Theranostic Liposome–Nanoparticle Hybrids for Drug Delivery and Bioimaging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
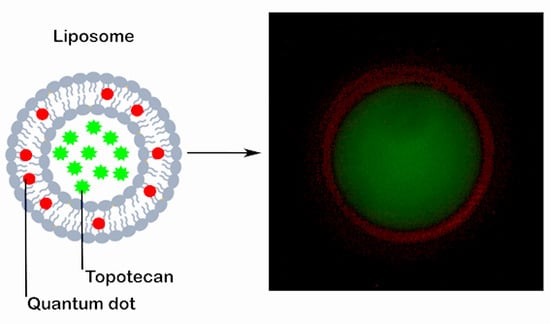
2.1. Synthesis and Characterization of TPT-Loaded Liposomal Formulations
2.2. In Vitro Drug Release
2.3. Cellular Uptake and Internalization
2.4. Cytotoxicity
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of L–QD Hybrids
3.3. Encapsulation of Model Drug TPT
3.4. Encapsulation Efficiency
3.5. Characterization
3.6. In Vitro Drug Release
3.7. Cell Culture
3.8. Cytotoxicity
3.9. Cellular Uptake and Internalization
3.10. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Seleci, M.; Ag Seleci, D.; Joncyzk, R.; Stahl, F.; Blume, C.; Scheper, T. Smart multifunctional nanoparticles in nanomedicine. BioNanoMaterials 2016, 17, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruchez, M.; Moronne, M.; Gin, P.; Weiss, S.; Alivisatos, A.P. Semiconductor nanocrystals as fluorescent biological labels. Science 1998, 281, 2013–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaiswal, J.K.; Mattoussi, H.; Mauro, J.M.; Simon, S.M. Long-term multiple color imaging of live cells using quantum dot bioconjugates. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resch-Genger, U.; Grabolle, M.; Cavaliere-Jaricot, S.; Nitschke, R.; Nann, T. Quantum dots versus organic dyes as fluorescent labels. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 763–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizvi, S.B.; Rouhi, S.; Taniguchi, S.; Yang, S.Y.; Green, M.; Keshtgar, M.; Seifalian, A.M. Near-infrared quantum dots for HER2 localization and imaging of cancer cells. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 1323–1337. [Google Scholar]
- Ag, D.; Bongartz, R.; Dogan, L.E.; Seleci, M.; Walter, J.-G.; Demirkol, D.O.; Stahl, F.; Ozcelik, S.; Timur, S.; Scheper, T. Biofunctional quantum dots as fluorescence probe for cell-specific targeting. Colloids Surf. B 2014, 114, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Cui, Y.; Levenson, R.M.; Chung, L.W.K.; Nie, S. In vivo cancer targeting and imaging with semiconductor quantum dots. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sounderya, N.; Zhang, Y. Use of core/shell structured nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Recent Pat. Biomed. Eng. 2008, 1, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, M.; Bongartz, R.; Walter, J.G.; Demirkol, D.O.; Stahl, F.; Timur, S.; Scheper, T. PAMAM-functionalized water soluble quantum dots for cancer cell targeting. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 11529–11536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.M.; Duan, H.; Rhyner, M.N.; Ruan, G.; Nie, S. A systematic examination of surface coatings on the optical and chemical properties of semiconductor quantum dots. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2006, 8, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Jamal, W.T.; Al Jamal, K.T.; Bomans, P.H.; Frederik, P.M.; Kostarelos, K. Functionalized Quantum dot liposome hybrids as multimodal nanoparticles for cancer. Small 2008, 4, 1406–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthu, M.S.; Kulkarni, S.A.; Raju, A.; Feng, S.-S. Theranostic liposomes of TPGS coating for targeted co-delivery of docetaxel and quantum dots. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 3494–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopalakrishnan, G.; Danelon, C.; Izewska, P.; Prummer, M.; Bolinger, P.Y.; Geissbahler, I.; Demurtas, D.; Dubochet, J.; Vogel, H. Multifunctional lipid/quantum dot hybrid nanocontainers for controlled targeting of live cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 5478–5483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Chen, W.; Bui, B.Q.; Xiang, G. Recent progress on the liposomes loaded with quantum dots. Rev. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 1, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riehemann, K.; Schneider, S.W.; Luger, T.A.; Godin, B.; Ferrari, M.; Fuchs, H. Nanomedicine-challenge and perspectives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 872–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthu, M.S.; Leong, D.T.; Mei, L.; Feng, S.-S. Nanotheranostics-application and further development of nanomedicine strategies for advanced theranostics. Theranostics 2014, 4, 660–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, B.; Kostarelos, K. The engineering of doxorubicin-loaded liposome-quantum dot hybrids for cancer theranostics. Chin. Phys. B. 2014, 23, 087805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.J.; Zhang, L.-W.; Al-Suwayeh, S.A.; Yen, T.-C.; Fang, J.-Y. Theranostic liposomes loaded with quantum dots and apomorphine for brain targeting and bioimaging. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 1599–1611. [Google Scholar]
