Dendrimeric Poly(Epsilon-Lysine) Delivery Systems for the Enhanced Permeability of Flurbiprofen across the Blood-Brain Barrier in Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
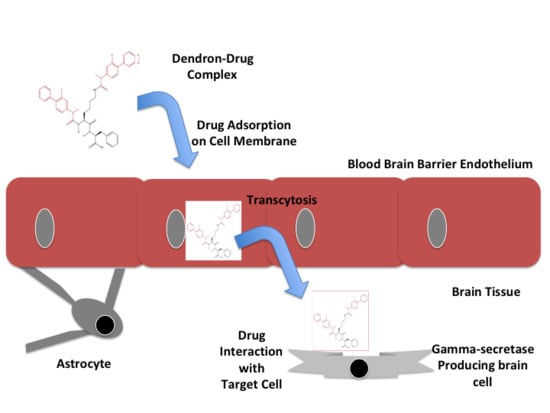
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterisation of Flurbiprofen (FP)-Loaded Dendrons
2.2. Cytotoxicity and Biocompatibility Studies
2.3. Penetration of Drug-Integrated Dendrons Across an in Vitro Model of The Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB)
2.4. Evaluation of Drug-Integrated Dendrons Activity on γ-Secretase Enzyme
2.5. Degradation Investigation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Synthesis of Delivery Systems
4.2. Characterisation of The FP-Loaded Dendrimeric Delivery Systems
4.2.1. Mass Spectrometry (MS)
4.2.2. Fourier Transform Infra-Red (FTIR)
4.3. Preparation of Cell Lines
4.4. Cytotoxicity and Biocompatibility Assays
4.5. Examination of FP-Loaded Dendrimeric Delivery Systems Penetration Across the in Vitro BBB Model
4.6. Evaluation of Drug-Integrated Dendrons Activity on γ-Secretase Enzyme
4.7. Degradation Investigation
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| AMT | Adsorptive-mediated transcytosis |
| Apo-E | Apolipoprotein E |
| APP | Amyloid precursor protein |
| Aβ | β-amyloid |
| BBB | Blood brain barrier |
| bEnd.3 | Immortalised brain endothelial cells |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified eagle’s medium |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immune-sorbent assay |
| FBS | Foetal bovine serum |
| FP | Flurbiprofen |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infra-red |
| G | Generation |
| G0K-FP | Generation 0 lysine dendron-2Flurbiprofen |
| G1K-FP | Generation 1 lysine dendron-4Flurbiprofen |
| GSMs | γ-secretase modulators |
| HPLC | High performance liquid chromatography |
| HUVEC | Human umbilical vein endothelial cells |
| LDH | Lactate dehydrogenase |
| m/z | Mass to charge ratio |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-3,5-diphenylformazan |
| MW | Molecular weight |
| ND | Neurodegenerative |
| NSAIDs | Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs |
| PAMAM | Poly amido amine dendrimers |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SPPS | Solid phase peptide synthesis |
| TEER | Transepithelial electrical resistance |
References
- Prince, M.; Comas-Herrera, A.; Knapp, M.; Guerchet, M.; Karagiannidou, M. Improving healthcare for people living with dementia: Coverage, quality and costs now and in the future. In Proceedings of the World Alzheimer Report 2016, London, UK, 26 September 2016; Alzheimer’s Disease International: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Banks, W. Drug delivery to the brain in Alzheimer’s disease: Consideration of the blood–brain barrier. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 629–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, Y.; Emmerling, M.; VigoPelfrey, C.; Kasunic, C.; Kirkpatrick, B.; Murdoch, H.; Ball, J.; Roher, E. Water-soluble Aβ (N-40, N-42) oligomers in normal and Alzheimer disease brains. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 4077–4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksen, J.; Sagi, S.; Smith, T.; Weggen, S.; Das, P.; McLendon, D.; Ozols, V.; Jessing, K.; Zavitz, K.; Koo, E.; et al. NSAIDs and enantiomers of Flurbiprofen target γ-secretase and lower Aβ 42 in vivo. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 440–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meister, S.; Zlatev, I.; Stab, J.; Docter, D.; Baches, S.; Stauber, R.; Deutsch, M.; Schmidt, R.; Ropele, S.; Windisch, M.; et al. Nanoparticulate Flurbiprofen reduces amyloid-β42 generation in an in vitro blood-brain barrier model. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2013, 5, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Re, F.; Gregori, M.; Masserini, M. Nanotechnology for neurodegenerative disorders. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2012, 73, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, L. Modern methods for delivery of drugs across the blood-brain barrier. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 640–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khawli, L.A.; Prabhu, S. Drug delivery across the blood-brain barrier. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 1471–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Y. Dendrimer advances for the central nervous system delivery of therapeutics. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2014, 5, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahoo, S.; Parveen, S.; Panda, J. The present and future of nanotechnology in human health care. Nanomedicine 2007, 3, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heather, A.; Kristi, L.; Ruth, H.; Anthony, H.; Chevelle, C.; Stephen, W.; Robert, S.; Brett, R.; Michael, H.; Megan, C. Evaluation of biotinylated PAMAM dendrimer toxicity in models of the blood brain barrier: A biophysical and cellular approach. J. Biomater. Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 2, 485–493. [Google Scholar]
