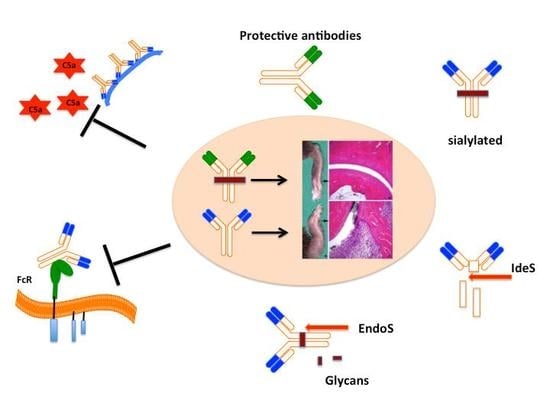
Targeting IgG in Arthritis: Disease Pathways and Therapeutic Avenues
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. CII-Specific Antibodies
3. COMP-Specific Antibodies
4. Anti-GPI Antibodies
5. Immune-Complex Mediated Arthritis
6. Anti-Citrullinated Peptide/Protein Antibodies
7. Antibody Induced Pain
8. Protective Autoantibodies
9. Targeting IgG to Treat Antibody Dependent Pathologies
10. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Orr, C.; Vieira-Sousa, E.; Boyle, D.L.; Buch, M.H.; Buckley, C.D.; Cañete, J.D.; Catrina, A.I.; Choy, E.H.S.; Emery, P.; Fearon, U.; et al. Synovial tissue research: A state-of-the-art review. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 463–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firestein, G.S.; McInnes, I.B. Immunopathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Immunity 2017, 46, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McInnes, I.B.; Schett, G. Pathogenetic insights from the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2017, 389, 2328–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raychaudhuri, S.; Sandor, C.; Stahl, E.A.; Freudenberg, J.; Lee, H.-S.; Jia, X.; Alfredsson, L.; Padyukov, L.; Klareskog, L.; Worthington, J.; et al. Five amino acids in three HLA proteins explain most of the association between MHC and seropositive rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 291–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McInnes, I.B.; Buckley, C.D.; Isaacs, J.D. Cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis—Shaping the immunological landscape. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, F.; Chan, A.C. B cell immunobiology in disease: Evolving concepts from the clinic. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 24, 467–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiner, G.; Smolen, J. Autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis and their clinical significance. Arthritis Res. 2002, 4 (Suppl. 2), S1–S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Yang, F.; Huang, C.; Huang, J.; Wang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Du, Y.; Zhao, L.; Gao, M.; Wang, F. Plasmapheresis therapy in combination with TNF-α inhibitor and DMARDs: A multitarget method for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2017, 27, 576–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, J.L.; Takase-Minegishi, K.; Ramiro, S.; Chatzidionysiou, K.; Smolen, J.S.; van der Heijde, D.; Bijlsma, J.W.; Burmester, G.R.; Dougados, M.; Scholte-Voshaar, M.; et al. Efficacy of biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: A systematic literature review informing the 2016 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1113–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmdahl, R.; Andersson, M.; Goldschmidt, T.J.; Gustafsson, K.; Jansson, L.; Mo, J.A. Type II collagen autoimmunity in animals and provocations leading to arthritis. Immunol. Rev. 1990, 118, 193–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensson, L.; Jirholt, J.; Holmdahl, R.; Jansson, L. B cell-deficient mice do not develop type II collagen-induced arthritis (CIA). Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1998, 111, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corthay, A.; Johansson, A.; Vestberg, M.; Holmdahl, R. Collagen-induced arthritis development requires alpha beta T cells but not gamma delta T cells: Studies with T cell-deficient (TCR mutant) mice. Int. Immunol. 1999, 11, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wooley, P.H.; Luthra, H.S.; Griffiths, M.M.; Stuart, J.M.; Huse, A.; David, C.S. Type II collagen-induced arthritis in mice. IV. Variations in immunogenetic regulation provide evidence for multiple arthritogenic epitopes on the collagen molecule. J. Immunol. 1985, 135, 2443–2451. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nabozny, G.H.; Baisch, J.M.; Cheng, S.; Cosgrove, D.; Griffiths, M.M.; Luthra, H.S.; David, C.S. HLA-DQ8 transgenic mice are highly susceptible to collagen-induced arthritis: A novel model for human polyarthritis. J. Exp. Med. 1996, 183, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosloniec, E.F.; Brand, D.D.; Myers, L.K.; Whittington, K.B.; Gumanovskaya, M.; Zaller, D.M.; Woods, A.; Altmann, D.M.; Stuart, J.M.; Kang, A.H. An HLA-DR1 transgene confers susceptibility to collagen-induced arthritis elicited with human type II collagen. J. Exp. Med. 1997, 185, 1113–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, E.C.; Hansen, B.E.; Jacobsen, H.; Madsen, L.S.; Andersen, C.B.; Engberg, J.; Rothbard, J.B.; McDevitt, G.S.; Malmström, V.; Holmdahl, R.; et al. Definition of MHC and T cell receptor contacts in the HLA-DR4restricted immunodominant epitope in type II collagen and characterization of collagen-induced arthritis in HLA-DR4 and human CD4 transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 7574–7579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaëlsson, E.; Andersson, M.; Engström, A.; Holmdahl, R. Identification of an immunodominant type-II collagen peptide recognized by T cells in H-2q mice: Self tolerance at the level of determinant selection. Eur. J. Immunol. 1992, 22, 1819–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosloniec, E.F.; Whittington, K.B.; Brand, D.D.; Myers, L.K.; Stuart, J.M. Identification of MHC class II and TCR binding residues in the type II collagen immunodominant determinant mediating collagen-induced arthritis. Cell. Immunol. 1996, 172, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, L.E.; Berling, J.S. Structural requirements for recognition of a type II collagen peptide by murine T cell hybridomas. Cell. Immunol. 1994, 153, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaëlsson, E.; Broddefalk, J.; Engström, A.; Kihlberg, J.; Holmdahl, R. Antigen processing and presentation of a naturally glycosylated protein elicits major histocompatibility complex class II-restricted, carbohydrate-specific T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 1996, 26, 1906–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaëlsson, E.; Malmström, V.; Reis, S.; Engström, A.; Burkhardt, H.; Holmdahl, R. T cell recognition of carbohydrates on type II collagen. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 180, 745–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corthay, A.; Bäcklund, J.; Broddefalk, J.; Michaëlsson, E.; Goldschmidt, T.J.; Kihlberg, J.; Holmdahl, R. Epitope glycosylation plays a critical role for T cell recognition of type II collagen in collagen-induced arthritis. Eur. J. Immunol. 1998, 28, 2580–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.A.; Bona, C.A.; Holmdahl, R. Variable region gene selection of immunoglobulin G-expressing B cells with specificity for a defined epitope on type II collagen. Eur. J. Immunol. 1993, 23, 2503–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, D.; Khmaladze, I.; Jia, H.; Bajtner, E.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Blom, T.; Mo, J.A.; Holmdahl, R. Pathogenic autoreactive B cells are not negatively selected toward matrix protein collagen II. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 4451–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trentham, D.E.; Townes, A.S.; Kang, A.H. Autoimmunity to type II collagen an experimental model of arthritis. J. Exp. Med. 1977, 146, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terato, K.; Hasty, K.A.; Cremer, M.A.; Stuart, J.M.; Townes, A.S.; Kang, A.H. Collagen-induced arthritis in mice. Localization of an arthritogenic determinant to a fragment of the type II collagen molecule. J. Exp. Med. 1985, 162, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuart, J.M.; Dixon, F.J. Serum transfer of collagen-induced arthritis in mice. J. Exp. Med. 1983, 158, 378–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Kristan, J.; Hao, L.; Lenkoski, C.S.; Shen, Y.; Matis, L.A. A role for complement in antibody-mediated inflammation: C5-deficient DBA/1 mice are resistant to collagen-induced arthritis. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 4340–4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajtner, E.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Engström, A.; Holmdahl, R. Chronic development of collagen-induced arthritis is associated with arthritogenic antibodies against specific epitopes on type II collagen. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2005, 7, R1148–R1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindh, I.; Snir, O.; Lönnblom, E.; Uysal, H.; Andersson, I.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Vierboom, M.; ’t Hart, B.; Malmström, V.; Holmdahl, R. Type II collagen antibody response is enriched in the synovial fluid of rheumatoid joints and directed to the same major epitopes as in collagen induced arthritis in primates and mice. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, R143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Plows, D.; Kontogeorgos, G.; Kollias, G. Mice lacking mature T and B lymphocytes develop arthritic lesions after immunization with type II collagen. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 1018–1023. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mo, J.A.; Holmdahl, R. The B cell response to autologous type II collagen: Biased V gene repertoire with V gene sharing and epitope shift. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 2440–2448. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nandakumar, K.S.; Lindqvist, A.-K.B.; Holmdahl, R. A dominant suppressive MHC class II haplotype interacting with autosomal genes controls autoantibody production and chronicity of arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 1664–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Förster, M.; Raposo, B.; Ekman, D.; Klaczkowska, D.; Popovic, M.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Lindvall, T.; Hultqvist, M.; Teneva, I.; Johannesson, M.; et al. Genetic control of antibody production during collagen-induced arthritis development in heterogeneous stock mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 3594–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raposo, B.; Dobritzsch, D.; Ge, C.; Ekman, D.; Xu, B.; Lindh, I.; Förster, M.; Uysal, H.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Schneider, G.; et al. Epitope-specific antibody response is controlled by immunoglobulin V(H) polymorphisms. J. Exp. Med. 2014, 211, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludwig, R.J.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; Leypoldt, F.; Kaya, Z.; Bieber, K.; McLachlan, S.M.; Komorowski, L.; Luo, J.; Cabral-Marques, O.; Hammers, C.M.; et al. Mechanisms of Autoantibody-Induced Pathology. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmdahl, R.; Jansson, L.; Larsson, A.; Jonsson, R. Arthritis in DBA/1 mice induced with passively transferred type II collagen immune serum. Immunohistopathology and serum levels of anti-type II collagen auto-antibodies. Scand. J. Immunol. 1990, 31, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wooley, P.H.; Luthra, H.S.; Singh, S.K.; Huse, A.R.; Stuart, J.M.; David, C.S. Passive transfer of arthritis to mice by injection of human anti-type II collagen antibody. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1984, 59, 737–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkova, S.B.; Konstantinov, K.N.; Sproule, T.J.; Lyons, B.L.; Awwami, M.A.; Roopenian, D.C. Human antibodies induce arthritis in mice deficient in the low-affinity inhibitory IgG receptor Fc gamma RIIB. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terato, K.; Hasty, K.A.; Reife, R.A.; Cremer, M.A.; Kang, A.H.; Stuart, J.M. Induction of arthritis with monoclonal antibodies to collagen. J. Immunol. 1992, 148, 2103–2108. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Terato, K.; Harper, D.S.; Griffiths, M.M.; Hasty, D.L.; Ye, X.J.; Cremer, M.A.; Seyer, J.M. Collagen-induced arthritis in mice: Synergistic effect of E. coli lipopolysaccharide bypasses epitope specificity in the induction of arthritis with monoclonal antibodies to type II collagen. Autoimmunity 1995, 22, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandakumar, K.S.; Svensson, L.; Holmdahl, R. Collagen type II-specific monoclonal antibody-induced arthritis in mice: Description of the disease and the influence of age, sex, and genes. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 163, 1827–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandakumar, K.S.; Holmdahl, R. Efficient promotion of collagen antibody induced arthritis (CAIA) using four monoclonal antibodies specific for the major epitopes recognized in both collagen induced arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. J. Immunol. Methods 2005, 304, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutamekalin, P.; Saito, T.; Yamaki, K.; Mizutani, N.; Brand, D.D.; Waritani, T.; Terato, K.; Yoshino, S. Collagen antibody-induced arthritis in mice: Development of a new arthritogenic 5-clone cocktail of monoclonal anti-type II collagen antibodies. J. Immunol. Methods 2009, 343, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandakumar, K.S.; Andrén, M.; Martinsson, P.; Bajtner, E.; Hellström, S.; Holmdahl, R.; Kleinau, S. Induction of arthritis by single monoclonal IgG anti-collagen type II antibodies and enhancement of arthritis in mice lacking inhibitory Fcgamma RIIB. Eur. J. Immunol. 2003, 33, 2269–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.-K.; Kang, S.-M.; Paik, D.-J.; Kim, J.M.; Youn, J. Essential roles of Toll-like receptor-4 signaling in arthritis induced by type II collagen antibody and LPS. Int. Immunol. 2005, 17, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelkka, T.; Hultqvist, M.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Holmdahl, R. Enhancement of antibody-induced arthritis via Toll-like receptor 2 stimulation is regulated by granulocyte reactive oxygen species. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 181, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagari, T.; Doi, H.; Shimozato, T. The importance of IL-1 beta and TNF-alpha, and the noninvolvement of IL-6, in the development of monoclonal antibody-induced arthritis. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandakumar, K.S.; Bäcklund, J.; Vestberg, M.; Holmdahl, R. Collagen type II (CII)-specific antibodies induce arthritis in the absence of T or B cells but the arthritis progression is enhanced by CII-reactive T cells. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2004, 6, R544–R550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Fathman, J.W.; Lugo-Villarino, G.; Scimone, L.; von Andrian, U.; Dorfman, D.M.; Glimcher, L.H. Transcription factor T-bet regulates inflammatory arthritis through its function in dendritic cells. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitamura, M.; Nakano, N.; Yonekawa, T.; Shan, L.; Kaise, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Yamashita, K.; Kikkawa, H.; Kinoshita, M. T cells are involved in the development of arthritis induced by anti-type II collagen antibody. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2007, 7, 1360–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-S.; Oh, Y.; Park, O.; Foss, C.A.; Lim, S.M.; Jo, D.-G.; Na, D.H.; Pomper, M.G.; Lee, K.C.; Lee, S. PEGylated TRAIL ameliorates experimental inflammatory arthritis by regulation of Th17 cells and regulatory T cells. J. Control. Release 2017, 267, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensson, L.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Johansson, A.; Jansson, L.; Holmdahl, R. IL-4-deficient mice develop less acute but more chronic relapsing collagen-induced arthritis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2002, 32, 2944–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandakumar, K.S.; Holmdahl, R. Arthritis induced with cartilage-specific antibodiesis IL-4-dependent. Eur. J. Immunol. 2006, 36, 1608–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, A.C.; Hansson, A.S.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Bäcklund, J.; Holmdahl, R. IL-10-deficient B10.Q mice develop more severe collagen-induced arthritis, but are protected from arthritis induced with anti-type II collagen antibodies. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 3505–3512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hietala, M.A.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Person, L.; Fahlen, S.; Holmdahl, R.; Pekna, M. Complement activation by both classical and alternative pathways is critical for the effector phase of arthritis. Mol. Immunol. 2003, 40, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banda, N.K.; Thurman, J.M.; Kraus, D.; Wood, A.; Carroll, M.C.; Arend, W.P.; Holers, V.M. Alternative complement pathway activation is essential for inflammation and joint destruction in the passive transfer model of collagen-induced arthritis. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 1904–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banda, N.K.; Levitt, B.; Glogowska, M.J.; Thurman, J.M.; Takahashi, K.; Stahl, G.L.; Tomlinson, S.; Arend, W.P.; Holers, V.M. Targeted inhibition of the complement alternative pathway with complement receptor 2 and factor H attenuates collagen antibody-induced arthritis in mice. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 5928–5937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banda, N.K.; Hyatt, S.; Antonioli, A.H.; White, J.T.; Glogowska, M.; Takahashi, K.; Merkel, T.J.; Stahl, G.L.; Mueller-Ortiz, S.; Wetsel, R.; et al. Role of C3a receptors, C5a receptors, and complement protein C6 deficiency in collagen antibody-induced arthritis in mice. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 1469–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banda, N.K.; Mehta, G.; Ferreira, V.P.; Cortes, C.; Pickering, M.C.; Pangburn, M.K.; Arend, W.P.; Holers, V.M. Essential role of surface-bound complement factor H in controlling immune complex-induced arthritis. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 3560–3569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banda, N.K.; Acharya, S.; Scheinman, R.I.; Mehta, G.; Takahashi, M.; Endo, Y.; Zhou, W.; Farrar, C.A.; Sacks, S.H.; Fujita, T.; et al. Deconstructing the Lectin Pathway in the Pathogenesis of Experimental Inflammatory Arthritis: Essential Role of the Lectin Ficolin B and Mannose-Binding Protein-Associated Serine Protease 2. J. Immunol. 2017, 199, 1835–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerard, C.; Gerard, N.P. C5A anaphylatoxin and its seven transmembrane-segment receptor. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1994, 12, 775–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jose, P.J.; Moss, I.K.; Maini, R.N.; Williams, T.J. Measurement of the chemotactic complement fragment C5a in rheumatoid synovial fluids by radioimmunoassay: Role of C5a in the acute inflammatory phase. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1990, 49, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heller, T.; Hennecke, M.; Baumann, U.; Gessner, J.E.; zu Vilsendorf, A.M.; Baensch, M.; Boulay, F.; Kola, A.; Klos, A.; Bautsch, W.; et al. Selection of a C5a receptor antagonist from phage libraries attenuating the inflammatory response in immune complex disease and ischemia/reperfusion injury. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Woodruff, T.M.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Tedesco, F. Inhibiting the C5-C5a receptor axis. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 48, 1631–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandakumar, K.S.; Jansson, Å.; Xu, B.; Rydell, N.; Blom, A.M. A Recombinant Vaccine Effectively Induces C5a-Specific Neutralizing Antibodies and Prevents Arthritis. PLoS ONE 2010, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macor, P.; Durigutto, P.; De Maso, L.; Garrovo, C.; Biffi, S.; Cortini, A.; Fischetti, F.; Sblattero, D.; Pitzalis, C.; Marzari, R.; et al. Treatment of experimental arthritis by targeting synovial endothelium with a neutralizing recombinant antibody to C5. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 2559–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shushakova, N.; Skokowa, J.; Schulman, J.; Baumann, U.; Zwirner, J.; Schmidt, R.E.; Gessner, J.E. C5a anaphylatoxin is a major regulator of activating versus inhibitory FcgammaRs in immune complex-induced lung disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 1823–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagari, T.; Tanaka, D.; Doi, H.; Shimozato, T. Essential role of Fc gamma receptors in anti-type II collagen antibody-induced arthritis. J. Immunol. 2003, 170, 4318–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan Sardjono, C.; Mottram, P.L.; van de Velde, N.C.; Powell, M.S.; Power, D.; Slocombe, R.F.; Wicks, I.P.; Campbell, I.K.; McKenzie, S.E.; Brooks, M.; et al. Development of spontaneous multisystem autoimmune disease and hypersensitivity to antibody-induced inflammation in Fcgamma receptor IIa-transgenic mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 3220–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-H.; Romain, G.; Yan, W.; Watanabe, M.; Charab, W.; Todorova, B.; Lee, J.; Triplett, K.; Donkor, M.; Lungu, O.I.; et al. IgG Fc domains that bind C1q but not effector Fcγ receptors delineate the importance of complement-mediated effector functions. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quigg, R.J.; Lim, A.; Haas, M.; Alexander, J.J.; He, C.; Carroll, M.C. Immune complex glomerulonephritis in C4- and C3-deficient mice. Kidney Int. 1998, 53, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjelm, F.; Carlsson, F.; Getahun, A.; Heyman, B. Antibody-mediated regulation of the immune response. Scand. J. Immunol. 2006, 64, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawlisch, H.; Belkaid, Y.; Baelder, R.; Hildeman, D.; Gerard, C.; Köhl, J. C5a negatively regulates toll-like receptor 4-induced immune responses. Immunity 2005, 22, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandakumar, K.S.; Holmdahl, R. Antibody-induced arthritis: Disease mechanisms and genes involved at the effector phase of arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowley, M.J.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Holmdahl, R. The role of collagen antibodies in mediating arthritis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2008, 18, 429–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandakumar, K.S. Pathogenic antibody recognition of cartilage. Cell Tissue Res. 2010, 339, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandakumar, K.S.; Holmdahl, R. Therapeutic cleavage of IgG: New avenues for treating inflammation. Trends Immunol. 2008, 29, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amirahmadi, S.F.; Pho, M.H.; Gray, R.E.; Crombie, D.E.; Whittingham, S.F.; Zuasti, B.B.; van Damme, M.-P.; Rowley, M.J. An arthritogenic monoclonal antibody to type II collagen, CII-C1, impairs cartilage formation by cultured chondrocytes. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2004, 82, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, R.E.; Seng, N.; Mackay, I.R.; Rowley, M.J. Measurement of antibodies to collagen II by inhibition of collagen fibril formation in vitro. J. Immunol. Methods 2004, 285, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amirahmadi, S.F.; Whittingham, S.; Crombie, D.E.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Holmdahl, R.; Mackay, I.R.; van Damme, M.-P.; Rowley, M.J. Arthritogenic anti-type II collagen antibodies are pathogenic for cartilage-derived chondrocytes independent of inflammatory cells. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 1897–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crombie, D.E.; Turer, M.; Zuasti, B.B.; Wood, B.; McNaughton, D.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Holmdahl, R.; van Damme, M.-P.; Rowley, M.J. Destructive effects of murine arthritogenic antibodies to type II collagen on cartilage explants in vitro. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2005, 7, R927–R937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croxford, A.M.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Holmdahl, R.; Tobin, M.J.; McNaughton, D.; Rowley, M.J. Chemical changes demonstrated in cartilage by synchrotron infrared microspectroscopy in an antibody-induced murine model of rheumatoid arthritis. J. Biomed. Opt. 2011, 16, 066004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croxford, A.M.; Whittingham, S.; McNaughton, D.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Holmdahl, R.; Rowley, M.J. Type II collagen–specific antibodies induce cartilage damage in mice independent of inflammation. Arthritis Rheum. 2013, 65, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandakumar, K.S.; Bajtner, E.; Hill, L.; Böhm, B.; Rowley, M.J.; Burkhardt, H.; Holmdahl, R. Arthritogenic antibodies specific for a major type II collagen triple-helical epitope bind and destabilize cartilage independent of inflammation. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagert, C.; Sareila, O.; Kelkka, T.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Collin, M.; Xu, B.; Guerard, S.; Bäcklund, J.; Jalkanen, S.; Holmdahl, R. Chronic active arthritis driven by macrophages without involvement of T cells. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 4 (Suppl. 3), S197–S211. [Google Scholar]
- Mörgelin, M.; Heinegård, D.; Engel, J.; Paulsson, M. Electron microscopy of native cartilage oligomeric matrix protein purified from the Swarm rat chondrosarcoma reveals a five-armed structure. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 6137–6141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oldberg, A.; Antonsson, P.; Lindblom, K.; Heinegård, D. COMP (cartilage oligomeric matrix protein) is structurally related to the thrombospondins. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 22346–22350. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carlsén, S.; Hansson, A.S.; Olsson, H.; Heinegård, D.; Holmdahl, R. Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP)-induced arthritis in rats. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1998, 114, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlsen, S.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Bäcklund, J.; Holmberg, J.; Hultqvist, M.; Vestberg, M.; Holmdahl, R. Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein induction of chronic arthritis in mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 2000–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, H.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Pramhed, A.; Aspberg, A.; Mattsson, R.; Holmdahl, R. Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein specific antibodies are pathogenic. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2012, 14, R191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouskoff, V.; Korganow, A.S.; Duchatelle, V.; Degott, C.; Benoist, C.; Mathis, D. Organ-specific disease provoked by systemic autoimmunity. Cell 1996, 87, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, I.; Staub, A.; Benoist, C.; Mathis, D. Arthritis provoked by linked T and B cell recognition of a glycolytic enzyme. Science 1999, 286, 1732–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, D.; Horvath, S.; Matsumoto, I.; Fremont, D.H.; Allen, P.M. Molecular basis for recognition of an arthritic peptide and a foreign epitope on distinct MHC molecules by a single TCR. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 5788–5796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubert, D.; Maier, B.; Morawietz, L.; Krenn, V.; Kamradt, T. Immunization with glucose-6-phosphate isomerase induces T cell-dependent peripheral polyarthritis in genetically unaltered mice. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 4503–4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwanami, K.; Matsumoto, I.; Tanaka, Y.; Inoue, A.; Goto, D.; Ito, S.; Tsutsumi, A.; Sumida, T. Arthritogenic T cell epitope in glucose-6-phosphate isomerase-induced arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2008, 10, R130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Korganow, A.S.; Ji, H.; Mangialaio, S.; Duchatelle, V.; Pelanda, R.; Martin, T.; Degott, C.; Kikutani, H.; Rajewsky, K.; Pasquali, J.L.; et al. From systemic T cell self-reactivity to organ-specific autoimmune disease via immunoglobulins. Immunity 1999, 10, 451–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccioni, M.; Zeder-Lutz, G.; Huang, H.; Ebel, C.; Gerber, P.; Hergueux, J.; Marchal, P.; Duchatelle, V.; Degott, C.; van Regenmortel, M.; et al. Arthritogenic monoclonal antibodies from K/BxN mice. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 195, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wipke, B.T.; Wang, Z.; Kim, J.; McCarthy, T.J.; Allen, P.M. Dynamic visualization of a joint-specific autoimmune response through positron emission tomography. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wipke, B.T.; Wang, Z.; Nagengast, W.; Reichert, D.E.; Allen, P.M. Staging the initiation of autoantibody-induced arthritis: A critical role for immune complexes. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 7694–7702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binstadt, B.A.; Patel, P.R.; Alencar, H.; Nigrovic, P.A.; Lee, D.M.; Mahmood, U.; Weissleder, R.; Mathis, D.; Benoist, C. Particularities of the vasculature can promote the organ specificity of autoimmune attack. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.M.; Friend, D.S.; Gurish, M.F.; Benoist, C.; Mathis, D.; Brenner, M.B. Mast cells: A cellular link between autoantibodies and inflammatory arthritis. Science 2002, 297, 1689–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wipke, B.T.; Allen, P.M. Essential role of neutrophils in the initiation and progression of a murine model of rheumatoid arthritis. J. Immunol. 2001, 167, 1601–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, J.P.; Wu, H.-J.; Benoist, C.; Mathis, D. IL-17-producing T cells can augment autoantibody-induced arthritis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21789–21794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monach, P.A.; Nigrovic, P.A.; Chen, M.; Hock, H.; Lee, D.M.; Benoist, C.; Mathis, D. Neutrophils in a mouse model of autoantibody-mediated arthritis: Critical producers of Fc receptor gamma, the receptor for C5a, and lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 753–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.-J.; Sawaya, H.; Binstadt, B.; Brickelmaier, M.; Blasius, A.; Gorelik, L.; Mahmood, U.; Weissleder, R.; Carulli, J.; Benoist, C.; et al. Inflammatory arthritis can be reined in by CpG-induced DC-NK cell cross talk. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 1911–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruhns, P.; Samuelsson, A.; Pollard, J.W.; Ravetch, J.V. Colony-stimulating factor-1-dependent macrophages are responsible for IVIG protection in antibody-induced autoimmune disease. Immunity 2003, 18, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, S.; Rajasekaran, N.; Jeisy-Walder, E.; Snapper, S.B.; Illges, H. A crucial role for macrophages in the pathology of K/B x N serum-induced arthritis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2005, 35, 3064–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corr, M.; Crain, B. The role of FcgammaR signaling in the K/B x N serum transfer model of arthritis. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 6604–6609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nigrovic, P.A.; Binstadt, B.A.; Monach, P.A.; Johnsen, A.; Gurish, M.; Iwakura, Y.; Benoist, C.; Mathis, D.; Lee, D.M. Mast cells contribute to initiation of autoantibody-mediated arthritis via IL-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 2325–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.; Pettit, A.; Ohmura, K.; Ortiz-Lopez, A.; Duchatelle, V.; Degott, C.; Gravallese, E.; Mathis, D.; Benoist, C. Critical roles for interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor alpha in antibody-induced arthritis. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 196, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, J.-Y.; Crain, B.; Wu, S.R.; Corr, M. Interleukin 1 receptor dependence of serum transferred arthritis can be circumvented by toll-like receptor 4 signaling. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 197, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.; Ohmura, K.; Mahmood, U.; Lee, D.M.; Hofhuis, F.M.A.; Boackle, S.A.; Takahashi, K.; Holers, V.M.; Walport, M.; Gerard, C.; et al. Arthritis critically dependent on innate immune system players. Immunity 2002, 16, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmura, K.; Nguyen, L.T.; Locksley, R.M.; Mathis, D.; Benoist, C. Interleukin-4 can be a key positive regulator of inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 1866–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohmura, K.; Johnsen, A.; Ortiz-Lopez, A.; Desany, P.; Roy, M.; Besse, W.; Rogus, J.; Bogue, M.; Puech, A.; Lathrop, M.; et al. Variation in IL-1beta gene expression is a major determinant of genetic differences in arthritis aggressivity in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 12489–12494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akilesh, S.; Petkova, S.; Sproule, T.J.; Shaffer, D.J.; Christianson, G.J.; Roopenian, D. The MHC class I-like Fc receptor promotes humorally mediated autoimmune disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 1328–1333. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Min, H.S.; Kim, S.; Park, W.S.; Park, S.H.; Chung, D.H. NKT cells promote antibody-induced joint inflammation by suppressing transforming growth factor beta1 production. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 201, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siragam, V.; Brinc, D.; Crow, A.R.; Song, S.; Freedman, J.; Lazarus, A.H. Can antibodies with specificity for soluble antigens mimic the therapeutic effects of intravenous IgG in the treatment of autoimmune disease? J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Lent, P.L.; van den Bersselaar, L.A.; van den Hoek, A.E.; van de Loo, A.A.; van den Berg, W.B. Cationic immune complex arthritis in mice—A new model. Synergistic effect of complement and interleukin-1. Am. J. Pathol. 1992, 140, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Van Lent, P.L.; van den Hoek, A.E.; van den Bersselaar, L.A.; Spanjaards, M.F.; Van Rooijen, N.; Dijkstra, C.D.; Van de Putte, L.B.; van den Berg, W.B. In vivo role of phagocytic synovial lining cells in onset of experimental arthritis. Am. J. Pathol. 1993, 143, 1226–1237. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nabbe, K.C.A.M.; Blom, A.B.; Holthuysen, A.E.M.; Boross, P.; Roth, J.; Verbeek, S.; van Lent, P.L.E.M.; van den Berg, W.B. Coordinate expression of activating Fc gamma receptors I and III and inhibiting Fc gamma receptor type II in the determination of joint inflammation and cartilage destruction during immune complex-mediated arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabbe, K.C.A.M.; Boross, P.; Holthuysen, A.E.M.; Sloëtjes, A.W.; Kolls, J.K.; Verbeek, S.; van Lent, P.L.E.M.; van den Berg, W.B. Joint inflammation and chondrocyte death become independent of Fcgamma receptor type III by local overexpression of interferon-gamma during immune complex-mediated arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabbe, K.C.; van Lent, P.L.; Holthuysen, A.E.; Kolls, J.K.; Verbeek, S.; van den Berg, W.B. FcgammaRI up-regulation induced by local adenoviral-mediated interferon-gamma production aggravates chondrocyte death during immune complex-mediated arthritis. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 163, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Lent, P.L.; Licht, R.; Dijkman, H.; Holthuysen, A.E.; Berden, J.H.; van den Berg, W.B. Uptake of apoptotic leukocytes by synovial lining macrophages inhibits immune complex-mediated arthritis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2001, 70, 708–714. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Burska, A.N.; Hunt, L.; Boissinot, M.; Strollo, R.; Ryan, B.J.; Vital, E.; Nissim, A.; Winyard, P.G.; Emery, P.; Ponchel, F. Autoantibodies to posttranslational modifications in rheumatoid arthritis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 492873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gaalen, F.A.; Linn-Rasker, S.P.; van Venrooij, W.J.; de Jong, B.A.; Breedveld, F.C.; Verweij, C.L.; Toes, R.E.M.; Huizinga, T.W.J. Autoantibodies to cyclic citrullinated peptides predict progression to rheumatoid arthritis in patients with undifferentiated arthritis: A prospective cohort study. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 709–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aletaha, D.; Neogi, T.; Silman, A.J.; Funovits, J.; Felson, D.T.; Bingham, C.O.; Birnbaum, N.S.; Burmester, G.R.; Bykerk, V.P.; Cohen, M.D.; et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 2569–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McInnes, I.B.; Schett, G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 2205–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmström, V.; Catrina, A.I.; Klareskog, L. The immunopathogenesis of seropositive rheumatoid arthritis: From triggering to targeting. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Woude, D.; Rantapää-Dahlqvist, S.; Ioan-Facsinay, A.; Onnekink, C.; Schwarte, C.M.; Verpoort, K.N.; Drijfhout, J.W.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Toes, R.E.M.; Pruijn, G.J.M. Epitope spreading of the anti-citrullinated protein antibody response occurs before disease onset and is associated with the disease course of early arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1554–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suwannalai, P.; van de Stadt, L.A.; Radner, H.; Steiner, G.; El-Gabalawy, H.S.; Zijde, C.M.J.-V.D.; van Tol, M.J.; van Schaardenburg, D.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Toes, R.E.M.; et al. Avidity maturation of anti-citrullinated protein antibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 1323–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rombouts, Y.; Ewing, E.; van de Stadt, L.A.; Selman, M.H.J.; Trouw, L.A.; Deelder, A.M.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Wuhrer, M.; van Schaardenburg, D.; Toes, R.E.M.; et al. Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies acquire a pro-inflammatory Fc glycosylation phenotype prior to the onset of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harre, U.; Georgess, D.; Bang, H.; Bozec, A.; Axmann, R.; Ossipova, E.; Jakobsson, P.-J.; Baum, W.; Nimmerjahn, F.; Szarka, E.; et al. Induction of osteoclastogenesis and bone loss by human autoantibodies against citrullinated vimentin. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 1791–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleyer, A.; Finzel, S.; Rech, J.; Manger, B.; Krieter, M.; Faustini, F.; Araujo, E.; Hueber, A.J.; Harre, U.; Engelke, K.; et al. Bone loss before the clinical onset of rheumatoid arthritis in subjects with anticitrullinated protein antibodies. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 73, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harre, U.; Lang, S.C.; Pfeifle, R.; Rombouts, Y.; Frühbeißer, S.; Amara, K.; Bang, H.; Lux, A.; Koeleman, C.A.; Baum, W.; et al. Glycosylation of immunoglobulin G determines osteoclast differentiation and bone loss. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seeling, M.; Hillenhoff, U.; David, J.P.; Schett, G.; Tuckermann, J.; Lux, A.; Nimmerjahn, F. Inflammatory monocytes and Fcγ receptor IV on osteoclasts are critical for bone destruction during inflammatory arthritis in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 10729–10734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamurthy, A.; Joshua, V.; Haj Hensvold, A.; Jin, T.; Sun, M.; Vivar, N.; Ytterberg, A.J.; Engström, M.; Fernandes-Cerqueira, C.; Amara, K.; et al. Identification of a novel chemokine-dependent molecular mechanism underlying rheumatoid arthritis-associated autoantibody-mediated bone loss. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wigerblad, G.; Bas, D.B.; Fernades-Cerqueira, C.; Krishnamurthy, A.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Rogoz, K.; Kato, J.; Sandor, K.; Su, J.; Jimenez-Andrade, J.M.; et al. Autoantibodies to citrullinated proteins induce joint pain independent of inflammation via a chemokine-dependent mechanism. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catrina, A.I.; Svensson, C.I.; Malmström, V.; Schett, G.; Klareskog, L. Mechanisms leading from systemic autoimmunity to joint-specific disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trouw, L.A.; Haisma, E.M.; Levarht, E.W.N.; van der Woude, D.; Ioan-Facsinay, A.; Daha, M.R.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Toes, R.E. Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies from rheumatoid arthritis patients activate complement via both the classical and alternative pathways. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 1923–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habets, K.L.L.; Trouw, L.A.; Levarht, E.W.N.; Korporaal, S.J.A.; Habets, P.A.M.; de Groot, P.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; Toes, R.E.M. Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies contribute to platelet activation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uysal, H.; Bockermann, R.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Sehnert, B.; Bajtner, E.; Engström, A.; Serre, G.; Burkhardt, H.; Thunnissen, M.M.G.M.; Holmdahl, R. Structure and pathogenicity of antibodies specific for citrullinated collagen type II in experimental arthritis. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uysal, H.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Kessel, C.; Haag, S.; Carlsen, S.; Burkhardt, H.; Holmdahl, R. Antibodies to citrullinated proteins: Molecular interactions and arthritogenicity. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 233, 9–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klareskog, L.; Rönnelid, J.; Lundberg, K.; Padyukov, L.; Alfredsson, L. Immunity to citrullinated proteins in rheumatoid arthritis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 26, 651–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goebel, A. Autoantibody pain. Autoimmun. Rev. 2016, 15, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agalave, N.M.; Larsson, M.; Abdelmoaty, S.; Su, J.; Baharpoor, A.; Lundbäck, P.; Palmblad, K.; Andersson, U.; Harris, H.; Svensson, C.I. Spinal HMGB1 induces TLR4-mediated long-lasting hypersensitivity and glial activation and regulates pain-like behavior in experimental arthritis. Pain 2014, 155, 1802–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christianson, C.A.; Corr, M.; Firestein, G.S.; Mobargha, A.; Yaksh, T.L.; Svensson, C.I. Characterization of the acute and persistent pain state present in K/BxN serum transfer arthritis. Pain 2010, 151, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bas, D.B.; Su, J.; Sandor, K.; Agalave, N.M.; Lundberg, J.; Codeluppi, S.; Baharpoor, A.