HDL-Mediated Lipid Influx to Endothelial Cells Contributes to Regulating Intercellular Adhesion Molecule (ICAM)-1 Expression and eNOS Phosphorylation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Internalization of HDL Lipids and HDL Protein
2.2. Kinetics of HDL Lipids Influx
2.3. HDL/LDL Cholesterol Competition Assays
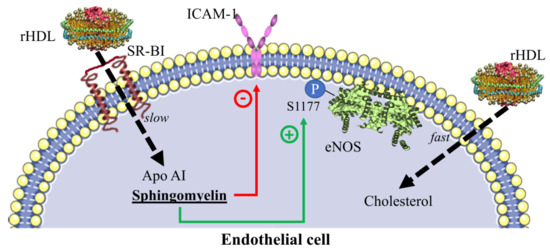
2.4. Contribution of SR-BI to HDL Internalization
2.5. Inhibition of Adhesion Molecules by rHDL
2.6. eNOS Phosphorylation in the Presence of rHDL
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Lipoprotein Isolation and Labeling
4.4. Synthesis of Reconstituted HDL (rHDL)
4.5. Inhibition of Adhesion Molecules
4.6. HDL Internalization Assay
4.7. Kinetics of HDL Lipids Influx
4.8. HDL/LDL Cholesterol Competition Assays
4.9. S1177-Phosphorylated eNOS Quantitation
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Talbot, C.P.J.; Plat, J.; Ritsch, A.; Mensink, R.P. Determinants of cholesterol efflux capacity in humans. Prog. Lipid Res. 2018, 69, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghikia, A.; Landmesser, U. High-Density Lipoproteins: Effects on Vascular Function and Role in the Immune Response. Cardiol. Clin. 2018, 36, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanoni, P.; Velagapudi, S.; Yalcinkaya, M.; Rohrer, L.; von Eckardstein, A. Endocytosis of lipoproteins. Atherosclerosis 2018, 275, 273–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, T.; Tomura, H.; Mogi, C.; Kuwabara, A.; Damirin, A.; Ishizuka, T.; Sekiguchi, A.; Ishiwara, M.; Im, D.S.; Sato, K.; et al. Role of scavenger receptor class B type I and sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors in high density lipoprotein-induced inhibition of adhesion molecule expression in endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 37457–37467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruhwurth, S.; Pavelka, M.; Bittman, R.; Kovacs, W.J.; Walter, K.M.; Rohrl, C.; Stangl, H. High-density lipoprotein endocytosis in endothelial cells. World J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 4, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohrer, L.; Ohnsorg, P.M.; Lehner, M.; Landolt, F.; Rinninger, F.; von Eckardstein, A. High-density lipoprotein transport through aortic endothelial cells involves scavenger receptor BI and ATP-binding cassette transporter G1. Circ. Res. 2009, 104, 1142–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plochberger, B.; Röhrl, C.; Preiner, J.; Rankl, C.; Brameshuber, M.; Madl, J.; Bittman, R.; Ros, R.; Sezgin, E.; Eggeling, C.; et al. HDL particles incorporate into lipid bilayers—A combined AFM and single molecule fluorescence microscopy study. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuhanna, I.S.; Zhu, Y.; Cox, B.E.; Hahner, L.D.; Osborne-Lawrence, S.; Lu, P.; Marcel, Y.L.; Anderson, R.G.; Mendelsohn, M.E.; Hobbs, H.H.; et al. High-density lipoprotein binding to scavenger receptor-BI activates endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeske, D.J.; Dietschy, J.M. Regulation of rates of cholesterol synthesis in vivo in the liver and carcass of the rat measured using [3H]water. J. Lipid Res. 1980, 21, 364–376. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saddar, S.; Carriere, V.; Lee, W.R.; Tanigaki, K.; Yuhanna, I.S.; Parathath, S.; Morel, E.; Warrier, M.; Sawyer, J.K.; Gerard, R.D.; et al. Scavenger receptor class B type I is a plasma membrane cholesterol sensor. Circ. Res. 2013, 112, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, N.R.; Cai, L.; Ziemba, K.S.; Yu, J.; Kindy, M.S.; van der Westhuyzen, D.R.; de Beer, F.C. The fate of HDL particles in vivo after SR-BI-mediated selective lipid uptake. J. Lipid Res. 2002, 43, 1890–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Helgadottir, A.; Sulem, P.; Thorgeirsson, G.; Gretarsdottir, S.; Thorleifsson, G.; Jensson, B.O.; Arnadottir, G.A.; Olafsson, I.; Eyjolfsson, G.I.; Sigurdardottir, O.; et al. Rare SCARB1 mutations associate with high-density lipoprotein cholesterol but not with coronary artery disease. Eur. Heart J. 2018, 39, 2172–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martinez-Beamonte, R.; Lou-Bonafonte, J.M.; Martinez-Gracia, M.V.; Osada, J. Sphingomyelin in high-density lipoproteins: Structural role and biological function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 7716–7741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Ramirez, M.; Madero, M.; Vargas-Alarcon, G.; Vargas-Barron, J.; Fragoso, J.M.; Rodriguez-Perez, J.M.; Martinez-Sanchez, C.; Gonzalez-Pacheco, H.; Bautista-Perez, R.; Carreon-Torres, E.; et al. HDL-sphingomyelin reduction after weight loss by an energy-restricted diet is associated with the improvement of lipid profile, blood pressure, and decrease of insulin resistance in overweight/obese patients. Clin. Chim. Acta 2016, 454, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohkawa, R.; Kurano, M.; Mishima, Y.; Nojiri, T.; Tokuhara, Y.; Kishimoto, T.; Nakamura, K.; Okubo, S.; Hosogaya, S.; Ozaki, Y.; et al. Possible involvement of sphingomyelin in the regulation of the plasma sphingosine 1-phosphate level in human subjects. Clin. Biochem. 