Metabolic Effect of an Oriental Herbal Medicine on Obesity and Its Comorbidities with Transcriptional Responses in Diet-Induced Obese Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Taeeumjowuitang (TJ) Lowered Both Body and White Adipose Tissue (WAT) Mass, and Improved Fat Tissue Morphology in Diet-Induced Obese (DIO) Mice
2.2. TJ Improved Lipid Profiles in Plasma and Liver, and Hepatic Tissue Morphology, While Altering Hepatic Lipid Regulating Enzyme Activities in DIO Mice
2.3. TJ Reduced Insulin Resistance and Plasma Glucose in DIO Mice
2.4. TJ Attenuated the Level of Plasma Adipokines and Inflammatory Cytokines in DIO Mice
2.5. TJ Enhances Energy Expenditure in DIO Mice
2.6. TJ Induces the Protein Expression Related to AMPK Pathway and Mitochondrial Function in eWAT
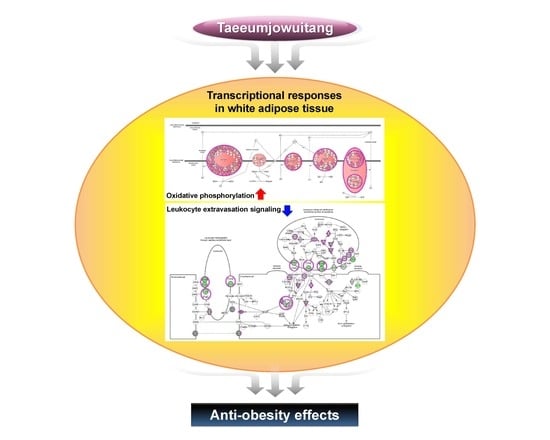
2.7. TJ Modulates Transcriptomic Networks of eWAT in DIO Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Measurements of Energy Expenditures
4.3. Analysis of Plasma, Hepatic, and Fecal Lipids
4.4. Plasma Glutamic Oxaloacetic Transaminase (GOT) and Glutamic Pyruvic Transaminase (GPT) Activities
4.5. Plasma Glucose and Insulin Resistance Index
4.6. Plasma Hormones, Adipokines, and Proinflammatory Cytokines
4.7. Hepatic enzyme Activities and Glycogen Concentration
4.8. Histological Analysis of Epididymal WAT (eWAT) and the Liver
4.9. RNA Preparation, Library Preparation, and RNA-Seq
4.10. Preprocessing of the RNA-Seq Data
4.11. RT-qPCR
4.12. Differential Transcriptome and Functional Analysis
4.13. Molecular Network and Pathway Analysis
4.14. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflict of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADRB3 | beta-3 adrenergic receptor |
| ATP5L | ATP synthase, H+ transporting, mitochondrial Fo complex subunit G |
| CPT | Carnitine palmitoyltransferase |
| DEGs | Differentially expressed genes |
| DIO | Diet-induced obesity |
| EE | Energy expenditure |
| eWAT | Epididymal WAT |
| FER | Food efficiency ratio |
| GOT | Glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase |
| GPT | Glutamic pyruvic transaminase |
| HFD | High-fat diet |
| HMGCR | HMG-CoA reductase |
| HOMA-IR | Homeostasis model assessment for insulin resistance |
| IFN-γ | Interferon γ |
| IPA | Ingenuity pathway analysis |
| MCP-1 | Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 |
| OXPHOS | Oxidative phosphorylation |
| PAI-1 | Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 |
| PBS | Phosphate buffered saline |
| PRKAG3 | Protein kinase, AMP-activated, gamma 3 non-catatlytic subunit |
| TJ | Taeeumjowuitang |
| UCP3 | Uncoupling protein 3 |
References
- Kopelman, P.G. Obesity as a medical problem. Nature 2000, 404, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gesta, S.; Tseng, Y.H.; Kahn, R.C. Developmental origin of fat: Tracking obesity to its source. Cell 2007, 131, 242–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kershaw, E.E.; Flier, J.S. Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 2548–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Barnes, G.T.; Yang, Q.; Tan, G.; Yang, D.; Chou, C.J.; Sole, J.; Nichols, A.; Ross, J.S.; Tartaglia, L.A.; Chen, H. Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1821–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, U.J.; Choi, M.S. Obesity and its metabolic complications: The role of adipokines and the relationship between obesity, inflammation, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 6184–6223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boden, G. Obesity and free fatty acids. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 37, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, M.P.; Attie, A.D. Physiological insights gained from gene expression analysis in obesity and diabetes. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2010, 30, 341–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choo, H.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kwon, O.B.; Lee, C.S.; Mun, J.Y.; Han, S.S.; Yoon, Y.S.; Yoon, G.; Choi, K.M.; Ko, Y.G. Mitochondria are impaired in the adipocytes of type 2 diabetic mice. Diabetologia 2006, 49, 784–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, J.X.; Qiu, Y.; Hansen, M.K.