- Sadekar, S.; Thiagarajan, G.; Bartlett, K.; Hubbard, D.; Ray, A.; McGill, D.; Ghandehari, H. Poly(amido amine) dendrimers as absorption enhancers for oral delivery of camptothecin. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 456, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Nan, A. Combination drug delivery approaches in metastatic breast cancer. J. Drug Deliv. 2012, 2012, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Man, N.; Xu, T.; Fu, R.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Wen, L. Transdermal delivery of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs mediated by polyamidoamine (PAMAM) dendrimers. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 96, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patri, A.; Simanek, E. Biological applications of dendrimers. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 341–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolhe, P.; Ekta, M.; Kannan, R.; Sujatha, K.; Mary, L. Drug complexation, in vitro release and cellular entry of dendrimers and hyperbranched polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 259, 143–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; He, H.; Jia, X.; Lu, L.; Lou, J.; Wei, Y. A dual-targeting nanocarrier based on poly(amidoamine) dendrimers conjugated with transferrin and tamoxifen for treating brain gliomas. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 3899–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crump, J.; Johnson, S.; Li, Y. Development and mechanism of γ-secretase modulators for Alzheimer’s disease. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 3197–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lleo, A.; Berezovska, O.; Herl, L.; Raju, S.; Deng, A.; Bacskai, J.; Frosch, P.; Irizarry, M.; Hyman, T. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs lower Aβ42 and change presenilin 1 conformation. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 1065–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertens, J.; Stuber, K.; Wunderlich, P.; Ladewig, J.; Kesavan, J.; Vandenberghe, R.; Vandenbulcke, M.; Van Damme, P.; Walter, J.; Brustle, O.; et al. APP processing in human pluripotent stem cell-derived neurons is resistant to NSAID-based γ-secretase modulation. Stem Cell Rep. 2013, 1, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukar, T.; Prescott, S.; Eriksen, J.; Holloway, V.; Murphy, M.; Koo, E.; Golde, T.; Nicolle, M. Chronic administration of R-flurbiprofen attenuates learning impairments in transgenic amyloid precursor protein mice. BMC Neurosci. 2007, 8, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, L.; Ho, C. Role of serum albumin as a nanoparticulate carrier for nose-to-brain delivery of R-flurbiprofen: Implications for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2018, 70, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz, S.; Calvo, M.; Eriksen, J.; Holloway, V.; Murphy, M.; Koo, E.; Golde, T.; Nicolle, M. Is it all said for NSAIDs in Alzheimer’s disease? Role of mitochondrial calcium uptake. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2018, 15, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGeer, P.; McGeer, E. NSAIDs and Alzheimer disease: Epidemiological, animal model and clinical studies. Neurobiol. Aging 2007, 28, 639–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, N. Clinical pharmacokinetics of Flurbiprofen and its enantiomers. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1995, 28, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, R.; Schneider, L.; Amato, D.; Beelen, A.; Wilcock, G.; Swabb, E.; Zavitz, K. Effect of tarenflurbil on cognitive decline and activities of daily living in patients with mild Alzheimer disease: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2009, 302, 2557–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcock, G.; Black, S.; Hendrix, S.; Zavitz, K.; Swabb, E.; Laughlin, M. Efficacy and safety of tarenflurbil in mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease: A randomised phase II trial. Lancet Neurol. 2008, 7, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downard, K. Mass Spectrometry: A Foundation Course, 1st ed.; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2004; p. 226. ISBN 9780854046096. [Google Scholar]
- Aparicio, J.; Martin, C.; Torres, I. In vitro screening of nanomedicines through the blood brain barrier: A critical review. Biomaterials 2016, 103, 229–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boer, A.; Gaillard, P. Drug targeting to the brain. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2007, 47, 323–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oller, B.; Sanchez, M.; Giralt, E.; Teixido, M. Blood-brain barrier shuttle peptides: An emerging paradigm for brain delivery. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 4690–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prashant, K.; Keerti, J.; Narendra, K. Dendrimer as nanocarrier for drug delivery. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 268–307. [Google Scholar]
