Cold Atmospheric Plasma in the Treatment of Osteosarcoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Osteosarcoma (OS) Therapy Options
1.2. Cold Atmospheric Plasma (CAP) and Plasma Oncology
1.3. CAP Devices and General Biological Impact
2. CAP Effects on OS Cells
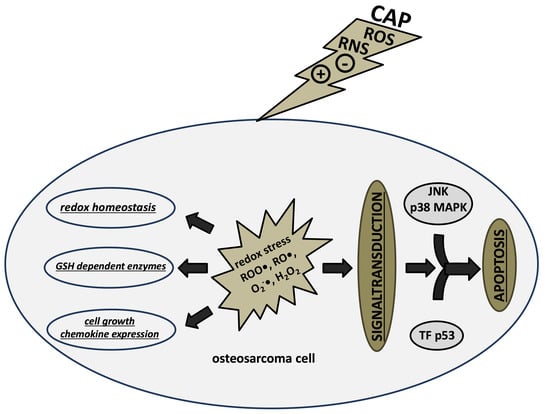
2.1. CAP-Induced Redox Effects and Redox Signaling
2.2. CAP-Induced Apoptosis
2.3. CAP-Induced Gene Expression and Epigenetic Changes
3. Clinical Prospects and Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bekeschus, S.; Iséni, S.; Reuter, S.; Masur, K.; Weltmann, K.D. Nitrogen Shielding of an Argon Plasma Jet and Its Effects on Human Immune Cells. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2015, 43, 776–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridman, A. Plasma Chemistry; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kalghatgi, S.; Kelly, C.M.; Cerchar, E.; Torabi, B.; Alekseev, O.; Fridman, A.; Friedman, G.; Azizkhan-Clifford, J. Effects of non-thermal plasma on mammalian cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laroussi, M. Nonthermal decontamination of biological media by atmospheric-pressure plasmas: Review, analysis, and prospects. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2002, 30, 1409–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laroussi, M. Low Temperature Plasma-Based Sterilization: Overview and State-of-the-Art. Plasma Process. Polym. 2005, 2, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, S.; Winter, J.; Iseni, S.; Peters, S.; Schmidt-Bleker, A.; Dünnbier, M.; Schäfer, J.; Foest, R.; Weltmann, K.D. Detection of ozone in a MHz argon plasma bullet jet. Plasma Sour. Sci. Technol. 2012, 21, 034015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakudo, A.; Misawa, T.; Shimizu, N.; Imanishi, Y. N2 gas plasma inactivates influenza virus mediated by oxidative stress. Front. Biosci. 2014, 6, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weltmann, K.D.; Th von, W. Plasma medicine—Current state of research and medical application. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 2017, 59, 014031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Woedtke, T.; Reuter, S.; Masur, K.; Weltmann, K.D. Plasmas for medicine. Phys. Rep. 2013, 530, 291–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, A.; Bekeschus, S.; Matthes, R.; Bender, C.; Stope, M.B.; Napp, M.; Lademann, O.; Lademann, J.; Weltmann, K.-D.; Schauer, F. Cold Physical Plasmas in the Field of Hygiene-Relevance, Significance, and Future Applications. Plasma Process. Polym. 2015, 12, 1410–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weltmann Klaus, D.; Kindel, E.; von Woedtke, T.; Hähnel, M.; Stieber, M.; Brandenburg, R. Atmospheric-pressure plasma sources: Prospective tools for plasma medicine. Pure Appl. Chem. 2010, 82, 1223–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luetke, A.; Meyers, P.A.; Lewis, I.; Juergens, H. Osteosarcoma treatment-where do we stand? A state of the art review. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2014, 40, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyers, P.A.; Chou, A.J. Muramyl tripeptide-phosphatidyl ethanolamine encapsulated in liposomes (L-MTP-PE) in the treatment of osteosarcoma. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 804, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kleinerman, E.S. Biologic therapy for osteosarcoma using liposome-encapsulated muramyl tripeptide. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 1995, 9, 927–938. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, T.; Zhang, X. Strategies and developments of immunotherapies in osteosarcoma. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Li, B.; Ren, Y.; Ye, Z. T-Cell-Based Immunotherapy for Osteosarcoma: Challenges and Opportunities. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindsey, B.A.; Markel, J.E.; Kleinerman, E.S. Osteosarcoma Overview. Rheumatol. Ther. 2017, 4, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Fang, W.; Xia, K.; Shao, J.; Wu, M.; Liu, B.; Liang, C.; et al. A review and outlook in the treatment of osteosarcoma and other deep tumors with photodynamic therapy: From basic to deep. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 39833–39848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markman, J.L.; Rekechenetskiy, A.; Holler, E.; Ljubimova, J.Y. Nanomedicine therapeutic approaches to overcome cancer drug resistance. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1866–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Fernandez, Y.; Imbuluzqueta, E.; Patino-Garcia, A.; Blanco-Prieto, M.J. Antitumoral-Lipid-Based Nanoparticles: A Platform for Future Application in Osteosarcoma therapy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 6104–6124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalili, A.; Irani, S.; Mirfakhraie, R. Combination of cold atmospheric plasma and iron nanoparticles in breast cancer: Gene expression and apoptosis study. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 5911–5917. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, D.; Sherman, J.H.; Keidar, M. Cold atmospheric plasma, a novel promising anti-cancer treatment modality. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 15977–15995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gay-Mimbrera, J.; Garcia, M.C.; Isla-Tejera, B.; Rodero-Serrano, A.; Garcia-Nieto, A.V.; Ruano, J. Clinical and Biological Principles of Cold Atmospheric Plasma Application in Skin Cancer. Adv. Ther. 2016, 33, 894–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiazi, R.; Akbari, M.E.; Norozi, A.; Etedadialiabadi, M. Application of Cold Atmospheric Plasma (CAP) in Cancer Therapy: A Review. Int. J. Cancer Manag. 2017, 10, e8728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, A.; Bekeschus, S.; von Woedtke, T.; Hasse, S. Cell migration and adhesion of a human melanoma cell line is decreased by cold plasma treatment. Clin. Plasma Med. 2015, 3, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sensenig, R.; Kalghatgi, S.; Cerchar, E.; Fridman, G.; Shereshevsky, A.; Torabi, B.; Arjunan, K.P.; Podolsky, E.; Fridman, A.; Friedman, G.; et al. Non-thermal plasma induces apoptosis in melanoma cells via production of intracellular reactive oxygen species. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 39, 674–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekeschus, S.; Rodder, K.; Fregin, B.; Otto, O.; Lippert, M.; Weltmann, K.D.; Wende, K.; Schmidt, A.; Gandhirajan, R.K. Toxicity and Immunogenicity in Murine Melanoma following Exposure to Physical Plasma-Derived Oxidants. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 4396467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, H.; Mizuno, M.; Ishikawa, K.; Nakamura, K.; Kajiyama, H.; Kano, H.; Kikkawa, F.; Hori, M. Plasma-Activated Medium Selectively Kills Glioblastoma Brain Tumor Cells by Down-Regulating a Survival Signaling Molecule, AKT Kinase. Plasma Med. 2011, 1, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeylen, S.; de Waele, J.; Vanuytsel, S.; de Backer, J.; van der Paal, J.; Ramakers, M.; Leyssens, K.; Marcq, E.; van Audenaerde, J.; Dewilde, S.; et al. Cold atmospheric plasma treatment of melanoma and glioblastoma cancer cells. Plasma Process. Polym. 2016, 13, 1195–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayun, Y.; Niki, N.; Annie, T.; Jonathan, H.S.; Michael, K. The strong anti-glioblastoma capacity of the plasma-stimulated lysine-rich medium. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2016, 49, 274001. [Google Scholar]
- Partecke, L.I.; Evert, K.; Haugk, J.; Doering, F.; Normann, L.; Diedrich, S.; Weiss, F.U.; Evert, M.; Huebner, N.O.; Guenther, C.; et al. Tissue tolerable plasma (TTP) induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.W.; Kang, S.U.; Shin, Y.S.; Seo, S.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Yang, S.S.; Lee, J.S.; Moon, E.; Lee, K.; Kim, C.H. Combination of NTP with cetuximab inhibited invasion/migration of cetuximab-resistant OSCC cells: Involvement of NF-κB signaling. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero-Preston, R.; Ogawa, T.; Uemura, M.; Shumulinsky, G.; Valle, B.L.; Pirini, F.; Ravi, R.; Sidransky, D.; Keidar, M.; Trink, B. Cold atmospheric plasma treatment selectively targets head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 34, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.U.; Cho, J.H.; Chang, J.W.; Shin, Y.S.; Kim, K.I.; Park, J.K.; Yang, S.S.; Lee, J.S.; Moon, E.; Lee, K.; et al. Nonthermal plasma induces head and neck cancer cell death: The potential involvement of mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirst, A.M.; Simms, M.S.; Mann, V.M.; Maitland, N.J.; O’Connell, D.; Frame, F.M. Low-temperature plasma treatment induces DNA damage leading to necrotic cell death in primary prostate epithelial cells. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 1536–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, M.; Gumbel, D.; Hanschmann, E.M.; Mandelkow, R.; Gelbrich, N.; Zimmermann, U.; Walther, R.; Ekkernkamp, A.; Sckell, A.; Kramer, A.; et al. Cold Atmospheric Plasma Treatment Induces Anti-Proliferative Effects in Prostate Cancer Cells by Redox and Apoptotic Signaling Pathways. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, M.; Gumbel, D.; Gelbrich, N.; Brandenburg, L.O.; Mandelkow, R.; Zimmermann, U.; Ziegler, P.; Burchardt, M.; Stope, M.B. Inhibition of Cell Growth of the Prostate Cancer Cell Model LNCaP by Cold Atmospheric Plasma. In Vivo 2015, 29, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhunussova, A.; Vitol, E.A.; Polyak, B.; Tuleukhanov, S.; Brooks, A.D.; Sensenig, R.; Friedman, G.; Orynbayeva, Z. Mitochondria-Mediated Anticancer Effects of Non-Thermal Atmospheric Plasma. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupu, A.R.; Georgescu, N.; Calugaru, A.; Cremer, L.; Szegli, G.; Kerek, F. The effects of cold atmospheric plasma jets on B16 and COLO320 tumoral cells. Roum. Arch. Microbiol. Immunol. 2009, 68, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Joseph-Marie, P.; Mohammed, Y.; Céline, F.; Olivier, E.; Bernard, D.; Nofel, M.; Valérie, L. Low-temperature plasma-induced antiproliferative effects on multi-cellular tumor spheroids. New J. Phys. 2014, 16, 043027. [Google Scholar]
- Tuhvatulin, A.I.; Sysolyatina, E.V.; Scheblyakov, D.V.; Logunov, D.Y.; Vasiliev, M.M.; Yurova, M.A.; Danilova, M.A.; Petrov, O.F.; Naroditsky, B.S.; Morfill, G.E.; et al. Non-thermal Plasma Causes p53-Dependent Apoptosis in Human Colon Carcinoma Cells. Acta Nat. 2012, 4, 82–87. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, J.; Ma, J.; Yu, K.N.; Li, W.; Cheng, C.; Bao, L.; Han, W. Non-thermal plasma treatment altered gene expression profiling in non-small-cell lung cancer A549 cells. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joh, H.M.; Choi, J.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Chung, T.H.; Kang, T.H. Effect of additive oxygen gas on cellular response of lung cancer cells induced by atmospheric pressure helium plasma jet. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Ballato, J.; Foy, P.; Hawkins, T.; Wei, Y.; Li, J.; Kim, S.O. Apoptosis of lung carcinoma cells induced by a flexible optical fiber-based cold microplasma. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 28, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, A.; Rödder, K.; Hasse, S.; Masur, K.; Toups, L.; Lillig, C.H.; von Woedtke, T.; Wende, K.; Bekeschus, S. Redox-regulation of activator protein 1 family members in blood cancer cell lines exposed to cold physical plasma-treated medium. Plasma Process. Polym. 2016, 13, 1179–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Xue, Z.; Yin, H.; Niu, Q.; Chen, H. The relation between doses or post-plasma time points and apoptosis of leukemia cells induced by dielectric barrier discharge plasma. AIP Adv. 2015, 5, 127220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeschus, S.; Wende, K.; Hefny, M.M.; Rodder, K.; Jablonowski, H.; Schmidt, A.; Woedtke, T.V.; Weltmann, K.D.; Benedikt, J. Oxygen atoms are critical in rendering THP-1 leukaemia cells susceptible to cold physical plasma-induced apoptosis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torii, K.; Yamada, S.; Nakamura, K.; Tanaka, H.; Kajiyama, H.; Tanahashi, K.; Iwata, N.; Kanda, M.; Kobayashi, D.; Tanaka, C.; et al. Effectiveness of plasma treatment on gastric cancer cells. Gastric Cancer 2015, 18, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brulle, L.; Vandamme, M.; Ries, D.; Martel, E.; Robert, E.; Lerondel, S.; Trichet, V.; Richard, S.; Pouvesle, J.M.; Le Pape, A. Effects of a non thermal plasma treatment alone or in combination with gemcitabine in a MIA PaCa2-luc orthotopic pancreatic carcinoma model. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hattori, N.; Yamada, S.; Torii, K.; Takeda, S.; Nakamura, K.; Tanaka, H.; Kajiyama, H.; Kanda, M.; Fujii, T.; Nakayama, G.; et al. Effectiveness of plasma treatment on pancreatic cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 1655–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binenbaum, Y.; Ben-David, G.; Gil, Z.; Slutsker, Y.Z.; Ryzhkov, M.A.; Felsteiner, J.; Krasik, Y.E.; Cohen, J.T. Cold Atmospheric Plasma, Created at the Tip of an Elongated Flexible Capillary Using Low Electric Current, Can Slow the Progression of Melanoma. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chernets, N.; Kurpad, D.S.; Alexeev, V.; Rodrigues, D.B.; Freeman, T.A. Reaction Chemistry Generated by Nanosecond Pulsed Dielectric Barrier Discharge Treatment is Responsible for the Tumor Eradication in the B16 Melanoma Mouse Model. Plasma Process. Polym. 2015, 12, 1400–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daeschlein, G.; Scholz, S.; Lutze, S.; Arnold, A.; von Podewils, S.; Kiefer, T.; Tueting, T.; Hardt, O.; Haase, H.; Grisk, O.; et al. Comparison between cold plasma, electrochemotherapy and combined therapy in a melanoma mouse model. Exp. Dermatol. 2013, 22, 582–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utsumi, F.; Kajiyama, H.; Nakamura, K.; Tanaka, H.; Mizuno, M.; Ishikawa, K.; Kondo, H.; Kano, H.; Hori, M.; Kikkawa, F. Effect of indirect nonequilibrium atmospheric pressure plasma on anti-proliferative activity against chronic chemo-resistant ovarian cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirpour, S.; Piroozmand, S.; Soleimani, N.; Jalali Faharani, N.; Ghomi, H.; Fotovat Eskandari, H.; Sharifi, A.M.; Mirpour, S.; Eftekhari, M.; Nikkhah, M. Utilizing the micron sized non-thermal atmospheric pressure plasma inside the animal body for the tumor treatment application. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandamme, M.; Robert, E.; Lerondel, S.; Sarron, V.; Ries, D.; Dozias, S.; Sobilo, J.; Gosset, D.; Kieda, C.; Legrain, B.; et al. ROS implication in a new antitumor strategy based on non-thermal plasma. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 130, 2185–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekeschus, S.; Schmidt, A.; Weltmann, K.-D.; von Woedtke, T. The plasma jet kINPen—A powerful tool for wound healing. Clin. Plasma Med. 2016, 4, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, A.; Conway, B.; Meissner, K.; Scholz, F.; Rauch, B.; Moroder, A.; Ehlers, A.; Meixner, A.; Heidecke, C.; Partecke, L.; et al. Cold atmospheric pressure plasma for treatment of chronic wounds: Drug or medical device? J. Wound Care 2017, 26, 470–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.Y.; Chen, T.M.; Dai, N.T.; Fu, J.P.; Chang, S.C.; Deng, S.C.; Chen, S.G. Do antibacterial-coated sutures reduce wound infection in head and neck cancer reconstruction? Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 37, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metelmann, H.-R.; Nedrelow, D.S.; Seebauer, C.; Schuster, M.; von Woedtke, T.; Weltmann, K.-D.; Kindler, S.; Metelmann, P.H.; Finkelstein, S.E.; von Hoff, D.D.; et al. Head and neck cancer treatment and physical plasma. Clin. Plasma Med. 2015, 3, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, M.; Seebauer, C.; Rutkowski, R.; Hauschild, A.; Podmelle, F.; Metelmann, C.; Metelmann, B.; von Woedtke, T.; Hasse, S.; Weltmann, K.D.; et al. Visible tumor surface response to physical plasma and apoptotic cell kill in head and neck cancer. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2016, 44, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keidar, M.; Walk, R.; Shashurin, A.; Srinivasan, P.; Sandler, A.; Dasgupta, S.; Ravi, R.; Guerrero-Preston, R.; Trink, B. Cold plasma selectivity and the possibility of a paradigm shift in cancer therapy. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nokhandani, A.; Otaghsara, S.; Abolfazli, M.; Karimi, M.; Adel, F.; Babapour, H.; Gholamreza, A. A review of new method of cold plasma in cancer treatment. Sch. Acad. J. Biosci. 2015, 3, 222–230. [Google Scholar]
