Exploring the Remote Ties between Helitron Transposases and Other Rolling-Circle Replication Proteins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Selecting and Preparing RCRE Domain Sequences
2.2. Major RCR Protein Phylogenetic Groups
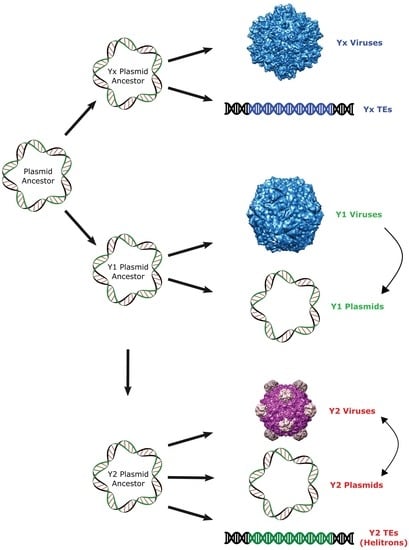
2.3. Helitron Transposase is More Similar to Prokaryotic Proteins
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sequences Retrieval and Selection
3.2. Sequence Alignment
3.3. NMDS and Phylogenetic Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RCR | Rolling-circle replication |
| TE | Transposable element |
| RCRE | Rolling-circle replication endonuclease domain |
| S1H | Superfamily 1 helicase |
| S3H | Superfamily 3 helicase |
| RepHel | Helitron transposase (Rep/Helicase) |
| ssDNA | Single-strand DNA |
| NMDS | Non-metric multidimensional scaling |
References
- Chandler, M.; De La Cruz, F.; Dyda, F.; Hickman, A.B.; Moncalian, G.; Ton-Hoang, B. Breaking and joining single-stranded DNA: The HUH endonuclease superfamily. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 525–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wawrzyniak, P.; Płucienniczak, G.; Bartosik, D. The Different Faces of Rolling-Circle Replication and Its Multifunctional Initiator Proteins. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapitonov, V.V.; Jurka, J. Helitrons on a roll: Eukaryotic rolling-circle transposons. Trends Genet. 2007, 23, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, J.; Pritham, E.J. Helitrons, the Eukaryotic Rolling-Circle Transposable Elements in Mobile DNA III, 3rd ed.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; pp. 893–926. [Google Scholar]
- Dias, G.B.; Heringer, P.; Kuhn, G.C. Helitrons in Drosophila: Chromatin modulation and tandem insertions. Mob. Genet. Elements 2016, 6, e1154638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabundzija, I.; Messing, S.A.; Thomas, J.; Cosby, R.L.; Bilic, I.; Miskey, C.; Jurka, J. A Helitron transposon reconstructed from bats reveals a novel mechanism of genome shuffling in eukaryotes. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grabundzija, I.; Hickman, A.B.; Dyda, F. Helraiser intermediates provide insight into the mechanism of eukaryotic replicative transposition. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koonin, E.V.; Dolja, V.V. Virus world as an evolutionary network of viruses and capsidless selfish elements. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2014, 78, 278–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupovic, M. Networks of evolutionary interactions underlying the polyphyletic origin of ssDNA viruses. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2013, 3, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchler-Bauer, A.; Bo, Y.; Han, L.; He, J.; Lanczycki, C.J.; Lu, S.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Geer, R.C.; Gonzales, N.R.; et al. CDD/SPARCLE: Functional classification of proteins via subfamily domain architectures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D200–D203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapitonov, V.V.; Jurka, J. Rolling-circle transposons in eukaryotes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 8714–8719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feschotte, C.; Wessler, S.R. Treasures in the attic: Rolling circle transposons discovered in eukaryotic genomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 8923–8924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bejarano, E.R.; Khashoggi, A.; Witty, M.; Lichtenstein, C. Integration of multiple repeats of geminiviral DNA into the nuclear genome of tobacco during evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 759–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krupovic, M.; Forterre, P. Single-stranded DNA viruses employ a variety of mechanisms for integration into host genomes. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2015, 1341, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Fu, Y.; Li, B.; Yu, X.; Xie, J.; Cheng, J.; Ghabrial, S.A.; Li, G.; Yi, X.; Jiang, D. Widespread horizontal gene transfer from circular single-stranded DNA viruses to eukaryotic genomes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2011, 11, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hickman, A.B.; Ronning, D.R.; Kotin, R.M.; Dyda, F. Structural unity among viral origin binding proteins: Crystal structure of the nuclease domain of adeno-associated virus Rep. Mol. Cell 2002, 10, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosario, K.; Duffy, S.; Breitbart, M. A field guide to eukaryotic circular single-stranded DNA viruses: Insights gained from metagenomics. Arch. Virol. 2012, 157, 1851–1871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björklund, Å.K.; Ekman, D.; Light, S.; Frey-Skött, J.; Elofsson, A. Domain rearrangements in protein evolution. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 353, 911–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulter, R.T.; Goodwin, T.J.; Butler, M. Vertebrate helentrons and other novel Helitrons. Gene 2003, 313, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazlauskas, D.; Varsani, A.; Krupovic, M. Pervasive Chimerism in the Replication-Associated Proteins of Uncultured Single-Stranded DNA Viruses. Viruses 2018, 10, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilyina, T.V.; Koonin, E.V. Conserved sequence motifs in the initiator proteins for rolling circle DNA replication encoded by diverse replicons from eubacteria, eucaryotes and archaebacteria. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992, 20, 3279–3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Di Tommaso, P.; Moretti, S.; Xenarios, I.; Orobitg, M.; Montanyola, A.; Chang, J.M.; Notredame, C. T-Coffee: A web server for the multiple sequence alignment of protein and RNA sequences using structural information and homology extension. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W13–W17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taly, J.F.; Magis, C.; Bussotti, G.; Chang, J.M.; Di Tommaso, P.; Erb, I.; Espinosa-Carrasco, J.; Kemena, C.; Notredame, C. Using the T-Coffee package to build multiple sequence alignments of protein, RNA, DNA sequences and 3D structures. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1669–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, B.; Cao, M.; Sima, L.; Prangishvili, D.; Chen, X.; Krupovic, M. Rolling-circle replication initiation protein of haloarchaeal sphaerolipovirus SNJ1 is homologous to bacterial transposases of the IS91 family insertion sequences. J. Gen. Virol. 2018, 99, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiewsakun, P.; Simmonds, P. The genomic underpinnings of eukaryotic virus taxonomy: Creating a sequence-based framework for family-level virus classification. Microbiome 2018, 6, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos-Olivas, R.; Louis, J.M.; Clérot, D.; Gronenborn, B.; Gronenborn, A.M. The structure of a replication initiator unites diverse aspects of nucleic acid metabolism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 10310–10315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergsten, J. A review of long-branch attraction. Cladistics 2005, 21, 163–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcillan-Barcia, M.P.; Bernales, I.; Mendiola, M.V.; de la Cruz, F. Single-stranded DNA intermediates in IS91 rolling-circle transposition. Mol. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochman, M.L.; Sabouri, N.; Zakian, V.A. Unwinding the functions of the Pif1 family helicases. DNA repair 2010, 9, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bochman, M.L.; Judge, C.P.; Zakian, V.A. The Pif1 family in prokaryotes: What are our helicases doing in your bacteria? Mol. Biol. Cell 2011, 22, 1955–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrillo-Tripp, M.; Shepherd, C.M.; Borelli, I.A.; Venkataraman, S.; Lander, G.; Natarajan, P.; Johnson, J.E.; Brooks, C.L.; Reddy, V.S. VIPERdb2: An enhanced and web API enabled relational database for structural virology. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D436–D442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, W.; Kojima, K.K.; Kohany, O. Repbase Update, a database of repetitive elements in eukaryotic genomes. Mob. DNA 2015, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, D.A.; Cavanaugh, M.; Clark, K.; Karsch-Mizrachi, I.; Lipman, D.J.; Ostell, J.; Sayers, E.W. GenBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D37–D42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritham, E.J.; Feschotte, C. Massive amplification of rolling-circle transposons in the lineage of the bat Myotis lucifugus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 1895–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zawar-Reza, P.; Argüello-Astorga, G.R.; Kraberger, S.; Julian, L.; Stainton, D.; Broady, P.A.; Varsani, A. Diverse small circular single-stranded DNA viruses identified in a freshwater pond on the McMurdo Ice Shelf (Antarctica). Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 26, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazlauskas, D.; Dayaram, A.; Kraberger, S.; Goldstien, S.; Varsani, A.; Krupovic, M. Evolutionary history of ssDNA bacilladnaviruses features horizontal acquisition of the capsid gene from ssRNA nodaviruses. Virology 2017, 504, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Sima, L.; Lv, J.; Huang, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Krupovic, M.; Chen, X. Identification, characterization, and application of the replicon region of the halophilic temperate sphaerolipovirus SNJ1. J. Bacteriol. 2016, 198, 1952–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, P. VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development for R; RStudio, Inc.: Boston, MA, USA, 2016; Available online: http://www.rstudio.com/ (accessed on 8 October 2018).
- Lefort, V.; Longueville, J.E.; Gascuel, O. SMS: Smart model selection in PhyML. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 2422–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive tree of life (iTOL) v3: An online tool for the display and annotation of phylogenetic and other trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W242–W245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heringer, P.; Kuhn, G.C.S. Exploring the Remote Ties between Helitron Transposases and Other Rolling-Circle Replication Proteins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3079. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103079
Heringer P, Kuhn GCS. Exploring the Remote Ties between Helitron Transposases and Other Rolling-Circle Replication Proteins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(10):3079. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103079
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeringer, Pedro, and Gustavo C. S. Kuhn. 2018. "Exploring the Remote Ties between Helitron Transposases and Other Rolling-Circle Replication Proteins" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 10: 3079. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103079
APA StyleHeringer, P., & Kuhn, G. C. S. (2018). Exploring the Remote Ties between Helitron Transposases and Other Rolling-Circle Replication Proteins. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(10), 3079. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103079