- Tomalia, D.; Svenson, S. Dendrimers in biomedical applications--reflections on the field. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 2106–2129. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, H.; Suarez, M.; Albericio, F. Convenient microwave-enhanced solid-phase synthesis of short chain N-methyl-rich peptides. J. Pept. Sci. 2010, 16, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Made, V.; Els-Heindl, S.; Beck-Sickinger, A. Automated solid-phase peptide synthesis to obtain therapeutic peptides. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2014, 10, 1197–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Menjoge, A.; Kannan, R.; Tomalia, D. Dendrimer-based drug and imaging conjugates: Design considerations for nanomedical applications. Drug Discov. Today 2010, 15, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Kao, W. Synthesis and characterization of nanoscale dendritic RGD clusters for potential applications in tissue engineering and drug delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2007, 2, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malik, N.; Wiwattanapatapee, R.; Klopsch, R.; Lorenz, K.; Frey, H.; Weener, J.W.; Meijer, E.W.; Paulus, W.; Duncan, R. Dendrimers: Relationship between structure and biocompatibility in vitro, and preliminary studies on the biodistribution of 125I-labelled polyamidoamine dendrimers in vivo. J. Control. Release 2000, 65, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Yin, F.; Peng, J.; Li, K.; Wu, L.; Deng, X. Immortalized mouse brain endothelial cell line Bend.3 displays the comparative barrier characteristics as the primary brain microvascular endothelial cells. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er 2010, 12, 474–478. [Google Scholar]
- Omidi, Y.; Campbell, L.; Barar, J.; Connell, D.; Akhtar, S.; Gumbleton, M. Evaluation of the immortalised mouse brain capillary endothelial cell line, b.End3, as an in vitro blood–brain barrier model for drug uptake and transport studies. Brain Res. 2003, 990, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.; Morris, A.; O’Neil, R. Tight junction protein expression and barrier properties of immortalized mouse brain microvessel endothelial cells. Brain Res. 2007, 1130, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patabendige, A.; Skinner, R.; Morgan, L.; Abbott, N. A detailed method for preparation of a functional and flexible blood-brain barrier model using porcine brain endothelial cells. Brain Res. 2013, 1521, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Pachter, J. Culture of murine brain microvascular endothelial cells that maintain expression and cytoskeletal association of tight junction-associated proteins. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Anim. 2003, 39, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebelegi, N.; Ekubo, T.; Ayawei, N.; Donbebe, W. A Review of Synthesis, characterization and applications of functionalized dendrimers. Am. J. Polym. Sci. 2017, 7, 8–14. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivas, N.; Anusha, G.; Malath, K.; Preetika, A. Dendrimer- for novel drug delivery system- a review article. Indo. Am. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 1, 295–304. [Google Scholar]
- Teow, H.; Zhou, Z.; Najlah, M.; Yusof, S.; Abbott, N.; D’Emanuele, A. Delivery of paclitaxel across cellular barriers using a dendrimer-based nanocarrier. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 441, 701–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madaan, K.; Kumar, S.; Poonia, N.; Lather, V.; Pandita, D. Dendrimers in drug delivery and targeting: Drug-dendrimer interactions and toxicity issues. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2014, 6, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Najlah, M.; Freeman, S.; Attwood, D.; D’Emanuele, A. In vitro evaluation of dendrimer prodrugs for oral drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 336, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesharwani, P.; Tekade, R.; Gajbhiye, V.; Jain, K.; Jain, K. Cancer targeting potential of some ligand-anchored poly(propylene imine) dendrimers: A comparison. Nanomedicine 2011, 7, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosnjakovic, A.; Mishra, M.; Ren, W.; Kurtoglu, E.; Shi, T.; Fan, D.; Kannan, M. Poly(amidoamine) dendrimer-erythromycin conjugates for drug delivery to macrophages involved in periprosthetic inflammation. Nanomedicine 2011, 7, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitchens, K.; El-Sayed, M.; Ghandehari, H. Transepithelial and endothelial transport of poly (amidoamine) dendrimers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 2163–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Najlah, M.; D’Emanuele, A. Crossing cellular barriers using dendrimer nanotechnologies. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2006, 6, 522–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nord, L.; Sundqvist, J.; Andersson, E.; Fried, G. Analysis of oestrogen regulation of α-, β- and γ-secretase gene and protein expression in cultured human neuronal and glial cells. Neurodegener. Dis. 2010, 7, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichert, W. Frontiers in Neuroengineering. In Indwelling Neural Implants: Strategies for Contending with The In Vivo Environment; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008; ISBN 9780849393624. [Google Scholar]
