Oncotoxic Properties of Serotonin Transporter Inhibitors and 5-HT1A Receptor Ligands
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Experimental Studies
2.2. Molecular Modelling
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Compounds
4.2. Cell Lines
4.2.1. PC-3 and SH-SY5Y, as well as HEK293 and Balb/c 3T3 Cells as a Reference
4.2.2. Preparation of a Stable Transfectant 5-HT1A—HEK293 Cell Line
4.3. Cell Cultures
4.4. Study of In Vitro Binding Affinity of Compounds for Serotonin Transporter (SERT)
4.5. Examination of the Functional Activity of 5-HT1A Receptor Ligands in Transformed HEK293
4.6. Determination of the Effect of Test Compounds on Cell Survival
4.7. Apoptosis Determination
4.8. Flow Cytometry
4.9. Molecular Modeling
4.10. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
6. Experimental Procedures
6.1. Preparation of N-Alkylaryl-6-nitroquipazines Derivatives 9 (AB5A) and 10 (AB9)

6.2. Preparation of 6-Nitroquipazine N-Cycloalkyl Derivatives 11 (AB21) and 12 (AB22)

Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Akt | serine-threonine protein kinase B |
| pAkt1 | phospho-Akt isoform 1 |
| Balb/c 3T3 | murine fibroblast cell line |
| cAMP | cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| 5-CT | 5-carboxamidotryptamine |
| 8-OH-DPAT | (R)-(+)-8- hydroxy-(2-di-n-propylamino)tetralin |
| DBU | 1,8-diazabicyclo(5.4.0)undec-7-ene |
| DU-145 | androgen-independent human prostate cancer cell line |
| EC50 | concentration inducing 50% of maximal response |
| ECL | extracellular loop |
| EDTA | disodium ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| ERK1/2 | extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 |
| pERK1/2 | phospho-ERK1/2 |
| EGFP | enhanced green fluorescent protein |
| HEK | human embryonic kidney cell line |
| 5-HT | 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) |
| 5-HT1A receptor | subtype of serotonin receptor 1A |
| IC50 | concentration showing 50% inhibition of maximal response |
| LNCaP | androgen-sensitive human prostate adenocarcinoma |
| MAPK | mitogen activated protein kinase |
| MEK | acronym from MAPK/ERK kinase |
| MTT | (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide) |
| NF-κB | nuclear transcription factor κB |
| PC-3 | androgen-independent human prostate cancer cell line |
| PI3K | phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase |
| SEM | standard error of the mean |
| SERT | serotonin transporter |
| SH-SY5Y | human neuroblastoma-like cell line |
| SI | selectivity index |
| SSRI | selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor |
| TMH | transmembrane helices |
| VLS | virtual ligand screening |
References
- Frick, L.R.; Rapanelli, M.; Arcos, M.L.; Cremaschi, G.A.; Genaro, A.M. Oral administration of fluoxetine alters the proliferation/apoptosis balance of lymphoma cells and upregulates T cell immunity in tumor-bearing mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 659, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chilmonczyk, Z.; Bojarski, A.J.; Pilc, A.; Sylte, I. Serotonin tranporter and receptor ligands with antidepressant activity as neuroprotective and proapoptotic agents. Pharm. Rep. 2017, 69, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dizeyi, N.; Hedlund, P.; Bjartell, A.; Tinzl, M.; Ustild-Tasken, K.; Abrahamsson, P.A. Serotonin activates MAP kinase and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways in prostate cancer cell lines. Urol. Oncol. 