Developmental Expression and Functions of the Small Heat Shock Proteins in Drosophila
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Structural Features of Drosophila sHsps
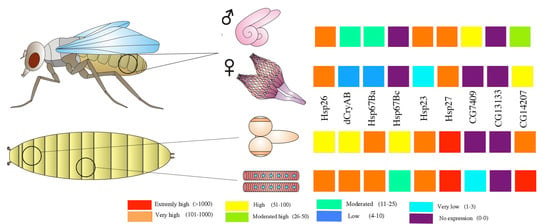
3. Developmental and Tissue-Specific Regulation of sHsps in Drosophila
4. sHsps in the Drosophila Reproductive System
4.1. Ovary
4.2. Testes
5. Functions of sHsps Expressed in the Developing Nervous System
6. Roles of sHsps Expressed in Developing Muscles
6.1. Drosophila l(2)efl/dCryAB Displays Stress-Independent Expression in Developing Larval Body Wall Muscles, and Is Required for Their Structural Integrity
6.2. Hsp67Bc Displays Evolutionarily Conserved Developmental Muscle Expression and Function
7. Concluding Remarks Conclusions?
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vos, M.J.; Carra, S.; Kanon, B.; Bosveld, F.; Klauke, K.; Sibon, O.C.M.; Kampinga, H.H. Specific protein homeostatic functions of small heat-shock proteins increase lifespan. Aging Cell 2016, 15, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raut, S.; Mallik, B.; Parichha, A.; Amrutha, V.; Sahi, C.; Kumar, V. RNAi-Mediated Reverse Genetic Screen Identified Drosophila Chaperones Regulating Eye and Neuromuscular Junction Morphology. G3 2017, 7, 2023–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrow, G.; Tanguay, R.M. Drosophila Small Heat Shock Protein: An Update on Their Features and Functions. In The Big Book on Small Heat Shock Proteins, Heat Shock Proteins 8; Tanguay, R.M., Hightower, L.E., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2015; Chapter 25; pp. 579–606. [Google Scholar]
- Arrigo, A.P.; Landry, J. Cell-specific expression and heat-shock induction of Hsps during spermatogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. In The Biology of Heat Shock Proteins and Molecular Chaperones; Morimoto, R.I., Tissieres, A., Georgopoulos, C., Eds.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 335–373. [Google Scholar]
- Michaud, S.; Marin, R.; Tanguay, R.M. Regulation of heat shock gene induction and expression during Drosophila development. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 1997, 53, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaud, S.; Morrow, G.; Marchand, J.; Tanguay, R.M. Drosophila small heat shock proteins: Cell and organelle-specific chaperones? Prog. Mol. Subcell. Biol. 2002, 28, 79–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wójtowicz, I.; Jabłońska, J.; Zmojdzian, M.; Taghli-Lamallem, O.; Renaud, Y.; Junion, G.; Daczewska, M.; Huelsmann, S.; Jagla, K.; Jagla, T. Drosophila small heat shock protein CryAB ensures structural integrity of developing muscles, and proper muscle and heart performance. Dev. Camb. Engl. 2015, 142, 994–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jabłońska, J.; Dubińska-Magiera, M.; Jagla, T.; Jagla, K.; Daczewska, M. Drosophila Hsp67Bc hot-spot variants alter muscle structure and function. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 4341–4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corces, V.; Holmgren, R.; Freund, R.; Morimoto, R.; Meselson, M. Four heat shock proteins of Drosophila melanogaster coded within a 12-kilobase region in chromosome subdivision 67B. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 5390–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingolia, T.D.; Craig, E.A. Four small Drosophila heat shock proteins are related to each other and to mammalian alpha-crystallin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 2360–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Southgate, R.; Ayme, A.; Voellmy, R. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the Drosophila small heat shock gene cluster at locus 67B. J. Mol. Biol. 1983, 165, 35–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Thonel, A.; Le Mouël, A.; Mezger, V. Transcriptional regulation of small HSP—HSF1 and beyond. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 44, 1593–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lis, J.; Wu, C. Protein traffic on the heat shock promoter: Parking, stalling, and trucking along. Cell 1993, 74, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Core, L.J.; Waterfall, J.J.; Lis, J.T. Nascent RNA Sequencing Reveals Widespread Pausing and Divergent Initiation at Human Promoters. Science 2008, 322, 1845–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomas, G.H.; Elgin, S.C. Protein/DNA architecture of the DNase I hypersensitive region of the Drosophila hsp26 promoter. EMBO J. 1988, 7, 2191–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheney, C.M.; Shearn, A. Developmental regulation of Drosophila imaginal disc proteins: Synthesis of a heat shock protein under non-heat-shock conditions. Dev. Biol. 1983, 95, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, R.S.; Meselson, M. Separate regulatory elements for the heat-inducible and ovarian expression of the Drosophila hsp26 gene. Cell 1985, 43, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, E.; Corces, V. Sequences involved in temperature and ecdysterone-induced transcription are located in separate regions of a Drosophila melanogaster heat shock gene. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1986, 6, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petko, L.; Lindquist, S. Hsp26 is not required for growth at high temperatures, nor for thermotolerance, spore development, or germination. Cell 1986, 45, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaud, S.; Marin, R.; Westwood, J.T.; Tanguay, R.M. Cell-specific expression and heat-shock induction of Hsps during spermatogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. J. Cell Sci. 1997, 110, 1989–1997. [Google Scholar]
- Michaud, S.; Tanguay, R.M. Expression of the Hsp23 chaperone during Drosophila embryogenesis: Association to distinct neural and glial lineages. BMC Dev. Biol. 2003, 3, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riddihough, G.; Pelham, H.R. Activation of the Drosophila hsp27 promoter by heat shock and by ecdysone involves independent and remote regulatory sequences. EMBO J. 1986, 5, 1653–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirotkin, K.; Davidson, N. Developmentally regulated transcription from Drosophila melanogaster chromosomal site 67B. Dev. Biol. 1982, 89, 196–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, J.L.; Petri, W.; Meselson, M. Accumulation of a specific subset of D. melanogaster heat shock mRNAs in normal development without heat shock. Cell 1983, 32, 1161–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doerwald, L.; van Rheede, T.; Dirks, R.P.; Madsen, O.; Rexwinkel, R.; van Genesen, S.T.; Martens, G.J.; de Jong, W.W.; Lubsen, N.H. Sequence and functional conservation of the intergenic region between the head-to-head genes encoding the small heat shock proteins alphaB-crystallin and HspB2 in the mammalian lineage. J. Mol. Evol. 2004, 59, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopal-Srivastava, R.; Piatigorsky, J. The murine alpha B-crystallin/small heat shock protein enhancer: Identification of alpha BE-1, alpha BE-2, alpha BE-3, and MRF control elements. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1993, 13, 7144–7152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunning, J. The Insect Ovary. Ultrastructure, Previtellogenic Growth and Evolution; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Tworzydlo, W.; Jablonska, A.; Kisiel, E.; Bilinski, S.M. Differing strategies of patterning of follicular cells in higher and lower brachycerans (Diptera: Brachycera). Genesis 2005, 43, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biggiogera, M.; Tanguay, R.M.; Marin, R.; Wu, Y.; Martin, T.E.; Fakan, S. Localization of heat shock proteins in mouse male germ cells: An immunoelectron microscopical study. Exp. Cell Res. 1996, 229, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Economou, K.; Kotsiliti, E.; Mintzas, A.C. Stage and cell-specific expression and intracellular localization of the small heat shock protein Hsp27 during oogenesis and spermatogenesis in the Mediterranean fruit fly, Ceratitis capitata. J. Insect Physiol. 2017, 96, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, R.; Valet, J.P.; Tanguay, R.M. hsp23 and hsp26 exhibit distinct spatial and temporal patterns of constitutive expression in Drosophila adults. Dev. Genet. 1993, 14, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lockwood, B.L.; Julick, C.R.; Montooth, K.L. Maternal loading of a small heat shock protein increases embryo thermal tolerance in Drosophila melanogaster. J. Exp. Biol. 2017, 220, 4492–4501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, R.; Landry, J.; Tanguay, R.M. Tissue-specific posttranslational modification of the small heat shock protein HSP27 in Drosophila. Exp. Cell Res. 1996, 223, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, R.W.; Tokuyasu, K.T.; Lindsley, D.L.; Garavito, M. The germinal proliferation center in the testis of Drosophila melanogaster. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 1979, 69, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, Y.M.; Fuller, M.T.; Jones, D.L. Signaling in stem cell niches: Lessons from the Drosophila germline. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauli, D.; Arrigo, A.P.; Vazquez, J.; Tonka, C.H.; Tissières, A. Expression of the small heat shock genes during Drosophila development: Comparison of the accumulation of hsp23 and hsp27 mRNAs and polypeptides. Genome 1989, 31, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrigo, A.P.; Tanguay, R.M. Expression of heat shock proteins during development in Drosophila. Results Probl. Cell Differ. 1991, 17, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Glaser, R.L.; Wolfner, M.F.; Lis, J.T. Spatial and temporal pattern of hsp26 expression during normal development. EMBO J. 1986, 5, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakayama, T.; Iseki, S. Specific expression of the mRNA for 25 kDA heat-shock protein in the spermatocytes of mouse seminiferous tubules. Anat. Embryol. (Berl.) 1999, 199, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adly, M.A.; Assaf, H.A.; Hussein, M.R.A. Heat shock protein 27 expression in the human testis showing normal and abnormal spermatogenesis. Cell Biol. Int. 2008, 32, 1247–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irobi, J.; Van Impe, K.; Seeman, P.; Jordanova, A.; Dierick, I.; Verpoorten, N.; Michalik, A.; De Vriendt, E.; Jacobs, A.; Van Gerwen, V.; et al. Hot-spot residue in small heat-shock protein 22 causes distal motor neuropathy. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, B.; Zhao, G.; Luo, W.; Xia, K.; Cai, F.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, F.; Liu, X.; Chen, B.; et al. Small heat-shock protein 22 mutated in autosomal dominant Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 2L. Hum. Genet. 2005, 116, 222–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparrow, J.C.; Schöck, F. The initial steps of myofibril assembly: Integrins pave the way. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huelsmann, S.; Ylänne, J.; Brown, N.H. Filopodia-like actin cables position nuclei in association with perinuclear actin in Drosophila nurse cells. Dev. Cell 2013, 26, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carra, S.; Boncoraglio, A.; Kanon, B.; Brunsting, J.F.; Minoia, M.; Rana, A.; Vos, M.J.; Seidel, K.; Sibon, O.C.M.; Kampinga, H.H. Identification of the Drosophila ortholog of HSPB8: Implication of HSPB8 loss of function in protein folding diseases. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 37811–37822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carra, S.; Seguin, S.J.; Lambert, H.; Landry, J. HspB8 chaperone activity toward poly(Q)-containing proteins depends on its association with Bag3, a stimulator of macroautophagy. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carra, S. The stress-inducible HspB8-Bag3 complex induces the eIF2alpha kinase pathway: Implications for protein quality control and viral factory degradation? Autophagy 2009, 5, 428–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jagla, T.; Dubińska-Magiera, M.; Poovathumkadavil, P.; Daczewska, M.; Jagla, K. Developmental Expression and Functions of the Small Heat Shock Proteins in Drosophila. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113441
Jagla T, Dubińska-Magiera M, Poovathumkadavil P, Daczewska M, Jagla K. Developmental Expression and Functions of the Small Heat Shock Proteins in Drosophila. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(11):3441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113441
Chicago/Turabian StyleJagla, Teresa, Magda Dubińska-Magiera, Preethi Poovathumkadavil, Małgorzata Daczewska, and Krzysztof Jagla. 2018. "Developmental Expression and Functions of the Small Heat Shock Proteins in Drosophila" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 11: 3441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113441
APA StyleJagla, T., Dubińska-Magiera, M., Poovathumkadavil, P., Daczewska, M., & Jagla, K. (2018). Developmental Expression and Functions of the Small Heat Shock Proteins in Drosophila. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(11), 3441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113441