Using the 6RLKu Minichromosome of Rye (Secale cereale L.) to Create Wheat-Rye 6D/6RLKu Small Segment Translocation Lines with Powdery Mildew Resistance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
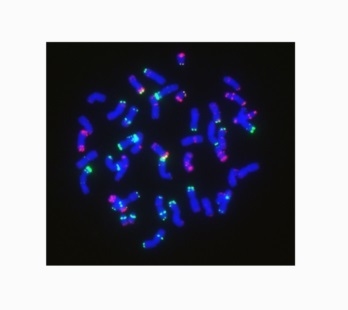
2.1. Obtaining Wheat-Rye 6RLKu Minichromosome Addition Line
2.2. Transmission of 6RLKu Minichromosome
2.3. Development of 6D/6RLKu Small Segment Translocation Lines
2.4. Transmission Rates of 6DS/6RLKumi200 and 6DL/6RLKumi119
2.5. Development of 6RLKu Minichromosome-Specific Markers
2.6. Sequence Characteristics of the Products Amplified by the 16 Markers
2.7. Powdery Mildew Resistance
3. Discussion
3.1. Extending Genetic Basis of Powdery Mildew Resistance Genes
3.2. 6RLKu Minichromosome Specific Markers
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials
4.2. Cytological Analysis
4.3. Development of 6RLKu Minichromosome-Specific PCR-Based Markers
4.4. PCR Analysis and Sequence Cloning
4.5. Powdery Mildew Resistance Test
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Friebe, B.; Heun, M.; Tuleen, N.; Zeller, F.J.; Gill, B.S. Cytogenetically monitored transfer of powdery mildew resistance from rye into wheat. Crop Sci. 1994, 34, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.H.; Sun, H.G.; Song, W.; Lu, M.; Huang, J.; Wu, L.F.; Wang, X.M.; Li, H.J. Genetic analysis and detection of the gene MlLX99 on chromosome 2BL conferring resistance to powdery mildew in the wheat cultivar Liangxing 99. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2013, 126, 3081–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, D.; Zheng, Q.; Luo, Q.; Ma, P.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Han, F.; Xu, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y. Molecular cytogenetic identification of a new wheat-rye 6R chromosome disomic addition line with powdery mildew resistance. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Zhuang, L.F.; Sun, L.; Feng, Y.G.; Pei, Z.Y.; Qi, Z.J. Allocation of a powdery mildew resistance locus to the chromosome arm 6RL of Secale cereale L. cv. ‘Jingzhouheimai’. Euphytica 2010, 176, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Ren, Z.; Chen, X.; Yan, B.; Tan, F.; Fu, T.; Tang, Z. New wheat-rye 5DS-4RS.4RL and 4RS-5DS.5DL translocation lines with powdery mildew resistance. J. Plant Res. 2014, 127, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Tang, Z.X.; Qiu, L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Tang, S.Y.; Fu, S.L. Identification and physical mapping of new PCR-based markers specific for the long arm of rye (Secale cereale L.) chromosome 6. J. Genet. Genomics 2016, 43, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.; Tang, Z.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, H. 2010 Transfer to wheat (Triticum aestivum) of small chromosome segments from rye (Secale cereale) carrying disease resistance genes. J. Appl. Genet. 2010, 51, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukaszewski, A.J. Alien Introgression in Wheat, 1st ed.; Molnár-Láng, M., Ceoloni, C., Doležel, J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Charpter 7; pp. 163–189. [Google Scholar]
- Friebe, B.; Hatchett, J.H.; Gill, B.S.; Mukai, Y.; Sebeata, E.E. Transfer of Hessian fly resistance from rye to wheat via radiation-induced terminal and intercalary chromosomal translocations. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1991, 83, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friebe, B.; Jiang, J.; Raupp, W.J.; McIntosh, R.A.; Gill, B.S. Characterization of wheat-alien translocations conferring resistance to diseases and pests: current status. Euphytica 1996, 91, 59–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, Y.; Friebe, B.; Hatchett, J.H.; Yamamoto, M.; Gill, B.S. Molecular cytogenetic analysis of radiation-induced wheat-rye terminal and intercalary chromosomal translocations and the detection of rye chromatin specifying resistance to Hessian fly. Chromosoma 1993, 102, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, E.; Schmutzer, T.; Barilar, I.; Mascher, M.; Gundlach, H.; Martis, M.M.; Twardziok, S.O.; Hackauf, B.; Gordillo, A.; Wilde, P.; et al. Towards a whole-genome sequence for rye (Secale cereale L.). Plant J. 2017, 89, 853–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.J.; Wang, X.M.; Song, F.J.; Wu, C.P.; Wu, X.F.; Zhang, N.