- Brekhov, E.; Kozlov, N.; Rebizov, V.; Tartynskiĭ, S.; Suslov, N.; Pekshev, A.; Naĭdenko, M. Experimental and clinical studies and prospects of using plasma flows. Khirurgiia 1989, 7, 94–96. [Google Scholar]
- Manner, H.; May, A.; Miehlke, S.; Dertinger, S.; Wigginghaus, B.; Schimming, W.; Kramer, W.; Niemann, G.; Stolte, M.; Ell, C. Ablation of nonneoplastic Barrett’s mucosa using argon plasma coagulation with concomitant esomeprazole therapy (APBANEX): A prospective multicenter evaluation. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 101, 1762–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metelmann, H.; Wende, K.; Masur, K.; Pouvesle, J.M.; Hasse, S.; Weltmann Klaus, D.; Woedtke, T.V.; Gerling, T.; Tanaka, H.; Fridman, A.; et al. Clinical experience with cold plasma in the treatment of locally advanced head and neck cancer. Clin. Plasma Med. 2017. submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Winter, J.; Brandenburg, R.; Weltmann, K.D. Atmospheric pressure plasma jets: An overview of devices and new directions. Plasma Sour. Sci. Technol. 2015, 24, 064001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laroussi, M.; Akan, T. Arc-Free Atmospheric Pressure Cold Plasma Jets: A Review. Plasma Process. Polym. 2007, 4, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Laroussi, M.; Puech, V. On atmospheric-pressure non-equilibrium plasma jets and plasma bullets. Plasma Sour. Sci. Technol. 2012, 21, 034005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DIN SPEC 91315 General Requirements for Plasma Sources in Medicine. Available online: https://www.beuth.de/en/technical-rule/din-spec-91315/203493369 (accessed on 13 August 2017).
- Dünnbier, M.; Schmidt-Bleker, A.; Winter, J.; Wolfram, M.; Hippler, R.; Weltmann, K.D.; Reuter, S. Ambient air particle transport into the effluent of a cold atmospheric-pressure argon plasma jet investigated by molecular beam mass spectrometry. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2013, 46, 435203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, R.H.; Evens, A.M. Oxidative stress and apoptosis: A new treatment paradigm in cancer. Front. Biosci. 2006, 11, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Seki, T.; Maeda, H. Therapeutic strategies by modulating oxygen stress in cancer and inflammation. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Lu, X.; He, G. The selective effect of plasma activated medium in an in vitro co-culture of liver cancer and normal cells. J. Appl. Phys. 2017, 121, 013302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Asai, T.; Fujiwara, K.; Sahara, J.; Koguchi, H.; Fukuda, N.; Suzuki-Karasaki, M.; Soma, M.; Suzuki-Karasaki, Y. Tumor-selective mitochondrial network collapse induced by atmospheric gas plasma-activated medium. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 19910–19927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, K.; Li, G.; Ma, Y. A Review on the Selective Apoptotic Effect of Nonthermal Atmospheric-Pressure Plasma on Cancer Cells. Plasma Med. 2014, 4, 193–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanschmann, E.M.; Godoy, J.R.; Berndt, C.; Hudemann, C.; Lillig, C.H. Thioredoxins, glutaredoxins, and peroxiredoxins—Molecular mechanisms and health significance: From cofactors to antioxidants to redox signaling. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 19, 1539–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hole, P.S.; Zabkiewicz, J.; Munje, C.; Newton, Z.; Pearn, L.; White, P.; Marquez, N.; Hills, R.K.; Burnett, A.K.; Tonks, A.; et al. Overproduction of NOX-derived ROS in AML promotes proliferation and is associated with defective oxidative stress signaling. Blood 2013, 122, 3322–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wende, K.; Reuter, S.; von Woedtke, T.; Weltmann, K.-D.; Masur, K. Redox-Based Assay for Assessment of Biological Impact of Plasma Treatment. Plasma Process. Polym. 2014, 11, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, P.M.; Arbabian, A.; Fleury, M.; Bauville, G.; Puech, V.; Dutreix, M.; Sousa, J.S. Synergistic Effect of H2O2 and NO2 in Cell Death Induced by Cold Atmospheric He Plasma. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bundscherer, L.; Bekeschus, S.; Tresp, H.; Hasse, S.; Reuter, S.; Weltmann, K.