Genomic Insight into the Role of lncRNAs in Cancer Susceptibility
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Novel lncRNAs Found in Different Types of Cancers
2.1. lncRNAs Have Been Found in Many Cancer Types
2.2. lncRNAs in Prostate Cancer
3. Genetic Variants Affect lncRNA Expression
4. Regulatory Mechanisms Underlying Risk SNPs and lncRNAs in Cancer
4.1. SNPs Reside in the lncRNAs
4.2. SNPs Reside Far Away from lncRNAs
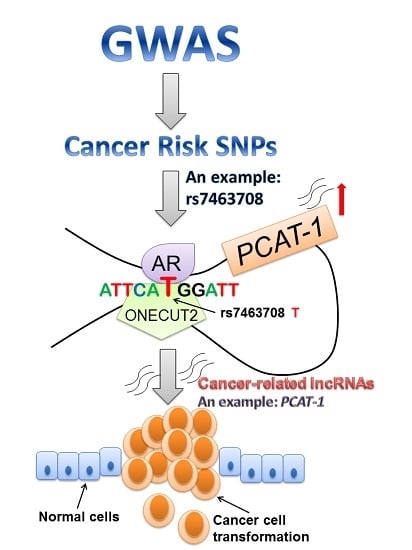
4.3. SNPs Affect lncRNA Expression through Disrupting DNA-Binding of Transcription Factors
5. Clinical Use of GWAS and lncRNA Findings for Cancer Risk Prediction and Future Remarks
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alexander, R.P.; Fang, G.; Rozowsky, J.; Snyder, M.; Gerstein, M.B. Annotating non-coding regions of the genome. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brosius, J. Waste not, want not—Transcript excess in multicellular eukaryotes. Trends Genet. 2005, 21, 287–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Li, D.; Pu, J.; Mei, H.; Yang, D.; Xiang, X.; Qu, H.; Huang, K.; Zheng, L.; Tong, Q. CTCF cooperates with noncoding RNA MYCNOS to promote neuroblastoma progression through facilitating MYCN expression. Oncogene 2016, 35, 3565–3576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigova, A.A.; Abraham, B.J.; Ji, X.; Molinie, B.; Hannett, N.M.; Guo, Y.E.; Jangi, M.; Giallourakis, C.C.; Sharp, P.A.; Young, R.A. Transcription factor trapping by RNA in gene regulatory elements. Science 2015, 350, 978–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derrien, T.; Johnson, R.; Bussotti, G.; Tanzer, A.; Djebali, S.; Tilgner, H.; Guernec, G.; Martin, D.; Merkel, A.; Knowles, D.G.; et al. The GENCODE v7 catalog of human long noncoding RNAs: Analysis of their gene structure, evolution, and expression. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1775–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Yu, M.; Li, Z.; Kong, C.; Bi, J.; Li, J.; Gao, Z.; Li, Z. ncRAN, a newly identified long noncoding RNA, enhances human bladder tumor growth, invasion, and survival. Urology 2011, 77, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, C.; Huo, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, B.; Yang, Q. SNHG16 contributes to breast cancer cell migration by competitively binding miR-98 with E2F5. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 485, 272–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, L.L.; True, K.; Hamilton, M.P.; Nielsen, M.M.; Damas, N.D.; Damgaard, C.K.; Ongen, H.; Dermitzakis, E.; Bramsen, J.B.; Pedersen, J.S.; et al. SNHG16 is regulated by the Wnt pathway in colorectal cancer and affects genes involved in lipid metabolism. Mol. Oncol. 2016, 10, 1266–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thrash-Bingham, C.A.; Tartof, K.D. aHIF: A natural antisense transcript overexpressed in human renal cancer and during hypoxia. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1999, 91, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertozzi, D.; Iurlaro, R.; Sordet, O.; Marinello, J.; Zaffaroni, N.; Capranico, G. Characterization of novel antisense HIF-1α transcripts in human cancers. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 3189–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, P.; Diederichs, S.; Wang, W.; Böing, S.; Metzger, R.; Schneider, P.M.; Tidow, N.; Brandt, B.; Buerger, H.; Bulk, E.; et al. MALAT-1, a novel noncoding RNA, and thymosin β4 predict metastasis and survival in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene 2003, 22, 8031–8041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Gao, J.; Tian, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 drives gastric cancer progression by regulating HMGB2 modulating the miR-1297. Cancer Cell Int. 2017, 17, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Huang, J.; Ni, J.; Song, D.; Ding, M.; Wang, J.; Huang, X.; Li, W. MALAT1 promotes osteosarcoma development by regulation of HMGB1 via miR-142-3p and miR-129-5p. Cell Cycle 2017, 16, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.H.; Liang, L.Z.; Liu, X.L.; Wu, J.N.; Su, K.; Chen, J.Y.; Zheng, Q.Y.; Huang, H.Z.; Liao, G.Q. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 interacts with miR-124 and modulates tongue cancer growth by targeting JAG1. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 2087–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohda, M.; Hoshiya, H.; Katoh, M.; Tanaka, I.; Masuda, R.; Takemura, T.; Fujiwara, M.; Oshimura, M. Frequent loss of imprinting of IGF2 and MEST in lung adenocarcinoma. Mol. Carcinog. 2001, 31, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Wang, X.; Tang, C.; Chen, X.; He, J. H19 promotes the migration and invasion of colon cancer by sponging miR-138 to upregulate the expression of HMGA1. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 50, 1801–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, M.; Blondeau, J.J.; Schmidt, D.; Perner, S.; Müller, S.C.; Ellinger, J. Identification of novel differentially expressed lncRNA and mRNA transcripts in clear cell renal cell carcinoma by expression profiling. Genom. Data 2015, 5, 173–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.Q.; Li, S.J.; Guo, G.X. Long noncoding RNA AFAP1-AS1 promotes cell proliferation and apoptosis of gastric cancer cells via PTEN/p-AKT pathway. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yang, C.; Cui, S.; Sun, Y.; Wang, L.; Fan, X.; Xu, S. The long non-coding RNA XIST controls non-small cell lung cancer proliferation and invasion by modulating miR-186-5p. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 41, 2221–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Han, T.; Zhang, T.; Ma, C.; Sun, C. lncRNA CHRF-induced miR-489 loss promotes metastasis of colorectal cancer via TWIST1/EMT signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Huang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Tang, D.; Kang, R.; Zhou, R.; Fan, X.G. The long non-coding RNA TP73-AS1 modulates HCC cell proliferation through miR-200a-dependent HMGB1/RAGE regulation. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Shen, X.; Zhu, W. Long non-coding RNA TUG1 promotes endometrial cancer development via inhibiting miR-299 and miR-34a-5p. Oncotarget 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, G.Y.; Miao, J.; Zhang, X.L. Long non-coding RNA XIST promotes osteosarcoma progression by targeting ras-related protein RAP2B via miR-320b. Oncol. Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arunkumar, G.; Murugan, A.K.; Prasanna Srinivasa Rao, H.; Subbiah, S.; Rajaraman, R.; Munirajan, A.K. Long non-coding RNA CCAT1 is overexpressed in oral squamous cell carcinomas and predicts poor prognosis. Biomed. Rep. 2017, 6, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J. Long noncoding RNAs: New players in prostate cancer. Cancer Lett. 2013, 339, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bussemakers, M.J.; Bokhoven, A.; Verhaegh, G.W.; Smit, F.P.; Karthaus, H.F.; Schalken, J.A.; Debruyne, F.M.; Ru, N.; Isaacs, W.B. DD3: A new prostate-specific gene, highly overexpressed in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 5975–5979. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prensner, J.R.; Iyer, M.K.; Sahu, A.; Asangani, I.A.; Cao, Q.; Patel, L.; Vergara, I.A.; Davicioni, E.; Erho, N.; Ghadessi, M.; et al. The long noncoding RNA SChLAP1 promotes aggressive prostate cancer and antagonizes the SWI/SNF complex. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1392–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srikantan, V.; Zou, Z.; Petrovics, G.; Xu, L.; Augustus, M.; Davis, L.; Livezey, J.R.; Connell, T.; Sesterhenn, I.A.; Yoshino, K.; et al. PCGEM1, a prostate-specific gene, is overexpressed in prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 12216–12221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Lin, C.; Jin, C.; Yang, J.C.; Tanasa, B.; Li, W.; Merkurjev, D.; Ohgi, K.A.; Meng, D.; Zhang, J.; et al. lncRNA-dependent mechanisms of androgen-receptor-regulated gene activation programs. Nature 2013, 500, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prensner, J.R.; Sahu, A.; Iyer, M.K.; Malik, R.; Chandler, B.; Asangani, I.A.; Poliakov, A.; Vergara, I.A.; Alshalalfa, M.; Jenkins, R.B.; et al. The lncRNAs PCGEM1 and PRNCR1 are not implicated in castration resistant prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 1434–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prensner, J.R.; Iyer, M.K.; Balbin, O.A.; Dhanasekaran, S.M.; Cao, Q.; Brenner, J.C.; Laxman, B.; Asangani, I.A.; Grasso, C.S.; Kominsky, H.D.; et al. Transcriptome sequencing across a prostate cancer cohort identifies PCAT-1, an unannotated lincRNA implicated in disease progression. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prensner, J.R.; Chen, W.; Iyer, M.K.; Cao, Q.; Ma, T.; Han, S.; Sahu, A.; Malik, R.; Wilder-Romans, K.; Navone, N.; et al. PCAT-1, a long noncoding RNA, regulates BRCA2 and controls homologous recombination in cancer. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 1651–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prensner, J.R.; Chen, W.; Han, S.; Iyer, M.K.; Cao, Q.; Kothari, V.; Evans, J.R.; Knudsen, K.E.; Paulsen, M.T.; Ljungman, M.; et al. The long non-coding RNA PCAT-1 promotes prostate cancer cell proliferation through cMyc. Neoplasia 2014, 16, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Gius, D.; Onyango, P.; Muldoon-Jacobs, K.; Karp, J.; Feinberg, A.P.; Cui, H. Epigenetic silencing of tumour suppressor gene p15 by its antisense RNA. Nature 2008, 451, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, K.L.; Li, S.; Muñoz-Cabello, A.M.; Raguz, S.; Zeng, L.; Mujtaba, S.; Gil, J.; Walsh, M.J.; Zhou, M.M. Molecular interplay of the noncoding RNA ANRIL and methylated histone H3 lysine 27 by polycomb CBX7 in transcriptional silencing of INK4a. Mol. Cell 2010, 38, 662–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, L.B.; Palumbo, A.; Mello, K.D.; Sternberg, C.; Caetano, M.S.; Oliveira, F.L.; Neves, A.F.; Nasciutti, L.E.; Goulart, L.R.; Gimba, E.R. PCA3 noncoding RNA is involved in the control of prostate-cancer cell survival and modulates androgen receptor signaling. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, A.L.; Tuzova, A.V.; Bolton, E.M.; Lynch, T.H.; Perry, A.S. Long noncoding RNAs and prostate carcinogenesis: the missing “linc”? Trends Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.; Zhang, J.; Kaipainen, A.; Lucas, J.M.; Yang, H. Long non-coding RNA: A newly deciphered “code” in prostate cancer. Cancer Lett. 2016, 375, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Z.; Xu, C.; Li, Y.; Cai, X.; Ren, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Chen, R.; Qu, M.; et al. A feed-forward regulatory loop between androgen receptor and PlncRNA-1 promotes prostate cancer progression. Cancer Lett. 2016, 374, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takayama, K.; Horie-Inoue, K.; Katayama, S.; Suzuki, T.; Tsutsumi, S.; Ikeda, K.; Urano, T.; Fujimura, T.; Takagi, K.; Takahashi, S.; et al. Androgen-responsive long noncoding RNA CTBP1-AS promotes prostate cancer. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 1665–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourtada-Maarabouni, M.; Pickard, M.R.; Hedge, V.L.; Farzaneh, F.; Williams, G.T. GAS5, a non-protein-coding RNA, controls apoptosis and is downregulated in breast cancer. Oncogene 2009, 28, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kino, T.; Hurt, D.E.; Ichijo, T.; Nader, N.; Chrousos, G.P. Noncoding RNA gas5 is a growth arrest- and starvation-associated repressor of the glucocorticoid receptor. Sci. Signal. 2010, 3, ra8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Batista, D.L.; Gejman, R.; Ansell, P.J.; Zhao, J.; Weng, C.; Klibanski, A. Activation of p53 by MEG3 non-coding RNA. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 24731–24742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichler, E.E.; Nickerson, D.A.; Altshuler, D.; Bowcock, A.M.; Brooks, L.D.; Carter, N.P.; Church, D.M.; Felsenfeld, A.; Guyer, M.; Lee, C.; et al. Completing the map of human genetic variation. Nature 2007, 447, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frazer, K.A.; Murray, S.S.; Schork, N.J.; Topol, E.J. Human genetic variation and its contribution to complex traits. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuzun, E.; Sharp, A.J.; Bailey, J.A.; Kaul, R.; Morrison, V.A.; Pertz, L.M.; Haugen, E.; Hayden, H.; Albertson, D.; Pinkel, D.; et al. Fine-scale structural variation of the human genome. Nat. Genet. 