D181A Site-Mutagenesis Enhances Both the Hydrolyzing and Transfructosylating Activities of BmSUC1, a Novel β-Fructofuranosidase in the Silkworm Bombyx mori
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
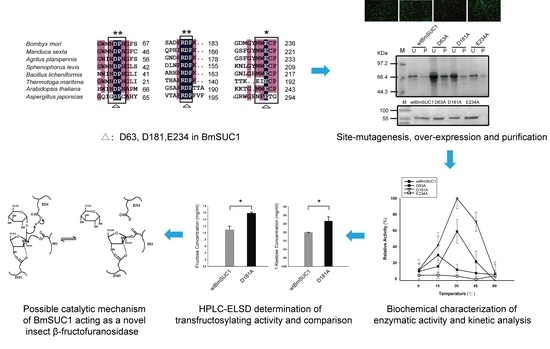
2.1. Analysis of Homology and Conserved Motifs
2.2. Site Mutagenesis of BmSUC1 and In Vitro Expression of the Recombinant Proteins
2.3. Biochemical Characterization of wtBmSUC1 and Mutants
2.4. Comparison of Substrate Affinity and Catalytic Efficiency between wtBmSUC1 and D181A
2.5. Quantitative Determination of Transfructosylating Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plasmid and Cell Strains
4.2. Sequence Analysis
4.3. Over-Expression of BmSuc1 in E. coli and Preparation of Polyclonal Antibody
4.4. Site-Directed Mutagenesis of BmSUC1
4.5. Construction and Identification of Recombinant Bacmids
4.6. Expression in BmN Cells and Purification of Recombinant Proteins
4.7. SDS-PAGE and Western Blot
4.8. Enzymatic Activity Assay and Kinetic Analysis
4.9. HPLC-ELSD Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GH32 | glycosyl-hydrolase family 32 |
| β-FFase | β-fructofuranosidase |
| FOS | fructooligosaccharides |
| D-AB1 | 1,4-dideoxy-1,4-imino-d-arabinitol |
| DNJ | 1-deoxynojirimycin |
| HGT | horizontal gene transfer |
| BmNPV | Bombyx mori nucleopolyhedrovirus |
| SDS-PAGE | sodium dodecylsulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| PVDF | polyvinylidene fluoride |
| DNS | dinitrosalicylic acid |
| Km | kinetic parameters of Michaelis constant |
| Kcat | catalytic rate constant |
| HPLC | high performance liquid chromatography |
| ELSD | evaporative light-scattering detector |
| T50 | temperature of 50% loss of activity |
References
- Linde, D.; Macias, I.; Fernandez-Arrojo, L.; Plou, F.J.; Jimenez, A.; Fernandez-Lobato, M. Molecular and biochemical characterization of a β-fructofuranosidase from Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sangeetha, P.T.; Ramesh, M.N.; Prapulla, S.G. Production of fructosyl transferase by Aspergillus oryzae CFR 202 in solid-state fermentation using agricultural by-products. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 65, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miguel, Á.-B.; de Miguel, A.; Francisco, P.; Julia, S.-A.; María, F.-L. New insights into the fructosyltransferase activity of Schwanniomyces occidentalis β-fructofuranosidase, emerging from nonconventional codon usage and directed mutation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 7491–7499. [Google Scholar]
- Álvaro-Benito, M.; Abreu, M.D.; Fernández-Arrojo, L.; Plou, F.J.; Jiménez-Barbero, J.; Ballesteros, A.; Polaina, J.; Fernández-Lobato, M. Characterization of a β-fructofuranosidase from Schwanniomyces occidentalis with transfructosylating activity yielding the prebiotic 6-kestose. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 132, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturm, A. Invertases. Primary structures, functions, and roles in plant development and sucrose partitioning. Plant Physiol. 1999, 121, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturm, A.; Tang, G.Q. The sucrose-cleaving enzymes of plants are crucial for development, growth and carbon partitioning: Trends in Plant Science. Trends Plant Sci. 1999, 4, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozimek, L.K.; Kralj, S.; Van der Maarel, M.J.; Dijkhuizen, L. The levansucrase and inulosucrase enzymes of Lactobacillus reuteri 121 catalyse processive and non-processive transglycosylation reactions. Microbiology 2006, 152, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahiri, M.; Tressol, J.J.; Bornet, F.R.; Bouteloup, D.C.; Feillet, C.C.; Brandolini, M.; Ducros, V.; Pepin, D.; Brouns, F.; Roussel, A.M. Effect of short-chain fructooligosaccharides on intestinal calcium absorption and calcium status in postmenopausal women: A stable-isotope study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberfroid, M.B.; Delzenne, N.M. Dietary fructans. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1998, 18, 117–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishizawa, K.; Nakajima, M.; Nabetani, H. A forced-flow membrane reactor for transfructosylation using ceramic membrane. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2000, 68, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narinder, K.; Anil, K.G. Applications of inulin and oligofructose in health and nutrition. J. Biosci. 2002, 27, 703–714. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, A.V. Dose-response effects of inulin and oligofructose on intestinal bifidogenesis effects. J. Nutr. 1999, 129, 1442S–1445S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumida, M.; Yuan, X.L.; Matsubara, F. Purification and some properties of soluble β-fructofuranosidase from larval midgut of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Comp. Biochem. 1994, 107, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.D.; Terra, W.R. Midgut α-glucosidase and β-fructosidase from Erinnyis ello larvae and imagoes: Physical and kinetic properties. Insect Biochem. 1986, 16, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, C.N.B.; Isejima, E.M.; Samuels, R.I.; Silva, C.P. Sucrose hydrolases from the midgut of the sugarcane stalk borer Diatraea saccharalis. J. Insect Physiol. 2004, 50, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daimon, T.; Taguchi, T.; Meng, Y.; Katsuma, S.; Mita, K.; Shimada, T. Beta-fructofuranosidase genes of the silkworm, Bombyx mori: Insights into enzymatic adaptation of B. mori to toxic alkaloids in mulberry latex. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 15271–15279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konno, K.; Ono, H.; Nakamura, M.; Tateishi, K.; Hirayama, C.; Tamura, Y.; Hattori, M.; Koyama, A.; Kohno, K. Mulberry latex rich in antidiabetic sugar-mimic alkaloids forces dieting on caterpillars. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 1337–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauchet, Y.; Muck, A.; Svatoš, A.; Heckel, D.G.; Preiss, S. Mapping the larval midgut lumen proteome of Helicoverpa armigera, a generalist herbivorous insect. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 1629–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauchet, Y.; Wilkinson, P.; Vogel, H.; Nelson, D.R.; Reynolds, S.E.; Heckel, D.G.; Ffrench-Constant, R.H. Pyrosequencing the Manduca sexta larval midgut transcriptome: Messages for digestion, detoxification and defence. Insect Mol. Biol. 2009, 19, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedezzi, R.; Fonseca, F.P.P.; Júnior, C.D.S.; Kishi, L.T.; Terra, W.R.; Henrique-Silva, F. A novel β-fructofuranosidase in Coleoptera: Characterization of a β-fructofuranosidase from the sugarcane weevil, Sphenophorus levis. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 55, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Doucet, D.; Mittapalli, O. Characterization of horizontally transferred β-fructofuranosidase (ScrB) genes in Agrilus planipennis. Insect Mol. Biol. 2014, 23, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keeling, C.I.; Yuen, M.M.; Liao, N.Y.; Docking, T.R.; Chan, S.K.; Taylor, G.A.; Palmquist, D.L.; Jackman, S.D.; Nguyen, A.; Li, M. Draft genome of the mountain pine beetle, Dendroctonus ponderosae Hopkins, a major forest pest. Genome Biol. 2013, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pons, T.; Naumoff, D.G.; Martinez-Fleites, C.; Hernandez, L. Three acidic residues are at the active site of a beta-propeller architecture in glycoside hydrolase families 32, 43, 62, and 68. Proteins 2004, 54, 424–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Nakagaki, K.; Zhao, T.; Zhao, A.; Meng, Y.; Nakagaki, M.; Park, E.Y.; Maenaka, K. Expression of spider flagelliform silk protein in Bombyx mori cell line by a novel Bac-to-Bac/BmNPV baculovirus expression system. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 71, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuankhayan, P.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Huang, Y.C.; Hsieh, Y.Y.; Guan, H.H.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Tien, Y.C.; Chen, C.D.; Chiang, C.M.; Chen, C.J. Crystal structures of Aspergillus japonicus fructosyltransferase complex with donor/acceptor substrates reveal complete subsites in the active site for catalysis. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 23251–23264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luckow, V.A.; Lee, S.C.; Barry, G.F.; Olins, P.O. Efficient generation of infectious recombinant baculoviruses by site-specific transposon-mediated insertion of foreign genes into a baculovirus genome propagated in Escherichia coli. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 4566–4579. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peakman, T.C.; Harris, R.A.; Gewert, D.R. Highly efficient generation of recombinant baculoviruses by enzymatically medicated site-specific in vitro recombination. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992, 20, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francois, A.; Christophe, B.; Gerlind, S.; Bernard, H.; Mirjam, C. The three-dimensional structure of invertase (-fructosidase) from Thermotoga maritima reveals a bimodular arrangement and an evolutionary relationship between retaining and inverting glycosidases. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 18903–18910. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, V.A.; Maley, F. Identification of an active-site residue in yeast invertase by affinity labeling and site-directed mutagenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 10817–10820. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meng, G.; Futterer, K. Structural framework of fructosyl transfer in Bacillus subtilis levansucrase. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2003, 10, 935–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammens, W.; Le Roy, K.; Schroeven, L.; van Laere, A.; Rabijns, A.; van den Ende, W. Structural insights into glycoside hydrolase family 32 and 68 enzymes: Functional implications. J. Exp. Bot. 2009, 60, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.S.; Yu, S.; Withers, S.G. Detailed dissection of a new mechanism for glycoside cleavage: Alpha-1,4-glucan lyase. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 13081–13090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isono, N.; Tochihara, T.; Kusnadi, Y.; Win, T.T.; Watanabe, K.; Obae, K.; Ito, H.; Matsui, H. Cloning and heterologous expression of a beta-fructofuranosidase gene from Arthrobacter globiformis IFO 3062, and site-directed mutagenesis of the essential aspartic acid and glutamic acid of the active site. J. Ferment. Technol. 2004, 97, 244–249. [Google Scholar]
- Gennady, Z.; Uri, C.; Noam, A.; Vered, S.; Gil, S.; Yuval, S. Mapping glycoside hydrolase substrate subsites by isothermal titration calorimetry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 11275–11280. [Google Scholar]
- Parfenyuk, E.V.; Davydova, O.I.; Lebedeva, N.S. Interactions of d-maltose and sucrose with some amino acids in aqueous solutions. J. Solut. Chem. 2004, 33, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonozuka, T.; Tamaki, A.; Yokoi, G.; Miyazaki, T.; Ichikawa, M.; Nishikawa, A.; Ohta, Y.; Hidaka, Y.; Katayama, K.; Hatada, Y. Crystal structure of a lactosucrose-producing enzyme, Arthrobacter sp. K-1 β-fructofuranosidase. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2012, 51, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritsema, T.; Hernández, L.; Verhaar, A.; Altenbach, D.; Boller, T.; Wiemken, A.; Smeekens, S. Developing fructan-synthesizing capability in a plant invertase via mutations in the sucrose-binding box. Plant J. 2006, 48, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeven, L.; Lammens, W.; van Laere, A.; van den Ende, W. Transforming wheat vacuolar invertase into a high affinity sucrose: Sucrose 1-fructosyltransferase. New Phytol. 2008, 180, 822–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritsema, T.; Verhaar, A.; Vijn, I.; Smeekens, S. Using natural variation to investigate the function of individual amino acids in the sucrose-binding box of fructan: Fructan 6G-fructosyltransferase (6G-FFT) in product formation. Plant Mol. Biol. 2005, 58, 597–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altenbach, D.; Rudiño-Pinera, E.; Olvera, C.; Boller, T.; Wiemken, A.; Ritsema, T. An acceptor-substrate binding site determining glycosyl transfer emerges from mutant analysis of a plant vacuolar invertase and a fructosyltransferase. Plant Mol. Biol. 2009, 69, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijn, I.; Dijken, A.V.; Lüscher, M.; Bos, A.; Smeets, E.; Weisbeek, P.; Wiemken, A.; Smeekens, S. Cloning of sucrose:sucrose 1-fructosyltransferase from onion and synthesis of structurally defined fructan molecules from sucrose. Plant Physiol. 1998, 117, 1507–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kritzinger, S.M.; Kilian, S.G.; Potgieter, M.A.; Preez, J.C.D. The effect of production parameters on the synthesis of the prebiotic trisaccharide, neokestose, by Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous (phaffia rhodozyma). Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2003, 32, 728–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obenland, D.M.; Simmen, U.; Boller, T.; Wiemken, A. Purification and characterization of three soluble invertases from barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) leaves. Plant Physiol. 