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Holmdahl, R.; Svensson, C.I. Collagen antibody-induced arthritis evokes persistent pain with spinal glial involvement and transient prostaglandin dependency. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 3886–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkhardt, H.; Koller, T.; Engström, A.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Turnay, J.; Kraetsch, H.G.; Kalden, J.R.; Holmdahl, R. Epitope-specific recognition of type II collagen by rheumatoid arthritis antibodies is shared with recognition by antibodies that are arthritogenic in collagen-induced arthritis in the mouse. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 46, 2339–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croxford, A.M.; Crombie, D.; McNaughton, D.; Holmdahl, R.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Rowley, M.J. Specific antibody protection of the extracellular cartilage matrix against collagen antibody-induced damage. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 3374–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Stadt, L.A.; van Schouwenburg, P.A.; Bryde, S.; Kruithof, S.; van Schaardenburg, D.; Hamann, D.; Wolbink, G.; Rispens, T. Monoclonal anti-citrullinated protein antibodies selected on citrullinated fibrinogen have distinct targets with different cross-reactivity patterns. Rheumatology 2013, 52, 631–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, C.; Xu, B.; liang, B.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Tong, D.; Lundqvist, C.; Urbonaviciute, V.; Lönnblom, E.; Ayoglu, B.; Nilsson, P.; et al. Autoantibodies specific for a citrulline side chain protect against arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018. in review. [Google Scholar]
- Durigutto, P.; Macor, P.; Ziller, F.; De Maso, L.; Fischetti, F.; Marzari, R.; Sblattero, D.; Tedesco, F. Prevention of arthritis by locally synthesized recombinant antibody neutralizing complement component C5. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandakumar, K.S.; Jansson, A.; Xu, B.; Rydell, N.; Ahooghalandari, P.; Hellman, L.; Blom, A.M.; Holmdahl, R. A recombinant vaccine effectively induces c5a-specific neutralizing antibodies and prevents arthritis. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, G.; Scheinman, R.I.; Holers, V.M.; Banda, N.K. A New Approach for the Treatment of Arthritis in Mice with a Novel Conjugate of an Anti-C5aR1 Antibody and C5 Small Interfering RNA. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 5446–5454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimmerjahn, F.; Ravetch, J.V. Fcgamma receptors as regulators of immune responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Xu, Y.; Cen, X.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Liu, S.; Cheng, K. Targeting pattern-recognition receptors to discover new small molecule immune modulators. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 144, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, D.J.; Kim, D.H.; Nah, S.-S.; Park, M.H.; Lee, H.P.; Han, S.B.; Venkatareddy, U.; Gann, B.; Rodriguez, K.; Burt, S.R.; et al. Novel synthetic (E)-2-methoxy-4-(3-(4-methoxyphenyl) prop-1-en-1-yl) phenol inhibits arthritis by targeting signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, S.F.; Ansari, M.A.; Nadeem, A.; Zoheir, K.M.A.; Bakheet, S.A.; Alsaad, A.M.S.; Al-Shabanah, O.A.; Attia, S.M. STA-21, a STAT-3 inhibitor, attenuates the development and progression of inflammation in collagen antibody-induced arthritis. Immunobiology 2017, 222, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hultqvist, M.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Björklund, U.; Holmdahl, R. The novel small molecule drug Rabeximod is effective in reducing disease severity of mouse models of autoimmune disorders. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hultqvist, M.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Björklund, U.; Holmdahl, R. Rabeximod reduces arthritis severity in mice by decreasing activation of inflammatory cells. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1527–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, J.H.; Lee, W.K.; Lee, Y.S.; Kang, J.S. Assessment of collagen antibody-induced arthritis in BALB/c mice using bioimaging analysis and histopathological examination. Lab. Anim. Res. 2016, 32, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, J.N.; Wormald, M.R.; Sim, R.B.; Rudd, P.M.; Dwek, R.A. The impact of glycosylation on the biological function and structure of human immunoglobulins. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 25, 21–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jefferis, R.; Lund, J.; Pound, J.D. IgG-Fc-mediated effector functions: Molecular definition of interaction sites for effector ligands and the role of glycosylation. Immunol. Rev. 1998, 163, 59–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrara, C.; Grau, S.; Jäger, C.; Sondermann, P.; Brünker, P.; Waldhauer, I.; Hennig, M.; Ruf, A.; Rufer, A.C.; Stihle, M.; et al. Unique carbohydrate-carbohydrate interactions are required for high affinity binding between FcgammaRIII and antibodies lacking core fucose. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 12669–12674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jennewein, M.F.; Alter, G. The Immunoregulatory Roles of Antibody Glycosylation. Trends Immunol. 2017, 38, 358–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mössner, E.; Brünker, P.; Moser, S.; Püntener, U.; Schmidt, C.; Herter, S.; Grau, R.; Gerdes, C.; Nopora, A.; van Puijenbroek, E.; et al. Increasing the efficacy of CD20 antibody therapy through the engineering of a new type II anti-CD20 antibody with enhanced direct and immune effector cell-mediated B-cell cytotoxicity. Blood 2010, 115, 4393–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneko, Y.; Nimmerjahn, F.; Ravetch, J.V. Anti-inflammatory activity of immunoglobulin G resulting from Fc sialylation. Science 2006, 313, 670–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimmerjahn, F.; Ravetch, J.V. The antiinflammatory activity of IgG: The intravenous IgG paradox. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwab, I.; Nimmerjahn, F. Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy: How does IgG modulate the immune system? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthony, R.M.; Nimmerjahn, F.; Ashline, D.J.; Reinhold, V.N.; Paulson, J.C.; Ravetch, J.V. Recapitulation of IVIG anti-inflammatory activity with a recombinant IgG Fc. Science 2008, 320, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthony, R.M.; Wermeling, F.; Karlsson, M.C.I.; Ravetch, J.V. Identification of a receptor required for the anti-inflammatory activity of IVIG. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 19571–19578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimmerjahn, F.; Ravetch, J.V. Anti-inflammatory actions of intravenous immunoglobulin. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 26, 513–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthony, R.M.; Ravetch, J.V. A novel role for the IgG Fc glycan: The anti-inflammatory activity of sialylated IgG Fcs. J. Clin. Immunol. 2010, 30 (Suppl. 1), S9–S14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthony, R.M.; Kobayashi, T.; Wermeling, F.; Ravetch, J.V. Intravenous gammaglobulin suppresses inflammation through a novel T(H)2 pathway. Nature 2011, 475, 110–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wermeling, F.; Anthony, R.M.; Brombacher, F.; Ravetch, J.V. Acute inflammation primes myeloid effector cells for anti-inflammatory STAT6 signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 13487–13491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohmi, Y.; Ise, W.; Harazono, A.; Takakura, D.; Fukuyama, H.; Baba, Y.; Narazaki, M.; Shoda, H.; Takahashi, N.; Ohkawa, Y.; et al. Sialylation converts arthritogenic IgG into inhibitors of collagen-induced arthritis. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cymer, F.; Beck, H.; Rohde, A.; Reusch, D. Therapeutic monoclonal antibody N-glycosylation—Structure, function and therapeutic potential. Biologicals 2017, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collin, M.; Olsén, A. EndoS, a novel secreted protein from Streptococcus pyogenes with endoglycosidase activity on human IgG. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 3046–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandakumar, K.S.; Collin, M.; Olsén, A.; Nimmerjahn, F.; Blom, A.M.; Ravetch, J.V.; Holmdahl, R. Endoglycosidase treatment abrogates IgG arthritogenicity: Importance of IgG glycosylation in arthritis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007, 37, 2973–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, H.; Collin, M.; Dudziak, D.; Ravetch, J.V.; Nimmerjahn, F. In vivo enzymatic modulation of IgG glycosylation inhibits autoimmune disease in an IgG subclass-dependent manner. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 15005–15009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collin, M.; Björck, L. Toward Clinical use of the IgG Specific Enzymes IdeS and EndoS against Antibody-Mediated Diseases. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1535, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nandakumar, K.S.; Collin, M.; Happonen, K.E.; Lundstrom, S.L.; Croxford, A.M.; Xu, B.; Zubarev, R.A.; Rowley, M.J.; Blom, A.M.; Kjellman, C.; et al. Streptococcal endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidase within IgG immune complexes potently suppress inflammation in vivo. Front. Immunol. In review.
- Collin, M.; Shannon, O.; Björck, L. IgG glycan hydrolysis by a bacterial enzyme as a therapy against autoimmune conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 4265–4270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Timmeren, M.M.; van der Veen, B.S.; Stegeman, C.A.; Petersen, A.H.; Hellmark, T.; Collin, M.; Heeringa, P. IgG glycan hydrolysis attenuates ANCA-mediated glomerulonephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 1103–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Otten, M.A.; Hellmark, T.; Collin, M.; Björck, L.; Zhao, M.-H.; Daha, M.R.; Segelmark, M. Successful treatment of experimental glomerulonephritis with IdeS and EndoS, IgG-degrading streptococcal enzymes. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 2479–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benkhoucha, M.; Molnarfi, N.; Santiago-Raber, M.-L.; Weber, M.S.; Merkler, D.; Collin, M.; Lalive, P.H. IgG glycan hydrolysis by EndoS inhibits experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allhorn, M.; Briceño, J.G.; Baudino, L.; Lood, C.; Olsson, M.L.; Izui, S.; Collin, M. The IgG-specific endoglycosidase EndoS inhibits both cellular and complement-mediated autoimmune hemolysis. Blood 2010, 115, 5080–5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirose, M.; Vafia, K.; Kalies, K.; Groth, S.; Westermann, J.; Zillikens, D.; Ludwig, R.J.; Collin, M.; Schmidt, E. Enzymatic autoantibody glycan hydrolysis alleviates autoimmunity against type VII collagen. J. Autoimmun. 2012, 39, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Zheng, J.; Collin, M.; Schmidt, E.; Zillikens, D.; Petersen, F. EndoS reduces the pathogenicity of anti-mCOL7 IgG through reduced binding of immune complexes to neutrophils. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Pawel-Rammingen, U.; Johansson, B.P.; Björck, L. IdeS, a novel streptococcal cysteine proteinase with unique specificity for immunoglobulin G. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 1607–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandakumar, K.S.; Johansson, B.P.; Björck, L.; Holmdahl, R. Blocking of experimental arthritis by cleavage of IgG antibodies in vivo. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 3253–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, S.C.; Lorant, T.; Choi, J.; Kjellman, C.; Winstedt, L.; Bengtsson, M.; Zhang, X.; Eich, T.; Toyoda, M.; Eriksson, B.-M.; et al. IgG Endopeptidase in Highly Sensitized Patients Undergoing Transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Järnum, S.; Bockermann, R.; Runström, A.; Winstedt, L.; Kjellman, C. The Bacterial Enzyme IdeS Cleaves the IgG-Type of B Cell Receptor (BCR), Abolishes BCR-Mediated Cell Signaling, and Inhibits Memory B Cell Activation. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 5592–5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagan, J.D.; Kitaoka, M.; Anthony, R.M. Engineered Sialylation of Pathogenic Antibodies In Vivo Attenuates Autoimmune Disease. Cell 2018, 172, 564–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Ponniah, G.; Zhang, H.-M.; Nowak, C.; Neill, A.; Gonzalez-Lopez, N.; Patel, R.; Cheng, G.; Kita, A.Z.; Andrien, B. In vitro and in vivo modifications of recombinant and human IgG antibodies. MAbs 2014, 6, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiller, K.E.; Tessier, P.M. Advances in Antibody Design. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 17, 191–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nandakumar, K.S. Targeting IgG in Arthritis: Disease Pathways and Therapeutic Avenues. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030677
Nandakumar KS. Targeting IgG in Arthritis: Disease Pathways and Therapeutic Avenues. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(3):677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030677
Chicago/Turabian StyleNandakumar, Kutty Selva. 2018. "Targeting IgG in Arthritis: Disease Pathways and Therapeutic Avenues" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 3: 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030677
APA StyleNandakumar, K. S. (2018). Targeting IgG in Arthritis: Disease Pathways and Therapeutic Avenues. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(3), 677. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030677