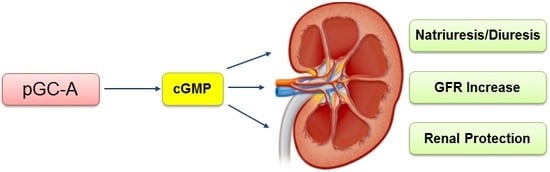
Particulate Guanylyl Cyclase A/cGMP Signaling Pathway in the Kidney: Physiologic and Therapeutic Indications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Particulate GC-A/cGMP in Sodium and Water Homeostasis
3. Particulate GC-A/cGMP Mediates Glomerular Function
4. Particulate GC-A/cGMP and Renal Protection
5. Novel Designer pGC-A Activator CRRL269
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| pGC-A | Particulate guanylyl cyclase A |
| NP | Natriuretic peptide |
| cGMP | 3′,5′-Cyclic guanosine monophosphate |
| PKG | Protein kinase G |
| AKI | Acute kidney injury |
| GFR | Glomerular filtration rate |
| ANP | Atrial natriuretic peptide |
| BNP | B-type natriuretic peptide |
| URO | Urodilatin |
| PDE | Phosphodiesterase |
| NKA | Na+-K+-ATPase |
| IMCD | Inner medullary collect duct |
| VSMC | Vascular smooth muscle cell |
| HF | Heart failure |
| RAAS | Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone-system |
References
- Ogawa, H.; Qiu, Y.; Ogata, C.M.; Misono, K.S. Crystal structure of hormone-bound atrial natriuretic peptide receptor extracellular domain: Rotation mechanism for transmembrane signal transduction. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 28625–28631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.Y.; Burnett, J.C., Jr. Natriuretic peptides and therapeutic applications. Heart Fail. Rev. 2007, 12, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellum, J.A.; Lameire, N.; Aspelin, P.; Barsoum, R.S.; Burdmann, E.A.; Goldstein, S.L.; Herzog, C.A.; Joannidis, M.; Kribben, A.; Levey, A.S. Kidney disease: Improving global outcomes (KDIGO) acute kidney injury work group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2012, 2, 1–138. [Google Scholar]
- Wonnacott, A.; Meran, S.; Amphlett, B.; Talabani, B.; Phillips, A. Epidemiology and outcomes in community-acquired versus hospital-acquired AKI. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 9, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoste, E.A.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Bellomo, R.; Cely, C.M.; Colman, R.; Cruz, D.N.; Edipidis, K.; Forni, L.G.; Gomersall, C.D.; Govil, D.; et al. Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: The multinational AKI-EPI study. Intensive Care Med. 2015, 41, 1411–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coca, S.G.; Singanamala, S.; Parikh, C.R. Chronic kidney disease after acute kidney injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Kidney Int. 2012, 81, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansal, N.; Matheny, M.E.; Greevy, R.A., Jr.; Eden, S.K.; Perkins, A.M.; Parr, S.K.; Fly, J.; Abdel-Kader, K.; Himmelfarb, J.; Hung, A.M.; et al. Acute Kidney Injury and Risk of Incident Heart Failure Among US Veterans. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2018, 71, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Caestecker, M.; Humphreys, B.D.; Liu, K.D.; Fissell, W.H.; Cerda, J.; Nolin, T.D.; Askenazi, D.; Mour, G.; Harrell, F.E., Jr.; Pullen, N.; et al. Bridging Translation by Improving Preclinical Study Design in AKI. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 2905–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mentzer, R.M., Jr.; Oz, M.C.; Sladen, R.N.; Graeve, A.H.; Hebeler, R.F., Jr.; Luber, J.M., Jr.; Smedira, N.G. Effects of perioperative nesiritide in patients with left ventricular dysfunction undergoing cardiac surgery: The NAPA Trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 49, 716–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sezai, A.; Hata, M.; Niino, T.; Yoshitake, I.; Unosawa, S.; Wakui, S.; Kimura, H.; Shiono, M.; Takayama, T.; Hirayama, A. Results of low-dose human atrial natriuretic peptide infusion in nondialysis patients with chronic kidney disease undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting: The NU-HIT (Nihon University working group study of low-dose HANP Infusion Therapy during cardiac surgery) trial for CKD. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 58, 897–903. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Bold, A.J.; Borenstein, H.B.; Veress, A.T.; Sonnenberg, H. A rapid and potent natriuretic response to intravenous injection of atrial myocardial extract in rats. Life Sci. 1981, 28, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, J.C., Jr.; Granger, J.P.; Opgenorth, T.J. Effects of synthetic atrial natriuretic factor on renal function and renin release. Am. J. Physiol. 