2011, 29, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, C.; Fernbach, N.; Rix, U.; Superti-Furga, G.; Holy, M.; Freissmuth, M.; Sitte, H.H.; Sexl, V. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors—A new modality for the treatment of lymphoma/leukaemia? Biochem. Pharmacol. 2007, 74, 1424–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosetti, M.; Frasnelli, M.; Tesei, A.; Zoli, W.; Conti, M. Cytotoxicity of different selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) against cancer cells. J. Exp. Ther. Oncol. 2006, 6, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gabrielsen, M.; Wołosewicz, K.; Zawadzka, A.; Kossakowski, J.; Nowak, G.; Wolak, M.; Stachowicz, K.; Siwek, A.; Ravna, A.W.; Kufareva, I.; et al. Synthesis, antidepressant evaluation and docking studies of long-chain alkylnitroquipazines as serotonin transporter inhibitors. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2013, 81, 695–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badisa, R.B.; Darling-Reed, S.F.; Joseph, P.; Cooperwood, J.S.; Latinwo, L.M.; Goodman, C.B. Selective cytotoxic activities of two novel synthetic drugs on human breast carcinoma MCF-7 Cells. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 2993–2996. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Milczarek, M.; Wiktorska, K.A.; Mielczarek, L.; Koronkiewicz, M.; Dąbrowska, A.; Lubelska, K.; Matosiuk, D.; Chilmonczyk, Z. Autophagic cell death and premature senescence: New mechanism of 5-fluorouracil and sulforaphane synergic anticancer effect in MDA-MB-231 triple negative breast cancer cell line. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 111, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiung, S.C.; Tamir, H.; Franke, T.F.; Liu, K.P. Roles of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and Akt signaling in coordinating nuclear transcription factor- kappaB-dependent cell survival after serotonin 1A receptor activation. J. Neurochem. 2005, 95, 1653–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adayev, T.; Ray, I.; Sondhi, R.; Sobocki, T.; Banerjee, P. The G protein-coupled 5- HT1A receptor causes suppression of caspase-3 through MAPK and protein kinase Calpha. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1640, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milligan, G.; Kellett, E.; Dacquet, C.; Dubreuil, V.; Jacoby, E.; Millan, M.J.; Lavielle, G.; Spedding, M. S14506: Novel receptor coupling at 5-HT1A receptors. Neuropharmacology 2001, 40, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, R.; Brocco, M.; Gobert, A.; Veiga, S.; Millan, M.J. The potent activity of the 5-HT1A receptor agonists, S 14506 and S 14671, in the rat forced swim test is blocked by 5-HT1A receptor antagonists. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1994, 271, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protais, P.; Chagraoui, A.; Arbaoui, J.; Mocaër, E. Dopamine receptor antagonist properties of S 14506, 8-OH-DPAT, raclopride and clozapine in rodents. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1994, 271, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylte, I.; Edvardsen, O.; Dahl, S.G. Molecular modeling of UH-301 and 5-HT(1a) receptor interactions. Protein Eng. 1996, 9, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warszycki, D.; Rueda, M.; Mordalski, S.; Kristiansen, K.; Satała, G.; Rataj, K.; Chilmonczyk, Z.; Sylte, I.; Abagyan, R.; Bojarski, A.J. From Homology Models to a Set of Predictive Binding Pockets-a 5-HT1A Receptor Case Study. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2017, 57, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuipers, W.; Link, R.; Standaar, P.J.; Stoit, A.R.; Van Wijngaarden ILeurs, R.; Ijzerman, A.P. Study of the Interaction Between Aryloxypropanolamines and Asn386 in Helix VII of the Human 5-Hydroxytryptamine1A Receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 1997, 51, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strader, C.D.; Candelore, M.R.; Hill, W.S.; Sigal, I.S.; Dixon, R.A. Identification of two serine residues involved in agonist activation of the beta-adrenergic receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 13572–13578. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ho, B.Y.; Karschin, A.; Branchek, T.; Davidson, N.; Lester, H.A. The role of conserved aspartate and serine residues in ligand binding and in function of the 5-HT1A receptor: A site-directed mutation study. FEBS Lett. 1992, 31, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strader, C.D.; Sigal, I.S.; Dixon, R.A. Structural basis of beta-adrenergic receptor function. FASEB J. 1989, 3, 1825–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigorieff, N.; Ceska, T.; Downing, K.; Baldwin, J.; Henderson, R. Electron crystallographic structure of bacteriorhodopsin. J. Mol. Biol. 1996, 259, 393–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Tao, L.Y.; Chen, X.P. Roles of NF-κB in central nervous system damage and repair. Neurosci. Bull. 2007, 23, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shih, R.H.; Wang, C.Y.; Yang, C.M. NF-kappaB signaling pathways in neurological inflammation: A mini review. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2015, 8, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abagyan, R.; Totrov, M.; Kuznetsow, D.N. ICM: A new method for protein modeling and design: Applications to docking and structure prediction from the distorted native conformation. J. Comput. Chem. 1994, 15, 488–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniele, S.; Da Pozzo, E.; Zappelli, E.; Martini, C. Trazodone treatment protects neuronal-like cells from inflammatory insult by inhibiting NF-kappaB, p38 and JNK. Cell Signal. 2015, 27, 1609–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chilmonczyk, Z.; Bojarski, A.J.; Pilc, A.; Sylte, I. Functional selectivity and antidepressant activity of serotonin 1A receptor ligands. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 18474–18506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Ma, J.; Wu, H.; Wacker, D.; Katritch, V.; Han, G.W.; Liu, W.; Huang, X.-P.; Vardy, E.; et al. Structural Basis for Molecular Recognition at Serotonin Receptors. Science 2013, 340, 610–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yin, W.; Zhou, X.E.; Yang, D.; de Waal, P.W.; Wang, M.; Dai, A.; Cai, X.; Huang, C.H.