr. Cancer 2011, 63, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyke, S.M.; Russell, S.T.; Tisdale, M.J. Induction of proteasome expression in skeletal muscle is attenuated by inhibitors of NF-κB activation. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 91, 1742–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Gong, Y.; Qiu, J.; Chen, Y.; Ding, F.; Zhao, Q. TRAF6 inhibition rescues dexamethasone-induced muscle atrophy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 11126–11141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azmi, S.; Ozog, A.; Taneja, R. Sharp-1/DEC2 inhibits skeletal muscle differentiation through repression of myogenic transcription factors. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 52643–52652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Gene Name | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer | Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAFbx | CGACCTGCCTGTGTGCTTAC | CTTGCGAATCTGCCTCTCTG | BC027211 |
| Murf1 | GGTGCCTACTTGCTCCTTGT | CTGGTGGCTATTCTCCTTGG | NC_000070 |
| GAPDH | TGCACCACCAACTGCTTAG | GGCATGGACTGTGGTCATGAG | BC096042 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, H.; Lee, S.-J.; Bae, G.-U.; Baek, N.-I.; Ryu, J.-H. Canadine from Corydalis turtschaninovii Stimulates Myoblast Differentiation and Protects against Myotube Atrophy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2748. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122748
Lee H, Lee S-J, Bae G-U, Baek N-I, Ryu J-H. Canadine from Corydalis turtschaninovii Stimulates Myoblast Differentiation and Protects against Myotube Atrophy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(12):2748. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122748
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Hyejin, Sang-Jin Lee, Gyu-Un Bae, Nam-In Baek, and Jae-Ha Ryu. 2017. "Canadine from Corydalis turtschaninovii Stimulates Myoblast Differentiation and Protects against Myotube Atrophy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 12: 2748. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122748
APA StyleLee, H., Lee, S. -J., Bae, G. -U., Baek, N. -I., & Ryu, J. -H. (2017). Canadine from Corydalis turtschaninovii Stimulates Myoblast Differentiation and Protects against Myotube Atrophy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(12), 2748. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122748