An AAAG-Rich Oligodeoxynucleotide Rescues Mice from Bacterial Septic Peritonitis by Interfering Interferon Regulatory Factor 5
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. MS19 Prolongs the Survival Time of Escherichia coli (E. coli) Infected Mice
2.2. MS19 Can Reduce the Production of Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and Tumor Necrosis Factor α (TNF-α) at 8 h after Infection
2.3. MS19 Down-Regulates Nitric Oxide Synthase (iNOS) Expression in the Peritoneal Lavage Cells (PLCs)
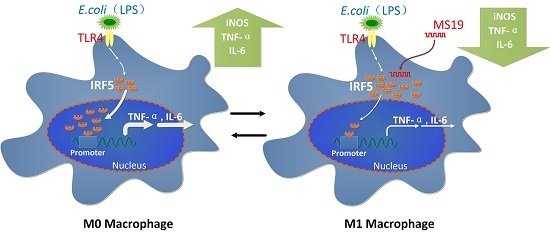
2.4. MS19 Can Down-Regulate the Production of IL-6 and TNF-α from Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Treated RAW264.7 Cells by Inhibiting Its Polarization to M1 Lineage
2.5. MS19 Inhibits the Polarization of Macrophages to M1 Type Possibly by Interfering Interferon Regulatory Factor 5 (IRF5)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Oligodeoxynucleotides
4.2. Cells
4.3. Mice
4.4. Animal Experiments
4.5. Flow Cytometry of PLCs
4.6. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
4.7. Western Blot Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sartelli, M.; Abu-Zidan, F.M.; Ansaloni, L.; Bala, M.; Beltrán, M.A.; Biffl, W.L.; Catena, F.; Chiara, O.; Coccolini, F.; Coimbra, R.; et al. The role of the open abdomen procedure in managing severe abdominal sepsis: WSES position paper. World J. Emerg. Surg. 2015, 10, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balk, R.A. Severe sepsis and septic shock. Definitions, epidemiology, and clinical manifestations. Crit. Care Clin. 2000, 16, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotchkiss, R.S.; Monneret, G.; Payen, D. Sepsis-induced immunosuppression: From cellular dysfunctions to immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 862–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deutschman, C.S.; Tracey, K.J. Sepsis: Current dogma and new perspectives. Immunity 2014, 40, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skirecki, T.; Borkowska-Zielinska, U.; Zlotorowicz, M.; Hoser, G. Sepsis immunopathology: Perspectives of monitoring and modulation of the immune disturbances. Arch Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2012, 60, 123–135. [Google Scholar]
- Gordon, S.; Mantovani, A. Diversity and plasticity of mononuclear phagocytes. Eur. J. Immunol. 2011, 41, 2470–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, C.L.; Odegaard, J.I.; Hsieh, M.H. Macrophages are required for host survival in experimental urogenital schistosomiasis. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.C.; Zou, X.B.; Chai, Y.F.; Yao, Y.M. Macrophage polarization in inflammatory diseases. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 10, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, M.F.; Costa-da-Silva, A.C.; dos Reis, G.A. Innate immunity to Leishmania infection: Within phagocytes. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 754965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takaoka, A.; Yanai, H.; Kondo, S.; Duncan, G.; Negishi, H.; Mizutani, T.; Kano, S.; Honda, K.; Ohba, Y.; Mak, T.W.; et al. Integral role of IRF-5 in the gene induction programme activated by Toll-like receptors. Nature 2005, 434, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, M.; Blazek, K.; Byrne, A.J.; Perocheau, D.P.; Udalova, I.A. IRF5 is a specific marker of inflammatory macrophages in vivo. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 245804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krausgruber, T.; Blazek, K.; Smallie, T.; Alzabin, S.; Lockstone, H.; Sahgal, N.; Hussell, T.; Feldmann, M.; Udalova, I.A. IRF5 promotes inflammatory macrophage polarization and TH1-TH17 responses. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang Foreman, H.C.; van Scoy, S.; Cheng, T.F.; Reich, N.C. Activation of interferon regulatory factor 5 by site specific phosphorylation. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, B.J.; Moore, P.A.; Pitha, P.M. Virus-specific activation of a novel Interferon Regulatory Factor, IRF-5, results in the induction of distinct interferon α genes. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 23382–23390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, N.; Kawakami, T.; Taniguchi, T. Recognition DNA sequences of interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF-1) and IRF-2, regulators of cell growth and the interferon system. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1993, 13, 4531–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayik, D.; Gursel, I.; Klinman, D.M. Structure, mechanism and therapeutic utility of immunosuppressive oligonucleotides. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 105, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, M.L.; Wan, M.; Guo, S.; Sun, R.; Yang, M.; Zhao, T.S.; Yan, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.S.; Huang, W.H.; Wu, X.L.; et al. An oligodeoxynucleotide capable of lessening acute lung inflammatory injury in mice infected by influenza virus. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 415, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.J.; Hua, L.; Meng, X.P.; Xiao, Y.; Hao, X.; Guo, S.; Zhao, P.Y.; Wang, L.W.; Dong, B.Q.; Yu, Y.L.; et al. Correlation of surface Toll-like receptor 9 expression with IL-17 production in neutrophils during septic peritonitis in mice induced by E. coli. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 3296307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, A.B.; Monick, M.M.; Hunninghake, G.W. Lipopolysaccharide-induced NF-κB activation and cytokine release in human alveolar macrophages is PKC-independent and TK- and PC-PLC-dependent. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1998, 18, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, M.; Wen, H.; Corsa, C.A.; Liu, T.; Coelho, A.L.; Allen, R.M.; Carson, W.F., 4th; Cavassani, K.A.; Li, X.; Lukacs, N.W.; et al. Epigenetic regulation of the alternatively activated macrophage phenotype. Blood 2009, 114, 3244–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Poppoe, F.; Chen, J.; Yu, L.; Deng, F.; Luo, Q.; Xu, Y.; Cai, Y.; Shen, J. Macrophages polarized by expression of toxoGRA15II inhibit growth of hepatic carcinoma. Front. Immunol. 2017, 13, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muris, A.H.; Damoiseaux, J.; Smolders, J.; Cohen Tervaert, J.W.; Hupperts, R.; Thewissen, M. Intracellular IL-10 detection in T cells by flow cytometry: The use of protein transport inhibitors revisited. J. Immunol. Methods 2012, 381, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delano, M.J.; Ward, P.A. Sepsis-induced immune dysfunction: Can immune therapies reduce mortality? J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darnell, J.E., Jr.; Kerr, I.M.; Stark, G.R. Jak–STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science 1994, 264, 1415–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, Y.; Shimizu, T.; Kusumoto, M.; Kyogoku, Y.; Taniguchi, T.; Hakoshima, T. Crystal structure of an IRF-DNA complex reveals novel DNA recognition and cooperative binding to a tandem repeat of core sequences. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 5028–5041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, B.J.; Kellum, M.J.; Pinder, K.E.; Frisancho, J.A.; Pitha, P.M. Interferon regulatory factor 5, a novel mediator of cell cycle arrest and cell death. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 6424–6431. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.; Mancl, M.E.; Barnes, B.J. Signaling through IFN regulatory factor-5 sensitizes p53-deficient tumors to DNA damage-induced apoptosis and cell death. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 7403–7412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paun, A.; Bankoti, R.; Joshi, T.; Pitha, P.M.; Stager, S. Critical role of IRF-5 in the development of T helper 1 responses to Leishmania donovani infection. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1001246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlos del Fresno, C.; Soulat, D.; Roth, S.; Blazek, K.; Udalova, I.; Sancho, D.; Ruland, J.; Ardavin, C. Interferon-β production via Dectin-1-Syk-IRF5 signaling in dendritic cells is crucial for immunity to C. albicans. Immunity 2013, 38, 1176–1186. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Feng, D.; Bi, X.; Stone, R.C.; Barnes, B.J. Monocytes from IRF5−/− mice have an intrinsic defect in their response to pristane-induced lupus. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 3741–3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courties, G.; Heidt, T.; Sebas, M.; Iwamoto, Y.; Jeon, D.; Truelove, J.; Tricot, B.; Wojtkiewicz, G.; Dutta, P.; Sager, H.B.; et al. In vivo silencing of the transcription factor IRF5 reprograms the macrophage phenotype and improves infarct healing. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 1556–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, B.J.; Kellum, M.J.; Field, A.E.; Pitha, P.M. Multiple regulatory domains of IRF-5 control activation, cellular localization and induction of chemokines that mediate recruitment of T lymphocytes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 5721–5740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, M.; Arikawa, T.; Chen, Y.H.; Moriwaki, Y.; Price, M.; Brown, M.; Perfect, J.R.; Shinohara, M.L. T cells down-regulate macrophage TNF production by IRAK1-mediated IL-10 expression and control innate hyper inflammation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5295–5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Name | Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|
| GAPDH | Forward: 5′-ATCACCATCTTCCAGGAGCGA-3′ Reverse: 5′-TCTCGTGGTTCACACCCATCA-3′ |
| iNOS | Forward: 5′-CTGCTGGTGGTGACAAGCACATTT-3′ Reverse: 5′-ATGTCATGAGCAAAGGCGCAGAAC-3′ |
| IRF5 | Forward: 5′-AGCGGGAAGTCAAGACGAAGCTCT-3′ Reverse: 5′- CTGAGAACATCTCCAGCAGCA-3′ |
| TNF-α | Forward: 5′-GGCTCCAGGCGGTGCTTGTT-3′ Reverse: 5′-GGCTTGTCACTCGGGGTTCG-3′ |
| IL-6 | Forward: 5′-GGATACCACTCCCAACAGACC-3′ Reverse: 5′-TCCAGTTTGGTAGCATCATCA-3′ |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, S.; Li, X.; Nie, S.; Yang, L.; Tu, L.; Dong, B.; Zhao, P.; Wang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, L.; et al. An AAAG-Rich Oligodeoxynucleotide Rescues Mice from Bacterial Septic Peritonitis by Interfering Interferon Regulatory Factor 5. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18051034
Gao S, Li X, Nie S, Yang L, Tu L, Dong B, Zhao P, Wang Y, Yu Y, Wang L, et al. An AAAG-Rich Oligodeoxynucleotide Rescues Mice from Bacterial Septic Peritonitis by Interfering Interferon Regulatory Factor 5. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(5):1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18051034
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Shuang, Xin Li, Shu Nie, Lei Yang, Liqun Tu, Boqi Dong, Peiyan Zhao, Yangyang Wang, Yongli Yu, Liying Wang, and et al. 2017. "An AAAG-Rich Oligodeoxynucleotide Rescues Mice from Bacterial Septic Peritonitis by Interfering Interferon Regulatory Factor 5" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 5: 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18051034
APA StyleGao, S., Li, X., Nie, S., Yang, L., Tu, L., Dong, B., Zhao, P., Wang, Y., Yu, Y., Wang, L., & Hua, S. (2017). An AAAG-Rich Oligodeoxynucleotide Rescues Mice from Bacterial Septic Peritonitis by Interfering Interferon Regulatory Factor 5. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(5), 1034. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18051034