Inflammation-Accelerated Senescence and the Cardiovascular System: Mechanisms and Perspectives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Mechanisms Behind Inflammation-Accelerated Senescence
2.1. Possible Triggers to Dysfunctional Immune System at Older Age
2.1.1. Genetics
2.1.2. Infections and Dysbiosis
2.1.3. Oxidative Stress
2.2. Effects on Innate and Adaptive Immunity
3. CV Consequences of Inflamm-Aging/Immunosenescence
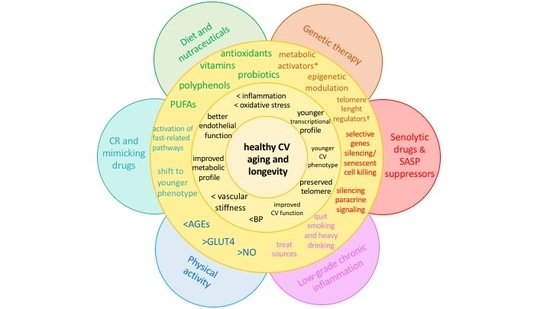
4. Strategies against Accelerated CV Aging
4.1. Diet and Nutraceuticals
4.2. Caloric Restriction and Mimicking Drugs
4.3. Senolytic Drugs and SASP Suppressors
4.4. Physical Activity
4.5. Other Potential Sources of Chronic, Low-Grade Inflammation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CVD | cardiovascular diseases |
| IL | interleukin |
| IFN | interferon |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
| TGF-β | transforming growth factor-β |
| SNPs | single nucleotide polymorphisms |
| DDRs | DNA damage response |
| mtDNA | mitochondrial DNA |
| mi-RNA | micro-RNA |
| si-RNA | short interfering RNAs |
| CMV | cytomegalovirus |
| HIV | human immunodeficiency virus |
| ROS | reactive-oxygen species |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| SOD | superoxide dismutase |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| TLRs | toll-like receptors |
| CR | caloric restriction |
| AGEs | advanced glycation end products |
References
- Franceschi, C.; Bonafè, M.; Valensin, S.; Olivieri, F.; De Luca, M.; Ottaviani, E.; De Benedictis, G. Inflamm-aging. An evolutionary perspective on immunosenescence. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 2000, 908, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.J.P.; Humphries, S.E. Cytokine and cytokine receptor gene polymorphisms and their functionality. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2009, 20, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiner, A.P.; Wurfel, M.M.; Lange, L.A.; Carlson, C.S.; Nord, A.S.; Carty, C.L.; Rieder, M.J.; Desmarais, C.; Jenny, N.S.; Iribarren, C.; et al. Polymorphisms of the IL1-receptor antagonist gene (IL1RN) are associated with multiple markers of systemic inflammation. Arterioscler Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 1407–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, K.J.; Dankwa, D.; Lee, R.; Schulze, J.; Zierath, D.; Tanzi, P.; Cain, K.; Dressel, A.; Shibata, D.; Weinstein, J. Stroke, IL-1ra, IL1RN, infection and outcome. Neurocrit Care 2014, 21, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhi, H.; Li, X.; Wei, P. Association Between 3 IL-10 Gene Polymorphisms and Cardiovascular Disease Risk: Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis and Trial Sequential Analysis. Medicine 2016, 95, e2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarwar, N.; Butterworth, A.S.; Freitag, D.F.; Gregson, J.; Willeit, P.; Gorman, D.N.; Gao, P.; Saleheen, D.; Rendon, A.; Nelson, C.P.; et al. Interleukin-6 receptor pathways in coronary heart disease: A collaborative meta-analysis of 82 studies. Lancet 2012, 379, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Swerdlow, D.I.; Holmes, M.V.; Kuchenbaecker, K.B.; Engmann, J.E.L.; Shah, T.; Sofat, R.; Guo, Y.; Chung, C.; Peasey, A.; Pfister, R.; et al. The interleukin-6 receptor as a target for prevention of coronary heart disease: A mendelian randomisation analysis. Lancet 2012, 379, 1214–1224. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mitrokhin, V.; Nikitin, A.; Brovkina, O.; Khodyrev, D.; Zotov, A.; Vachrushev, N.; Dragunov, D.; Shim, A.; Mladenov, M.; Kamkin, A. Association between interleukin-6/6R gene polymorphisms and coronary artery disease in Russian population: Influence of interleukin-6/6R gene polymorphisms on inflammatory markers. J. Inflamm. Res. 2017, 10, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnabel, R.B.; Kerr, K.F.; Lubitz, S.A.; Alkylbekova, E.L.; Marcus, G.M.; Sinner, M.F.; Magnani, J.W.; Wolf, P.A.; Deo, R.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; et al. Large-scale candidate gene analysis in whites and African Americans identifies IL6R polymorphism in relation to atrial fibrillation: The National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute’s Candidate Gene Association Resource (CARe) project. Circ. Cardiovasc Genet. 