Anti-Biofilm Effect of Biodegradable Coatings Based on Hemibastadin Derivative in Marine Environment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
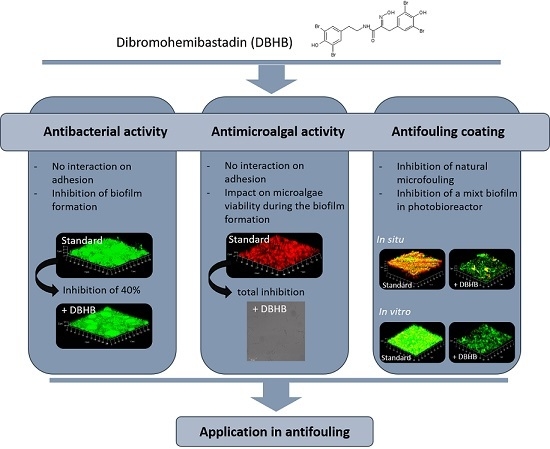
2.1. Dibromohemibastadin (DBHB) Bioactivity
2.1.1. Anti-Bacterial Activity
2.1.2. Microalgae Activity
2.2. In Vitro Activity of Coatings
2.3. In Vivo Activity of Varnishes
2.4. Potentiality of DBHB Coating
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Microorganism’s Strains and Growth
3.2. Anti-Bacterial Activities in Microplate
3.3. Anti-Microalgal Activities in Microplate
3.4. Anti-Adhesion Assay
3.5. Diatoms Detachment Assay
3.6. Antibiofilm Assay
3.7. Coatings Preparation
3.8. Anti-Bacterial and Anti-Microalgal Activity of Coatings
3.9. Mixed Biofilm Test Conditions
3.10. Natural Seawater Exposition
3.11. Statistical Analysis of Data
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AF | Antifouling |
| AHL | Acyl homoserine lactone |
| ASW | Artificial Seawater |
| CDP | Controled Depletion Paint |
| CLSM | Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy |
| DBHB | Dibromohemibastadin-1 |
| FR | Foulinf Release |
| MIC | Minimal inhibition Concentration |
| PBR | Photo-bioreactor |
| P(CL-VL) | Poly(ε-caprolactone-co-δ-valerolactone) |
| QS | Quorum Sensing |
| SPC | Self Polishing Coatings |
| TBT | Tributyltin |
References
- Soroldoni, S.; Abreu, F.; Castro, I.B.; Duarte, A.; Lopes Leaes Pinho, G. Are antifouling paint particles a continuous source of toxic chemicals to the marine environment? J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 330, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson, R.T.; Damon, M.; Johnson, L.T.; Gonzalez, J.A. Conceptual issues in designing a policy to phase out metal-based antifouling paints on recreational boats in San Diego Bay. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2460–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cima, F.; Bragadin, M.; Ballarin, L. Toxic effects of new antifouling compounds on tunicate haemocytes: I. Sea-Nine 211™ and chlorothanlonil. Aquat. Toxicol. 2008, 86, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, P.Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, Y.; Li, Y.; Fusetani, N. Mini-review: Marine natural products and their synthetic analogs as antifouling compounds: 2009–2014. Biofouling 2015, 31, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, P.Y.; Xu, Y.; Fusetani, N. Natural products as antifouling compounds: Recent progress and future perspectives. Biofouling 2010, 26, 223–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, P.Y.; Chen, L.; Xu, Y. Mini-review: Molecular mechanisms of antifouling compunds. Biofouling 2013, 29, 381–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satheesh, S.; Ba-akdah, M.A.; Al-Sofyani, A.A. Natural antifouling compound production by microbes associated with marine macroorganisms—A review. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 21, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, S.R.; Jensen, P.R.; Henkel, T.P.; Fenical, W.; Pawlik, J.R. Effects of Caribbean sponge extracts on bacterial attachment. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2003, 31, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogata, Y.; Kitano, Y. Isocyano Compounds as Non-toxic antifoulants. In Antifouling Compounds; Fusetani, N., Clare, A.S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006; pp. 87–104. [Google Scholar]
- Stowe, S.D.; Richards, J.J.; Tucker, A.T.; Thompson, R.; Melander, C.; Cavanagh, J. Anti-biofilm compounds derived from marine sponges. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2010–2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melander, C.; Moeller, P.D.R.; Ballard, E.; Richards, J.J.; Huigens, R.W.; Cavanagh, J. Evaluation of dihydrooroidin as an antifouling additive in marine paint. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2009, 63, 529–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjögren, M.; Dahlström, M.; Göransson, U.; Jonsson, P.R.; Bohlin, L. Recruitement in the field of balanus improvises and mytilus edulis in response to the antifouling cyclopeptides barettin and 8,9-dihydrobarettin from the marine sponge geodia barrette. Biofouling 2004, 20, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanssen, K.; Cervin, G.; Trepos, R.; Petitbois, J.; Haug, T.; Hansen, E.; Andersen, J.H.; Pavia, H.; Hellio, C.; Svenson, J. The bromotyrosine derivative lanthelline isolated from the artic marine sponge stryphnus fortis inhibits marine micro- and macrobiofouling. Mar. Biotechnol. 