-Y.; Liu, P.; Wang, X.; et al. Crystal structure of the human 5-HT1B serotonin receptor bound to an inverse agonist. Cell Discov. 2018, 4, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeosun, S.O.; Albert, P.R.; Austin, M.C.; Iyo, A.H. 17β-estradiol-induced regulation of the novel 5-HT1A-related transcription factors NUDR and Freud-1 in SH SY5Y Cells. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2012, 32, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dizeyi, N.; Bjartell, A.; Nilsson, E.; Hansson, J.; Gadaleanu, V.; Cross, N.; Abrahamsson, P.A. Expression of serotonin receptors and role of serotonin in human prostate cancer tissue and cell lines. Prostate 2004, 59, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, M.J.; Morgan, W.N.; Plott, S.J.; Nemeroff, C.B. Neurotransmitter receptor and transporter binding profile of antidepressants and their metabolites. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1997, 283, 1305–1322. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Prusoff, W.H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 percent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1973, 22, 3099–3108. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cherezov, V.; Rosenbaum, D.M.; Hanson, M.A.; Rasmussen, S.G.F.; Thian, F.S.; Kobilka, T.S.; Choi, H.-J.; Kuhn, P.; Weis, W.I.; Kobilka, B.K.; et al. High-Resolution Crystal Structure of an Engineered Human beta2-Adrenergic G Protein-Coupled Receptor. Science 2007, 318, 1258–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schapira, M.; Totrov, M.; Abagyan, R. Prediction of the binding energy for small molecules, peptides and proteins. J. Mol. Recognit. 1999, 12, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Compound | Structure | Symbol | SERT Ki ± SEM, nM |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6 |  | KW117 | 20.8 ± 3.8 [6] |
| 7 |  | AZ05 | 1.8 ± 0.2 [6] |
| 8 |  | AZ07 | 12.6 ± 1.3 [6] |
| 9 |  | AB5A | 7.4 ± 2.4 |
| 10 |  | AB9 | 1.3 ± 0.6 |
| 11 |  | AB21 | 14.9 ± 1.6 |
| 12 |  | AB22 | 7.6 ± 0.8 |
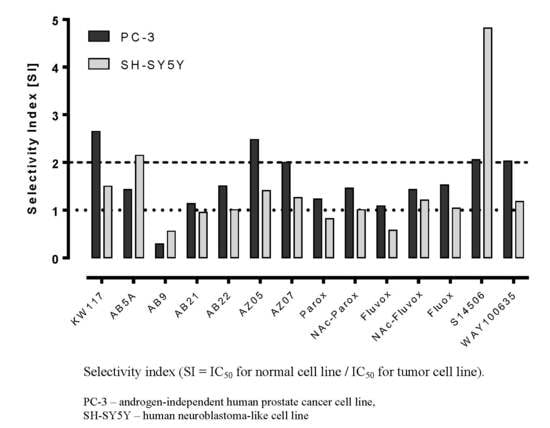
| No. | Ligand | Cells | IC50 ± SEM (µM) | Selectivity Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Fluoxetine (1) | PC-3 | 17.10 ± 1.38 * | 1.53 |
| SH-SY5Y | 25.30 ± 4.41 | 1.04 | ||
| Balb/c 3T3 | 26.20 ± 2.71 | |||
| 2. | Paroxetine (2) | PC-3 | 12.10 ± 0.37 * | 1.23 |
| SH-SY5Y | 18.10 ± 0.48 * | 0.82 | ||
| Balb/c 3T3 | 14.90 ± 0.24 | |||
| 3. | N-Ac-Paroxetine (3) | PC-3 | 45.30 ± 1.44 * | 1.46 |
| SH-SY5Y | 65.60 ± 1.01 | 1.01 | ||
| Balb/c 3T3 | 66.17 ± 2.35 | |||
| 4. | Fluvoxamine (4) | PC-3 | 47.80 ± 2.85 | 1.09 |
| SH-SY5Y | 89.40 ± 3.64 * | 0.58 | ||
| Balb/c 3T3 | 52.00 ± 5.40 | |||
| 5. | N-Ac-Fluvoxamine (5) | PC-3 | 92.23 ± 9.65 | 1.43 |
| SH-SY5Y | 112.00 ± 3.85 | 1.21 | ||
| Balb/c 3T3 | 135.95 ± 3.95 | |||
| 6. | KW117 (6) | PC-3 | 14.40 ± 1.70 * | 2.65 |
| SH-SY5Y | 25.40 ± 2.66 | 1.50 | ||
| Balb/c 3T3 | 38.10 ± 6.54 | |||
| 7. | AZ05 (7) | PC-3 | 9.85 ± 0.79 * | 2.48 |
| SH-SY5Y | 17.30 ± 1.85 * | 1.41 | ||
| Balb/c 3T3 | 24.40 ± 1.49 | |||
| 8. | AZ07 (8) | PC-3 | 5.74 ± 1.02 * | 2.00 |
| SH-SY5Y | 9.15 ± 0.74 | 1.26 | ||