2005, 37, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, G.M.; Zerr, T.; Kidd, J.M.; Eichler, E.E.; Nickerson, D.A. Systematic assessment of copy number variant detection via genome-wide SNP genotyping. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1199–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korbel, J.O.; Urban, A.E.; Affourtit, J.P.; Godwin, B.; Grubert, F.; Simons, J.F.; Kim, P.M.; Palejev, D.; Carriero, N.J.; Du, L.; et al. Paired-end mapping reveals extensive structural variation in the human genome. Science 2007, 318, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaja, R.; Zhang, J.; MacDonald, J.R.; He, Y.; Joseph-George, A.M.; Wei, J.; Rafiq, M.A.; Qian, C.; Shago, M.; Pantano, L.; et al. Genome assembly comparison identifies structural variants in the human genome. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 1413–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Westra, H.J.; Karjalainen, J.; Zhernakova, D.V.; Esko, T.; Hrdlickova, B.; Almeida, R.; Zhernakova, A.; Reinmaa, E.; Võsa, U.; et al. Human disease-associated genetic variation impacts large intergenic non-coding RNA expression. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Miao, X.; Guo, A.Y. lncRNASNP: A database of SNPs in lncRNAs and their potential functions in human and mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D181–D186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhaegh, G.W.; Verkleij, L.; Vermeulen, S.H.; Heijer, M.; Witjes, J.A.; Kiemeney, L.A. Polymorphisms in the H19 gene and the risk of bladder cancer. Eur. Urol. 2008, 54, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Wang, M.; Kang, M.; Wang, Q.; Wu, B.; Chu, H.; Zhong, D.; Qin, C.; Yin, C.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Association between lncrna PCGEM1 polymorphisms and prostate cancer risk. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2013, 16, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewing, C.M.; Ray, A.M.; Lange, E.M.; Zuhlke, K.A.; Robbins, C.M.; Tembe, W.D.; Wiley, K.E.; Isaacs, S.D.; Johng, D.; Wang, Y.; et al. Germline mutations in HOXB13 and prostate-cancer risk. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kote-Jarai, Z.; Mikropoulos, C.; Leongamornlert, D.A.; Dadaev, T.; Tymrakiewicz, M.; Saunders, E.J.; Jones, M.; Jugurnauth-Little, S.; Govindasami, K.; Guy, M.; et al. Prevalence of the HOXB13 G84E germline mutation in British men and correlation with prostate cancer risk, tumour characteristics and clinical outcomes. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 756–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.C.; Palanisamy, N.; Zuhlke, K.A.; Johnson, A.M.; Siddiqui, J.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; Kunju, L.P.; Cooney, K.A.; Tomlins, S.A. HOXB13 G84E-related familial prostate cancers: A clinical, histologic, and molecular survey. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2014, 38, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Liu, H.L.; Liu, Z.S.; Owzar, K.; Han, Y.H.; Su, L.; Wei, Y.Y.; Hung, J.R.; McLaughlin, J.; Brhane, Y.; et al. A Novel genetic variant in long non-coding RNA gene NEXN-AS1 is associated with risk of lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Yang, C.; Tong, S.; Ding, Y.; Deng, W.; Song, D.; Xiao, K. Genetic variation of long non-coding RNA TINCR contribute to the susceptibility and progression of colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 33536–33543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingle, J.N.; Xie, F.; Ellis, M.J.; Goss, P.E.; Shepherd, L.E.; Chapman, J.W.; Chen, B.E.; Kubo, M.; Furukawa, Y.; Momozawa, Y.; et al. Genetic polymorphisms in the long noncoding RNA MIR2052HG offer a pharmacogenomic basis for the response of breast cancer patients to aromatase inhibitor therapy. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 7012–7023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taheri, M.; Habibi, M.; Noroozi, R.; Rakhshan, A.; Sarrafzadeh, S.; Sayad, A.; Omrani, D.M.; Ghafouri-Fard, S. HOTAIR genetic variants are associated with prostate cancer and benign prostate hyperplasia in an Iranian population. Gene 2017, 613, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Huang, X.; Tan, W.; Yu, D.; Du, Z.L.; Chang, J.; Wei, L.X.; Han, Y.L.; Wang, C.F.; Che, X.; et al. Pancreatic cancer risk variant in LINC00673 creates a miR-1231 binding site and interferes with PTPN11 degradation. Nat. Genet. 