Developing and Evaluating a Flexible Wireless Microcoil Array Based Integrated Interface for Epidural Cortical Stimulation
Abstract
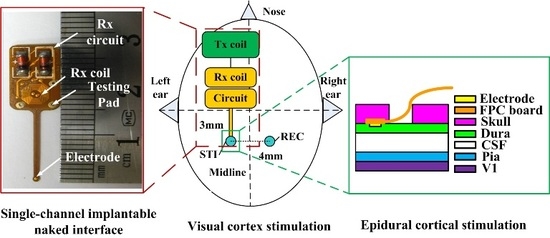
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Benchtop Testing
2.2. In Vivo Study
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. System Schematic
Benchtop Testing
4.2. Anesthesia and Surgery
4.3. Stimulation and Recording Paradigms
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CCEP | Cortico-Cortical Evoked Potential |
| ECS | Epidural Cortical Stimulation |
| IPG | Implantable Pulse Generator |
| FPC | Flexible Printed Circuit |
References
- Geurts, M.; Petersson, J.; Brizzi, M.; Luijckx, G.; Algra, A.; Dippel, D.; Kappelle, L.; van der Worp, H. Coolist: Cooling for ischaemic stroke trial. A multicenter, open, randomized, phase II clinical trial. Int. J. Stroke 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowe, F.J.; Walker, M.; Rockliffe, J.; Pollock, A.; Noonan, C.; Howard, C.; Glendinning, R.; Feechan, R.; Currie, J. Care provision for poststroke visual impairment. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2015, 24, 1131–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, G.N.; Wycoco, V.; Ghosh, S. Transient visual hallucinations due to posterior callosal stroke. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2015, 24, E147–E148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, R.M.; Harvey, R.L.; Kissela, B.M.; Winstein, C.J.; Lutsep, H.L.; Parrish, T.B.; Cramer, S.C.; Venkatesan, L. Epidural electrical stimulation for stroke rehabilitation: Results of the prospective, multicenter, randomized, single-blinded everest trial. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2016, 30, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nudo, R.J. Plasticity. NeuroRx 2006, 3, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karabanov, A.; Ziemann, U.; Hamada, M.; George, M.S.; Quartarone, A.; Classen, J.; Massimini, M.; Rothwell, J.; Siebner, H.R. Consensus paper: Probing homeostatic plasticity of human cortex with non-invasive transcranial brain stimulation. Brain Stimul. 2015, 8, 993–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plautz, E.J.; Barbay, S.; Frost, S.B.; Friel, K.M.; Dancause, N.; Zoubina, E.V.; Stowe, A.M.; Quaney, B.M.; Nudo, R.J. Post-infarct cortical plasticity and behavioral recovery using concurrent cortical stimulation and rehabilitative training: A feasibility study in primates. Neurol. Res. 2003, 25, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plow, E.; Machado, A. Invasive neurostimulation in stroke rehabilitation. Neurotherapeutics 2014, 11, 572–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, K.; Matsunaga, T.; Tomite, T.; Yoshikawa, T.; Shimada, Y. Effect of electrical stimulation therapy on upper extremity functional recovery and cerebral cortical changes in patients with chronic hemiplegia. Biomed. Res. 2012, 33, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, R.; Ruland, S.; Weinand, M.; Lowry, D.; Dafer, R.; Bakay, R. Cortical stimulation for the rehabilitation of patients with hemiparetic stroke: A multicenter feasibility study of safety and efficacy. J. Neurosurg. 2008, 108, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.A.; Lutsep, H.L.; Weinand, M.; Cramer, S.C. Motor cortex stimulation for the enhancement of recovery from stroke: A prospective, multicenter safety study. Neurosurgery 2006, 58, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Bryant, A.J.; Adkins, D.L.; Sitko, A.A.; Combs, H.L.; Nordquist, S.K.; Jones, T.A. Enduring poststroke motor functional improvements by a well-timed combination of motor rehabilitative training and cortical stimulation in rats. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2016, 30, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherney, L.R. Epidural cortical stimulation as adjunctive treatment for nonfluent aphasia: Phase 1 clinical trial follow-up findings. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2016, 30, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, P.M.; Rosenfeld, J.V. Electrical stimulation of the brain and the development of cortical visual prostheses: An historical perspective. Brain Res. 2016, 1630, 208–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, P.M.; Ackland, H.M.; Lowery, A.J.; Rosenfeld, J.V. Restoration of vision in blind individuals using bionic devices: A review with a focus on cortical visual prostheses. Brain Res. 2015, 1595, 51–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clair, W.K.; Montgomery, J.A.; Ellis, C.R. Apparent failure to sense during temporary pacing with a permanent pulse generator. Pace Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2015, 38, 772–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swerdlow, C.D.; Kalahasty, G.; Ellenbogen, K.A. Implantable cardiac defibrillator lead failure and management. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 67, 1358–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabi, J.; Anitescu, M. Late extrusion of an implantable pulse generator of a spinal cord stimulator. Pain Physician 2016, 19, E671–E674. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Akbar, U.; Raike, R.S.; Hack, N.; Hess, C.W.; Skinner, J.; Martinez-Ramirez, D.; DeJesus, S.; Okun, M.S. Randomized, blinded pilot testing of nonconventional stimulation patterns and shapes in Parkinson’s disease and essential tremor: Evidence for further evaluating narrow and biphasic pulses. Neuromodulation 2016, 19, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, H.; Li, G.; Lin, L.; Zhang, W.; Xu, R. Transcutaneous Coupling Implantable Stimulator. In Life System Modeling and Intelligent Computing; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; pp. 230–237. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson-Corley, K.N.; Flouty, O.; Oya, H.; Gillies, G.T.; Howard, M.A. Postsurgical pathologies associated with intradural electrical stimulation in the central nervous system: Design implications for a new clinical device. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhao, T.; Jiang, W.; Jia, R.; Niu, D.; Qiu, G.; Fan, L.; Li, X.; Liu, W.; Chen, B.; et al. Flexible battery-less bioelectronic implants: Wireless powering and manipulation by near-infrared light. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 7071–7079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badia, J.; Raspopovic, S.; Carpaneto, J.; Micera, S.; Navarro, X. Spatial and functional selectivity of peripheral nerve signal recording with the transversal intrafascicular multichannel electrode (time). IEEE Trans. Neural Syst Rehabil. Eng. 2016, 24, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Zhen, G.; Puttgen, A.; Zhang, J.; Chen, T. Improved long-term recording of nerve signal by modified intrafascicular electrodes in rabbits. Microsurgery 2008, 28, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, X.; Koenig, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, T.; Chen, Z. Residual motor signal in long-term human severed peripheral nerves and feasibility of neural signal-controlled artificial limb. J. Hand Surg. Am. Vol. 2007, 32A, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewitus, D.; Vogelstein, R.; Zhen, G.; Choi, Y.; Kohn, J.; Harshbarger, S.; Jia, X. Designing tyrosine-derived polycarbonate polymers for biodegradable regenerative type neural interface capable of neural recording. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2011, 19, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-F.; Hu, N.; Liu, N.; Guo, B.; Yao, J.; Xia, L.; Zheng, X.; Hou, W.; Yin, Z.Q. The design and preparation of a flexible bio-chip for use as a visual prosthesis, and evaluation of its biological features. Cell Tissue Res. 2010, 340, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobelle, W. Artificial vision for the blind by connecting a television camera to the visual cortex. Asaio J. 2000, 46, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mahfoudh, R.; Chan, Y.; Chong, H.P.; Farah, J.O. Twiddler's syndrome in spinal cord stimulation. Acta Neurochir. 2016, 158, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mou, Z.X.; Hou, W.S.; Zheng, X.L.; Zheng, J.; Wu, X.Y.; Jiang, Y.T.; Hu, N.; Xia, N. Microcoil-array-based multichannel transcutaneous transmission for implantable neural electrical stimulation. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 2012, 32, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilic, M.; Schmid, A. An Implantable High-Voltage Cortical Stimulator for Post-Stroke Rehabilitation Enhancement with High-Current Driving Capacity. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Lisbon, Portugal, 24–27 May 2015; pp. 758–761.