1984, 247 Pt 2, F863–F866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weidmann, P.; Hasler, L.; Gnadinger, M.P.; Lang, R.E.; Uehlinger, D.E.; Shaw, S.; Rascher, W.; Reubi, F.C. Blood levels and renal effects of atrial natriuretic peptide in normal man. J. Clin. Investig. 1986, 77, 734–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colucci, W.S.; Elkayam, U.; Horton, D.P.; Abraham, W.T.; Bourge, R.C.; Johnson, A.D.; Wagoner, L.E.; Givertz, M.M.; Liang, C.S.; Neibaur, M.; et al. Intravenous nesiritide, a natriuretic peptide, in the treatment of decompensated congestive heart failure. Nesiritide Study Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nonoguchi, H.; Sands, J.M.; Knepper, M.A. Atrial natriuretic factor inhibits vasopressin-stimulated osmotic water permeability in rat inner medullary collecting duct. J. Clin. Investig. 1988, 82, 1383–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Li, C.; Nejsum, L.N.; Li, H.; Kim, S.W.; Kwon, T.-H.; Jonassen, T.E.; Knepper, M.A.; Thomsen, K.; Frøkiær, J. Biphasic effects of ANP infusion in conscious, euvolumic rats: Roles of AQP2 and ENaC trafficking. Am. J. Physiol.-Renal Physiol. 2006, 290, F530–F541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvin, J.L. ANF inhibits norepinephrine-stimulated fluid absorption in rat proximal straight tubules. Am. J. Physiol. 1992, 263 Pt 2, F581–F585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantiello, H.F.; Ausiello, D.A. Atrial natriuretic factor and cGMP inhibit amiloride-sensitive Na+ transport in the cultured renal epithelial cell line, LLC-PK1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1986, 134, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Light, D.B.; Schwiebert, E.M.; Karlson, K.H.; Stanton, B.A. Atrial natriuretic peptide inhibits a cation channel in renal inner medullary collecting duct cells. Science 1989, 243, 383–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeidel, M.L.; Seifter, J.L.; Lear, S.; Brenner, B.M.; Silva, P. Atrial peptides inhibit oxygen consumption in kidney medullary collecting duct cells. Am. J. Physiol. 1986, 251 Pt 2, F379–F383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeidel, M.L.; Silva, P.; Brenner, B.M.; Seifter, J.L. cGMP mediates effects of atrial peptides on medullary collecting duct cells. Am. J. Physiol. 1987, 252 Pt 2, F551–F559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scavone, C.; Scanlon, C.; McKee, M.; Nathanson, J.A. Atrial natriuretic peptide modulates sodium and potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase through a mechanism involving cyclic GMP and cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1995, 272, 1036–1043. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Light, D.B.; Corbin, J.D.; Stanton, B.A. Dual ion-channel regulation by cyclic GMP and cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase. Nature 1990, 344, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.H.; Siragy, H.M.; Carey, R.M. Renal interstitial cGMP mediates natriuresis by direct tubule mechanism. Hypertension 2001, 38, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- MacFarland, R.T.; Zelus, B.D.; Beavo, J.A. High concentrations of a cGMP-stimulated phosphodiesterase mediate ANP-induced decreases in cAMP and steroidogenesis in adrenal glomerulosa cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nikolaev, V.O.; Gambaryan, S.; Engelhardt, S.; Walter, U.; Lohse, M.J. Real-time monitoring of the PDE2 activity of live cells: Hormone-stimulated cAMP hydrolysis is faster than hormone-stimulated cAMP synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 1716–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Harty, G.J.; Huntley, B.K.; Iyer, S.R.; Heublein, D.M.; Harders, G.E.; Meems, L.M.G.; Pan, S.; Sangaralingham, S.J.; Ichiki, T.; et al. CRRL269: A Novel Designer and Renal Enhancing pGC-A Peptide Activator. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, S.J.; Espiner, E.A.; Richards, A.M.; Yandle, T.G.; Frampton, C. Renal, endocrine, and hemodynamic effects of human brain natriuretic peptide in normal man. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1993, 76, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.H.; Huntley, B.K.; Schirger, J.A.; Cataliotti, A.; Burnett, J.C., Jr. Maximizing the renal cyclic 3′-5′-guanosine monophosphate system with type V phosphodiesterase inhibition and exogenous natriuretic peptide: A novel strategy to improve renal function in experimental overt heart failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 2742–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.L.; Ives, H.E.; Cogan, M.G. In vivo evidence that cGMP is the second messenger for atrial natriuretic factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 8015–8018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, A.M.; Tonolo, G.; Montorsi, P.; Finlayson, J.; Fraser, R.; Inglis, G.; Towrie, A.; Morton, J.J. Low dose infusions of 26- and 28-amino acid human atrial natriuretic peptides in normal man. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1988, 66, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, O.; Hong, S.-M.; Ramesh, G. Diminished NO generation by injured endothelium and loss of macula densa nNOS may contribute to sustained acute kidney injury after ischemia-reperfusion. Am. J. Physiol.-Renal Physiol. 2009, 296, F25–F33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.Y.; Huntley, B.K.; McCormick, D.J.; Ichiki, T.; Sangaralingham, S.J.; Lisy, O.; Burnett, J.C., Jr. Cenderitide: Structural requirements for the creation of a novel dual particulate guanylyl cyclase receptor agonist with renal-enhancing in vivo and ex vivo actions. Eur. Heart J.-Cardiovasc. Pharmacother. 2015, 2, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikkawa, R.; Haneda, M.; Sakamoto, K.; Koya, D.; Shikano, T.; Nakanishi, S.; Matsuda, Y.; Shigeta, Y. Antagonist for atrial natriuretic peptide receptors ameliorates glomerular hyperfiltration in diabetic rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1993, 193, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashatwar, S.S.; Cornwell, T.L.; Lincoln, T.M. Effects of 8-bromo-cGMP on Ca2+ levels in vascular smooth muscle cells: Possible regulation of Ca2+-ATPase by cGMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 5685–5689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubo, M.; Nakaya, Y.; Matsuoka, S.; Saito, K.; Kuroda, Y. Atrial natriuretic factor and isosorbide dinitrate modulate the gating of ATP-sensitive K+ channels in cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ. Res. 1994, 74, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnett, J.C., Jr.; Opgenorth, T.J.; Granger, J.P. The renal action of atrial natriuretic peptide during control of glomerular filtration. Kidney Int. 1986, 30, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, B.R.; Ichikawa, I.; Pfeffer, J.M.; Troy, J.L.; Brenner, B.M. Renal and systemic hemodynamic effects of synthetic atrial natriuretic peptide in the anesthetized rat. Circ. Res. 1986, 59, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin-Grez, M.; Fleming, J.T.; Steinhausen, M. Atrial natriuretic peptide causes pre-glomerular vasodilatation and post-glomerular vasoconstriction in rat kidney. Nature 1986, 324, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, M.-G.; Prieto, M.C.; Navar, L.G. Nebivolol-induced vasodilation of renal afferent arterioles involves β3-adrenergic receptor and nitric oxide synthase activation. Am. J. Physiol.-Renal Physiol. 2012, 303, F775–F782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appel, R.G.; Wang, J.; Simonson, M.S.; Dunn, M.J. A mechanism by which atrial natriuretic factor mediates its glomerular actions. Am. J. Physiol. 1986, 251 Pt 2, F1036–F1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer-Lehnert, H.; Tsai, P.; Caramelo, C.; Schrier, R.W. ANF inhibits vasopressin-induced Ca2+ mobilization and contraction in glomerular mesangial cells. Am. J. Physiol. 1988, 255 Pt 2, F771–F780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshihara, F.; Tokudome, T.; Kishimoto, I.; Otani, K.; Kuwabara, A.; Horio, T.; Kawano, Y.; Kangawa, K. Aggravated renal tubular damage and interstitial fibrosis in mice lacking guanylyl cyclase-A (GC-A), a receptor for atrial and B-type natriuretic peptides. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2015, 19, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Gogulamudi, V.R.; Periasamy, R.; Raghavaraju, G.; Subramanian, U.; Pandey, K.N. Inhibition of HDAC enhances STAT acetylation, blocks NF-kappaB, and suppresses the renal inflammation and fibrosis in Npr1 haplotype male mice. Am. J. Physiol.-Renal Physiol. 