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, V.; Xie, M.; Okamoto, Y.; Mattie, M.D.; Higashiyama, H.; Asano, S.; et al. Adipose mitochondrial biogenesis is suppressed in db/db and high-fat diet-fed mice and improved by rosiglitazone. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1751–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlman, I.; Forsgren, M.; Sjögren, A.; Nordström, E.A.; Kaaman, M.; Näslund, E.; Attersand, A.; Arner, P. Downregulation of electron transport chain genes in visceral adipose tissue in type 2 diabetes independent of obesity and possibly involving tumor necrosis factor-α. Diabetes 2006, 55, 1792–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Burkart, A.; Nicoloro, S.M.; Czech, M.P.; Straubhaar, J.; Corvera, S. Paradoxical effect of mitochondrial respiratory chain impairment on insulin signaling and glucose transport in adipose cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 30658–30667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patti, M.E.; Corvera, S. The role of mitochondria in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Endocr. Rev. 2010, 31, 364–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.H.; Ryu, S.H.; Chung, K.H.; Choi, D.G.; Jeong, I.G.; Lee, H.H. Effects of Taeyeumjoweetang and exercise administration on enzymes and fat accumulation of the liver tissue in rats. Exerc. Sci. 2002, 11, 345–357. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.W.; Yoo, J.H.; Lee, S.K.; Keum, K.S.; Ryu, D.G.; Kwon, K.B. Taeyeumjoweetang affects body weight and obesity-related genes in mice. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2009, 6, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.H.; Kim, C.H.; Jung, J.G.; Jung, H.W.; Choi, C.H. The effects of Taeyeumjowee-tang and Taeyeumjoweebaemahwang-tang on obese rats. Korea J. Herbol. 2010, 25, 103–109. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.; Nahmkoong, W.; Cheon, C.H.; Park, J.S.; Jang, B.H.; Shin, Y.C.; Kim, K.S.; Go, H.; Song, Y.K.; Ko, S.G. Efficacy and Safety of Taeeumjowi-tang in Obese Korean Adults: A Double-Blind, Randomized, and Placebo-Controlled Pilot Trial. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 498935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grundy, S.M. Obesity, metabolic syndrome, and cardiovascular disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 2595–2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granneman, J.G.; Li, P.; Zhu, Z.; Lu, Y. Metabolic and cellular plasticity in white adipose tissue II: Role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 289, E617–E626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Minokoshi, Y.; Ito, Y.; Waki, H.; Uchida, S.; Yamashita, S.; Noda, M.; Kita, S.; Ueki, K.; et al. Adiponectin stimulates glucose utilization and fatty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadowaki, T.; Yamauchi, T.; Kubota, N.; Hara, K.; Ueki, K.; Tobe, K. Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in insulin resistance, diabetes, and the metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1784–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Y.; Nie, Z.; Lee, Y.S.; Singhal, N.S.; Scherer, P.E.; Lazar, M.A.; Ahima, R.S. Loss of resistin improves glucose homeostasis in leptin deficiency. Diabetes 2006, 55, 3083–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skurk, T.; Alberti-Huber, C.; Herder, C.; Hauner, H. Relationship between adipocyte size and adipokine expression and secretion. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 1023–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Soejima, Y.; Fukusato, T. Animal models of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 2300–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.M.; Ahn, I.S.; Kim, D.S.; Kang, S.A.; Kwon, D.Y.; Yang, H.J. Anti-obesity effects of Tae-Um-Jo-Wee-Tang and Do-Dam-Tang in female rats with diet-induced obesity. J. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2010, 53, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reagan-Shaw, S.; Nihal, M.; Ahmad, N. Dose translation from animal to human studies revisited. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 659–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane-Stanley, G.H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lazarow, P.B. Assay of peroxisomal β-oxidation of fatty acids. Methods Enzymol. 