- Silverman, R.; Holladay, M. Prodrugs and drug delivery systems. In The Organic Chemistry of Drug Design and Drug Action, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 423–468. [Google Scholar]
- Hamblett, K.; Senter, P.; Chace, D.; Sun, M.; Lenox, J.; Cerveny, C.; Kissler, K.; Bernhardt, S.; Kopcha, A.; Zabinski, R.; et al. Effects of drug loading on the antitumor activity of a monoclonal antibody drug conjugate. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 7063–7070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karolina, W.; Winiewski, M.; Terzyk, A.; Furmaniak, S. The Chemistry of bioconjugation in nanoparticles-based drug delivery system. Adv. Condens. Matter Phys. 2015, 2015, 20–27. [Google Scholar]
- Safari, J.; Zarnegar, Z. Advanced drug delivery systems: Nanotechnology of health design A review. J. Saudi. Chem. Soc. 2014, 18, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, A.; Topp, E. Release from polymeric prodrugs: Linkages and their degradation. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 93, 1962–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Huh, J.; Ahn, H.; Lee, M.; Park, G. Synthesis of novel biodegradable cationic dendrimers. Macromol. Rapid. Comm. 2006, 27, 1608–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandare, J.; Kumar, S. Biodegradable dendrimers and dendritic polymers. In Handbook of Biodegradable Polymers; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2011; pp. 237–262. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, S.; Fu, W. Drug candidates in clinical trials for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 24, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Strooper, B. Lessons from a failed g-secretase Alzheimer trial. Cell 2014, 159, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meikle, S.; Perugini, V.; Guildford, A.; Santin, M. Synthesis, characterisation and in vitro anti-angiogenic potential of dendron VEGF blockers. Macromol. Biosci. 2011, 11, 1761–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perugini, V. Poly-ε-Lysine dendron aptamers as regulators of angiogenesis in tissue regeneration. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Brighton, Brighton, UK, 18 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol Methods. 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Molecule | Time | No. of Readings | % Of Permeability (Mean ± SD) | p Value to FP | p Value to G0K-FP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FP | 1 h | 6 | 2.71 ± 1.52 | ||
| 4 h | 6 | 8.50 ± 1.32 | |||
| G0K-FP | 1 h | 6 | 5.31 ± 2.73 | >0.05 | |
| 4 h | 6 | 12.48 ± 3.42 | >0.05 | ||
| G1K-FP | 1 h | 6 | 4.32 ± 1.05 | <0.05 | >0.05 |
| 4 h | 6 | 14.79 ± 2.06 | <0.05 | >0.05 |
| Molecule | No. of Readings | γ-Secretase Enzyme Concentration pg/mL (Mean ± SD) | p Value to FP | p Value to Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 6 | 28.43 ± 8.32 | <0.05 | |
| FP | 6 | 8.20 ± 3.80 | ||
| G0K-FP | 6 | 12.69 ± 4.85 | >0.05 | <0.05 |
| G1K-FP | 6 | 16.04 ± 3.18 | <0.05 | <0.05 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-azzawi, S.; Masheta, D.; Guildford, A.L.; Phillips, G.; Santin, M. Dendrimeric Poly(Epsilon-Lysine) Delivery Systems for the Enhanced Permeability of Flurbiprofen across the Blood-Brain Barrier in Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3224. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103224
Al-azzawi S, Masheta D, Guildford AL, Phillips G, Santin M. Dendrimeric Poly(Epsilon-Lysine) Delivery Systems for the Enhanced Permeability of Flurbiprofen across the Blood-Brain Barrier in Alzheimer’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(10):3224. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103224
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-azzawi, Shafq, Dhafir Masheta, Anna L. Guildford, Gary Phillips, and Matteo Santin. 2018. "Dendrimeric Poly(Epsilon-Lysine) Delivery Systems for the Enhanced Permeability of Flurbiprofen across the Blood-Brain Barrier in Alzheimer’s Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 10: 3224. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103224
APA StyleAl-azzawi, S., Masheta, D., Guildford, A. L., Phillips, G., & Santin, M. (2018). Dendrimeric Poly(Epsilon-Lysine) Delivery Systems for the Enhanced Permeability of Flurbiprofen across the Blood-Brain Barrier in Alzheimer’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(10), 3224. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103224