-D.; Lindequist, U.; Masur, K. Viability of Human Blood Leukocytes Compared with Their Respective Cell Lines after Plasma Treatment. Plasma Med. 2013, 3, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablonowski, H.; von Woedtke, T. Research on plasma medicine-relevant plasm–liquid interaction: What happened in the past five years? Clin. Plasma Med. 2015, 3, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, B.G. The emerging role of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in redox biology and some implications for plasma applications to medicine and biology. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2012, 45, 263001. [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, G.; Graves, D.B. Mechanisms of Selective Antitumor Action of Cold Atmospheric Plasma-Derived Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species. Plasma Process. Polym. 2016, 13, 1157–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablonowski, H.; Bussiahn, R.; Hammer, M.U.; Weltmann, K.-D.; Woedtke, T.V.; Reuter, S. Impact of plasma jet vacuum ultraviolet radiation on reactive oxygen species generation in bio-relevant liquids. Phys. Plasmas 2015, 22, 122008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.; Lackmann, J.W.; Narberhaus, F.; Bandow, J.E.; Denis, B.; Benedikt, J. Separation of VUV/UV photons and reactive particles in the effluent of a He/O2 atmospheric pressure plasma jet. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2011, 44, 295201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Mark, J.K. Atmospheric pressure dielectric barrier discharges interacting with liquid covered tissue. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2014, 47, 165201. [Google Scholar]
- Danil, D.; Gregory, F.; Gary, F.; Alexander, F. Physical and biological mechanisms of direct plasma interaction with living tissue. New J. Phys. 2009, 11, 115020. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Holmes, B.; Cheng, X.; Zhu, W.; Keidar, M.; Zhang, L.G. Cold atmospheric plasma for selectively ablating metastatic breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 8, e73741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gumbel, D.; Gelbrich, N.; Weiss, M.; Napp, M.; Daeschlein, G.; Sckell, A.; Ender, S.A.; Kramer, A.; Burchardt, M.; Ekkernkamp, A.; et al. New Treatment Options for Osteosarcoma—Inactivation of Osteosarcoma Cells by Cold Atmospheric Plasma. Anticancer Res. 2016, 36, 5915–5922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gumbel, D.; Gelbrich, N.; Napp, M.; Daeschlein, G.; Kramer, A.; Sckell, A.; Burchardt, M.; Ekkernkamp, A.; Stope, M.B. Peroxiredoxin Expression of Human Osteosarcoma Cells Is Influenced by Cold Atmospheric Plasma Treatment. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leduc, M.; Guay, D.; Leask, R.L.; Coulombe, S. Cell permeabilization using a non-thermal plasma. New J. Phys. 2009, 11, 115021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonson, S.; Coulombe, S.; Léveillé, V.; Leask, R.L. Cell treatment and surface functionalization using a miniature atmospheric pressure glow discharge plasma torch. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2006, 39, 3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkman, A.S.; Hara-Chikuma, M.; Papadopoulos, M.C. Aquaporins—New players in cancer biology. J. Mol. Med. 2008, 86, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayun, Y.; Haijie, X.; Wei, Z.; Niki, N.; Lijie Grace, Z.; Ka, B.; Keidar, M. The role of aquaporins in the anti-glioblastoma capacity of the cold plasma-stimulated medium. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2017, 50, 055401. [Google Scholar]
- Ahn, H.J.; Kim, K.I.; Kim, G.; Moon, E.; Yang, S.S.; Lee, J.S. Atmospheric-pressure plasma jet induces apoptosis involving mitochondria via generation of free radicals. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Mills, L.; Worth, L.L. Expression of human glutathione S-transferase P1 mediates the chemosensitivity of osteosarcoma cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 1610–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brun, P.; Pathak, S.; Castagliuolo, I.; Palu, G.; Brun, P.; Zuin, M.; Cavazzana, R.; Martines, E. Helium generated cold plasma finely regulates activation of human fibroblast-like primary cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panngom, K.; Baik, K.Y.; Nam, M.K.; Han, J.H.; Rhim, H.; Choi, E.H. Preferential killing of human lung cancer cell lines with mitochondrial dysfunction by nonthermal dielectric barrier discharge plasma. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekeschus, S.; von Woedtke, T.; Kramer, A.; Weltmann, K.-D.; Masur, K. Cold Physical Plasma Treatment Alters Redox Balance in Human Immune Cells. Plsama Med. 2013, 3, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekeschus, S.; Kolata, J.; Winterbourn, C.; Kramer, A.; Turner, R.; Weltmann, K.D.; Broker, B.; Masur, K. Hydrogen peroxide: A central player in physical plasma-induced oxidative stress in human blood cells. Free Radic. Res. 2014, 48, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, A.; Dietrich, S.; Steuer, A.; Weltmann, K.D.; von Woedtke, T.; Masur, K.; Wende, K. Non-thermal plasma activates human keratinocytes by stimulation of antioxidant and phase II pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 6731–6750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, M.; Li, Z.; Gao, P.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, J. Bufalin induces apoptosis in the U2OS human osteosarcoma cell line via triggering the mitochondrial pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 817–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Ao, P.Y.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Huang, S.Z.; Jin, Y.; Liu, J.J.; Luo, J.P.; Zheng, J.; Shi, D.P. Effect and mechanism of dihydroartemisinin on proliferation, metastasis and apoptosis of human osteosarcoma cells. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2015, 29, 881–887. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Shao, Z.; Xiong, L.; Yang, S. Inhibition of autophagy enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis in the MG63 human osteosarcoma cell line. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 2941–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barry, M.A.; Behnke, C.A.; Eastman, A. Activation of programmed cell death (apoptosis) by cisplatin, other anticancer drugs, toxins and hyperthermia. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1990, 40, 2353–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, S.; Wacker, E.; Li, Y.F.; Shimizu, T.; Thomas, H.M.; Morfill, G.E.; Karrer, S.; Zimmermann, J.L.; Bosserhoff, A.K. Cold atmospheric plasma, a new strategy to induce senescence in melanoma cells. Exp. Dermatol. 2013, 22, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canal, C.; Fontelo, R.; Hamouda, I.; Guillem-Marti, J.; Cvelbar, U.; Ginebra, M.P. Plasma-induced selectivity in bone cancer cells death. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 110, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majno, G.; Joris, I. Apoptosis, oncosis, and necrosis. An overview of cell death. Am. J. Pathol. 1995, 146, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mandelkow, R.; Gumbel, D.; Ahrend, H.; Kaul, A.; Zimmermann, U.; Burchardt, M.; Stope, M.B. Detection and Quantification of Nuclear Morphology Changes in Apoptotic Cells by Fluorescence Microscopy and Subsequent Analysis of Visualized Fluorescent Signals. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 2239–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Zou, F.; Zhao, S.; Lu, X.; He, G.; Xiong, Z.; Xiong, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Deng, P.; Huang, J.; et al. On the Mechanism of Plasma Inducing Cell Apoptosis. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 2010, 38, 2451–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Cui, H.; Zhu, W.; Nourmohammadi, N.; Milberg, J.; Zhang, L.G.; Sherman, J.H.; Keidar, M. The Specific Vulnerabilities of Cancer Cells to the Cold Atmospheric Plasma-Stimulated Solutions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, A.; von Woedtke, T.; Bekeschus, S. Periodic Exposure of Keratinocytes to Cold Physical Plasma: An In Vitro Model for Redox-Related Diseases of the Skin. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 9816072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekeschus, S.; Schmidt, A.; Bethge, L.; Masur, K.; von Woedtke, T.; Hasse, S.; Wende, K. Redox Stimulation of Human THP-1 Monocytes in Response to Cold Physical Plasma. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 5910695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, A.; Wende, K.; Bundscherer, L.; Hasse, S.; Schmidt, A.; Bekeschus, S.; Weltmann, K.-D.; Lindequist, U.; Masur, K. Nonthermal Plasma Increases Expression of Wound Healing Related Genes in a Keratinocyte Cell Line. Plasma Med. 2013, 3, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arndt, S.; Landthaler, M.; Zimmermann, J.L.; Unger, P.; Wacker, E.; Shimizu, T.; Li, Y.F.; Morfill, G.E.; Bosserhoff, A.K.; Karrer, S. Effects of cold atmospheric plasma (CAP) on ss-defensins, inflammatory cytokines, and apoptosis-related molecules in keratinocytes in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arndt, S.; Unger, P.; Wacker, E.; Shimizu, T.; Heinlin, J.; Li, Y.F.; Thomas, H.M.; Morfill, G.E.; Zimmermann, J.L.; Bosserhoff, A.K.; et al. Cold atmospheric plasma (CAP) changes gene expression of key molecules of the wound healing machinery and improves wound healing in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, S.Y.; Dong, Y.Y.; Liu, D.X.; Xu, D.H.; Xiao, S.X.; Chen, H.L.; Kong, M.G. Surface air plasma-induced cell death and cytokine release of human keratinocytes in the context of psoriasis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2016, 174, 542–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.B.; Kim, B.; Bae, H.; Lee, H.; Lee, S.; Choi, E.H.; Kim, S.J. Differential Epigenetic Effects of Atmospheric Cold Plasma on MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aryal, S.; Bisht, G. New Paradigm for a Targeted Cancer Therapeutic Approach: A Short Review on Potential Synergy of Gold Nanoparticles and Cold Atmospheric Plasma. Biomedicines 2017, 5, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Species | Tumor | Cell Line |
|---|---|---|
| human | non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) | MR65, SW900 |
| human | hepatocellular carcinoma | HepG2, BEL-7402 |
| human | melanoma cells | A2058, G361, SK-MEL-28 |
| human | cervical cancer | HeLa |
| human | colon carcinoma | COLO320DM, HCT-116, SW480, LoVo |
| mouse | melanoma cells | B16-F10, 1205Lu, Mel Juso, Mel Ei, Mel Ho, Mel Im, Mel Ju, HTZ19, A375 |
| human | breast cancer | MCF-7, MDA-MB-231 |
| human | glioblastoma cells | U87, T98G, LN18, LN229 |
| human | bladder cancer cells | SCaBER |
| mouse | lung carcinoma cells | TC-1 |
| human | acute lymphoblastic leukaemia cells | CCRF-CEM |
| human | pancreatic cancer cells | MIA PaCa2-luc, Colo-357, PaTu8988T |
| human | ovarian cancer cells | SKOV-3, HRA |
| mouse | pancreatic cancer cells | 6606PDA |
| human | acute monocytic leukaemia cells | THP-1 |
| human | skin cancer | PAM212 |
| human | lung cancer | H460, A549 |
| mouse | neuroblastoma | Neuro2a |
| human | head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells | JHU-022, JHU-028, JHU-029, SCC25, FaDu, OSC 19 |
| human | prostate cancer | LNCaP, BPH-1, PC-3 |
| human | oral squamous cell carcinoma cells | HSC-2, SCC-15 |
| human | multiple myeloma cells | RPMI8226, LP-1 |
| human | lymphoma | U937 |
| human | osteosarcoma | U2-OS, MNNG, SaOS-2 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gümbel, D.; Bekeschus, S.; Gelbrich, N.; Napp, M.; Ekkernkamp, A.; Kramer, A.; Stope, M.B. Cold Atmospheric Plasma in the Treatment of Osteosarcoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18092004
Gümbel D, Bekeschus S, Gelbrich N, Napp M, Ekkernkamp A, Kramer A, Stope MB. Cold Atmospheric Plasma in the Treatment of Osteosarcoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(9):2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18092004
Chicago/Turabian StyleGümbel, Denis, Sander Bekeschus, Nadine Gelbrich, Matthias Napp, Axel Ekkernkamp, Axel Kramer, and Matthias B. Stope. 2017. "Cold Atmospheric Plasma in the Treatment of Osteosarcoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 9: 2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18092004
APA StyleGümbel, D., Bekeschus, S., Gelbrich, N., Napp, M., Ekkernkamp, A., Kramer, A., & Stope, M. B. (2017). Cold Atmospheric Plasma in the Treatment of Osteosarcoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(9), 2004. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18092004