2015, 48, 690–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barenholz, Y. Sphingomyelin and cholesterol: From membrane biophysics and rafts to potential medical applications. Subcell. Biochem. 2004, 37, 167–215. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Munoz-Vega, M.; Masso, F.; Paez, A.; Carreon-Torres, E.; Cabrera-Fuentes, H.A.; Fragoso, J.M.; Perez-Hernandez, N.; Martinez, L.O.; Najib, S.; Vargas-Alarcon, G.; et al. Characterization of immortalized human dermal microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC-1) for the study of HDL functionality. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perisa, D.; Rohrer, L.; Kaech, A.; von Eckardstein, A. Itinerary of high density lipoproteins in endothelial cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1861, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Gillard, B.K.; Gotto, A.M., Jr.; Rosales, C.; Pownall, H.J. ABCA1-Derived Nascent High-Density Lipoprotein-Apolipoprotein AI and Lipids Metabolically Segregate. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 2260–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieland, T.J.; Penman, M.; Dori, L.; Krieger, M.; Kirchhausen, T. Discovery of chemical inhibitors of the selective transfer of lipids mediated by the HDL receptor SR-BI. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15422–15427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serhan, N.; Cabou, C.; Verdier, C.; Lichtenstein, L.; Malet, N.; Perret, B.; Laffargue, M.; Martinez, L.O. Chronic pharmacological activation of P2Y13 receptor in mice decreases HDL-cholesterol level by increasing hepatic HDL uptake and bile acid secretion. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1831, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardouat, G.; Duparc, T.; Fried, S.; Perret, B.; Najib, S.; Martinez, L.O. Ectopic adenine nucleotide translocase activity controls extracellular ADP levels and regulates the F1-ATPase-mediated HDL endocytosis pathway on hepatocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2017, 1862, 832–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavelier, C.; Ohnsorg, P.M.; Rohrer, L.; von Eckardstein, A. The beta-chain of cell surface F(0)F(1) ATPase modulates apoA-I and HDL transcytosis through aortic endothelial cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hafiane, A.; Jabor, B.; Ruel, I.; Ling, J.; Genest, J. High-density lipoprotein mediated cellular cholesterol efflux in acute coronary syndromes. Am. J. Cardiol. 2014, 113, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L. A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science 1986, 232, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, J.J.; Miguel, R.; Graham, D. High density lipoprotein inhibits low density lipoprotein binding and uptake by bovine aortic endothelial cells. Angiology 1990, 41, 1065–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, J.J.; Miguel, R.; Graham, D. Competitive inhibition of LDL binding and uptake by HDL in aortic endothelial cells. J. Surg. Res. 1990, 49, 248–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaney, J.B. Reconstitution of apolipoprotein A-I from human high density lipoprotein with bovine brain sphingomyelin. J. Biol. Chem. 1983, 258, 1254–1259. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kontush, A.; Therond, P.; Zerrad, A.; Couturier, M.; Negre-Salvayre, A.; de Souza, J.A.; Chantepie, S.; Chapman, M.J. Preferential sphingosine-1-phosphate enrichment and sphingomyelin depletion are key features of small dense HDL3 particles: Relevance to antiapoptotic and antioxidative activities. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 1843–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, D.; Bhowmick, T.; Chadha, R.; Garnacho, C.; Muro, S. Intercellular adhesion molecule 1 engagement modulates sphingomyelinase and ceramide, supporting uptake of drug carriers by the vascular endothelium. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amos, C.; Romero, I.A.; Schultze, C.; Rousell, J.; Pearson, J.D.; Greenwood, J.; Adamson, P. Cross-linking of brain endothelial intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1 induces association of ICAM-1 with detergent-insoluble cytoskeletal fraction. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2001, 21, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Bartolo, B.A.; Vanags, L.Z.; Tan, J.T.; Bao, S.; Rye, K.A.; Barter, P.J.; Bursill, C.A. The apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptide, ETC-642, reduces chronic vascular inflammation in the rabbit. Lipids Health Dis. 2011, 10, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Denimal, D.; Monier, S.; Brindisi, M.C.; Petit, J.M.; Bouillet, B.; Nguyen, A.; Demizieux, L.; Simoneau, I.; Pais de Barros, J.P.; Verges, B.; et al. Impairment of the Ability of HDL From Patients With Metabolic Syndrome but Without Diabetes Mellitus to Activate eNOS: Correction by S1P Enrichment. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.Y.; Silvius, J.R. Different sphingolipids show differential partitioning into sphingolipid/cholesterol-rich domains in lipid bilayers. Biophys. J. 2000, 79, 1478–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenson, R.S.; Brewer, H.B., Jr.; Ansell, B.J.; Barter, P.; Chapman, M.J.; Heinecke, J.W.; Kontush, A.; Tall, A.R.; Webb, N.R. Dysfunctional HDL and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2016, 13, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ades, E.W.; Candal, F.J.; Swerlick, R.A.; George, V.G.; Summers, S.; Bosse, D.C.; Lawley, T.J. HMEC-1: Establishment of an immortalized human microvascular endothelial cell line. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1992, 99, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Marure, R.; Huesca-Gomez, C.; Ibarra-Sanchez, M.J.; Zentella, A.; Perez-Mendez, O. Dehydroepiandrosterone delays LDL oxidation in vitro and attenuates several oxLDL-induced inflammatory responses in endothelial cells. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Targets 2007, 6, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonas, A. Reconstitution of high-density lipoproteins. Methods Enzymol. 1986, 128, 553–582. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huesca-Gomez, C.; Carreon-Torres, E.; Nepomuceno-Mejia, T.; Sanchez-Solorio, M.; Galicia-Hidalgo, M.; Mejia, A.M.; Montano, L.F.; Franco, M.; Posadas-Romero, C.; Perez-Mendez, O. Contribution of cholesteryl ester transfer protein and lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase to HDL size distribution. Endocr. Res. 2004, 30, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muñoz-Vega, M.; Massó, F.; Páez, A.; Vargas-Alarcón, G.; Coral-Vázquez, R.; Mas-Oliva, J.; Carreón-Torres, E.; Pérez-Méndez, Ó. HDL-Mediated Lipid Influx to Endothelial Cells Contributes to Regulating Intercellular Adhesion Molecule (ICAM)-1 Expression and eNOS Phosphorylation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3394. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113394
Muñoz-Vega M, Massó F, Páez A, Vargas-Alarcón G, Coral-Vázquez R, Mas-Oliva J, Carreón-Torres E, Pérez-Méndez Ó. HDL-Mediated Lipid Influx to Endothelial Cells Contributes to Regulating Intercellular Adhesion Molecule (ICAM)-1 Expression and eNOS Phosphorylation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(11):3394. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113394
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuñoz-Vega, Mónica, Felipe Massó, Araceli Páez, Gilberto Vargas-Alarcón, Ramón Coral-Vázquez, Jaime Mas-Oliva, Elizabeth Carreón-Torres, and Óscar Pérez-Méndez. 2018. "HDL-Mediated Lipid Influx to Endothelial Cells Contributes to Regulating Intercellular Adhesion Molecule (ICAM)-1 Expression and eNOS Phosphorylation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 11: 3394. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113394
APA StyleMuñoz-Vega, M., Massó, F., Páez, A., Vargas-Alarcón, G., Coral-Vázquez, R., Mas-Oliva, J., Carreón-Torres, E., & Pérez-Méndez, Ó. (2018). HDL-Mediated Lipid Influx to Endothelial Cells Contributes to Regulating Intercellular Adhesion Molecule (ICAM)-1 Expression and eNOS Phosphorylation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(11), 3394. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113394