Beneficial Effects of Melatonin on the In Vitro Maturation of Sheep Oocytes and Its Relation to Melatonin Receptors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Melatonin Receptors in Sheep Oocytes, Cumulus Cells, and Granulosa Cells
2.2. The Effect of Melatonin on Cumulus Expansion and Nuclear Maturation of Oocytes
2.3. The Effect of Melatonin on Embryo Development
2.4. The Effect of Melatonin on the Embryo Development-Related Genes Expression in Oocytes and Cumulus Cells
2.5. MT Promoted Maturation of Sheep Oocytes through Melatonin Receptors
2.6. The Effect of Melatonin on cAMP and cGMP Concentration in Oocytes and Cumulus Cells
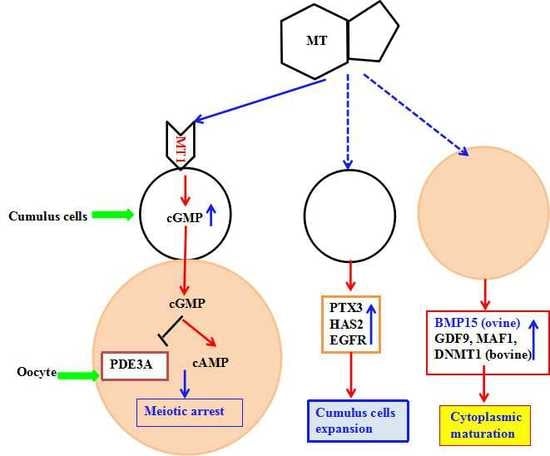
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Animal Studies
4.3. Ovary Collection and Cumulus–Oocyte Complex Aspiration
4.4. In Vitro Maturation of Oocytes
4.5. Parthenogenetic Activation
4.6. Detection of Melatonin Receptors in COCs by Immunofluorescence
4.7. Detection of Melatonin Receptors by Western Blotting
4.8. Assessment of Cumulus Cells Expansion and Polar Body Extrusion
4.9. Assessment of Embryo Quality
4.10. RNA Isolation and Quantitative RT-PCR
4.11. Determination of Intracellular Concentrations of cAMP and cGMP
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dobrinsky, J.R.; Johnson, L.A.; Rath, D. Development of a culture medium (BECM-3) for porcine embryos: Effects of bovine serum albumin and fetal bovine serum on embryo development. Biol. Reprod. 1996, 55, 1069–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adriaens, I.; Jacquet, P.; Cortvrindt, R.; Janssen, K.; Smitz, J. Melatonin has dose-dependent effects on folliculogenesis, oocyte maturation capacity and steroidogenesis. Toxicology 2006, 228, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.T.; Koo, O.J.; Kwon, D.K.; Park, H.J.; Jang, G.; Kang, S.K.; Lee, B.C. Effects of melatonin on in vitro maturation of porcine oocyte and expression of melatonin receptor RNA in cumulus and granulosa cells. J. Pineal Res. 2009, 46, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Tian, X.; Zhou, G.; Wang, L.; Gao, C.; Zhu, S.; Zeng, S.; Tian, J.; Liu, G. Melatonin exists in porcine follicular fluid and improves in vitro maturation and parthenogenetic development of porcine oocytes. J. Pineal Res. 2009, 47, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papis, K.; Poleszczuk, O.; Wenta-Muchalska, E.; Modlinski, J.A. Melatonin effect on bovine embryo development in vitro in relation to oxygen concentration. J. Pineal Res. 2007, 43, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishizuka, B.; Kuribayashi, Y.; Murai, K.; Amemiya, A.; Itoh, M.T. The effect of melatonin on in vitro fertilization and embryo development in mice. J. Pineal Res. 2000, 28, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Wen, Q.; Shi, J.; Wang, L.; Zeng, S.; Tian, J.; Zhou, G.; Zhu, S.; Liu, G. Effects of melatonin on in vitro development of mouse two-cell embryos cultured in HTF medium. Endocr. Res. 2010, 35, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Han, H.; Tian, X.; Tan, D.; Wang, L.; Zhou, G.; Zhu, S.; Liu, G. Melatonin promotes embryonic development and reduces reactive oxygen species in vitrified mouse 2-cell embryos. J. Pineal Res. 2012, 52, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Raey, M.; Geshi, M.; Somfai, T.; Kaneda, M.; Hirako, M.; Abdel-Ghaffar, A.E.; Sosa, G.A.; El-Roos, M.E.; Nagai, T. Evidence of melatonin synthesis in the cumulus oocyte complexes and its role in enhancing oocyte maturation in vitro in cattle. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2011, 78, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; He, C.; Zhu, K.; Xu, Z.; Ma, T.; Tao, J.; Liu, G. Melatonin protects porcine oocyte in vitro maturation from heat stress. J. Pineal Res. 2015, 59, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Do, L.T.; Shibata, Y.; Taniguchi, M.; Nii, M.; Nguyen, T.V.; Tanihara, F.; Takagi, M.; Otoi, T. Melatonin supplementation during in vitro maturation and development supports the development of porcine embryos. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2015, 50, 1054–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Tian, X.; Ma, T.; Tao, J.; Zhu, K.; Song, Y.; et al. Mitochondria synthesize melatonin to ameliorate its function and improve mice oocyte’s quality under in vitro conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 939–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Yi, J.; He, C.; Wang, F.; Tian, X.; Yang, M.; Song, Y.; Liu, G. Resveratrol compares with melatonin in improving in vitro porcine oocyte maturation under heat stress. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Wang, F.; He, C.; Zhang, L.; Tan, D.; Reiter, R.J.; Xu, J.; Ji, P.; Liu, G. Beneficial effects of melatonin on bovine oocytes maturation: A mechanistic approach. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 57, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Gouic, S.; Delagrange, P.; Atgie, C.; Nibbelink, M.; Hanoun, N.; Casteilla, L.; Renard, P.; Lesieur, D.; Guardiola-Lemaitre, B.; Ambid, L. Effects of both a melatonin agonist and antagonist on seasonal changes in body mass and energy intake in the garden dormouse. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1996, 20, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Woo, M.M.; Tai, C.J.; Kang, S.K.; Nathwani, P.S.; Pang, S.F.; Leung, P.C. Direct action of melatonin in human granulosa-luteal cells. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 4789–4797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirotkin, A.V.; Schaeffer, H.J. Direct regulation of mammalian reproductive organs by serotonin and melatonin. J. Endocrinol. 1997, 154, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiske, V.M.; Parker, K.L.; Ulmer, R.A.; Ow, C.H.; Aziz, N. Effect of melatonin alone or in combination with human chorionic gonadotropin or ovine luteinizing hormone on the in vitro secretion of estrogens or progesterone by granulosa cells of rats. Endocrinology 1984, 114, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baratta, M.; Tamanini, C. Effect of melatonin on the in vitro secretion of progesterone and estradiol 17 β by ovine granulosa cells. Acta Endocrinol. Copenh. 1992, 127, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murayama, T.; Kawashima, M.; Takahashi, T.; Yasuoka, T.; Kuwayama, T.; Tanaka, K. Direct action of melatonin on hen ovarian granulosa cells to lower responsiveness to luteinizing hormone. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1997, 215, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, J.J.; Masana, M.I.; Ersahin, C.; Dubocovich, M.L. Functional melatonin receptors in rat ovaries at various stages of the estrous cycle. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2003, 306, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horton, T.H.; Yellon, S.M. Aging, reproduction, and the melatonin rhythm in the Siberian hamster. J. Biol. Rhythm. 2001, 16, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Poon, A.M.; Pang, S. Pharmacological characterization, molecular subtyping, and autoradiographic localization of putative melatonin receptors in uterine endometrium of estrous rats. Life Sci. 2000, 66, 1581–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luboshitzky, R.; Shen-Orr, Z.; Shochat, T.; Herer, P.; Lavie, P. Melatonin administered in the afternoon decreases next-day luteinizing hormone levels in men: Lack of antagonism by flumazenil. J. Mol. Neurosci. 1999, 12, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yie, S.M.; Niles, L.P.; Younglai, E.V. Melatonin receptors on human granulosa cell membranes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1995, 80, 1747–1749. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Niles, L.P.; Wang, J.; Shen, L.; Lobb, D.K.; Younglai, E.V. Melatonin receptor mRNA expression in human granulosa cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1999, 156, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekel, N. Regulation of oocyte maturation. The role of cAMP. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1988, 541, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, M.R.; Foster, J.S.; Bukovsky, A.; Wimalasena, J. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases by gonadotropins and cyclic adenosine 5′-monophosphates in porcine granulosa cells. Biol. Reprod. 1996, 55, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Maizels, E.T.; DeManno, D.; St, C.E.; Adam, S.A.; Hunzicker-Dunn, M. A stimulatory role of cyclic adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate in follicle-stimulating hormone-activated mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway in rat ovarian granulosa cells. Endocrinology 1996, 137, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Huo, L.; Zhong, Z.; Chen, D.; Schatten, H.; Sun, Q. Cyclic adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate-dependent activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase in cumulus cells is essential for germinal vesicle breakdown of porcine cumulus-enclosed oocytes. Endocrinology 2005, 146, 4437–4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eppig, J.J. The participation of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) in the regulation of meiotic maturation of oocytes in the laboratory mouse. J. Reprod. Fertil. Suppl. 1989, 38, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, D.; Albano, C.; Adriaenssens, T.; Cortvrindt, R.; Bourgain, C.; Devroey, P.; Smitz, J. Human oocytes reversibly arrested in prophase I by phosphodiesterase type 3 inhibitor in vitro. Biol. Reprod. 