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, X.Y. Response to powdery mildew and detection of resistance genes in wheat cultivars from China. Acta Agron. Sin. 2011, 37, 943–954, (in Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Wang, Q.L.; Wu, J.H.; Xue, W.B.; Zeng, Q.D.; Huang, L.L.; Kang, Z.S.; Han, D.J. Distribution of powdery mildew resistance gene Pm21 in Chinese winter wheat cultivars and breeding lines based on gene-specific marker. Scientia Agri. Sin. 2014, 47, 2078–2087, (in Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.H.; Chen, Y.X.; Li, D.; Wang, Z.Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, C.G.; Wang, X.C.; Zhao, H.; Cao, T.J.; Liu, Z.Y. Large scale detection of powdery mildew resistance genes in wheat via SNP and bulked segregate analysis. Acta Agron. Sin. 2018, 44, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, M.; Luo, J.; Fan, C.; Yi, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yuan, Z.; Ning, S.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, D. Introgression of powdery mildew resistance gene Pm56 on rye chromosome arm 6RS into wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dundas, I.S.; Frappell, D.E.; Crack, D.M.; Fisher, J.M. Deletion mapping of a nematode resistance gene on rye chromosome 6R in wheat. Crop Sci. 2001, 1771–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuillet, C.; Langridge, P.; Waugh, R. Cereal breeding takes a walk on the wild side. Trends Genet. 2008, 24, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tester, M.; Langridge, P. Breeding technologies to increase crop production in a changing world. Science 2010, 327, 818–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, L.; Tang, Z.X.; Li, M.; Fu, S.L. Development of new PCR-based markers specific for chromosome arms of rye (Secale cereal L.). Genome 2016, 59, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.X.; Yang, Z.J.; Fu, S.L. Oligonucleotides replacing the roles of repetitive sequences pAs1, pSc119.2, pTa-535, pTa71, CCS1, and pAWRC.1 for FISH analysis. J. Appl. Genet. 2014, 55, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.L.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Li, M.; Yang, Z.J.; Qiu, L.; Yan, B.J.; Ren, Z.L.; Tang, Z.X. Oligonucleotide probes for ND-FISH analysis to identify rye and wheat chromosomes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, F.P.; Lamb, J.C.; Birchler, A. High frequency of centromere inactivation resulting in stable dicentric chromosomes of maize. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 3238–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duan, Q.; Wang, Y.Y.; Qiu, L.; Ren, T.H.; Li, Z.; Fu, S.L.; Tang, Z.X. Physical location of new PCR-based markers and powdery mildew resistance gene(s) on rye (Secale cereale L.) chromosome 4 using 4R dissection lines. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Yu, C.; Li, Y.; Lam, T.W.; Yiu, S.M.; Kristiansen, K.; Wang, J. SOAP2: an improved ultrafast tool for short read alignment. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1966–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






| Small Segment Translocation Lines | Small Segment Translocation Chromosomes |
|---|---|
| 16T379-1 | one 6DS/6RLKumi200 and one 6DL/6RLKumi119 |
| 16T379-4 | two 6DS/6RLKumi200 and two 6DL/6RLKumi119 |
| 16T379-6 | one 6DS/6RLKumi200 and one 6DL/6RLKumi119 |
| 16T379-8 | two 6DS/6RLKumi200 and two 6DL/6RLKumi119 |
| 16T379-9 | one 6DS/6RLKumi200 and one 6DL/6RLKumi119 |
| 16T379-11 | one 6DS/6RLKumi200 and one 6DL/6RLKumi119 |