- Harvey, R.L.; Winstein, C.J.; Everest Trial, G. Design for the everest randomized trial of cortical stimulation and rehabilitation for arm function following stroke. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2009, 23, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, D.; Neely, R.M.; Shen, K.; Singhal, U.; Alon, E.; Rabaey, J.M.; Carmena, J.M.; Maharbiz, M.M. Wireless recording in the peripheral nervous system with ultrasonic neural dust. Neuron 2016, 91, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercier, P.P.; Lysaght, A.C.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Chandrakasan, A.P.; Stankovic, K.M. Energy extraction from the biologic battery in the inner ear. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 1240–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salama, R.; Kharkovsky, S.; Liyanapathirana, R.; Gunawardana, U. Wireless power transmission in human tissue for nerve stimulation. IET Microw. Antennas Propag. 2016, 10, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.B.; Zheng, X.L.; Lu, Z.G.; Wang, X.; Yin, Z.Q.; Hou, W.S.; Meng, M. Decoding brain responses to pixelized images in the primary visual cortex: Implications for visual cortical prostheses. Neural Regen. Res. 2015, 10, 1622–1627. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cogan, S.F.; Ludwig, K.A.; Welle, C.G.; Takmakov, P. Tissue damage thresholds during therapeutic electrical stimulation. J. Neural Eng. 2016, 13, 021001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadler, J.A., III; Ellens, D.J.; Rosenow, J.M. Deep brain stimulation and motor cortical stimulation for neuropathic pain. Curr. Pain Headache Rep. 2011, 15, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langguth, B.; de Ridder, D.; Kleinjung, T.; Elgoyhen, A.B. Treatment: Pharmacological, Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation, Epidural Stimulation, and Deep Brain Stimulation. In Tinnitus; Eggermont, J.J., Zeng, F.-G., Popper, A.N., Fay, R.R., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 255–289. [Google Scholar]
- Miocinovic, S.; Lempka, S.F.; Russo, G.S.; Maks, C.B.; Butson, C.R.; Sakaie, K.E.; Vitek, J.L.; McIntyre, C.C. Experimental and theoretical characterization of the voltage distribution generated by deep brain stimulation. Exp. Neurol. 2009, 216, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shivdasani, M.N.; Luu, C.D.; Cicione, R.; Fallon, J.B.; Allen, P.J.; Leuenberger, J.; Suaning, G.J.; Lovell, N.H.; Shepherd, R.K.; Williams, C.E. Evaluation of stimulus parameters and electrode geometry for an effective suprachoroidal retinal prosthesis. J. Neural Eng. 2010, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelvanayagam, D.; Vickery, R.; Kirkcaldie, M.; Coroneo, M.; Morley, J. Multichannel surface recordings on the visual cortex: Implications for a neuroprosthesis. J. Neural Eng. 2008, 5, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Thakor, N.V.; Jia, X. Laser Speckle Imaging Reveals Multiple Aspects of Cerebral Vascular Responses to Whole Body Mild Hypothermia in Rats. In Proceedings of Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society; Annual Conference; IEEE Service Center: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 2049–2052. [Google Scholar]
- Tusa, R.J.; Palmer, L.A.; Rosenquist, A.C. Retinotopic organization of area-17 (striate cortex) in cat. J. Comp. Neurol. 1978, 177, 213–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| TX | Vpc/V | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RX | Vo1/mV | 100 | 200 | 300 | 300 | 350 | 250 | 400 | 430 |
| Vo2/mV | 500 | 600 | 700 | 900 | 1000 | 1200 | 1600 | 1650 | |
| Vo3/mV | 250 | 400 | 350 | 500 | 600 | 700 | 1000 | 1000 | |
| Vo/mV | 283 | 400 | 450 | 566 | 650 | 717 | 1000 | 1027 | |
| TX | Vpc/V | 12.9 | 13.9 | 14.9 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| RX | Vo1/mV | 450 | 500 | 520 | 500 | 550 | 600 | 700 | 750 |
| Vo2/mV | 1600 | 1600 | 2100 | 2200 | 2300 | 1500 | 2300 | 2600 | |
| Vo3/mV | 950 | 650 | 930 | 1000 | 1500 | 1500 | 1600 | 1500 | |
| Vo/mV | 1000 | 917 | 1183 | 1233 | 1450 | 1200 | 1533 | 1617 |
| FPC Board | Thickness (mm) | Soft Level | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrode Center | Electrode Periphery | Wire | Circuit/Connect | ||
| Six-layer | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.10 | 0.33 | More rigid |
| Four-layer | 0.16 | 0.14 | 0.04 | 0.17 | More soft |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Chaudhry, S.A.; Hou, W.; Jia, X. Developing and Evaluating a Flexible Wireless Microcoil Array Based Integrated Interface for Epidural Cortical Stimulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020335
Wang X, Chaudhry SA, Hou W, Jia X. Developing and Evaluating a Flexible Wireless Microcoil Array Based Integrated Interface for Epidural Cortical Stimulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(2):335. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020335
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xing, Sharjeel A. Chaudhry, Wensheng Hou, and Xiaofeng Jia. 2017. "Developing and Evaluating a Flexible Wireless Microcoil Array Based Integrated Interface for Epidural Cortical Stimulation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 2: 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020335
APA StyleWang, X., Chaudhry, S. A., Hou, W., & Jia, X. (2017). Developing and Evaluating a Flexible Wireless Microcoil Array Based Integrated Interface for Epidural Cortical Stimulation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(2), 335. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020335