2003, 69, 1042–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, R.E.; Armstrong, D.T.; Gilchrist, R.B. Differential effects of specific phosphodiesterase isoenzyme inhibitors on bovine oocyte meiotic maturation. Dev. Biol. 2002, 244, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, R.E.; Thompson, J.G.; Armstrong, D.T.; Gilchrist, R.B. Effect of specific phosphodiesterase isoenzyme inhibitors during in vitro maturation of bovine oocytes on meiotic and developmental capacity. Biol. Reprod. 2004, 71, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luciano, A.M.; Pocar, P.; Milanesi, E.; Modina, S.; Rieger, D.; Lauria, A.; Gandolfi, F. Effect of different levels of intracellular cAMP on the in vitro maturation of cattle oocytes and their subsequent development following in vitro fertilization. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 1999, 54, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubocovich, M.L.; Markowska, M. Functional MT1 and MT2 melatonin receptors in mammals. Endocrine 2005, 27, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wert, S.E.; Hendrix, E.M.; Russell, P.T.; Cannon, M.; Larsen, W.J. Hyaluronic acid synthesis and gap junction endocytosis are necessary for normal expansion of the cumulus mass. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 1990, 26, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y.; Shi, W.; Ding, J.; Sha, J.; Fan, B. Predictive value of the area of expanded cumulus mass on development of porcine oocytes matured and fertilized in vitro. J. Reprod. Dev. 2003, 49, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutnisky, C.; Dalvit, G.C.; Pintos, L.N.; Thompson, J.G.; Beconi, M.T.; Cetica, P.D. Influence of hyaluronic acid synthesis and cumulus mucification on bovine oocyte in vitro maturation, fertilisation and embryo development. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 2007, 19, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eppig, J.J. The relationship between cumulus cell-oocyte coupling, oocyte meiotic maturation, and cumulus expansion. Dev. Biol. 1982, 89, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighat, N.; Van Winkle, L.J. Developmental change in follicular cell-enhanced amino acid uptake into mouse oocytes that depends on intact gap junctions and transport system Gly. J. Exp. Zool. 1990, 253, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurincik, J.; Kroslak, P.; Hyttel, P.; Pivko, J.; Sirotkin, A.V. Bovine cumulus expansion and corona-oocyte disconnection during culture in vitro. Reprod. Nutr. Dev. 1992, 32, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buccione, R.; Schroeder, A.C.; Eppig, J.J. Interactions between somatic cells and germ cells throughout mammalian oogenesis. Biol. Reprod. 1990, 43, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuelke, K.A.; Brackett, B.G. Luteinizing hormone-enhanced in vitro maturation of bovine oocytes with and without protein supplementation. Biol. Reprod. 1990, 43, 784–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Park, S.M.; Lee, E.; Kim, J.H.; Jeong, Y.I.; Lee, J.Y.; Park, S.W.; Kim, H.S.; Hossein, M.S.; Jeong, Y.W.; et al. Anti-apoptotic effect of melatonin on preimplantation development of porcine parthenogenetic embryos. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2008, 75, 1127–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugino, N.; Takiguchi, S.; Kashida, S.; Karube, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Kato, H. Superoxide dismutase expression in the human corpus luteum during the menstrual cycle and in early pregnancy. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2000, 6, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taketani, T.; Tamura, H.; Takasaki, A.; Lee, L.; Kizuka, F.; Tamura, I.; Taniguchi, K.; Maekawa, R.; Asada, H.; Shimamura, K.; et al. Protective role of melatonin in progesterone production by human luteal cells. J. Pineal Res. 2011, 51, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilchrist, R.B.; Lane, M.; Thompson, J.G. Oocyte-secreted factors: Regulators of cumulus cell function and oocyte quality. Hum. Reprod. Update 2008, 14, 159–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.; Clelland, E.; Tan, Q. Potential role of bone morphogenetic protein-15 in zebrafish follicle development and oocyte maturation. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2009, 153, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gode, F.; Gulekli, B.; Dogan, E.; Korhan, P.; Dogan, S.; Bige, O.; Cimrin, D.; Atabey, N. Influence of follicular fluid GDF9 and BMP15 on embryo quality. Fertil. Steril. 