Anemia in Kawasaki Disease: Hepcidin as a Potential Biomarker
Abstract
:1. Kawasaki Disease: The Most Common Acute Coronary Vasculitis Disease in Children
2. Anemia in Patients with Kawasaki Disease
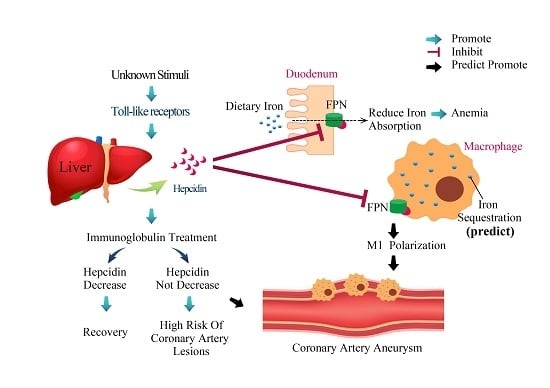
3. Hepcidin Expression Is Correlated with Kawasaki Disease Outcomes
4. Hepcidin-Induced Iron Deficiency Is Correlated with Transient Hyposideremia and Anemia in KD Patients
5. Additional Studies Regarding Hepcidin in Kawasaki Disease
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CAL | Coronary artery lesions |
| CAA | Coronary artery aneurysm |
| IVIG | Intravenous immunoglobulin |
| KD | Kawasaki disease |
References
- Kawasaki, T.; Kosaki, F.; Okawa, S.; Shigematsu, I.; Yanagawa, H. A new infantile acute febrile mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome (MLNS) prevailing in Japan. Pediatrics 1974, 54, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.L.; Wu, Y.T.; Liu, C.A.; Kuo, H.C.; Yang, K.D. Kawasaki disease: Infection, immunity and genetics. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2005, 24, 998–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newburger, J.W.; Takahashi, M.; Burns, J.C.; Beiser, A.S.; Chung, K.J.; Duffy, C.E.; Glode, M.P.; Mason, W.H.; Reddy, V.; Sanders, S.P.; et al. The treatment of Kawasaki syndrome with intravenous gamma globulin. N. Engl. J. Med. 1986, 315, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newburger, J.W.; Takahashi, M.; Beiser, A.S.; Burns, J.C.; Bastian, J.; Chung, K.J.; Colan, S.D.; Duffy, C.E.; Fulton, D.R.; Glode, M.P.; et al. A single intravenous infusion of gamma globulin as compared with four infusions in the treatment of acute Kawasaki syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 324, 1633–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, H.C.; Liang, C.D.; Wang, C.L.; Yu, H.R.; Hwang, K.P.; Yang, K.D. Serum albumin level predicts initial intravenous immunoglobulin treatment failure in Kawasaki disease. Acta Paediatr. 2010, 99, 1578–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Principi, N.; Rigante, D.; Esposito, S. The role of infection in Kawasaki syndrome. J. Infect. 2013, 67, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigante, D.; Tarantino, G.; Valentini, P. Non-infectious makers of Kawasaki syndrome: Tangible or elusive triggers? Immunol. Res. 2016, 64, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.H.; Li, S.C.; Huang, L.H.; Chen, P.C.; Lin, Y.Y.; Lin, C.C.; Kuo, H.C. Identifying genetic hypomethylation and upregulation of toll-like receptors in Kawasaki disease. Oncotarget 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, M.M.; Tseng, W.N.; Ko, C.H.; Pan, H.M.; Hsieh, K.S.; Kuo, H.C. Th17- and Treg-related cytokine and mRNA expression are associated with acute and resolving Kawasaki disease. Allergy 2015, 70, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-C.; Kuo, H.-C.; Chang, J.-S.; Chang, L.-Y.; Huang, L.-M.; Chen, M.-R.; Liang, C.-D.; Chi, H.; Huang, F.-Y.; Lee, M.-L.; et al. Two new susceptibility loci for Kawasaki disease identified through genome-wide association analysis. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 522–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, H.-C.; Yang, K.D.; Juo, S.-H.H.; Liang, C.-D.; Chen, W.-C.; Wang, Y.-S.; Lee, C.-H.; Hsi, E.; Yu, H.-R.; Woon, P.-Y.; et al. ITPKC single nucleotide polymorphism associated with the Kawasaki disease in a Taiwanese population. PLoS ONE 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, H.C.; Yang, K.D.; Chang, W.C.; Ger, L.P.; Hsieh, K.S. Kawasaki disease: An update on diagnosis and treatment. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2012, 53, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.H.; Hsu, Y.W.; Lu, H.F.; Wong, H.S.; Yu, H.R.; Kuo, H.C.; Huang, F.C.; Chang, W.C.; Kuo, H.C. Interferon-gamma Genetic Polymorphism and Expression in Kawasaki Disease. Medicine 2016, 95, e3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, H.C.; Chang, J.C.; Kuo, H.C.; Yu, H.R.; Wang, C.L.; Lee, C.P.; Huang, L.T.; Yang, K.D. Identification of an association between genomic hypomethylation of FCGR2A and susceptibility to Kawasaki disease and intravenous immunoglobulin resistance by DNA methylation array. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 828–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, H.C.; Hsu, Y.W.; Wu, M.S.; Chien, S.C.; Liu, S.F.; Chang, W.C. Intravenous immunoglobulin, pharmacogenomics, and Kawasaki disease. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2016, 49, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, H.C.; Wang, C.L.; Yang, K.D.; Lo, M.H.; Hsieh, K.S.; Li, S.C.; Huang, Y.H. Plasma Prostaglandin E2 Levels Correlated with the Prevention of Intravenous Immunoglobulin Resistance and Coronary Artery Lesions Formation via CD40L in Kawasaki Disease. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0161265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newburger, J.W.; Takahashi, M.; Gerber, M.A.; Gewitz, M.H.; Tani, L.Y.; Burns, J.C.; Shulman, S.T.; Bolger, A.F.; Ferrieri, P.; Baltimore, R.S.; et al. Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management of Kawasaki disease: A statement for health professionals from the Committee on Rheumatic Fever, Endocarditis and Kawasaki Disease, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young, American Heart Association. Circulation 2004, 110, 2747–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, H.C.; Ho, J.C.; Guo, M.M.; Lo, M.H.; Hsieh, K.S.; Tsai, W.C.; Kuo, H.C.; Lee, C.H. Bull’s eye dermatoscopy pattern at bacillus Calmette-Guerin inoculation site correlates with systemic involvements in patients with Kawasaki disease. J. Dermatol. 2016, 43, 1044–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.H.; Kuo, H.C.; Huang, F.C.; Yu, H.R.; Hsieh, K.S.; Yang, Y.L.; Sheen, J.M.; Li, S.C.; Kuo, H.C. Hepcidin-Induced Iron Deficiency Is Related to Transient Anemia and Hypoferremia in Kawasaki Disease Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, N.R.; Magalhaes, C.M.; Almeida Rde, F.; Santos, R.C.; Gandolfi, L.; Pratesi, R. Prospective study of Kawasaki disease complications: Review of 115 cases. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2011, 57, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushige, J.; Takahashi, N.; Ueda, Y.; Ueda, K. Incidence and clinical features of incomplete Kawasaki disease. Acta Paediatr. 1994, 83, 1057–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, H.C.; Wang, C.L.; Liang, C.D.; Yu, H.R.; Chen, H.H.; Wang, L.; Yang, K.D. Persistent monocytosis after intravenous immunoglobulin therapy correlated with the development of coronary artery lesions in patients with Kawasaki disease. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2007, 40, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kuo, H.C.; Yang, K.D.; Liang, C.D.; Bong, C.N.; Yu, H.R.; Wang, L.; Wang, C.L. The relationship of eosinophilia to intravenous immunoglobulin treatment failure in Kawasaki disease. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2007, 18, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, X.B.; Lau, K.; Kanegaye, J.T.; Pan, Z.; Peng, S.; Ji, J.; Liu, G.; Sato, Y.; Yu, T.T.; Whitin, J.C.; et al. A diagnostic algorithm combining clinical and molecular data distinguishes Kawasaki disease from other febrile illnesses. BMC Med. 2011, 9, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.J.; Cheng, M.C.; Lo, M.H.; Chien, S.J. Early Differentiation of Kawasaki Disease Shock Syndrome and Toxic Shock Syndrome in a Pediatric Intensive Care Unit. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2015, 34, 1163–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, M.; Watanabe, N.; Okuno, M.; Kondo, M.; Okagawa, H.; Taga, T. Severe hemolytic anemia following high-dose intravenous immunoglobulin administration in a patient with Kawasaki disease. Am. J. Hematol. 2000, 63, 160–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorpe, S.J. Specifications for anti-A and anti-B in intravenous immunoglobulin: History and rationale. Transfusion 2015, 55 (Suppl. S2), S80–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemeth, E.; Ganz, T. Anemia of inflammation. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 28, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keel, S.B.; Abkowitz, J.L. The microcytic red cell and the anemia of inflammation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 1904–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, G.; Goodnough, L.T. Anemia of chronic disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1011–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hohaus, S.; Massini, G.; Giachelia, M.; Vannata, B.; Bozzoli, V.; Cuccaro, A.; D′Alo, F.; Larocca, L.M.; Raymakers, R.A.; Swinkels, D.W.; et al. Anemia in Hodgkin’s lymphoma: The role of interleukin-6 and hepcidin. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2538–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Jeong, S.H.; Park, Y.S.; Hwang, J.H.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, N.; Lee, D.H. Serum prohepcidin levels in chronic hepatitis C, alcoholic liver disease, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Korean J. Hepatol. 2010, 16, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, A.; Neitz, S.; Magert, H.J.; Schulz, A.; Forssmann, W.G.; Schulz-Knappe, P.; Adermann, K. LEAP-1, a novel highly disulfide-bonded human peptide, exhibits antimicrobial activity. FEBS Lett. 2000, 480, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girelli, D.; Nemeth, E.; Swinkels, D.W. Hepcidin in the diagnosis of iron disorders. Blood 2016, 127, 2809–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meli, R.; Mattace Raso, G.; Irace, C.; Simeoli, R.; di Pascale, A.; Paciello, O.; Pagano, T.B.; Calignano, A.; Colonna, A.; Santamaria, R. High Fat Diet Induces Liver Steatosis and Early Dysregulation of Iron Metabolism in Rats. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dongiovanni, P.; Lanti, C.; Gatti, S.; Rametta, R.; Recalcati, S.; Maggioni, M.; Fracanzani, A.L.; Riso, P.; Cairo, G.; Fargion, S.; et al. High fat diet subverts hepatocellular iron uptake determining dysmetabolic iron overload. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armitage, A.E.; Eddowes, L.A.; Gileadi, U.; Cole, S.; Spottiswoode, N.; Selvakumar, T.A.; Ho, L.P.; Townsend, A.R.; Drakesmith, H. Hepcidin regulation by innate immune and infectious stimuli. Blood 2011, 118, 4129–4139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Mast, Q.; Nadjm, B.; Reyburn, H.; Kemna, E.H.; Amos, B.; Laarakkers, C.M.; Silalye, S.; Verhoef, H.; Sauerwein, R.W.; Swinkels, D.W.; et al. Assessment of urinary concentrations of hepcidin provides novel insight into disturbances in iron homeostasis during malarial infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 199, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Khalek, M.A.; El-Barbary, A.M.; Essa, S.A.; Ghobashi, A.S. Serum hepcidin: A direct link between anemia of inflammation and coronary artery atherosclerosis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2011, 38, 2153–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirag, M.D.; Haznedaroglu, S.; Sancak, B.; Konca, C.; Gulbahar, O.; Ozturk, M.A.; Goker, B. Circulating hepcidin in the crossroads of anemia and inflammation associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Intern. Med. 2009, 48, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isoda, M.; Hanawa, H.; Watanabe, R.; Yoshida, T.; Toba, K.; Yoshida, K.; Kojima, M.; Otaki, K.; Hao, K.; Ding, L.; et al. Expression of the peptide hormone hepcidin increases in cardiomyocytes under myocarditis and myocardial infarction. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2010, 21, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sihler, K.C.; Raghavendran, K.; Westerman, M.; Ye, W.; Napolitano, L.M. Hepcidin in trauma: Linking injury, inflammation, and anemia. J. Trauma 2010, 69, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Giudice, E.M.; Santoro, N.; Amato, A.; Brienza, C.; Calabro, P.; Wiegerinck, E.T.; Cirillo, G.; Tartaglione, N.; Grandone, A.; Swinkels, D.W.; et al. Hepcidin in obese children as a potential mediator of the association between obesity and iron deficiency. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 5102–5107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasai, M.; Iso, Y.; Mizukami, T.; Tomosugi, N.; Sambe, T.; Miyazaki, A.; Suzuki, H. Potential contribution of the hepcidin-macrophage axis to plaque vulnerability in acute myocardial infarction in human. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 227, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, H.C.; Yang, Y.L.; Chuang, J.H.; Tiao, M.M.; Yu, H.R.; Huang, L.T.; Yang, K.D.; Chang, W.C.; Lee, C.P.; Huang, Y.H. Inflammation-induced hepcidin is associated with the development of anemia and coronary artery lesions in Kawasaki disease. J. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 32, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaskell, H.; Derry, S.; Moore, R.A. Is there an association between low dose aspirin and anemia (without overt bleeding)? Narrative review. BMC Geriatr. 2010, 10, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, H.C.; Lo, M.H.; Hsieh, K.S.; Guo, M.M.; Huang, Y.H. High-Dose Aspirin Is Associated with Anemia and Does Not Confer Benefit to Disease Outcomes in Kawasaki Disease. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, N.T.; Richardson, D.R. Ferroportin1: A new iron export molecule? Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 2002, 34, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, D.M.; Kaplan, J. Ferroportin-mediated iron transport: Expression and regulation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1823, 1426–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemeth, E.; Tuttle, M.S.; Powelson, J.; Vaughn, M.B.; Donovan, A.; Ward, D.M.; Ganz, T.; Kaplan, J. Hepcidin regulates cellular iron efflux by binding to ferroportin and inducing its internalization. Science 2004, 306, 2090–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.; Nemeth, E. New insights into iron regulation and erythropoiesis. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 2015, 22, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallalio, G.; Law, E.; Means, R.T., Jr. Hepcidin inhibits in vitro erythroid colony formation at reduced erythropoietin concentrations. Blood 2006, 107, 2702–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, G.R.; Cherrick, I.; Karayalcin, G.; Valderrama, E.; Lanzkowsky, P. Transient erythroblastopenia in a child with Kawasaki syndrome: A case report. Am. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 1994, 16, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, M.; Mertens, C.; Brune, B. Macrophage iron homeostasis and polarization in the context of cancer. Immunobiology 2015, 220, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosser, D.M.; Edwards, J.P. Exploring the full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 958–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corna, G.; Campana, L.; Pignatti, E.; Castiglioni, A.; Tagliafico, E.; Bosurgi, L.; Campanella, A.; Brunelli, S.; Manfredi, A.A.; Apostoli, P.; et al. Polarization dictates iron handling by inflammatory and alternatively activated macrophages. Haematologica 2010, 95, 1814–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.-H.; Kuo, H.-C. Anemia in Kawasaki Disease: Hepcidin as a Potential Biomarker. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 820. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040820
Huang Y-H, Kuo H-C. Anemia in Kawasaki Disease: Hepcidin as a Potential Biomarker. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(4):820. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040820
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Ying-Hsien, and Ho-Chang Kuo. 2017. "Anemia in Kawasaki Disease: Hepcidin as a Potential Biomarker" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 4: 820. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040820
APA StyleHuang, Y. -H., & Kuo, H. -C. (2017). Anemia in Kawasaki Disease: Hepcidin as a Potential Biomarker. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(4), 820. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040820