2014, 16, 684–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusetani, N. Biofouling and antifouling. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2004, 21, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayer, M.; Hellio, C.; Maréchal, J.P.; Walter, F.; Lin, W.; Weber, H.; Proksch, P. Antifouling bastadin congeners target mussel phenoloxidase and complex copper(II) ions. Mar. Biotechnol. 2011, 13, 1148–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemann, H.; Hagenow, J.; Chung, M.Y.; Hellio, C.; Weber, H.; Proksch, P. SAR of sponge-inspired hemibastadin congeners inhibiting blue mussel phenoloxidase. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 3061–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortlepp, S.; Sjögren, M.; Dahlström, M.; Weber, H.; Ebel, R.; Edrada, R.; Thoms, C.; Schupp, P.; Bohlin, L.; Proksch, P. Antifouling activity of bromotyrosine-derived sponge metabolites and synthetic analogues. Mar. Biotechnol. 2007, 9, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faÿ, F.; Renard, E.; Langlois, V.; Linossier, I.; Vallée-Rehel, K. Development of poly(ε-caprolactone-co-l-lactide) and poly(ε-caprolactone-co-δ-valerolactone) as new degradable binder used for antifouling paint. Eur. Polym. Sci. 2007, 43, 4800–4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carteau, D.; Vallée-Réhel, K.; Linossier, I.; Quiniou, F.; Davy, R.; Compère, C.; Delbury, M.; Faÿ, F. Development of environmentally friendly antifouling paints using biodegradable polymer and lower toxic substances. Prog. Org. Coat. 2014, 77, 485–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loriot, M.; Linossier, I.; Vallée-Réhel, K.; Faÿ, F. Influence of biodegradable polymer properties on antifouling paints activity. Polymers 2017, 9, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasland, B.; Mitalane, J.; Briandet, R.; Quemener, E.; Meylheuc, T.; Linossier, I.; Vallée-Réhel, K.; Haras, D. Bacterial biofilm in seawater: Cell surface properties of early-attached marine bacteria. Biofouling 2003, 19, 307–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dheilly, A.; Soum-Soutéra, E.; Klein, G.L.; Bazire, A.; Compère, C.; Haras, D.; Dufour, A. Antibiofilm activity of marine bacterium Pseudoalteromonas sp. strain 3J6. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 3452–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, J.R.; Vasconcelos, V. Natural antifouling compounds: Effectiveness in preventing invertebrate settlement and adhesion. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, W.E.G.; Wang, X.; Proksch, P.; Perry, C.C.; Osinga, R.; Gardères, J.; Schröder, H. Principles of biofouling protection in marine sponges: A model for the design of novel biomimetic and bio-inspired coatings in the marine environment? Mar. Biotechnol. 2013, 15, 375–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintana, J.; Brango-Vanegas, J.; Costa, G.M.; Castellanos, L.; Arévalo, C.; Duque, C. Marine organisms as source of extracts to disrupt bacterial communication: Bioguided isolation and identification of quorum sensing inhibitors from Ircinia felix. Revis. Bras. Farmacogn. 2015, 25, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saurav, K.; Bar-Shalom, R.; Haber, M.; Burgsdorf, I.; Oliviero, G.; Costantino, V.; Morgenstern, D.; Steindler, L. In search of alternative antibiotic drugs: Quorum-quenching activity in sponges and their bacterial isolates. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skindersoe, M.; Etting-Epstein, P.; Rasmussen, T.; Bjarnsholt, T.; de Nys, R.; Givskov, M. Quorum sensing antagonism from marine organisms. Mar. Biotechnol. 2008, 10, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantino, V.; Della Sala, G.; Saurav, K.; Teta, R.; Bar-Shalom, R.; Mangoni, A.; Steindler, L. Plakofuranolactone as a quorum quenching agent from the Indonesian sponge plakortis cf. lita. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, L.; Konig, G.M.; Wright, A.D.; Pukall, R.; Stackebrandt, E.; Eberl, L.; Riedel, K. Secondary metabolites of Flustra foliacea and their influence on bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 3469–3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacristan-Soriano, O.; Banaigs, B.; Becerro, M. Temporal trends in the secondary metabolite production of the sponge Aplysina aerophoba. Mar. Drugs 2012, 10, 677–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andjouh, S.; Blache, Y. Click-based synthesis of bromotyrosine alkaloid analogs as potential anti-biofilm leads for SAR studies. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 5762–5766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballard, T.E.; Richards, J.J.; Wolfe, A.L.; Melander, C. Synthesis and antibiofilm activity of a second-generation reverse-amide oroidin library: A structure-activity relationship study. Chem. Eur. J. 2008, 14, 10745–10761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richard, J.J.; Ballard, T.E.; Huigens, R.W.; Melander, C. Synthesis and screening of an oroidin library against Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Chembiochem 2008, 9, 1267–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofson, A.; Yakushijin, K.; Horne, D.A. Synthesis of marine sponge alkaloids oroidin, clathrodin, and dispacamides. Preparation and transformation of 2-amino-4,5-dialkoxy-4,5-dihydroimidazolines from 2-aminoimidazoles. J. Org. Chem. 1998, 63, 1248–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huigens, R.W., III; Ma, L.; Gambino, C.; Moeller, P.D.R.; Basso, A.; Cavanagh, J.; Wozniak, D.J.; Melander, C. Control of bacterial biofilms with marine alkaloids derivatives. Mol. Biosyst. 2008, 4, 614–621. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiao, N.; Cottrell, M.T.; Kirchman, D.L. Contribution of major bacterial groups to bacterial biomass production along a salinity gradient in the South China Sea. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2006, 43, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delattre, D.; Pierre, G.; Laroche, C.; Michaud, P. Production, extraction and characterization of microalgal and cyanobacterial exopolysaccharide. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 1159–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, T.; Regan, F. Marine diatom settlement on microtextured materials in static field trials. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 5846–5856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doiron, K.; Linossier, I.; Faÿ, F.; Yong, J.; Wahid, E.A.; Hadjiev, D.; Bourgougnon, N. Dynamic approaches of mixed species biofilm formation using modern terchnologies. Mar. Environ. Res. 2012, 78, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Song, G.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, S.; Xia, C. The influence of bacterial quorum-sensing inhibitors against the formation of the diatom-biofilm. Chem. Ecol. 2016, 32, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Fang, S.; Chen, D.; Wang, J.; Liu, F.; Xia, C. The possible role of bacterial signal molecules N-acyl homoserine lactones in the formation of diatom-biofilm (Cylindrotheca sp.). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 107, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alles, M.; Rosenhahn, A. Microfluidic detachment assay to probe the adhesion strength of diatoms. Biofouling 2015, 31, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLachlan, D.H.; Underwood, G.J.C. Calcium release form intracellular stores is necessary for the photophobic response in the benthic diatom navicular perminuta (bacillariophyceae). J. Phycol. 2012, 48, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landoulsi, J.; Cooksey, K.E.; Dupres, V. Interactions between diatoms and stainless steel: Focus on biofouling and biocorrosion. Biofouling 2011, 27, 1105–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Costa, P.; Chandrashekar, A. The effect of bacteria on diatom community structure—The “antibiotics” approach. Res. Microbiol. 2011, 162, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawkins, M.L.; Faÿ, F.; Réhel, K.; Linossier, I.; Grunlan, I. Bacteria and diatom of silicones modified with PEO-silane amphiphiles. Biofouling 2014, 30, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faÿ, F.; Hawkins, M.L.; Réhel, K.; Grunlan, M.A.; Linossier, I. Non toxic, anti-fouling silicones with variable PEO-silane amphiphile content. Green Mater. 2016, 4, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faÿ, F.; Carteau, D.; Linossier, I.; Vallée-Réhel, K. Evaluation of anti-microfouling activity of marine paints by microscopical techniques. Prog. Org. Coat. 2011, 72, 579–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamjunke, N.; Spohn, U.; Füting, M.; Wagner, G.; Scharf, E.M.; Sandrock, S.; Zippel, B. Use of confocal laser scanning microscopy for biofilm investigation on paints under field conditions. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2012, 69, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molino, P.J.; Campbell, E.; Wetherbee, R. Development of the initial diatom microfouling layer on antifouling and fouling release surfaces in temperate and tropical Australia. Biofouling 2009, 25, 685–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molino, P.J.; Childs, S.; Hubbard, M.R.E.; Carey, J.M.; Burgman, M.A.; Wetherbee, R. Development of the primary bacterial microfouling layer on antifouling and fouling release coatings in temperate and tropical environments in Eastern Australia. Biofouling 2009, 25, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Xia, C.; Qian, P.Y. Optimization of antifouling coatings incorporating butenolide, a potent antifouling agent via field and laboratory tests. Prog. Org. Coat. 2017, 109, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupak, M.E.; Garcia, M.T.; Pérez, M.C. Non-toxic alternative compounds for marine antifouling paints. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2003, 52, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, M.S.; Puentes, C.; Carreno, K.; Leon, J.G.; Stupak, M.; Garcia, M.; Pérez, M.; Blustein, G. Antifouling paints based on marine natural products from Colombian Caribbean. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2013, 83, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellali, R.; Campistron, I.; Pasetto, P.; Laguerre, A.; Gohier, F.; Hellio, C.; Pilard, J.F.; Mouget, J.L. Antifouling activity of novel polyisoprene-based coatings made from photocurable natural rubber derived oligomers. Prog. Org. Coat. 2013, 76, 1203–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forjan, E.; Navarro, F.; Cuaresma, M.; Vaquero, I.; Ruiz-Dominguez, M.C.; Gojkovic, Z.; Vasquez, M.; Marquez, M.; Mogedas, B.; Bermejo, E.; et al. Microalgae: Fast-growth sustainable green factories. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 1705–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellio, C.; Trepos, R.; Aguila-Ramirez, R.N.; Hernandez-Guerrero, J. Protocol for assessing antifouling activities of macroalgal extracts. In Natural Products from Marine Algae; Stengel, D.B., Connan, S., Eds.; Methods in Molecular Biology: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 421–435. [Google Scholar]
- Thabard, M.; Gros, O.; Hellio, C.; Marechal, J.P. Sargassium polyceratium (phaephyceae, fucaceae) surface molecule activity towards fouling organisms and embryonic development of benthic species. Bot. Mar. 2011, 54, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolker-Nielson, T.; Sternberg, C. Methods for studying biofilm formation: Flow cells and confocal laser scanning microscopy. In Pseudomonas Methods and Protocols; Filloux, A., Ramos, J.L., Eds.; Methods in Molecular Biology: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 615–629. [Google Scholar]
- Heydorn, A.; Nielson, A.T.; Hentzer, M.; Sternberg, C.; Givskov, M.; Ersboll, B.K.; Molin, S. Quantification of biofilm structures by the novel computer program comstat. Microbiology 2000, 146, 2395–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]












| 4M6 | 5M6 | 4J6 |
|---|---|---|
| 39.6% | 0.11% | 0.18% |
| Microorganisms | Coatings | In Situ 1 | In Vitro 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial biovolume (μm3/μm2) | Varnish | 10.8 ± 0.7 | 18.4 ± 3.8 |
| DBHB varnish | 1.6 ± 0.8 | 2.3 ± 0.5 | |
| Inhibition (%) | 85 | 88 | |
| Microalgal biovolume (μm3/μm2) | Varnish | 21.1 ± 2.5 | 1.1 ± 0.2 |
| DBHB varnish | 0.3 ± 0.2 | 0.13 ± 0.03 | |
| Inhibition (%) | 99 | 88 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Norcy, T.L.; Niemann, H.; Proksch, P.; Linossier, I.; Vallée-Réhel, K.; Hellio, C.; Faÿ, F. Anti-Biofilm Effect of Biodegradable Coatings Based on Hemibastadin Derivative in Marine Environment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071520
Norcy TL, Niemann H, Proksch P, Linossier I, Vallée-Réhel K, Hellio C, Faÿ F. Anti-Biofilm Effect of Biodegradable Coatings Based on Hemibastadin Derivative in Marine Environment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(7):1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071520
Chicago/Turabian StyleNorcy, Tiffany Le, Hendrik Niemann, Peter Proksch, Isabelle Linossier, Karine Vallée-Réhel, Claire Hellio, and Fabienne Faÿ. 2017. "Anti-Biofilm Effect of Biodegradable Coatings Based on Hemibastadin Derivative in Marine Environment" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 7: 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071520
APA StyleNorcy, T. L., Niemann, H., Proksch, P., Linossier, I., Vallée-Réhel, K., Hellio, C., & Faÿ, F. (2017). Anti-Biofilm Effect of Biodegradable Coatings Based on Hemibastadin Derivative in Marine Environment. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(7), 1520. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071520