2011, 95, 2274–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takasaki, A.; Nakamura, Y.; Tamura, H.; Shimamura, K.; Morioka, H. Melatonin as a new drug for improving oocyte quality. Reprod. Med. Biol. 2003, 2, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjunatha, B.M.; Devaraj, M.; Gupta, P.S.; Ravindra, J.P.; Nandi, S. Effect of taurine and melatonin in the culture medium on buffalo in vitro embryo development. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2009, 44, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, K.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Yoon, T.; Cha, K.; Lee, D. Effect of melatonin on the maturation of mouse GV oocytes and apoptosis of cumulus cells in vitro. Fertil. Steril. 2005, 84, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.W.; Gong, Y.; McDonough, C.W.; Langaee, T.Y.; Beitelshees, A.L.; Gums, J.G.; Chapman, A.B.; Turner, S.T.; Johnson, J.A.; Cooper-DeHoff, R.M. Melatonin pathway and atenolol-related glucose dysregulation: Is there a correlation? Clin. Transl. Sci. 2016, 9, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luciano, A.M.; Modina, S.; Vassena, R.; Milanesi, E.; Lauria, A.; Gandolfi, F. Role of intracellular cyclic adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate concentration and oocyte-cumulus cells communications on the acquisition of the developmental competence during in vitro maturation of bovine oocyte. Biol. Reprod. 2004, 70, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, F.J.; Tsafriri, A.; Conti, M. Role of phosphodiesterase type 3A in rat oocyte maturation. Biol. Reprod. 2001, 65, 1444–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaccari, S.; Weeks, J.N.; Hsieh, M.; Menniti, F.S.; Conti, M. Cyclic GMP signaling is involved in the luteinizing hormone-dependent meiotic maturation of mouse oocytes. Biol. Reprod. 2009, 81, 595–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norris, R.P.; Ratzan, W.J.; Freudzon, M.; Mehlmann, L.M.; Krall, J.; Movsesian, M.A.; Wang, H.; Ke, H.; Nikolaev, V.O.; Jaffe, L.A. Cyclic GMP from the surrounding somatic cells regulates cyclic AMP and meiosis in the mouse oocyte. Development 2009, 136, 1869–1878. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Hajian, M.; Moulavi, F.; Asgari, V.; Forouzanfar, M.; Nasr-Esfahani, M.H. Cloned sheep blastocysts derived from oocytes enucleated manually using a pulled pasteur pipette. Cell. Reprogr. 2013, 15, 15–23. [Google Scholar]










| Gene Name | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) | Fragment Size (bp) | Reference Sequence Accession Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| LHR | TCTGCTCACCCAAGACACTCC | 247 | XM_005686598.1 |
| GAGGCAATGAGTAGCAGGTAGAG | |||
| FSHR | CTTCCAGAACCTTCCCAACC | 201 | NM_001285636.1 |
| TCCCATTCTTACTCAGCCATAC | |||
| PTX3 | TCTGCGATGGTGTTCTCAGCA | 206 | XM_005675400.1 |
| CTCTCTCCTTCAACTGGCGTATG | |||
| EGFR | CACTCATGCTCTATGACCCTACCAC | 176 | XM_005695500.1 |
| GTGGACACCATCTTCCTCTACCTC | |||
| GDF9 | AAGGTTCTGTATGATGGGCACG | 149 | NM_001285708.1 |
| AGCCGAACAGTGTTGTAGAGGTG | |||
| BMP15 | CTTCACCTAACTCATTCCCACCTC | 248 | JQ350891.1 |
| TGCCACCAGAACTCAAGAACCT | |||
| DMNT1 | GGACATAATCGGAGATGCTTTGA | 206 | XM_005688873.1 |
| AACAGGCTTTGGATGATGAGGT | |||
| HAS2 | CTTCTCCTGATTCTACGCTTCCT | 223 | XM_005688874.1 |
| AACAGGCTTTGGATGATGAGGT | |||
| GAPDH | GTGTCTGTTGTGGATCTGACCTG | 162 | NM_001190390.1 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, L.; He, C.; Ji, P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Lv, D.; Abulizi, W.; Wang, X.; et al. Beneficial Effects of Melatonin on the In Vitro Maturation of Sheep Oocytes and Its Relation to Melatonin Receptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040834
Tian X, Wang F, Zhang L, He C, Ji P, Wang J, Zhang Z, Lv D, Abulizi W, Wang X, et al. Beneficial Effects of Melatonin on the In Vitro Maturation of Sheep Oocytes and Its Relation to Melatonin Receptors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(4):834. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040834
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Xiuzhi, Feng Wang, Lu Zhang, Changjiu He, Pengyun Ji, Jing Wang, Zhenzhen Zhang, Dongying Lv, Wusiman Abulizi, Xuguang Wang, and et al. 2017. "Beneficial Effects of Melatonin on the In Vitro Maturation of Sheep Oocytes and Its Relation to Melatonin Receptors" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 4: 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040834
APA StyleTian, X., Wang, F., Zhang, L., He, C., Ji, P., Wang, J., Zhang, Z., Lv, D., Abulizi, W., Wang, X., Lian, Z., & Liu, G. (2017). Beneficial Effects of Melatonin on the In Vitro Maturation of Sheep Oocytes and Its Relation to Melatonin Receptors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(4), 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18040834