2015, 48, 747–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomerantz, M.M.; Ahmadiyeh, N.; Jia, L.; Herman, P.; Verzi, M.P.; Doddapaneni, H.; Beckwith, C.A.; Chan, J.A.; Hills, A.; Davis, M.; et al. The 8q24 cancer risk variant rs6983267 shows long-range interaction with MYC in colorectal cancer. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 882–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuupanen, S.; Turunen, M.; Lehtonen, R.; Hallikas, O.; Vanharanta, S.; Kivioja, T.; Björklund, M.; Wei, G.; Yan, J.; Niittymäki, I.; et al. The common colorectal cancer predisposition SNP rs6983267 at chromosome 8q24 confers potential to enhanced Wnt signaling. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sur, I.K.; Hallikas, O.; Vähärautio, A.; Yan, J.; Turunen, M.; Enge, M.; Taipale, M.; Karhu, A.; Aaltonen, L.A.; Taipale, J. Mice lacking a Myc enhancer that includes human SNP rs6983267 are resistant to intestinal tumors. Science 2012, 338, 1360–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegeman, S.; Amankwah, E.; Klein, K.; Mara, A.T.; Kim, D.; Lin, H.Y.; Permuth-Wey, J.; Sellers, A.T.; Srinivasan, S.; Eeles, R.; et al. A large scale analysis of genetic variants within putative miRNA binding sites in prostate cancer. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wei, G.H.; Liu, D.P.; Liang, C.C. Unravelling the world of cis-regulatory elements. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2007, 45, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, G.H.; Liu, D.P.; Liang, C.C. Charting gene regulatory networks: Strategies, challenges and perspectives. Biochem. J. 2004, 381 Pt 1, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Ahmed, M.; Zhang, F.; Yao, C.Q.; Li, S.; Liang, Y.; Hua, J.; Soares, F.; Sun, Y.; Langstein, J.; et al. Modulation of long noncoding RNAs by risk SNPs underlying genetic predispositions to prostate cancer. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1142–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Whitington, T.; Gao, P.; Lindberg, J.F.; Yang, Y.; Sun, J.; Väisänen, M.R.; Szulkin, R.; Annala, M.; Yan, J.; et al. A prostate cancer susceptibility allele at 6q22 increases RFX6 expression by modulating HOXB13 chromatin binding. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitington, T.; Gao, P.; Song, W.; Ross-Adams, H.; Lamb, A.D.; Yang, Y.; Svezia, I.; Klevebring, D.; Mills, I.G.; Karlsson, R.; et al. Gene regulatory mechanisms underpinning prostate cancer susceptibility. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirschhorn, J.N.; Daly, M.J. Genome-wide association studies for common diseases and complex traits. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2005, 6, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freedman, M.L.; Monteiro, A.N.; Gayther, S.A.; Coetzee, G.A.; Risch, A.; Plass, C.; Casey, G.; de Biasi, M.; Carlson, C.; Duggan, D.; et al. Principles for the post-GWAS functional characterization of cancer risk loci. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, M.I.; Abecasis, G.R.; Cardon, L.R.; Goldstein, D.B.; Little, J.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Hirschhorn, J.N. Genome-wide association studies for complex traits: Consensus, uncertainty and challenges. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 356–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ariel, I.; Sughayer, M.; Fellig, Y.; Pizov, G.; Ayesh, S.; Podeh, D.; Libdeh, B.A.; Levy, C.; Birman, T.; Tykocinski, M.L.; et al. The imprinted H19 gene is a marker of early recurrence in human bladder carcinoma. Mol. Pathol. 