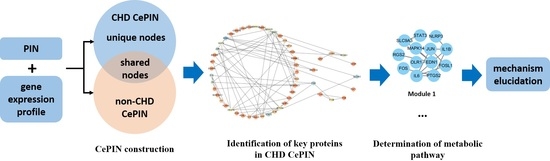
Using Coexpression Protein Interaction Network Analysis to Identify Mechanisms of Danshensu Affecting Patients with Coronary Heart Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Source of Protein Information Related to Danshensu (DSS)
2.2. Construction of Coexpression Protein Interaction Networks (CePIN)
2.3. Comparative Analysis of CePIN
2.3.1. Comparative Analysis of Topological Parameters of Proteins in CePIN
2.3.2. Comparative Analysis of the Expression Level of the Gene Corresponding to the Proteins in CePIN
2.4. Gene Ontology (GO) Enrichment Analysis of CePIN
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Construction of Protein Interaction Networks (PIN)
4.2 Construction of CePIN
4.3. Comparative Analysis of CePIN
4.3.1. Comparative Analysis of Topological Parameters of Proteins in CePIN
4.3.2. Comparative analysis of the expression level of the gene corresponding to the proteins in CePIN
4.4. GO Enrichment Analysis of CePIN
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CHD | coronary heart disease |
| PPIs | protein–protein interactions |
| TCM | traditional Chinese medicine |
| DSS | Danshensu |
| PIN | protein–protein interaction network |
| CePIN | coexpression protein interaction network |
| CePPIs | coexpression protein-protein interactions |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
References
- Lee, I.M.; Shiroma, E.J.; Lobelo, F.; Puska, P.; Blair, S.N.; Katzmarzyk, P.T. Effect of physical inactivity on major non-communicable diseases worldwide: An analysis of burden of disease and life expectancy. Lancet 2012, 380, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Huang, F.; Zhang, S.; Leung, S.W. Is danshen (Salvia miltiorrhiza) dripping pill more effective than isosorbide dinitrate in treating angina pectoris? A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Int. J. Cardiol. 2012, 157, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Liu, Z.; Li, H.; Little, P.J.; Liu, P.; Xu, S. Cardiovascular actions and therapeutic potential of tanshinone IIA. Atherosclerosis 2011, 220, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Qi, D.; Lian, W.; Li, Q.Z.; Li, H.J.; Fan, H.Y. Effects of Danshensu on platelet aggregation and thrombosis: In vivo arteriovenous shunt and venous thrombosis models in rats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Guan, Y.; Duan, J.; Guo, W.; Zhu, Y.; Wei, Q.; Guo, C.; Zhou, D.; Wang, Y.; Xi, M. Cardioprotective effect of Danshensu against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury and inhibits apoptosis of H9c2 cardiomyocytes via Akt and ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 699, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.; Sun, C.; Tao, X.; Ren, Y. Anti-inflammatory effects of active constituents extracted from Chinese medicinal herbs against Propionibacterium acnes. Nat. Prod. Res. 2012, 26, 1746–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, P.; Wang, S.; Xiao, C.; Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, W.; Zheng, X.; Zhao, G.; Zang, W.; Zheng, X. The anti-atherosclerotic effect of tanshinol borneol ester using fecal metabolomics based on liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Analyst 2015, 141, 1112–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Wang, S.; Xiao, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Shen, X.; He, D.; Zheng, X.; Zhai, Y. DBZ blocks LPS-induced monocyte activation and foam cell formation via inhibiting nuclear factor-κB. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2011, 28, 649–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.W.; Zhou, Y.Q.; Ul Qamar, M.T.; Chen, L.L.; Ding, Y.D. Prediction of protein–protein interactions by evidence combining methods. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patrik, D.; Church, G.M. Estimating and improving protein interaction error rates. In Proceedings of the Computational Systems Bioinformatics Conference, Stanford, CA, USA, 19 August 2004; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 216–223. [Google Scholar]