1981, 72, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Markwell, M.A.; McGroarty, E.J.; Bieber, L.L.; Tolbert, N.E. The Subcellular Distribution of Carnitine Acyltransferases in Mammalian Liver and Kidney A new peroxisomal enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 1973, 248, 3426–3432. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, D.J.; Nordstrom, J.L.; Mitschelen, J.J.; Rodwell, V.W.; Schimke, R.T. Micro assay for 3-hdyroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase in rat liver and in L-cell fibroblasts. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1974, 370, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seifter, S.; Dayton, S.; Novic, B.; Muntwyler, E. The estimation of glycogen with the anthrone reagent. Arch. Biochem. 1950, 25, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Do, G.M.; Jung, U.J.; Park, H.J.; Kwon, E.Y.; Jeon, S.M.; McGregor, R.A.; Choi, M.S. Resveratrol ameliorates diabetes-related metabolic changes via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase and its downstream targets in db/db mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 1282–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trapnell, C.; Williams, B.A.; Pertea, G.; Mortazavi, A.; Kwan, G.; van Baren, M.J.; Salzberg, S.L.; Wold, B.J.; Pachter, L. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 8, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anders, S.; Pyl, P.T.; Huber, W. HTSeq—A Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2014, 31, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Nishiyama, T.; Shimizu, K.; Kadota, K. TCC: An R package for comparing tag count data with robust normalization strategies. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Parameters | HFD | TJ |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Intake (kcal/day) | 13.63 ± 0.07 | 13.33 ± 0.20 |
| FER | 0.022 ± 0.001 | 0.016 ± 0.00 *** |
| Organ Weights (g/100 g Body Weight) | ||
| Liver | 3.96 ± 0.19 | 3.31 ± 0.18 * |
| Kidney | 0.75 ± 0.02 | 0.83 ± 0.02 * |
| Muscle | 0.72 ± 0.02 | 0.85 ± 0.04 ** |
| Adipose Tissue Weights (g/100 g Body Weight) | ||
| Epididymal WAT | 5.89 ± 0.19 | 5.33 ± 0.37 |
| Perirenal WAT | 0.96 ± 0.05 | 0.68 ± 0.06 ** |
| Subcutaneous WAT | 3.11 ± 0.24 | 2.73 ± 0.31 |
| Retroperitoneum WAT | 1.53 ± 0.05 | 1.50 ± 0.09 |
| Mesenteric WAT | 2.54 ± 0.14 | 1.28 ± 0.18 *** |
| Interscapular WAT | 3.14 ± 0.08 | 2.46 ± 0.18 ** |
| Interscapular BAT | 0.42 ± 0.01 | 0.34 ± 0.03 ** |
| Visceral WAT | 10.79 ± 0.16 | 8.79 ± 0.59 ** |
| Total WAT | 17.04 ± 0.31 | 13.98 ± 0.96 * |
| Parameters | HFD | TJ |
|---|---|---|
| Leptin (ng/mL) | 66.05 ± 6.03 | 20.40 ± 3.70 ** |
| Resistin (ng/mL) | 320.21 ± 5.74 | 197.11 ± 25.67 ** |
| Adiponectin (ug/mL) | 6.99 ± 0.47 | 8.76 ± 0.26 ** |
| PAI-1 (ng/mL) | 2.46 ± 0.36 | 1.50 ± 0.10 * |
| IFN-γ (pg/mL) | 8.12 ± 0.72 | 6.19 ± 0.48 * |
| MCP-1 (pg/mL) | 281.14 ± 42.81 | 173.53 ± 23.68 * |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, J.-Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Cho, S.-J.; Kwon, E.-Y.; Ryu, R.; Choi, M.-S. Metabolic Effect of an Oriental Herbal Medicine on Obesity and Its Comorbidities with Transcriptional Responses in Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040747
Choi J-Y, Kim YJ, Cho S-J, Kwon E-Y, Ryu R, Choi M-S. Metabolic Effect of an Oriental Herbal Medicine on Obesity and Its Comorbidities with Transcriptional Responses in Diet-Induced Obese Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(4):747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040747
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Ji-Young, Ye Jin Kim, Su-Jung Cho, Eun-Young Kwon, Ri Ryu, and Myung-Sook Choi. 2017. "Metabolic Effect of an Oriental Herbal Medicine on Obesity and Its Comorbidities with Transcriptional Responses in Diet-Induced Obese Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 4: 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040747
APA StyleChoi, J. -Y., Kim, Y. J., Cho, S. -J., Kwon, E. -Y., Ryu, R., & Choi, M. -S. (2017). Metabolic Effect of an Oriental Herbal Medicine on Obesity and Its Comorbidities with Transcriptional Responses in Diet-Induced Obese Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(4), 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040747