2011, 4, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, H.; Wang, C.; Sun, F.; Zhao, L.; Dun, A.; Sun, Z. Association of interleukin-6 gene polymorphism with coronary artery disease: An updated systematic review and cumulative meta-analysis. Inflamm. Res. 2015, 64, 707–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.; Kanetsky, P.; Raj, D. Genetic polymorphisms of the RAS-cytokine pathway and chronic kidney disease. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2008, 23, 1037–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kerkhof, H.J.M.; Doherty, M.; Arden, N.K.; Abramson, S.B.; Attur, M.; Bos, S.D.; Cooper, C.; Dennison, E.M.; Doherty, S.A.; Evangelou, E.; et al. Large-scale meta-analysis of interleukin-1 beta and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist polymorphisms on risk of radiographic hip and knee osteoarthritis and severity of knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2011, 19, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smith, A.J.P.; Keen, L.J.; Billingham, M.J.; Perry, M.J.; Elson, C.J.; Kirwan, J.R.; Sims, J.E.; Doherty, M.; Spector, T.D.; Bidwell, J.L. Extended haplotypes and linkage disequilibrium in the IL1R1-IL1A-IL1B-IL1RN gene cluster: Association with knee osteoarthritis. Genes Immun. 2004, 5, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marenholz, I.; Esparza-Gordillo, J.; Rüschendorf, F.; Bauerfeind, A.; Strachan, D.P.; Spycher, B.D.; Baurecht, H.; Margaritte-Jeannin, P.; Sääf, A.; Kerkhof, M.; et al. Meta-analysis identifies seven susceptibility loci involved in the atopic march. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eyre, S.; Bowes, J.; Diogo, D.; Lee, A.; Barton, A.; Martin, P.; Zhernakova, A.; Stahl, E.; Viatte, S.; McAllister, K.; et al. High-density genetic mapping identifies new susceptibility loci for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1336–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.; Bang, S.-Y.; Lee, H.-S.; Cho, S.-K.; Choi, C.-B.; Sung, Y.-K.; Kim, T.H.; Jun, J.B.; Yoo, D.H.; Kang, Y.M.; et al. High-density genotyping of immune loci in Koreans and Europeans identifies eight new rheumatoid arthritis risk loci. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, M.A.R.; Matheson, M.C.; Duffy, D.L.; Marks, G.B.; Hui, J.; Le Souëf, P.; Danoy, P.; Baltic, S.; Nyholt, D.R.; Jenkins, M.; et al. Identification of IL6R and chromosome 11q13.5 as risk loci for asthma. Lancet 2011, 378, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, L.; Liu, D.; Guo, H.; Wang, Y.; Bai, Y. Association between polymorphism in the promoter region of Interleukin 6 (-174 G/C) and risk of Alzheimer’s disease: A meta-analysis. J. Neurol. 2012, 259, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Xuan, H.; Green, C.D.; Han, Y.; Sun, N.; Shen, H.; McDermott, J.; Bennett, D.A.; Lan, F.; Han, J.J. Repression of human and mouse brain inflammaging transcriptome by broad gene-body histone hyperacetylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 7611–7616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewitt, G.; Jurk, D.; Marques, F.D.M.; Correia-Melo, C.; Hardy, T.; Gackowska, A.; Anderson, R.; Taschuk, M.; Mann, J.; Passos, J.F. Telomeres are favoured targets of a persistent DNA damage response in ageing and stress-induced senescence. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olivieri, F.; Albertini, M.C.; Orciani, M.; Ceka, A.; Cricca, M.; Procopio, A.D.; Bonafè, M. DNA damage response (DDR) and senescence: Shuttled inflamma-miRNAs on the stage of inflamm-aging. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 35509–35521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschi, C.; Garagnani, P.; Vitale, G.; Capri, M.; Salvioli, S. Inflammaging and “Garb-aging”. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 28, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiaofei, E.; Kowalik, T.F. The DNA damage response induced by infection with human cytomegalovirus and other viruses. Viruses 2014, 6, 2155–2185. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Savva, G.M.; Pachnio, A.; Kaul, B.; Morgan, K.; Huppert, F.A.; Brayne, C.; Moss, P.A. Cytomegalovirus infection is associated with increased mortality in the older population. Aging Cell 2013, 12, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.C.Y.; Leung, J.M.; Ngan, D.A.; Nashta, N.F.; Guillemi, S.; Harris, M.; Lima, V.D.; Um, S.J.; Li, Y.; Tam, S.; et al. Absolute leukocyte telomere length in HIV-infected and uninfected individuals: Evidence of accelerated cell senescence in HIV-associated chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinoza, J.L.; Minami, M. Sensing Bacterial-Induced DNA Damaging Effects Natural Killer Group 2 Member D Immune Receptor: From Dysbiosis to Autoimmunity and Carcinogenesis. Front Immunol. 