miR-542-5p Attenuates Fibroblast Activation by Targeting Integrin α6 in Silica-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. miR-542-5p is Decreased in Mouse Lung Tissues in a Model. of Silica-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis
2.2. miR-542-5p Attenuates Silica-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis In Vivo
2.3. miR-542-5p Inhibits the Pro-Fibrotic Effect of TGF-β1 In Vitro
2.4. miR-542-5p Inhibits Proliferation, Migration and Cell. Cycle of NIH-3T3 Cells
2.5. miR-542-5p Directly Binds to the 3’-UTR of Itga6
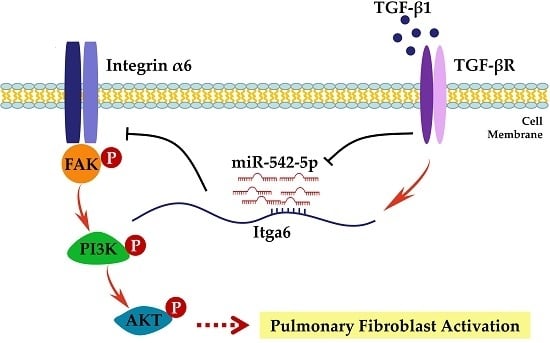
2.6. Itga6 Affects Fibroblast Activation through the FAK Signaling Pathway
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Animal Studies
4.3. Cell. Culture and Treatment
4.4. Histopathology
4.5. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.6. Western Blotting
4.7. miRNA Mimic and siRNA Transfection
4.8. Wound-Healing Assay
4.9. CCK-8 Assay
4.10. Luciferase Assays
4.11. Immunofluorescence
4.12. Cell. Cycle Assays
4.13. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cullinan, P.; Reid, P. Pneumoconiosis. Prim. Care Respir. J. 2013, 22, 249–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leung, C.C.; Tak Sun Yu, I.; Chen, W. Silicosis. Lancet 2012, 379, 2008–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, P.A.; Reid, P.T. Occupational lung disease. J. R. Coll. Phys. Edinb. 2013, 43, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steenland, K.; Ward, E. Silica: A lung carcinogen. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2014, 64, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminski, N.; Chen, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Hnizdo, E.; Sun, Y.; Su, L.; Zhang, X.; Weng, S.; Bochmann, F.; et al. Long-Term Exposure to Silica Dust and Risk of Total and Cause-Specific Mortality in Chinese Workers: A Cohort Study. PLoS Med. 2012, 9, e1001206. [Google Scholar]
- Ambros, V. microRNAs: Tiny Regulators with Great Potential. Cell 2001, 107, 823–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, E.J.; Carrington, J.C. Specialization and evolution of endogenous small RNA pathways. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 884–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Rajewsky, N. The evolution of gene regulation by transcription factors and microRNAs. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2007, 8, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Ingolia, N.T.; Weissman, J.S.; Bartel, D.P. Mammalian microRNAs predominantly act to decrease target mRNA levels. Nature 2010, 466, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stolzenburg, L.R.; Wachtel, S.; Dang, H.; Harris, A. miR-1343 attenuates pathways of fibrosis by targeting the TGF- receptors. Biochem. J. 2015, 473, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, G.; Takanashi, M.; Tanaka, M.; Fujita, K.; Ohira, T.; Kuroda, M.; Ikeda, N. Isolation of miRNAs that target EGFR mRNA in human lung cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 420, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, R.; Ji, X.; Rong, R.; Li, Y.; Yao, W.; Yuan, J.; Wu, Q.; Yang, J.; Yan, W.; Han, L.; et al. MiR-449a regulates autophagy to inhibit silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis through targeting Bcl2. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 94, 1267–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Han, L.; Yan, W.; Ji, X.; Han, R.; Yang, J.; Yuan, J.; Ni, C. miR-489 inhibits silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis by targeting MyD88 and Smad3 and is negatively regulated by lncRNA CHRF. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Shi, C.; Wang, C.; Liu, W.; Chu, Y.; Xiang, Z.; Hu, K.; Dong, P.; Han, X. The role of miR-497-5p in myofibroblast differentiation of LR-MSCs and pulmonary fibrogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ji, X.; Wu, B.; Fan, J.; Han, R.; Luo, C.; Wang, T.; Yang, J.; Han, L.; Zhu, B.; Wei, D.; et al. The Anti-fibrotic Effects and Mechanisms of MicroRNA-486-5p in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Althoff, K.; Lindner, S.; Odersky, A.; Mestdagh, P.; Beckers, A.; Karczewski, S.; Molenaar, J.J.; Bohrer, A.; Knauer, S.; Speleman, F.; et al. miR-542-3p exerts tumor suppressive functions in neuroblastoma by downregulating Survivin. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 1308–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, I.; Tivnan, A.; Bryan, K.; Foley, N.H.; Watters, K.M.; Tracey, L.; Davidoff, A.M.; Stallings, R.L. MicroRNA-542-5p as a novel tumor suppressor in neuroblastoma. Cancer Lett. 2011, 303, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramaiah, M.J.; Pushpavalli, S.N.C.V.L.; Lavanya, A.; Bhadra, K.; Haritha, V.; Patel, N.; Tamboli, J.R.; Kamal, A.; Bhadra, U.; Pal-Bhadra, M. Novel anthranilamide-pyrazolo [1,5-a]pyrimidine conjugates modulate the expression of p53-MYCN associated micro RNAs in neuroblastoma cells and cause cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 5699–5706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulte, J.H.; Marschall, T.; Martin, M.; Rosenstiel, P.; Mestdagh, P.; Schlierf, S.; Thor, T.; Vandesompele, J.; Eggert, A.; Schreiber, S.; et al. Deep sequencing reveals differential expression of microRNAs in favorable versus unfavorable neuroblastoma. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 5919–5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schulte, J.H.; Schowe, B.; Mestdagh, P.; Kaderali, L.; Kalaghatgi, P.; Schlierf, S.; Vermeulen, J.; Brockmeyer, B.; Pajtler, K.; Thor, T.; et al. Accurate prediction of neuroblastoma outcome based on miRNA expression profiles. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 2374–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, R.-Q.; Li, X.-J.; Liang, L.; Xie, Y.; Luo, D.-Z.; Ma, J.; Peng, Z.-G.; Hu, X.-H.; Chen, G. The suppressive role of miR-542-5p in NSCLC: The evidence from clinical data and in vivo validation using a chick chorioallantoic membrane model. BMC Cancer 2017, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Wang, H.; Zhou, K.; Luo, X.; Pan, X.; Shi, B.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, K.; Wang, H.M.; et al. A Novel EGFR Isoform Confers Increased Invasiveness to Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 7056–7067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, D.D.; Yu, T.; Hu, T.; Yao, M.; Fan, C.Y.; Yang, Q.C. MiR-542-5p is a negative prognostic factor and promotes osteosarcoma tumorigenesis by targeting HUWE1. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 42761–42772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lulla, R.R.; Costa, F.F.; Bischof, J.M.; Chou, P.M.; de F Bonaldo, M.; Vanin, E.F.; Soares, M.B. Identification of Differentially Expressed MicroRNAs in Osteosarcoma. Sarcoma 2011, 2011, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Faraonio, R.; Salerno, P.; Passaro, F.; Sedia, C.; Iaccio, A.; Bellelli, R.; Nappi, T.C.; Comegna, M.; Romano, S.; Salvatore, G.; et al. A set of miRNAs participates in the cellular senescence program in human diploid fibroblasts. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 19, 713–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anderson, N.A.; Campbell, I.B.; Fallon, B.J.; Lynn, S.M.; Macdonald, S.J.; Pritchard, J.M.; Procopiou, P.A.; Sollis, S.L.; Thorp, L.R. Synthesis and determination of absolute configuration of a non-peptidic alphavbeta6 integrin antagonist for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 5992–6009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagnato, G.; Irrera, N.; Pizzino, G.; Santoro, D.; Roberts, W.N.; Bagnato, G.; Pallio, G.; Vaccaro, M.; Squadrito, F.; Saitta, A.; et al. Dual alphavbeta3 And alphavbeta5 Blockade Attenuates Fibrotic And Vascular Alterations In A Murine Model Of Systemic Sclerosis. Clin. Sci. (Lond) 2018, 132, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, H.; Cambier, S.; Somanath, S.; Barker, T.; Minagawa, S.; Markovics, J.; Goodsell, A.; Publicover, J.; Reichardt, L.; Jablons, D.; et al. Mouse and human lung fibroblasts regulate dendritic cell trafficking, airway inflammation and fibrosis through integrin alphavbeta8-mediated activation of TGF-beta. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2863–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luzina, I.G.; Todd, N.W.; Nacu, N.; Lockatell, V.; Choi, J.; Hummers, L.K.; Atamas, S.P. Regulation of pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis through expression of integrins alphaVbeta3 and alphaVbeta5 on pulmonary T lymphocytes. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 1530–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatler, A.L.; Goodwin, A.T.; Gbolahan, O.; Saini, G.; Porte, J.; John, A.E.; Clifford, R.L.; Violette, S.M.; Weinreb, P.H.; Parfrey, H.; et al. Amplification of TGFbeta Induced ITGB6 Gene Transcription May Promote Pulmonary Fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerber, E.E.; Gallo, E.M.; Fontana, S.C.; Davis, E.C.; Wigley, F.M.; Huso, D.L.; Dietz, H.C. Integrin-modulating therapy prevents fibrosis and autoimmunity in mouse models of scleroderma. Nature 2013, 503, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goodwin, A.; Jenkins, G. Role of integrin-mediated TGFβ activation in the pathogenesis of pulmonary fibrosis. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2009, 37, 849–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Huang, W.; Li, K.; Zhang, K.; Lin, C.; Han, R.; Hu, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Sun, F.; et al. Metformin attenuates gefitinib-induced exacerbation of pulmonary fibrosis by inhibition of TGF-β signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 43605–43619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Danielle, L.; Peacock, B.; Luciana, P.; Schwab, R.K.; Deanna, N.P.; Aarti, S.; David, H.; Alexandra, S.; Lauren, G.; Meiyun, F.; et al. ITGA6 is directly regulated by hypoxiainducible factors and enriches for cancer stem cell activity and invasion in metastatic breast cancer models. Mol. Cancer 2016, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandova, J.; Mason, C.J.; Pawar, S.C.; Watts, G.S. Fn14 receptor promotes invasive potential and metastatic capacity of non-small lung adenocarcinoma cells through the up-regulation of integrin α6. Neoplasma 2015, 62, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Qu, J.; Huang, X.; Kurundkar, A.; Zhu, L.; Yang, N.; Venado, A.; Ding, Q.; Liu, G.; Antony, V.B.; et al. Mechanosensing by the α6-integrin confers an invasive fibroblast phenotype and mediates lung fibrosis. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alanko, J.; Ivaska, J. Endosomes: Emerging Platforms for Integrin-Mediated FAK Signalling. Trends Cell Boil. 2016, 26, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hicks-Berthet, J.; Varelas, X. Integrin-FAK-CDC42-PP1A signaling gnaws at YAP/TAZ activity to control incisor stem cells. Bioessays 2017, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carduner, L.; Picot, C.R.; Leroy-Dudal, J.; Blay, L.; Kellouche, S.; Carreiras, F. Cell cycle arrest or survival signaling through αv integrins, activation of PKC and ERK1/2 lead to anoikis resistance of ovarian cancer spheroids. Exp. Cell Res. 2014, 320, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, M.; Wilkes, M.C.; Penheiter, S.G.; Gupta, S.K.; Edens, M.; Leof, E.B. Non-Smad transforming growth factor-beta signaling regulated by focal adhesion kinase binding the p85 subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 17841–17850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horowitz, J.C.; Rogers, D.S.; Sharma, V.; Vittal, R.; White, E.S.; Cui, Z.; Thannickal, V.J. Combinatorial activation of FAK and AKT by transforming growth factor-beta1 confers an anoikis-resistant phenotype to myofibroblasts. Cell Signal. 