- De la Fuente, A. From “differential expression” to “differential networking”-identification of dysfunctional regulatory networks in diseases. Trends Genet. 2010, 26, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinrouweler, C.E.; van Uitert, M.; Moerland, P.D.; Ris-Stalpers, C.; van der Post, J.A.M.; Afink, G.B. Differentially Expressed Genes in the Pre-Eclamptic Placenta: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, J.R.; Ghaemmaghami, S.; Ihmels, J.; Breslow, D.K.; Noble, M.; Derisi, J.L.; Weissman, J.S. Single-cell proteomic analysis of S. cerevisiae reveals the architecture of biological noise. Nature 2006, 441, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Jiang, R.; Zhang, M.Q.; Li, S. Network-based global inference of human disease genes. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2008, 4, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, I.W.; Linding, R.; Warde-Farley, D.; Liu, Y.; Pesquita, C.; Faria, D.; Bull, S.; Pawson, T.; Morris, Q.; Wrana, J.L. Dynamic modularity in protein interaction networks predicts breast cancer outcome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostka, D.; Spang, R. Finding disease specific alterations in the co-expression of genes. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, S.L.; Brechbühler, C.M.; Griffin, M.; Bond, A.T. Gene co-expression network topology provides a framework for molecular characterization of cellular state. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 2242–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, N.J.; Reverter, A.; Dalrymple, B.P. A differential wiring analysis of expression data correctly identifies the gene containing the causal mutation. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2009, 5, e1000382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assenov, Y.; Ramírez, F.; Schelhorn, S.E.; Lengauer, T.; Albrecht, M. Computing topological parameters of biological networks. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vecchio, F.; Miraglia, F.; Curcio, G.; Altavilla, R.; Scrascia, F.; Giambattistelli, F.; Quattrocchi, C.C.; Bramanti, P.; Vernieri, F.; Rossini, P.M. Cortical Brain Connectivity Evaluated by Graph Theory in Dementia: A Correlation Study Between Functional and Structural Data. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2015, 45, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eguíluz, V.M.; Chialvo, D.R.; Cecchi, G.A.; Baliki, M.; Apkarian, A.V. Scale-free brain functional networks. Phys.Rev. Lett. 2005, 94, 018102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murugesan, M.; Sujith, R.I. Detecting the Onset of an Impending Thermoacoustic Instability Using Complex Networks. J. Propul. Power 2016, 32, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernabò, N.; Barboni, B.; Maccarrone, M. Systems biology analysis of the endocannabinoid system reveals a scale-free network with distinct roles for anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol. OMICS 2013, 17, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Hua, P.; Hui, L.; Zhang, L.L.; Hu, Z.; Zhu, Y.W. Identification of hub genes and pathways associated with hepatocellular carcinoma based on network strategy. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 12, 2109–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laubitz, D.; Harrison, C.A.; Midura-Kiela, M.T.; Ramalingam, R.; Larmonier, C.B.; Chase, J.H.; Caporaso, J.G.; Besselsen, D.G.; Ghishan, F.K.; Kiela, P.R. Reduced Epithelial Na+/H+ Exchange Drives Gut Microbial Dysbiosis and Promotes Inflammatory Response in T Cell-Mediated Murine Colitis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothenbacher, D.; Müllerscholze, S.; Herder, C.; Koenig, W.; Kolb, H. Differential Expression of Chemokines, Risk of Stable Coronary Heart Disease, and Correlation with Established Cardiovascular Risk Markers. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sie, M.P.; Isaacs, A.; de Maat, M.P.; Mattace-Raso, F.U.; Uitterlinden, A.G.; Kardys, I.; Hofman, A.; Hoeks, A.P.; Reneman, R.S.; van Duijn, C.M. Genetic variation in the fibrinogen-alpha and fibrinogen-γ genes in relation to arterial stiffness: The Rotterdam Study. J. Hypertens. 2009, 27, 1392–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Ma, Y.T.; Yang, Y.N.; Fu, Z.Y.; Li, X.M.; Huang, D.; Ma, X.; Chen, B.D.; Liu, F. Interaction between COX-2 G-765C and smoking in relation to coronary artery disease in a Chinese Uighur population. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2011, 49, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cappelletti, A.; Zanussi, M.; Mazzavillani, M.; Magni, V.; Calori, G.; Godino, C.; Ferrari, M.; Margonato, A. Association of LOXIN, a new functional splicing isoform of the OLR1 gene, with severity and prognostic localization of critical coronary artery stenoses. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2014, 15, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterworth, D.M.; Li, L.; Scott, R.; Warren, L.; Gillson, C.; Aponte, J.; Sarovblat, L.; Sprecher, D.; Dupuis, J.; Reiner, A. A low-frequency variant in MAPK14 provides mechanistic evidence of a link with myeloperoxidase: A prognostic cardiovascular risk marker. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2014, 3, 845–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formiga, F.R.; Pelacho, B.; Garbayo, E.; Imbuluzqueta, I.; Díazherráez, P.; Abizanda, G.; Gavira, J.J.; Simónyarza, T.; Albiasu, E.; Tamayo, E. Controlled delivery of fibroblast growth factor-1 and neuregulin-1 from biodegradable microparticles promotes cardiac repair in a rat myocardial infarction model through activation of endogenous regeneration. J. Control. Release 2014, 173, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, L.; Liu, W.; Yan, Y.; Su, L.; Wu, G.; Liang, B.; Tan, J.; Huang, G. Influence of the β-fibrinogen-455G/A polymorphism on development of ischemic stroke and coronary heart disease. Thromb. Res. 2014, 133, 993–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, C.; Sai, J.; Li, F.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, F. Xueshuan Xinmaining Tablet Treats Blood Stasis through Regulating the Expression of F13a1, Car1, and Tbxa2r. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 704390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- März, W.; Seelhorst, U.; Wellnitz, B.; Tiran, B.; Obermayerpietsch, B.; Renner, W.; Boehm, B.O.; Ritz, E.; Hoffmann, M.M. Alanine to serine polymorphism at position 986 of the calcium-sensing receptor associated with coronary heart disease, myocardial infarction, all-cause, and cardiovascular mortality. J. Clin. Endocr. Metab. 2007, 92, 2363–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, M.; Von, M.C.; Campillos, M.; Jensen, L.J.; Bork, P. STITCH: Interaction networks of chemicals and proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, D684–D688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, M.; Szklarczyk, D.; Pletscherfrankild, S.; Blicher, T.H.; Mering, C.V.; Jensen, L.J.; Bork, P. STITCH 4: Integration of protein-chemical interactions with user data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Lu, F.; Chen, Y.K.; Luo, G.G.; Jiang, L.D.; Qiao, L.S.; Zhang, Y.L.; Xiang, Y.H. Discovery of Potential Orthosteric and Allosteric Antagonists of P2Y1R from Chinese Herbs by Molecular Simulation Methods. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 4320201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, L.S.; Zhang, X.B.; Jiang, L.D.; Zhang, Y.L.; Li, G.Y. Identification of potential ACAT-2 selective inhibitors using pharmacophore, SVM and SVR from Chinese herbs. Mol. Divers. 2016, 20, 933–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, G.; Fang, L.; Qiao, L.; Xi, C.; Li, G.; Zhang, Y. Discovery of Potential Inhibitors of Aldosterone Synthase from Chinese Herbs Using Pharmacophore Modeling, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation Studies. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 4182595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, F.; Luo, G.; Qiao, L.; Jiang, L.; Li, G.; Zhang, Y. Virtual Screening for Potential Allosteric Inhibitors of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 2 from Traditional Chinese Medicine. Molecules 2016, 21, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; He, Y.; Luo, G.; Yang, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, Y. Discovery of potential novel microsomal triglyceride transfer protein inhibitors via virtual screening of pharmacophore modelling and molecular docking. Mol. Simul. 2016, 42, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.S.; Li, B.; Chen, Y.K.; Li, L.L.; Chen, X.; Wang, L.Z.; Lu, F.; Luo, G.G.; Li, G.Y.; Zhang, Y.L. Discovery of Anti-Hypertensive Oligopeptides from Adlay Based on In Silico Proteolysis and Virtual Screening. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 12, 2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Franceschini, A.; Kuhn, M.; Simonovic, M.; Roth, A.; Minguez, P.; Doerks, T.; Stark, M.; Muller, J.; Bork, P. The STRING database in 2011: Functional interaction networks of proteins, globally integrated and scored. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D561–D568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smoot, M.E.; Ono, K.; Ruscheinski, J.; Wang, P.L.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape 2.8: New features for data integration and network visualization. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 431–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, T.; Troup, D.B.; Wilhite, S.E.; Ledoux, P.; Rudnev, D.; Evangelista, C.; Kim, I.F.; Soboleva, A.; Tomashevsky, M.; Edgar, R. NCBI GEO: Mining tens of millions of expression profiles—Database and tools update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, D760–D765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Yuan, Z.; Guo, D.; Hou, B.; Yin, C.; Zhang, W.; Li, F. Genome-wide identification of long noncoding RNA genes and their potential association with fecundity and virulence in rice brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.D.; Bertin, N.; Hao, T.; Goldberg, D.S.; Berriz, G.F.; Zhang, L.V.; Dupuy, D.; Walhout, A.J.; Cusick, M.E.; Roth, F.P. Evidence for dynamically organized modularity in the yeast protein-protein interaction network. Nature 2004, 430, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Chow, T.W.S. Effective strategy of adding nodes and links for maximizing the traffic capacity of scale-free network. Chaos 2010, 20, 033123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdollahi, A.; Schwager, C.; Kleeff, J.; Esposito, I.; Domhan, S.; Peschke, P.; Kai, H.; Hahnfeldt, P.; Hlatky, L.; Debus, J. Transcriptional Network Governing the Angiogenic Switch in Human Pancreatic Cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 12890–12895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achard, S.; Salvador, R.; Whitcher, B.; Suckling, J.; Bullmore, E. A resilient, low-frequency, small-world human brain functional network with highly connected association cortical hubs. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfitzner, R.; Scholtes, I.; Garas, A.; Tessone, C.J.; Schweitzer, F. Betweenness Preference: Quantifying Correlations in the Topological Dynamics of Temporal Networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 110, 198701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, K.I.; Kahng, B.; Kim, D. Universal behavior of load distribution in scale-free networks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2001, 87, 278701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fares, Z.C.; Mervi, G.; Ben-Hur, N.D.O.; Vural, Ö.; Eija, K.; Gürsoy, U.K. A Systems Biology Approach to Reveal Putative Host-Derived Biomarkers of Periodontitis by Network Topology Characterization of MMP-REDOX/NO and Apoptosis Integrated Pathways. Front. Cell. Infect. Mi. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Kim, P.M.; Sprecher, E.; Trifonov, V.; Gerstein, M. The importance of bottlenecks in protein networks: Correlation with gene essentiality and expression dynamics. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2007, 3, e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rokkedallausch, T.; Lykke, M.; Hansen, M.S.; Nielsen, R.O. Normative values for the foot posture index between right and left foot: A descriptive study. Gait Posture 2013, 38, 843–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Zheng, X.; Li, W.; Yang, L.; Jiang, J. Exploring the mechanism of non-small-cell lung cancer cell lines resistant to epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2016, 12, 121. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, M.; Chen, J.; Pan, Y. A Fast Hierarchical Clustering Algorithm for Functional Modules Discovery in Protein Interaction Networks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2011, 8, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhong, J.; Chen, G.; Li, M.; Wu, F.; Pan, Y. ClusterViz: A Cytoscape APP for Cluster Analysis of Biological Network. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinf. 2015, 12, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, D.; Xie, P.; Ren, G.; Sun, G.; Zeng, X.; Sun, X. MiR-106b and MiR-15b Modulate Apoptosis and Angiogenesis in Myocardial Infarction. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 29, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consortium, G.O. The Gene Ontology (GO) database and informatics resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, D258–D261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Uniprot ID | Proteins | Source | Uniprot ID | Proteins | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P09601 | HMOX1 | STITCH | P12821 | ACE | Pharmacophore |
| P30556 | AGTR1 | Pharmacophore | P09917 | ALOX5 | Pharmacophore |
| P25101 | EDNRA | Pharmacophore | P29466 | CASP1 | Pharmacophore |
| P24530 | EDNRB | Pharmacophore | P00742 | F10 | Pharmacophore |
| P24941 | CDK2 | Pharmacophore | - | - | - |
| Items | Proteins | CePPIs |
|---|---|---|
| CHD CePIN | 91 | 98 |
| Non-CHD CePIN | 99 | 110 |
| Overlap amount | 66 | 33 |
| Overlap ratio | 69% | 32% |
| Name | Category | Hub/Bottleneck | Betweenness | Degree |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EDN1 | shared | hub-bottleneck | 0.63673203 a | 7 b |
| FGG | unique | bottleneck | 0.51450980 a | 4 |
| SLC9A3 | unique | bottleneck | 0.49411765 a | 2 |
| STAT3 | shared | bottleneck | 0.48627451 a | 2 |
| F10 | shared | - | 0.41058824 | 5 |
| JUN | shared | hub | 0.37490196 | 7 b |
| F8 | shared | - | 0.32156863 | 4 |
| KNG1 | shared | hub | 0.28313725 | 7 b |
| CCND1 | unique | - | 0.21803922 | 3 |
| TBXA2R | shared | - | 0.15137255 | 5 |
| Average | - | - | 0.091432882 | 2.7307692 |
| +1 SD | - | - | 0.254025973 | 4.4810116 |
| +2 SD | - | - | 0.416619064 | 6.2312540 |
| Removed Node | Category | Hub/Bottleneck | Shortest Paths | Characteristic Path Length | Network Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EDN1 | shared | hub-bottleneck | 988 (38%) | 3.332 | 7 |
| FGG | unique | bottleneck | 1238 (48%) | 3.313 | 7 |
| SLC9A3 | unique | bottleneck | 1232 (50%) | 3.344 | 7 |
| STAT3 | shared | bottleneck | 1310 (51%) | 3.382 | 7 |
| KNG1 | shared | hub | 1828 (71%) | 4.658 | 11 |
| JUN | shared | hub | 1934 (75%) | 5.411 | 12 |
| without removing | - | - | 2652 (100%) | 5.572 | 13 |
| Module | p-Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 7.76 × 10−9 | inflammatory response |
| 2 | 4.89 × 10−7 | G-protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway |
| 3 | 4.91 × 10−11 | regulation of cell cycle |
| 4 | 5.23 × 10−11 | heme catabolic process |
| 5 | 6.08 × 10−8 | regulation of I-κB kinase/NF-κB signaling |
| 6 | 4.89 × 10−9 | blood coagulation |
| 7 | 2.12 × 10−10 | arachidonic acid metabolic process |
| 8 | 1.42 × 10−6 | regulation of blood volume by renin-angiotensin |
| 9 | 1.51 × 10−7 | G-protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huo, M.; Wang, Z.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, Y. Using Coexpression Protein Interaction Network Analysis to Identify Mechanisms of Danshensu Affecting Patients with Coronary Heart Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1298. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061298
Huo M, Wang Z, Wu D, Zhang Y, Qiao Y. Using Coexpression Protein Interaction Network Analysis to Identify Mechanisms of Danshensu Affecting Patients with Coronary Heart Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(6):1298. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061298
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuo, Mengqi, Zhixin Wang, Dongxue Wu, Yanling Zhang, and Yanjiang Qiao. 2017. "Using Coexpression Protein Interaction Network Analysis to Identify Mechanisms of Danshensu Affecting Patients with Coronary Heart Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 6: 1298. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061298
APA StyleHuo, M., Wang, Z., Wu, D., Zhang, Y., & Qiao, Y. (2017). Using Coexpression Protein Interaction Network Analysis to Identify Mechanisms of Danshensu Affecting Patients with Coronary Heart Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(6), 1298. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061298