2000, 53, 320–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calin, G.A.; Liu, C.G.; Ferracin, M.; Hyslop, T.; Spizzo, R.; Sevignani, C.; Fabbri, M.; Cimmino, A.; Lee, E.J.; Wojcik, S.E.; et al. Ultraconserved regions encoding ncRNAs are altered in human leukemias and carcinomas. Cancer Cell 2007, 12, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, A.M.; Guttman, M.; Huarte, M.; Garber, M.; Raj, A.; Morales, D.R.; Thomas, K.; Presser, A.; Bernstein, B.E.; van Oudenaarden, A.; et al. Many human large intergenic noncoding RNAs associate with chromatin-modifying complexes and affect gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 11667–11672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, M.T.; Hu, J.W.; Yin, R.; Xu, L. Long noncoding RNA: An emerging paradigm of cancer research. Tumour Biol. 2013, 34, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelles, D.A.; Fang, M.Y.; O’Connell, M.R.; Xu, J.L.; Markmiller, S.J.; Doudna, J.A.; Yeo, G.W. Programmable RNA tracking in live cells with CRISPR/Cas9. Cell 2016, 165, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| lncRNA Name | Cancer Type | Potential Mechanism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| AFAP1-AS1 | Gastric Cancer | Via the PTEN/p-AKT pathway | [18] |
| XIST | Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer | XIST and miR-186-5p are likely in the same RNA-induced silencing complex | [19] |
| lncRNA CHRF | Colorectal Cancer | Inhibits miR-489 expression | [20] |
| SNHG16 | Bladder Lung Colorectal | Wnt pathway, binding miR-98 with E2F5 | [6,7,8] |
| HIF1A-AS | Renal Cancer | No report | [9,10] |
| MALAT1 | Lung Gastric Osteosarcoma Tongue | Interacts with miR-124, miR-142-3p, miR-129-5p and miR-1297 | [11,12,13,14] |
| H19 | Lung Colon | Upregulates the expression of HMGA1 by sponging miR-138 | [15,16] |
| TP73-AS1 | Hepatocellular Carcinoma | Inversely correlated with miR-200a | [21] |
| TUG1 | Endometrial | Inhibiting miR-299 and miR-34a-5p | [22] |
| XIST | Osteosarcoma | Directly binds to miR-320b and repressed miR-320b expression | [23] |
| CCAT1 | Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas | Through miR155-5p and let7b-5p | [24] |
| lncRNA Name | Cancer Type | Potential Mechanism | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Onco-lncRNAs: overexpression in cancer | |||
| CDKN2B-AS1 (ANRIL, p15AS) | Prostate, others | Epigenetic silencing of the locus by interaction with CBX7 and PRC2 | [34,35] |
| PCA3/DD3 | Prostate | Modulating AR signaling | [36] |
| PCAT-1 | Prostate | Inhibits BRCA2 and activates MYC, silencing gene through PRC2 | [32,33] |
| PCAT6 | Prostate, others | Oncogenic phenotypic effects, molecular mechanisms are unknown | [37] |
| PCAT7 | Prostate, others | Oncogenic phenotypic effects, but molecular mechanisms are unknown | [37] |
| PVT1 | Prostate, others | Oncogenic phenotypic effects, molecular mechanisms are unknown | [37] |
| PCGEM1 | Prostate | Inhibits apoptosis; promotes cell proliferation | [30] |
| MALAT1 | Prostate, others | Alternative splicing of pre-mRNAs | [38] |
| HOTAIR | Prostate, others | Binds and stabilizes AR | [38] |
| PlncRNA-1 | Prostate, others | Inhibits AR-targeting microRNAs | [39] |
| CTBP1-AS | Prostate | Androgen-responsive gene | [40] |
| SCHLAP1 (PCAT11) | Prostate | Interacts with the SWIF/SNIF complex | [27] |
| Tumor suppressor-lncRNAs: reduced expression in cancer | |||
| PTENP1 | Prostate, others | Binds anti-PTEN miRNA | [38] |
| GAS5 | Prostate | Prevents glucocorticoid receptor-induced gene expression | [41,42] |
| MEG3 | Prostate, others | Downregulates MDM2 and promotes p53 accumulation | [43] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, P.; Wei, G.-H. Genomic Insight into the Role of lncRNAs in Cancer Susceptibility. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061239
Gao P, Wei G-H. Genomic Insight into the Role of lncRNAs in Cancer Susceptibility. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(6):1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061239
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Ping, and Gong-Hong Wei. 2017. "Genomic Insight into the Role of lncRNAs in Cancer Susceptibility" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 6: 1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061239
APA StyleGao, P., & Wei, G. -H. (2017). Genomic Insight into the Role of lncRNAs in Cancer Susceptibility. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(6), 1239. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061239