| 16T379-13 | one 6DS/6RLKumi200 and one 6DL/6RLKumi119 |
| 16T379-14 | two 6DS/6RLKumi200 and two 6DL/6RLKumi119 |
| 16T380-2 | one 6DS/6RLKumi200 and one 6DL/6RLKumi119 |
| 16T380-3 | one 6DS/6RLKumi200 and one 6DL/6RLKumi119 |
| Marker | Forward (5′-3′) | Reverse (5′-3′) | GenBank Accession Number of Amplified Sequence | Similarity of Amplified Sequence with the S. cereale Lo7 Scaffolds |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6RL-M8 | CAACCTATTCGGACCAGAGC | GATTAAACCGCTGGTGAGAAAC | MK051036 | 99% similarity with 7794–8206 bp of Lo7_v2_scaffold_453717 6R |
| 6RL-M11 | GGGGGAACTTTGAGTATGCTT | GATCGGATCGGTTGAGTTGT | MK051037 | 99% similarity with 464–1239 bp of Lo7_v2_scaffold_651086 0R |
| 6RL-M55 | TGATGCAAGTTCGTTGGTGT | CGTTGACTCCCTTCCGTTAG | MK051038 | 91% similarity with 1–108 bp of Lo7_v2_scaffold_457844 6R |
| 6RL-M63 | TCGAAATGCATCGGACAAT | TCCATGGTCTCCTCGAGTGT | MK051039 | 100% similarity with 144–422 bp of Lo7_v2_scaffold_492428 6R |
| 6RL-M102 | CGGGAGAGGACTGGTTCTT | CATATGTACAACAGAGGCATCTTC | MK051040 | 98% similarity with 26957–27168 bp, 27841-27881 bp and 27923-28047 bp of Lo7_v2_scaffold_445202 6R |
| 6RL-M118 | TCCCCCTTCTAGGGTTTCAT | ATAGCCCCATCTGCAAACAC | MK051041 | 100% similarity with 488–896 bp of Lo7_v2_scaffold_484582 6R |
| 6RL-M149 | AATGGCTGCAATTTCTTGGA | AAAAAGCCACAAAACACTGC | MK051042 | 100% similarity with 34805–34422 bp of Lo7_v2_scaffold_445202 6R |
| 6RL-M220 | GCACAAGTCCATGTCCTTCA | GATCCATCTGGCTGTGTGTG | MK051043 | 99% similarity with 4112–4449 bp of Lo7_v2_scaffold_448816 6R |
| 6RL-M221 | CGCTATATGCAATGCAGGTG | CTTGCTTGCAACACCAAAAA | MK051044 | 98% similarity with 41511–41912 bp of Lo7_v2_scaffold_445202 6R |
| 6RL-M255 | CCTTATGACCACCCATGCTC | TTCATAGCTGCCTCTTTTAGGTG | MK051045 | 99% similarity with 31812–32230 bp of Lo7_v2_scaffold_445202 6R |
| 6RL-M710 | CAAACTCACACGAAGCCAAA | CTGATCCAAATTTGCCCAGT | MK051046 | 92% similarity with 3600–3681 bp of Lo7_v2_scaffold_457146 6R |
| 6RL-M828 | TTTGTCGAGAGCAACAATGG | CCCGCTTCTAAGTTCAATCG | MK051047 | 100% similarity with 39318–39668 bp of Lo7_v2_scaffold_445202 6R |
| 6RL-M869 | GGGTCAACCCATCTTGTTTC | CCTCTTCCACTGCAGAGCTT | MK051048 | 99% similarity with 589–962 bp of Lo7_v2_scaffold_451612 6R |
| 6RL-M896 | GACGAAACACAACAAATCATTCA | GGGAAAATCGAAAACTGCAA | MK051049 | 100% similarity with 10161–10344 bp of Lo7_v2_scaffold_620512 0R |
| 6RL-M1074 | AAAGCCGATGAAAAATGGTG | GAAGAAGAAGAAGATGGGGTGTT | MK051050 | 100% similarity with 9159–9365 bp of Lo7_v2_scaffold_445253 6R |
| 6RL-M1081 | TTGCATGCTCGCTTTAGTTG | CCACTTGACGTTGCCCTATT | MK051051 | 100% similarity with 8940–9193 bp of Lo7_v2_scaffold_445253 6R |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, H.; Tang, Z.; Duan, Q.; Tang, S.; Fu, S. Using the 6RLKu Minichromosome of Rye (Secale cereale L.) to Create Wheat-Rye 6D/6RLKu Small Segment Translocation Lines with Powdery Mildew Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123933
Du H, Tang Z, Duan Q, Tang S, Fu S. Using the 6RLKu Minichromosome of Rye (Secale cereale L.) to Create Wheat-Rye 6D/6RLKu Small Segment Translocation Lines with Powdery Mildew Resistance. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(12):3933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123933
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Haimei, Zongxiang Tang, Qiong Duan, Shuyao Tang, and Shulan Fu. 2018. "Using the 6RLKu Minichromosome of Rye (Secale cereale L.) to Create Wheat-Rye 6D/6RLKu Small Segment Translocation Lines with Powdery Mildew Resistance" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 12: 3933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123933
APA StyleDu, H., Tang, Z., Duan, Q., Tang, S., & Fu, S. (2018). Using the 6RLKu Minichromosome of Rye (Secale cereale L.) to Create Wheat-Rye 6D/6RLKu Small Segment Translocation Lines with Powdery Mildew Resistance. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(12), 3933. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123933