2018, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Pinto, R.; Ferri, C.; Cominelli, F. Vitamin D Axis in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Role, Current Uses and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietropaoli, D.; Del Pinto, R.; Corridoni, D.; Rodriguez-Palacios, A.; Di Stefano, G.; Monaco, A.; Weinberg, A.; Cominelli, F. Occurrence of spontaneous periodontal disease in the SAMP1/YitFc murine model of Crohn disease. J. Periodontol. 2014, 85, 1799–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, H.; Thaiss, C.A.; Levy, M.; Elinav, E. The cross talk between microbiota and the immune system: Metabolites take center stage. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2014, 30, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrucci, L.; Fabbri, E. Inflammageing: Chronic inflammation in ageing, cardiovascular disease, and frailty. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 505–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, M.D.; Atay, C.; Heringer, J.; Romrig, F.K.; Schwitalla, S.; Aydin, B.; Ziegler, P.K.; Varga, J.; Reindl, W.; Pommerenke, C.; et al. High-fat-diet-mediated dysbiosis promotes intestinal carcinogenesis independently of obesity. Nature 2014, 514, 508–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jackson, S.P.; Bartek, J. The DNA-damage response in human biology and disease. Nature 2009, 461, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pietropaoli, D.; Monaco, A.; Del Pinto, R.; Cifone, M.G.; Marzo, G.; Giannoni, M. Advanced glycation end products: Possible link between metabolic syndrome and periodontal diseases. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2012, 25, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkel, T.; Holbrook, N.J. Oxidants, oxidative stress and the biology of ageing. Nature 2000, 408, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, L.; Fuehr, K. Low oxygen concentration extends the lifespan of cultured human diploid cells. Nature 1977, 267, 423–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliaccio, E.; Giorgio, M.; Mele, S.; Pelicci, G.; Reboldi, P.; Pandolfi, P.P.; Lanfrancone, L.; Pelicci, P.G. The p66shc adaptor protein controls oxidative stress response and life span in mammals. Nature 1999, 402, 309–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, A.W. Insulin Stimulates the Phosphorylation of the 66- and 52-Kilodalton Shc Isoforms by Distinct Pathways. Endocrinology 1997, 138, 2474–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valcheva, P.; Cardus, A.; Panizo, S.; Parisi, E.; Bozic, M.; Lopez Novoa, J.M.; Dusso, A.; Fernández, E.; Valdivielso, J.M. Lack of vitamin D receptor causes stress-induced premature senescence in vascular smooth muscle cells through enhanced local angiotensin-II signals. Atherosclerosis 2014, 235, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietropaoli, D.; Ortu, E.; Severino, M.; Ciarrocchi, I.; Gatto, R.; Monaco, A. Glycation and oxidative stress in the failure of dental implants: A case series. BMC Res Notes. 2013, 6, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pararasa, C.; Bailey, C.J.; Griffiths, H.R. Ageing, adipose tissue, fatty acids and inflammation. Biogerontology 2015, 16, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everitt, A.V.; Rattan, S.I.S.; Le Couteur, D.G.; De Cabo, R. (Eds.) History of Caloric Restriction, Aging and Longevity; Calorie Restriction, Aging and Longevity; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 3–14. [Google Scholar]
- Baturcam, E.; Abubaker, J.; Tiss, A.; Abu-Farha, M.; Khadir, A.; Al-Ghimlas, F.; Al-Khairi, I.; Cherian, P.; Elkum, N.; Hammad, M.; et al. Physical exercise reduces the expression of RANTES and its CCR5 receptor in the adipose tissue of obese humans. Mediators Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 627150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleeson, M.; Bishop, N.C.; Stensel, D.J.; Lindley, M.R.; Mastana, S.S.; Nimmo, M.A. The anti-inflammatory effects of exercise: Mechanisms and implications for the prevention and treatment of disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, I.; Yoshida, Y.; Minamino, T. Pathological role of adipose tissue dysfunction in cardio-metabolic disorders. Int. Heart J. 2015, 56, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abderrazak, A.; Syrovets, T.; Couchie, D.; El Hadri, K.; Friguet, B.; Simmet, T.; Rouis, M. NLRP3 inflammasome: From a danger signal sensor to a regulatory node of oxidative stress and inflammatory diseases. Redox Biol. 2015, 4, 296–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montgomery, R.R.; Shaw, A.C. Paradoxical changes in innate immunity in aging: Recent progress and new directions. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2015, 98, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molony, R.D.; Malawista, A.; Montgomery, R.R. Reduced dynamic range of antiviral innate immune responses in aging. Exp. Gerontol. 2018, 107, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Shen, H.; Schenten, D.; Shan, P.; Lee, P.J.; Goldstein, D.R. Aging enhances the basal production of IL-6 and CCL2 in vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furman, D.; Chang, J.; Lartigue, L.; Bolen, C.R.; Haddad, F.; Gaudilliere, B.; Ganio, E.A.; Fragiadakis, G.K.; Spitzer, M.H.; Douchet, I.; et al. Expression of specific inflammasome gene modules stratifies older individuals into two extreme clinical and immunological states. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kawaguchi, M.; Takahashi, M.; Hata, T.; Kashima, Y.; Usui, F.; Morimoto, H.; Izawa, A.; Takahashi, Y.; Masumoto, J.; Koyama, J.; et al. Inflammasome activation of cardiac fibroblasts is essential for myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Circulation 2011, 123, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, W.; Rao, S. Mechanisms Underlying T Cell Immunosenescence: Aging and Cytomegalovirus Infection. Front Microbiol. 2016, 7, 2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.H.; Kozlovsky, B.F.; Effros, R.B.; Grubeck-Loebenstein, B.; Edelman, R.; Sztein, M.B. Vaccination in the elderly: An immunological perspective. Trends Immunol. 2009, 30, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponnappan, S.; Ponnappan, U. Aging and immune function: Molecular mechanisms to interventions. Antioxid. Redox. Signal 2011, 14, 1551–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fumagalli, M.; d’Adda di Fagagna, F. SASPense and DDRama in cancer and ageing. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 921–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Pinto, R.; Pietropaoli, D.; Ferri, C. Diastolic blood pressure and risk profile in renal and cardiovascular diseases. Results from the SPRINT trial. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2018, 12, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townsend, R.R.; Chang, T.I.; Cohen, D.L.; Cushman, W.C.; Evans, G.W.; Glasser, S.P.; Haley, W.E.; Olney, C.; Oparil, S.; Del Pinto, R.; et al. Orthostatic changes in systolic blood pressure among SPRINT participants at baseline. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2016, 10, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ungvari, Z.; Tarantini, S.; Kiss, T.; Wren, J.D.; Giles, C.B.; Griffin, C.T.; Murfee, W.L.; Pacher, P.; Csiszar, A. Endothelial dysfunction and angiogenesis impairment in the ageing vasculature. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csiszar, A.; Labinskyy, N.; Jimenez, R.; Pinto, J.T.; Ballabh, P.; Losonczy, G.; Pearson, K.J.; de Cabo, R.; Ungvari, Z. Anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory vasoprotective effects of caloric restriction in aging: Role of circulating factors and SIRT1. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2009, 130, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van der Loo, B.; Labugger, R.; Skepper, J.N.; Bachschmid, M.; Kilo, J.; Powell, J.M.; Palacios-Callender, M.; Erusalimsky, J.D.; Quaschning, T.; Malinski, T.; et al. Enhanced peroxynitrite formation is associated with vascular aging. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 1731–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Csiszar, A.; Ungvari, Z.; Edwards, J.G.; Kaminski, P.; Wolin, M.S.; Koller, A.; Kaley, G. Aging-induced phenotypic changes and oxidative stress impair coronary arteriolar function. Circ. Res. 2002, 90, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Mital, S.; Ojaimi, C.; Csiszar, A.; Kaley, G.; Hintze, T.H. Premature death and age-related cardiac dysfunction in male eNOS-knockout mice. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2004, 37, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, P.; Liu, J.; Shan, Z.; Wu, R.; Yao, C.; Cui, J.; Zhu, X.; Wang, J.; Burnett, M.S.; Wang, S.; et al. miR-125a-5p impairs endothelial cell angiogenesis in aging mice via RTEF-1 downregulation. Aging Cell 2014, 13, 926–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ungvari, Z.; Orosz, Z.; Labinskyy, N.; Rivera, A.; Xiangmin, Z.; Smith, K.; Csiszar, A. Increased mitochondrial H2O2 production promotes endothelial NF-kappaB activation in aged rat arteries. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2007, 293, H37–H47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashi, Y.; Sukhanov, S.; Anwar, A.; Shai, S.-Y.; Delafontaine, P. Aging, atherosclerosis, and IGF-1. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2012, 67, 626–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruidavets, J.B.; Luc, G.; Machez, E.; Genoux, A.L.; Kee, F.; Arveiler, D.; Morange, P.; Woodside, J.V.; Amouyel, P.; Evans, A.; et al. Effects of insulin-like growth factor 1 in preventing acute coronary syndromes: The PRIME study. Atherosclerosis. 2011, 218, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goodman-Gruen, D.; Barrett-Connor, E. IGF-1 and ischemic heart disease in older people. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2000, 48, 860–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brugts, M.P.; van den Beld, A.W.; Hofland, L.J.; van der Wansem, K.; van Koetsveld, P.M.; Frystyk, J.; Lamberts, S.W.; Janssen, J.A. Low circulating insulin-like growth factor I bioactivity in elderly men is associated with increased mortality. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 2515–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, J.A.M.J.L.; Stolk, R.P.; Pols, H.A.P.; Grobbee, D.E.; Lamberts, S.W.J. Serum Total IGF-I, Free IGF-I, and IGFBP-1 Levels in an Elderly Population. Arterioscler Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1998, 18, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ungvari, Z.; Sonntag, W.E. Brain and cerebrovascular aging—New mechanisms and insights. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014, 69, 1307–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banki, E.; Sosnowska, D.; Tucsek, Z.; Gautam, T.; Toth, P.; Tarantini, S.; Tamas, A.; Helyes, Z.; Reglodi, D.; Sonntag, W.E.; et al. Age-related decline of autocrine pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide impairs angiogenic capacity of rat cerebromicrovascular endothelial cells. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2015, 70, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, S.F.; Zahradka, P. Vascular smooth muscle cell motility: From migration to invasion. Exp. Clin. Cardiol. 2010, 15, e75–e85. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mozos, I.; Malainer, C.; Horbańczuk, J.; Gug, C.; Stoian, D.; Luca, C.T.; Atanasov, A.G. Inflammatory Markers for Arterial Stiffness in Cardiovascular Diseases. Front Immunol. 2017, 8, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNeil, J.J.; Nelson, M.R.; Woods, R.L.; Lockery, J.E.; Wolfe, R.; Reid, C.M.; Kirpach, B.; Shah, R.C.; Ives, D.G.; Storey, E.; et al. Effect of Aspirin on All-Cause Mortality in the Healthy Elderly. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNeil, J.J.; Woods, R.L.; Nelson, M.R.; Reid, C.M.; Kirpach, B.; Wolfe, R.; Storey, E.; Shah, R.C.; Lockery, J.E.; Tonkin, A.M.; et al. Effect of Aspirin on Disability-free Survival in the Healthy Elderly. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, P.C.; Bosco, N.; Bourdet-Sicard, R.; Capuron, L.; Delzenne, N.; Doré, J.; Franceschi, C.; Lehtinen, M.J.; Recker, T.; Salvioli, S.; et al. Health relevance of the modification of low grade inflammation in ageing (inflammageing) and the role of nutrition. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 40, 95–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vauzour, D.; Camprubi-Robles, M.; Miquel-Kergoat, S.; Andres-Lacueva, C.; Bánáti, D.; Barberger-Gateau, P.; Bowman, G.L.; Caberlotto, L.; Clarke, R.; Hogervorst, E.; et al. Nutrition for the ageing brain: Towards evidence for an optimal diet. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 35, 222–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Calder, P.C.; Ahluwalia, N.; Brouns, F.; Buetler, T.; Clement, K.; Cunningham, K.; Esposito, K.; Jönsson, L.S.; Kolb, H.; Lansink, M.; et al. Dietary factors and low-grade inflammation in relation to overweight and obesity. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 106, S5–S78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrucci, L.; Cherubini, A.; Bandinelli, S.; Bartali, B.; Corsi, A.; Lauretani, F.; Martin, A.; Andres-Lacueva, C.; Senin, U.; Guralnik, J.M. Relationship of plasma polyunsaturated fatty acids to circulating inflammatory markers. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, P.C. Marine omega-3 fatty acids and inflammatory processes: Effects, mechanisms and clinical relevance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1851, 469–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zittermann, A.; Frisch, S.; Berthold, H.K.; Götting, C.; Kuhn, J.; Kleesiek, K.; Stehle, P.; Koertke, H.; Koerfer, R. Vitamin D supplementation enhances the beneficial effects of weight loss on cardiovascular disease risk markers. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 1321–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, D.; Han, S.N.; Meydani, M.; Meydani, S.N. Effect of Concomitant Consumption of Fish Oil and Vitamin E on T Cell Mediated Function in the Elderly: A Randomized Double-Blind Trial. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2006, 25, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moro-García, M.A.; Alonso-Arias, R.; Baltadjieva, M.; Fernández Benítez, C.; Fernández Barrial, M.A.; Díaz Ruisánchez, E.; Alonso Santos, R.; Alvarez Sánchez, M.; Saavedra Miján, J.; López-Larrea, C. Oral supplementation with Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus 8481 enhances systemic immunity in elderly subjects. Age 2013, 35, 1311–1326. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gude, N.A.; Broughton, K.M.; Firouzi, F.; Sussman, M.A. Cardiac ageing: Extrinsic and intrinsic factors in cellular renewal and senescence. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 523–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, J.; Yokota, T.; Ashihara, H.; Lean, M.E.J.; Crozier, A. Plant foods and herbal sources of resveratrol. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 3337–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurst, W.J.; Glinski, J.A.; Miller, K.B.; Apgar, J.; Davey, M.H.; Stuart, D.A. Survey of the trans-resveratrol and trans-piceid content of cocoa-containing and chocolate products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 8374–8378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcaín, F.J.; Villalba, J.M. Sirtuin activators. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2009, 19, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, M.; Liang, M.; Yang, X.; Xu, X.; Zou, H.; Qiu, J. Activation of Sirt1 by resveratrol inhibits TNF-α induced inflammation in fibroblasts. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, R.A.; Qin, B.; Canini, F.; Poulet, L.; Roussel, A.M. Cinnamon counteracts the negative effects of a high fat/high fructose diet on behavior, brain insulin signaling and Alzheimer-associated changes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, D.W.; George, R.C.; Scaramozzino, F.; LaPointe, N.E.; Anderson, R.A.; Graves, D.J.; Lew, J. Cinnamon Extract Inhibits Tau Aggregation Associated with Alzheimer’s Disease In Vitro. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2009, 17, 585–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastroiacovo, D.; Kwik-Uribe, C.; Grassi, D.; Necozione, S.; Raffaele, A.; Pistacchio, L.; Righetti, R.; Bocale, R.; Lechiara, M.C.; Marini, C.; et al. Cocoa flavanol consumption improves cognitive function, blood pressure control, and metabolic profile in elderly subjects: The Cocoa, Cognition, and Aging (CoCoA) Study—A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 101, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, C.J.; Choudhry, F.; Peacey, E.; Perkinton, M.S.; Richardson, J.C.; Howlett, D.R.; Lichtenthaler, S.F.; Francis, P.T.; Williams, R.J. Dietary (−)-epicatechin as a potent inhibitor of βγ-secretase amyloid precursor protein processing. Neurobiol. Aging. 2015, 36, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schroeter, H.; Heiss, C.; Balzer, J.; Kleinbongard, P.; Keen, C.L.; Hollenberg, N.K.; Sies, H.; Kwik-Uribe, C.; Schmitz, H.H.; Kelm, M. (-)-Epicatechin mediates beneficial effects of flavanol-rich cocoa on vascular function in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 1024–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bodkin, N.L.; Alexander, T.M.; Ortmeyer, H.K.; Johnson, E.; Hansen, B.C. Mortality and morbidity in laboratory-maintained Rhesus monkeys and effects of long-term dietary restriction. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2003, 58, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattison, J.A.; Colman, R.J.; Beasley, T.M.; Allison, D.B.; Kemnitz, J.W.; Roth, G.S.; Ingram, D.K.; Weindruch, R.; de Cabo, R.; Anderson, R.M. Caloric restriction improves health and survival of rhesus monkeys. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Most, J.; Tosti, V.; Redman, L.M.; Fontana, L. Calorie restriction in humans: An update. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 39, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cruzen, C.; Colman, R.J. Effects of caloric restriction on cardiovascular aging in non-human primates and humans. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2009, 25, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, L.; Meyer, T.E.; Klein, S.; Holloszy, J.O. Long-term calorie restriction is highly effective in reducing the risk for atherosclerosis in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 6659–6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stein, P.K.; Soare, A.; Meyer, T.E.; Cangemi, R.; Holloszy, J.O.; Fontana, L. Caloric restriction may reverse age-related autonomic decline in humans. Aging Cell 2012, 11, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mercken, E.M.; Crosby, S.D.; Lamming, D.W.; JeBailey, L.; Krzysik-Walker, S.; Villareal, D.T.; Capri, M.; Franceschi, C.; Zhang, Y.; Becker, K.; et al. Calorie restriction in humans inhibits the PI3K/AKT pathway and induces a younger transcription profile. Aging Cell 2013, 12, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.; Tchkonia, T.; Pirtskhalava, T.; Gower, A.C.; Ding, H.; Giorgadze, N.; Palmer, A.K.; Ikeno, Y.; Hubbard, G.B.; Lenburg, M.; et al. The Achilles’ heel of senescent cells: From transcriptome to senolytic drugs. Aging Cell 2015, 14, 644–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Tchkonia, T.; Fuhrmann-Stroissnigg, H.; Dai, H.M.; Ling, Y.Y.; Stout, M.B.; Pirtskhalava, T.; Giorgadze, N.; Johnson, K.O.; Giles, C.B.; et al. Identification of a novel senolytic agent, navitoclax, targeting the Bcl-2 family of anti-apoptotic factors. Aging Cell 2016, 15, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkland, J.L.; Tchkonia, T. Cellular Senescence: A Translational Perspective. EBioMedicine 2017, 21, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, M.; Tchkonia, T.; Ding, H.; Ogrodnik, M.; Lubbers, E.R.; Pirtskhalava, T.; White, T.A.; Johnson, K.O.; Stout, M.B.; Mezera, V.; et al. JAK inhibition alleviates the cellular senescence-associated secretory phenotype and frailty in old age. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E6301–E6310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caocci, G.; Greco, M.; Delogu, G.; Secchi, C.; Perra, A.; Ghiani, S.; Orru, F.; Vacca, A.; Galimi, F.; La Nasa, G. Ruxolitinib therapy and telomere length in myelofibrosis. Blood Cancer J. 2016, 6, e479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Higashi, Y.; Sukhanov, S.; Shai, S.-Y.; Danchuk, S.; Tang, R.; Snarski, P.; Li, Z.; Lobelle-Rich, P.; Wang, M.; Wang, D.; et al. Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 Receptor Deficiency in Macrophages Accelerates Atherosclerosis and Induces an Unstable Plaque Phenotype in Apolipoprotein E-Deficient Mice. Circulation 2016, 133, 2263–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, E.; Carrozza, C.; Capoluongo, E.; Volpe, M.; Crea, F.; Zuppi, C.; Andreotti, F. Insulin-like growth factor-1 as a vascular protective factor. Circulation 2004, 110, 2260–2265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.-S.; Kim, J. Insulin-like growth factor-1 signaling in cardiac aging. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 1931–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, S.N. Influences of cardiorespiratory fitness and other precursors on cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality in men and women. JAMA 1996, 276, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, A.; Oh, P.I.; Faulkner, G.E.; Bajaj, R.R.; Silver, M.A.; Mitchell, M.S.; Alter, D.A. Sedentary time and its association with risk for disease incidence, mortality, and hospitalization in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 162, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seals, D.R.; Kaplon, R.E.; Gioscia-Ryan, R.A.; LaRocca, T.J. You’re Only as Old as Your Arteries: Translational Strategies for Preserving Vascular Endothelial Function with Aging. Physiology 2014, 29, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fontana, L. Interventions to promote cardiometabolic health and slow cardiovascular ageing. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2018, 15, 566–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holloszy, J.O. Regulation of Mitochondrial Biogenesis and GLUT4 Expression by Exercise. Compr. Physiol. 2011, 1, 921–940. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, C.K.; Won, D.; Pruthi, S.; Lin, S.S.; Barnard, R.J. Effect of a diet and exercise intervention on oxidative stress, inflammation and monocyte adhesion in diabetic men. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2006, 73, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, C.K.; Vaziri, N.D.; Barnard, R.J. Effect of diet and exercise intervention on blood pressure, insulin, oxidative stress, and nitric oxide availability. Circulation 2002, 106, 2530–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashor, A.W.; Lara, J.; Siervo, M.; Celis-Morales, C.; Mathers, J.C. Effects of Exercise Modalities on Arterial Stiffness and Wave Reflection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanick, M.L.; Mackey, S.; Sheehan, M.; Ellsworth, N.; Haskell, W.L.; Wood, P.D. Effects of Diet and Exercise in Men and Postmenopausal Women with Low Levels of HDL Cholesterol and High Levels of LDL Cholesterol. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 339, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deldicque, L.; Atherton, P.; Patel, R.; Theisen, D.; Nielens, H.; Rennie, M.J.; Francaux, M. Effects of resistance exercise with and without creatine supplementation on gene expression and cell signaling in human skeletal muscle. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008, 104, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Öhman, H.; Savikko, N.; Strandberg, T.E.; Pitkälä, K.H. Effect of physical exercise on cognitive performance in older adults with mild cognitive impairment or dementia: A systematic review. Dement Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2014, 38, 347–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietropaoli, D.; Del Pinto, R.; Ferri, C.; Wright, J.T.; Giannoni, M.; Ortu, E.; Monaco, A. Poor oral health and blood pressure control among us hypertensive adults results from the national health and nutrition examination survey 2009 to 2014. Hypertension 2018, 72, 1365–1373. [Google Scholar]
- Poli, P.P.; Beretta, M.; Grossi, G.B.; Maiorana, C. Risk indicators related to peri-implant disease: An observational retrospective cohort study. J. Periodontal Implant. Sci. 2016, 46, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philibert, R.; Erwin, C. A Review of Epigenetic Markers of Tobacco and Alcohol Consumption. Behav. Sci. Law. 2015, 33, 675–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prasad, K.; Dhar, I.; Caspar-Bell, G. Role of Advanced Glycation End Products and Its Receptors in the Pathogenesis of Cigarette Smoke-Induced Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Angiol. 2015, 24, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rosen, A.D.; Robertson, K.D.; Hlady, R.A.; Muench, C.; Lee, J.; Philibert, R.; Horvath, S.; Kaminsky, Z.A.; Lohoff, F.W. DNA methylation age is accelerated in alcohol dependence. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djoussé, L.; Lee, I.-M.; Buring, J.E.; Gaziano, J.M. Alcohol consumption and risk of cardiovascular disease and death in women: Potential mediating mechanisms. Circulation 2009, 120, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ockene, I.S.; Miller, N.H. Cigarette smoking, cardiovascular disease, and stroke: A statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association. American Heart Association Task Force on Risk Reduction. Circulation 1997, 96, 3243–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwyer, J.T.; Coates, P.M.; Smith, M.J. Dietary Supplements: Regulatory Challenges and Research Resources. Nutrients 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Del Pinto, R.; Ferri, C. Inflammation-Accelerated Senescence and the Cardiovascular System: Mechanisms and Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123701
Del Pinto R, Ferri C. Inflammation-Accelerated Senescence and the Cardiovascular System: Mechanisms and Perspectives. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(12):3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123701
Chicago/Turabian StyleDel Pinto, Rita, and Claudio Ferri. 2018. "Inflammation-Accelerated Senescence and the Cardiovascular System: Mechanisms and Perspectives" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 12: 3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123701
APA StyleDel Pinto, R., & Ferri, C. (2018). Inflammation-Accelerated Senescence and the Cardiovascular System: Mechanisms and Perspectives. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(12), 3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123701