Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Provides Novel Insight into Morphologic and Metabolic Changes in the Fat Body during Silkworm Metamorphosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
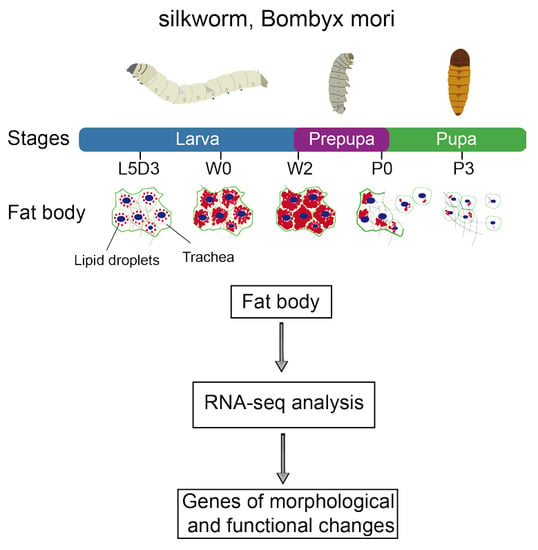
2.1. Morphological Dynamic Changes of the Fat Body and Lipid Droplets during Silkworm Metamorphosis
2.2. RNA-Seq Analysis of the Silkworm Fat Body Transcriptomes
2.3. Inventory of Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) in the Silkworm Fat Body among Different Developmental Stages
2.4. DEGs Involved in Lipid Metabolism in the Fat Body during Silkworm Metamorphosis
2.5. DEGs Involved in the Fat Body Remodeling during Silkworm Metamorphosis
2.6. Downregulation of Either Dpp or Gbb Inhibits Morphological Alteration and Promotes Lipid Mobilization in the Fat Body during Silkworm Metamorphosis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Silkworm Strain
4.2. Morphological Observation of the Silkworm Fat Body
4.3. RNA Sequencing
4.4. Data Analysis
4.5. Quantitative RT-PCR Analysis
4.6. Triacylglycerol (TAG) Measurements
4.7. Injection of Double-Stranded RNA (dsRNA)
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DEG | Differentially expressed gene |
| TAG | Triacylglycerol |
| TOR | Target of rapamycin |
| GO | Gene ontology |
| Hat | Hours after treatment |
References
- Arrese, E.L.; Soulages, J.L. Insect fat body: Energy, metabolism, and regulation. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2010, 55, 207–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, J.H.; Wells, M.A. Insects as biochemical models. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 16335–16338. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Keeley, L.L. Physiology and biochemistry of the fat body. In Comprehensive Insect Physiology, Biochemistry and Pharmacology; Kerkut, G.A., Gilbert, L.I., Eds.; Pergamon: New York, NY, USA, 1985; Volume 3, pp. 211–248. [Google Scholar]
- Mirth, C.K.; Riddiford, L.M. Size assessment and growth control: How adult size is determined in insects. Bioessays 2007, 29, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Yang, X.; Xi, Y. Fat body remodeling and homeostasis control in Drosophila. Life Sci. 2016, 167, 22–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelliot, A.; Bond, N.; Hoshizaki, D.K. Fat-body remodeling in Drosophila melanogaster. Genesis 2006, 44, 396–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubrovsky, E.B. Hormonal cross talk in insect development. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 16, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thummel, C.S. Molecular mechanisms of developmental timing in C. elegans and Drosophila. Dev. Cell 2001, 1, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, B.A.; Guo, M. Caspase-dependent cell death in Drosophila. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2006, 22, 623–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Q.; Liu, S.; Wen, D.; Cheng, Y.; Bendena, W.G.; Wang, J.; Li, S. Juvenile hormone and 20-hydroxyecdysone coordinately control the developmental timing of matrix metalloproteinase–induced fat body cell dissociation. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 21504–21516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindmo, K.; Simonsen, A.; Brech, A.; Finley, K.; Rusten, T.E.; Stenmark, H. A dual function for Deep orange in programmed autophagy in the Drosophila melanogaster fat body. Exp. Cell Res. 2006, 312, 2018–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bond, N.D.; Hoshizaki, D.K.; Gibbs, A.G. The role of 20-hydroxyecdysone signaling in Drosophila pupal metabolism. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2010, 157, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, S. Mmp1 and Mmp2 cooperatively induce Drosophila fat body cell dissociation with distinct roles. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cherbas, L.; Hu, X.; Zhimulev, I.; Belyaeva, E.; Cherbas, P. EcR isoforms in Drosophila: Testing tissue-specific requirements by targeted blockade and rescue. Development 2003, 130, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palanker, L.; Tennessen, J.M.; Lam, G.; Thummel, C.S. Drosophila HNF4 regulates lipid mobilization and β-oxidation. Cell Metab. 2009, 9, 228–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrese, E.L.; Canavoso, L.E.; Jouni, Z.E.; Pennington, J.E.; Tsuchida, K.; Wells, M.A. Lipid storage and mobilization in insects: Current status and future directions. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2001, 31, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baud, L.; Pascal, M. Annales de la nutrition et de l’alimentation. In Comparative Study of the Formation of Glycogen and Trehalose during Starvation in the Lepidoptera Bombyx mori L.; Annales de la nutrition et de l’alimentation: Paris, France, 1977; pp. 323–329. [Google Scholar]
- Kanost, M.R.; Kawooya, J.K.; Law, J.H.; Ryan, R.O.; Van Heusden, M.C.; Ziegler, R. Insect haemolymph proteins. Adv. Insect Physiol. 1990, 22, 299–396. [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto, A.; Nakato, H.; Izumi, S.; Tomino, S. Biosynthesis of major plasma proteins in the primary culture of fat body cells from the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Cell Tissue Res. 1999, 297, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, S.; Wang, S.; Jiang, R.J.; Li, S. Hormonal and nutritional regulation of insect fat body development and function. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2009, 71, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baker, K.D.; Thummel, C.S. Diabetic larvae and obese flies—Emerging studies of metabolism in Drosophila. Cell Metab. 2007, 6, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, D.E.; Hall, M.N. The expanding TOR signaling network. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2005, 17, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarbassov, D.D.; Guertin, D.A.; Ali, S.M.; Sabatini, D.M. Phosphorylation and regulation of Akt/PKB by the rictor-mTOR complex. Science 2005, 307, 1098–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, S.; Huh, J.; Hwang, I.; Kim, J.; Kim, J. Adipose Tissue Remodeling: Its Role in Energy Metabolism and Metabolic Disorders. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2016, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Wang, X.; Guo, P.; Ge, W.; Yan, Q.; Gao, W.; Xi, Y.; Yang, X. Premature remodeling of fat body and fat mobilization triggered by platelet-derived growth factor/VEGF receptor in Drosophila. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 1964–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, S.; Parton, R.G. Lipid droplets: A unified view of a dynamic organelle. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiam, A.R.; Farese, R.V., Jr.; Walther, T.C. The biophysics and cell biology of lipid droplets. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thiele, C.; Spandl, J. Cell biology of lipid droplets. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2008, 20, 378–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanley-Samuelson, D.W.; Jurenka, R.A.; Cripps, C.; Blomquist, G.J.; de Renobales, M. Fatty acids in insects: Composition, metabolism, and biological significance. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 1988, 9, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prentki, M.; Madiraju, S.M. Glycerolipid metabolism and signaling in health and disease. Endocr. Rev. 2008, 29, 647–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inagaki, S.; Yamashita, O. Metabolic shift from lipogenesis to glycogenesis in the last instar larval fat body of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. 1986, 16, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, N.; Rewitz, K.F.; O’Connor, M.B. Ecdysone control of developmental transitions: Lessons from Drosophila research. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 497–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, Y.X.; Liu, J.; Yang, C.; Feng, Q.L.; Xu, W.H. A regulatory pathway, ecdysone-transcription factor relish-cathepsin L., is involved in insect fat body dissociation. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.J.; Han, G.; Yun, H.M.; Lim, J.J.; Noh, S.; Lee, J.; Hyun, S. Steroid signaling mediates nutritional regulation of juvenile body growth via IGF-binding protein in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 5992–5997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Bubnoff, A.; Cho, K.W. Intracellular BMP signaling regulation in vertebrates: Pathway or network? Dev. Biol. 2001, 239, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballard, S.L.; Jarolimova, J.; Wharton, K.A. Gbb/BMP signaling is required to maintain energy homeostasis in Drosophila. Dev. Biol. 2010, 337, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Pertea, G.; Trapnell, C.; Pimentel, H.; Kelley, R.; Salzberg, S.L. TopHat2: Accurate alignment of transcriptomes in the presence of insertions, deletions and gene fusions. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anders, S.; Theodor Pyl, P.; Huber, W. HTSeq—A Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinform. Oxf. Engl. 2015, 31, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Feng, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X. DEGseq: An R package for identifying differentially expressed genes from RNA-seq data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 136–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolde, R. Pheatmap: Pretty Heatmaps. R Package Version 1.0.8. 2015. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=pheatmap (accessed on 11 December 2015).
- Mengjun, W.; Lei, G. TCseq: Time Course Sequencing Data Analysis. 2017. Available online: https://rdrr.io/bioc/TCseq/f/inst/doc/TCseq.pdf (accessed on 9 May 2017).







© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, J.; Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, P.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, T.; Guo, M.; Meng, M.; Zhang, T.; Qian, W.; et al. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Provides Novel Insight into Morphologic and Metabolic Changes in the Fat Body during Silkworm Metamorphosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3525. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113525
Peng J, Li Z, Yang Y, Wang P, Zhou X, Zhao T, Guo M, Meng M, Zhang T, Qian W, et al. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Provides Novel Insight into Morphologic and Metabolic Changes in the Fat Body during Silkworm Metamorphosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(11):3525. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113525
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Jian, Zheng Li, Yan Yang, Peng Wang, Xuan Zhou, Tujing Zhao, Mengpei Guo, Meng Meng, Tianlei Zhang, Wenliang Qian, and et al. 2018. "Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Provides Novel Insight into Morphologic and Metabolic Changes in the Fat Body during Silkworm Metamorphosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 11: 3525. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113525
APA StylePeng, J., Li, Z., Yang, Y., Wang, P., Zhou, X., Zhao, T., Guo, M., Meng, M., Zhang, T., Qian, W., Xia, Q., Cheng, D., & Zhao, P. (2018). Comparative Transcriptome Analysis Provides Novel Insight into Morphologic and Metabolic Changes in the Fat Body during Silkworm Metamorphosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(11), 3525. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113525