2007, 19, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thannickal, V.J.; Lee, D.Y.; White, E.S.; Cui, Z.; Larios, J.M.; Chacon, R.; Horowitz, J.C.; Day, R.M.; Thomas, P.E. Myofibroblast Differentiation by Transforming Growth Factor-β1 Is Dependent on Cell Adhesion and Integrin Signaling via Focal Adhesion Kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 12384–12389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheaton, A.K.; Agarwal, M.; Jia, S.; Kim, K.K. Lung Epithelial Cell Focal Adhesion Kinase Signaling Inhibits Lung Injury and Fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2017, 312, L722–L730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Fan, G.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, F.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, W. Targeted inhibition of Focal Adhesion Kinase Attenuates Cardiac Fibrosis and Preserves Heart Function in Adverse Cardiac Remodeling. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, X.; Wei, T.; Liao, B.; Ai, J.; Zhou, L.; Gong, L.; Chen, Y.; He, Q.; Cheng, L.; Wang, K. Physiological stretch induced proliferation of human urothelial cells via integrin α6-FAK signaling pathway. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2018, 37, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Groups | Lesion Severity Grade | Average Severity Grade | Lesion Distribution Grade | Average Severity Grade | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| Control | 8 | 8 | ||||||||||||
| SiO2 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1.75 ± 0.89 | 6 | 2 | 1.25 ± 0.46 | |||||||
| SiO2 + miR-NC | 4 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2.12 ± 1.46 | 4 | 3 | 1 | 1.75 ± 1.04 | |||||
| SiO2 + miR-542-5p | 4 | 4 | 0.62 ± 0.52 * | 3 | 4 | 1 | 0.75 ± 0.71 * | |||||||
| Groups | Lesion Severity Grade | Average Severity Grade | Lesion Distribution Grade | Average Severity Grade | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |||
| Control | 8 | 8 | ||||||||||||
| SiO2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 3.38 ± 2.07 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 2.00 ± 1.20 | |||
| SiO2 + miR-NC | 1 | 4 | 1 | 4 | 2.63 ± 1.69 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2.75 ± 1.67 | ||
| SiO2 + miR-542-5p | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1.63 ± 1.41 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1.13 ± 0.83 * | ||||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, J.; Li, P.; Pan, H.; Li, Y.; Xu, Q.; Xu, T.; Ji, X.; Liu, Y.; Yao, W.; Han, L.; et al. miR-542-5p Attenuates Fibroblast Activation by Targeting Integrin α6 in Silica-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3717. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123717
Yuan J, Li P, Pan H, Li Y, Xu Q, Xu T, Ji X, Liu Y, Yao W, Han L, et al. miR-542-5p Attenuates Fibroblast Activation by Targeting Integrin α6 in Silica-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(12):3717. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123717
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Jiali, Ping Li, Honghong Pan, Yan Li, Qi Xu, Tiantian Xu, Xiaoming Ji, Yi Liu, Wenxi Yao, Lei Han, and et al. 2018. "miR-542-5p Attenuates Fibroblast Activation by Targeting Integrin α6 in Silica-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 12: 3717. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123717
APA StyleYuan, J., Li, P., Pan, H., Li, Y., Xu, Q., Xu, T., Ji, X., Liu, Y., Yao, W., Han, L., & Ni, C. (2018). miR-542-5p Attenuates Fibroblast Activation by Targeting Integrin α6 in Silica-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(12), 3717. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123717