- Grahn, A.Y.; Bankiewicz, K.S.; Dugich-Djordjevic, M.; Bringas, J.R.; Hadaczek, P.; Johnson, G.A.; Eastman, S.; Luz, M. Non-PEGylated liposomes for convection-enhanced delivery of topotecan and gadodiamide in malignant glioma: Initial experience. J. Neurooncol. 2009, 95, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.J.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, B.B.; Zhang, H.Y. Development and evaluation of topotecan loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: A study in cervical cancer cell lines. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2016, 165, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.L.; Deng, Y.-J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.M.; Zhong, H.-J.; Suo, X.-B. In vitro and in vivo studies of different liposomes containing topotecan. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2005, 28, 626–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tardi, P.; Choice, E.; Masin, D.; Redelmeier, T.; Bally, M.; Madden, T.D. Liposomal encapsulation of topotecan enhances anticancer efficacy in murine and human xenograft models. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 3389–3393. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mayer, L.D.; Tai, L.C.; Ko, D.S.; Masin, D.; Ginsberg, R.S.; Cullis, P.R.; Bally, M.B. Influence of vesicle size, lipid composition, and drug-to-lipid ratio on the biological activity of liposomal doxorubicin in mice. Cancer Res. 1989, 49, 5922–5930. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.J.; Masin, D.; McIntosh, N.L.; Madden, T.D.; Bally, M.B. Role of drug release and liposome-mediated drug delivery in governing the therapeutic activity of liposomal mitoxantrone used to treat human A431 and LS180 solid tumors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000, 292, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Semple, S.C.; Chonn, A.; Cullis, P.R. Influence of cholesterol on the association of plasma proteins with liposomes. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 2521–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozzuto, G.; Molinari, A. Liposomes as nanomedical devices. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 975–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magarkar, A.; Dhawan, V.; Kallinteri, P.; Viitala, T.; Elmowafy, M.; Róg, T.; Bunker, A. Cholesterol level affects surface charge of lipid membranes in saline solution. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.; Laurent, S.; Tawil, N.; Yahia, L.H.; Mahmoudi, M. Nanoparticle and protein corona. In Protein–Nanoparticle Interactions; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2013; pp. 21–44. ISBN 978-3-642-37554-5. [Google Scholar]
- Farokhzad, O.C.; Jon, S.; Langer, R. A. Ptamers and cancer nanotechnology. In Nanotechnology for Cancer Therapy; Amiji, M.M., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 289–341. ISBN 978-0-8493-7194-3. [Google Scholar]
- Brigger, I.; Dubernet, C.; Couvreur, P. Nanoparticles in cancer therapy and diagnosis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev 2002, 54, 631–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.J.; Liang, M.; Toth, I.; Monteiro, M.; Minchin, R.F. Plasma protein binding of positively and negatively charged polymer-coated gold nanoparticles elicits different biological responses. Nanotoxicology 2013, 7, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gessner, A.; Lieske, A.; Paulke, B.R.; Muller, R.H. Influence of surface charge density on protein adsorption on polymeric nanoparticles: Analysis by two-dimensional electrophoresis. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2002, 54, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, E.; Shen, H.; Ferrari, M. Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levchenko, T.S.; Rammohan, R.; Lukyanov, A.N.; Whiteman, K.R.; Torchilin, V.P. Liposome clearance in mice: The effect of a separate and combined presence of surface charge and polymer coating. Int. J. Pharm. 2002, 240, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhuang, S.; Qi, X.-R. Comparative study of the in vitro and in vivo characteristics of cationic and neutral liposomes. Int. J. Nanomed. 2011, 6, 3087–3098. [Google Scholar]