| Balb/c 3T3 | 11.50 ± 0.62 | |||
| 9. | AB5A (9) | PC-3 | 27.20 ± 3.20 * | 1.43 |
| SH-SY5Y | 18.07 ± 1.68 * | 2.15 | ||
| Balb/c 3T3 | 38.90 ± 4.08 | |||
| 10. | AB9 (10) | PC-3 | 75.80 ± 6.46 * | 0.29 |
| SH-SY5Y | 39.33 ± 1.36 | 0.56 | ||
| Balb/c 3T3 | 22.20 ± 6.21 | |||
| 11. | AB21 (11) | PC-3 | 18.00 ± 1.88 | 1.14 |
| SH-SY5Y | 21.60 ± 1.07 | 0.95 | ||
| Balb/c 3T3 | 20.50 ± 3.50 | |||
| 12. | AB22 (12) | PC-3 | 23.50 ± 2.21 | 1.51 |
| SH-SY5Y | 35.00 ± 8.96 | 1.01 | ||
| Balb/c 3T3 | 35.50 ± 8.71 | |||
| 13. | 8-OH-DPAT (13) | PC-3 | n.c. | n.c. |
| SH-SY5Y | n.c. | n.c. | ||
| Balb/c 3T3 | n.c. | |||
| 14. | S14506 HCl (14) | PC-3 | 9.98 ± 1.26 * | 2.06 |
| SH-SY5Y | 4.27 ± 0.41 | 4.82 | ||
| Balb/c 3T3 | 20.60 ± 2.58 | |||
| 15. | WAY100635 (15) | PC-3 | 43.30 ± 4.05 * | 2.03 |
| SH-SY5Y | 74.30 ± 11.80 | 1.18 | ||
| Balb/c 3T3 | 88.00 ± 13.53 |
| Entry | Agonists | cAMP EC50 (M) | ERK1/2 EC50 (M) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 5-CT | 8.20 × 10−9 | 11.50 × 10−9 |
| 2. | 8-OH-DPAT | 29.30 × 10−9 | 91.00 × 10−9 |
| 3. | S14506 HCl | 25.40 × 10−12 | 62.02 × 10−12 |
| AB22 | A | 13.80 × 10−9 | |
| Paroxetine | A | 0.15 × 10−6 | |
| N-Ac-Paroxetine | A | 4.23 × 10−6 | |
| Antagonists | cAMP IC50 (M) | ERK1/2 IC50 (M) | |
| 4. | WAY100635 | 1.40 × 10−9 | 8.23 × 10−9 |
| 5. | Spiperone | 6.80 × 10−6 | 2.77 × 10−6 |
| 6. | Fluoxetine | 0.54 × 10−6 | 0.83 × 10−6 |
| 7. | KW117 | n.c. | 7.18 × 10−6 |
| 8. | AB5A | 96.90 × 10−6 | 17.90 × 10−6 |
| 9. | AB9 | 11.08 × 10−6 | 5.00 × 10−6 |
| 10. | AB21 | 2.00 × 10−9 | 0.78 × 10−6 |
| 11. | AB22 | 76.08 × 10−6 | b |
| 12. | AZ05 | 9.70 × 10−6 | 1.28 × 10−6 |
| 14. | AZ07 | 73.00 × 10−8 | 0.90 × 10−6 |
| 15. | Paroxetine | 51.10 × 10−9 | b |
| 16. | N-Ac-Paroxetine | 1.00 × 10−6 | b |
| 17. | Fluvoxamine | 8.24 × 10−6 | 10.60 × 10−6 |
| 18. | N-Ac-Fluvoxamine | 20.10 × 10−6 | 11.20 × 10−6 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Walory, J.; Mielczarek, L.; Jarończyk, M.; Koronkiewicz, M.; Kossakowski, J.; Bugno, R.; Bojarski, A.J.; Chilmonczyk, Z. Oncotoxic Properties of Serotonin Transporter Inhibitors and 5-HT1A Receptor Ligands. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103260
Walory J, Mielczarek L, Jarończyk M, Koronkiewicz M, Kossakowski J, Bugno R, Bojarski AJ, Chilmonczyk Z. Oncotoxic Properties of Serotonin Transporter Inhibitors and 5-HT1A Receptor Ligands. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(10):3260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103260
Chicago/Turabian StyleWalory, Jarosław, Lidia Mielczarek, Małgorzata Jarończyk, Mirosława Koronkiewicz, Jerzy Kossakowski, Ryszard Bugno, Andrzej J. Bojarski, and Zdzisław Chilmonczyk. 2018. "Oncotoxic Properties of Serotonin Transporter Inhibitors and 5-HT1A Receptor Ligands" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 10: 3260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103260
APA StyleWalory, J., Mielczarek, L., Jarończyk, M., Koronkiewicz, M., Kossakowski, J., Bugno, R., Bojarski, A. J., & Chilmonczyk, Z. (2018). Oncotoxic Properties of Serotonin Transporter Inhibitors and 5-HT1A Receptor Ligands. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(10), 3260. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103260