1993, 101, 1331–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omori, T.; Ueno, K.; Muramatsu, K.; Kikuchi, M.; Onodera, S.; Shiomi, N. Characterization of recombinant beta-fructofuranosidase from Bifidobacterium adolescentis G1. Chem. Cent. J. 2010, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warchol, M.; Perrin, S.; Grill, J.P.; Schneider, F. Characterization of a purified β-fructofuranosidase from Bifidobacterium infantis ATCC 15697. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2002, 35, 462–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.J.; Jeon, S.J.; You, D.J.; Kim, K.H.; Jeong, Y.K.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, Y.M.; Kim, B.W. Cloning and characterization of an exoinulinase from Bacillus polymyxa. Biotechnol. Lett. 2003, 25, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, X.J.; Zhong, X.; Lin, X.Y.; Huang, X.H.; Yu, X.Q. Characterization of a novel Manduca sexta β-1,3-glucan recognition protein (βGRP3) with multiple functions. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 52, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Fang, Q.; Qian, C.; Wang, F.; Yu, X.Q.; Ye, G. Inhibition of host cell encapsulation through inhibiting immune gene expression by the parasitic wasp venom calreticulin. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 43, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Gong, M.; Shu, R.; Li, X.; Gao, J.; Meng, Y. Molecular and enzymatic characterization of two enzymes BmPCD and BmDHPR involving in the regeneration pathway of tetrahydrobiopterin from the silkworm Bombyx mori. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 186, 20–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Taxonomy | Species (Accession Number) | Identity (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Insect | Helicoverpa armigera (ABU98615) | 43 |
| Agrilus planipennis (AIR93898) | 40 | |
| Manduca sexta (ACX49762) | 39 | |
| Sphenophorus levis (AIL92341) | 39 | |
| Bacterium | Bacillus licheniformis (WP_003186470) | 46 |
| Bacillus megaterium (KWU53447) | 44 | |
| Staphylococcus pasteuri (WP_023374434) | 43 | |
| Thermotoga maritima (1UYP_A) | 33 | |
| Plant | Arabidopsis thaliana (AAA63802) | 31 |
| Cichorium intybus (CAC37922) | 30 | |
| Fungus | Arthrobacter globiformis (ADK46938) | 31 |
| Aspergillus japonicus (WP_003803118) | 13 |
| Name of Primer Pair | Primer Sequence (5′→3′) |
|---|---|
| D63AM1/M2 | GAAAAGCCGTTAGGGGCATTCATCCA |
| TGGATGAATGCCCCTAACGGCTTT TC | |
| D181AM1/M2 | CCAAATCTTGGGGGCTCTGAAATCAGC |
| GCTGATTTCAGAGCCCCCAAGATTTGG | |
| E234AM1/M2 | CATGCCCACATGTAGCCCAT |
| ATGGGCTACATGTGGGCATG | |
| BmSUC1F/R | ATTTGCGGCCGCTATGTTCGCCTGGAGC |
| CCCAAGCTTTTAATGATGATGATGATGATGAGCGGGTACACT | |
| GFPF/R | CCGCTCGAGATGGTGAGCAAGGGC |
| CGGGGTACCTTACTTGTACAGCTC |
| Substrate | Enzyme | Km (mM) | Kcat (S−1) | Kcat/Km (S−1mM−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sucrose | BmSUC1 | 88.32 ± 11.75 | 0.022 ± 0.0009 | 2.49 × 10−4 |
| D181A | 52.87 ± 6.85 | 0.025 ± 0.0004 | 4.73 × 10−4 | |
| Raffinose | BmSUC1 | 52.32 ± 17.22 | 0.025 ± 0.0028 | 2.91 × 10−4 |
| D181A | 32.03 ± 4.43 | 0.021 ± 0.0014 | 6.56 × 10−4 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gan, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Wu, L.; Ye, C.; Wang, Y.; Gao, J.; Meng, Y. D181A Site-Mutagenesis Enhances Both the Hydrolyzing and Transfructosylating Activities of BmSUC1, a Novel β-Fructofuranosidase in the Silkworm Bombyx mori. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030683
Gan Q, Li X, Zhang X, Wu L, Ye C, Wang Y, Gao J, Meng Y. D181A Site-Mutagenesis Enhances Both the Hydrolyzing and Transfructosylating Activities of BmSUC1, a Novel β-Fructofuranosidase in the Silkworm Bombyx mori. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(3):683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030683
Chicago/Turabian StyleGan, Quan, Xin Li, Xinwei Zhang, Lanlan Wu, Chongjun Ye, Ying Wang, Junshan Gao, and Yan Meng. 2018. "D181A Site-Mutagenesis Enhances Both the Hydrolyzing and Transfructosylating Activities of BmSUC1, a Novel β-Fructofuranosidase in the Silkworm Bombyx mori" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 3: 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030683
APA StyleGan, Q., Li, X., Zhang, X., Wu, L., Ye, C., Wang, Y., Gao, J., & Meng, Y. (2018). D181A Site-Mutagenesis Enhances Both the Hydrolyzing and Transfructosylating Activities of BmSUC1, a Novel β-Fructofuranosidase in the Silkworm Bombyx mori. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(3), 683. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030683