- Padhi, S.; Mirza, M.A.; Verma, D.; Khuroo, T.; Panda, A.K.; Talegaonkar, S.; Khar, R.K.; Iqbal, Z. Revisiting the nanoformulation design approach for effective delivery of topotecan in its stable form: An appraisal of its in vitro Behavior and tumor amelioration potential. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 2827–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yingchoncharoen, P.; Kalinowski, D.S.; Richardson, D.R. Lipid-based drug delivery systems in cancer therapy: What is available and what is yet to come. Pharmacol. Rev. 2016, 68, 701–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torchilin, V.P. Recent advances with liposomes as pharmaceutical carriers. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2005, 4, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoorob, G.; Burke, T. Enzymology and drugs. In DNA Topoisomerase Protocols; Osheroff, N., Bjornsti, M.A., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2001; Volume II, pp. 215–227. ISBN 978-1-59259-057-5. [Google Scholar]
- Kollmannsberger, C.; Mross, K.; Jakob, A.; Kanz, L.; Bokemeyer, C. Topotecan—A novel topoisomerase I inhibitor: Pharmacology and clinical experience. Oncology 1999, 56, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubertret, B.; Skourides, P.; Norris, D.J.; Noireaux, V.; Brivanlou, A.H.; Libchaber, A. In vivo imaging of quantum dots encapsulated in phospholipid micelles. Science 2002, 298, 1759–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinnathambi, S.; Abu, N.; Hanagata, N. Biocompatible CdSe/ZnS quantum dot micelles for long-term cell imaging without alteration to the native structure of the blood plasma protein human serum albumin. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 2392–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.L.; Deng, Y.J.; Chen, Y.; Hao, A.J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, K.Z. In Vitro cytotoxicity, in vivo biodistribution and anti-tumour effect of PEGylated liposomal topotecan. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2005, 57, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, B.; Al-Jamal, K.T.; Kostarelos, K. Doxorubicin-loaded lipid-quantum dot hybrids: Surface topography and release properties. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 416, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonali; Singh, R.P.; Singh, N.; Sharma, G.; Vijayakumar, M.R.; Koch, B.; Singh, S.; Singh, U.; Dash, D.; Pandey, B.L. Transferrin liposomes of docetaxel for brain-targeted cancer applications: Formulation and brain theranostics. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 1261–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, S.A.; Edwards, K.; Karlsson, G.; Hudon, N.; Mayer, L.D.; Bally, M.B. An evaluation of transmembrane ion gradient-mediated encapsulation of topotecan within liposomes. J. Control. Release 2004, 96, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Liu, C.; Liu, W.; Yu, H.; Zheng, H.; Zhou, W.; Hu, Y. Preparation and characterization of nanoliposomes entrapping medium-chain fatty acids and vitamin C by lyophilization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 19763–19773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flowing Software; 1.47v; Software for Image Processing; National Institutes of Health: Bethesda, ML, USA, 1997. Available online: https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/index.html (accessed on 27 June 2017).
- Flowing Software; 2.5.1v; Software for Flow Cytometry Data Analysis; Turku Centre for Biotechnology: Turku, Finland, 2013; Available online: http://flowingsoftware.btk.fi/index.php?page=1 (accessed on 27 June 2017).





| Samples | Size (nm) | PDI | ζ-Potential (mV) | EE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L | 131.8 ± 0.8 | 0.082 | −13.6 ± 1.6 | - |
| L–QD | 138.1 ± 0.7 | 0.014 | −7.8 ± 0.1 | - |
| L–TPT | 134.1 ± 1.2 | 0.073 | −10.6 ± 0.1 | 43.8 |
| L–QD–TPT | 137.1 ± 1.7 | 0.069 | −6.0 ± 0.1 | 39.5 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seleci, M.; Ag Seleci, D.; Scheper, T.; Stahl, F. Theranostic Liposome–Nanoparticle Hybrids for Drug Delivery and Bioimaging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071415
Seleci M, Ag Seleci D, Scheper T, Stahl F. Theranostic Liposome–Nanoparticle Hybrids for Drug Delivery and Bioimaging. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(7):1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071415
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeleci, Muharrem, Didem Ag Seleci, Thomas Scheper, and Frank Stahl. 2017. "Theranostic Liposome–Nanoparticle Hybrids for Drug Delivery and Bioimaging" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 7: 1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071415
APA StyleSeleci, M., Ag Seleci, D., Scheper, T., & Stahl, F. (2017). Theranostic Liposome–Nanoparticle Hybrids for Drug Delivery and Bioimaging. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(7), 1415. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071415