2017, 313, F781–F795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holditch, S.J.; Schreiber, C.A.; Nini, R.; Tonne, J.M.; Peng, K.W.; Geurts, A.; Jacob, H.J.; Burnett, J.C.; Cataliotti, A.; Ikeda, Y. B-Type Natriuretic Peptide Deletion Leads to Progressive Hypertension, Associated Organ Damage, and Reduced Survival: Novel Model for Human Hypertension. Hypertension 2015, 66, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.F.; Chao, J.; Chao, L. Atrial natriuretic peptide gene delivery attenuates hypertension, cardiac hypertrophy, and renal injury in salt-sensitive rats. Hum. Gene Ther. 1998, 9, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitaker, R.M.; Wills, L.P.; Stallons, L.J.; Schnellmann, R.G. cGMP-selective phosphodiesterase inhibitors stimulate mitochondrial biogenesis and promote recovery from acute kidney injury. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2013, 347, 626–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambaryan, S.; Wagner, C.; Smolenski, A.; Walter, U.; Poller, W.; Haase, W.; Kurtz, A.; Lohmann, S.M. Endogenous or overexpressed cGMP-dependent protein kinases inhibit cAMP-dependent renin release from rat isolated perfused kidney, microdissected glomeruli, and isolated juxtaglomerular cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 9003–9008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannken, T.; Schroeder, R.; Stahl, R.A.; Wolf, G. Atrial natriuretic peptide attenuates ANG II-induced hypertrophy of renal tubular cells. Am. J. Physiol.-Renal Physiol. 2001, 281, F81–F90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, K.N.; Nguyen, H.T.; Li, M.; Boyle, J.W. Natriuretic peptide receptor-A negatively regulates mitogen-activated protein kinase and proliferation of mesangial cells: Role of cGMP-dependent protein kinase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 271, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schinner, E.; Schramm, A.; Kees, F.; Hofmann, F.; Schlossmann, J. The cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase Ialpha suppresses kidney fibrosis. Kidney Int. 2013, 84, 1198–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Tong, X.; Maimaitiyiming, H.; Clemons, K.; Cao, J.M.; Wang, S. Overexpression of cGMP-dependent protein kinase I (PKG-I) attenuates ischemia-reperfusion-induced kidney injury. Am. J. Physiol.-Renal Physiol. 2012, 302, F561–F570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maimaitiyiming, H.; Li, Y.; Cui, W.; Tong, X.; Norman, H.; Qi, X.; Wang, S. Increasing cGMP-dependent protein kinase I activity attenuates cisplatin-induced kidney injury through protection of mitochondria function. Am. J. Physiol.-Renal Physiol. 2013, 305, F881–F890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meems, L.M.G.; Burnett, J.C., Jr. Innovative Therapeutics: Designer Natriuretic Peptides. JACC Basic Transl. Sci. 2016, 1, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Burnett, J.C., Jr. Biochemistry, Therapeutics, and Biomarker Implications of Neprilysin in Cardiorenal Disease. Clin. Chem. 2017, 63, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felker, G.M.; O’Connor, C.M.; Braunwald, E. Loop diuretics in acute decompensated heart failure: Necessary? Evil? A necessary evil? Circ. Heart Fail. 2009, 2, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cataliotti, A.; Boerrigter, G.; Costello-Boerrigter, L.C.; Schirger, J.A.; Tsuruda, T.; Heublein, D.M.; Chen, H.H.; Malatino, L.S.; Burnett, J.C., Jr. Brain natriuretic peptide enhances renal actions of furosemide and suppresses furosemide-induced aldosterone activation in experimental heart failure. Circulation 2004, 109, 1680–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Burnett, J.C. Particulate Guanylyl Cyclase A/cGMP Signaling Pathway in the Kidney: Physiologic and Therapeutic Indications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041006
Chen Y, Burnett JC. Particulate Guanylyl Cyclase A/cGMP Signaling Pathway in the Kidney: Physiologic and Therapeutic Indications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(4):1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041006
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yang, and John C. Burnett. 2018. "Particulate Guanylyl Cyclase A/cGMP Signaling Pathway in the Kidney: Physiologic and Therapeutic Indications" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 4: 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041006
APA StyleChen, Y., & Burnett, J. C. (2018). Particulate Guanylyl Cyclase A/cGMP Signaling Pathway in the Kidney: Physiologic and Therapeutic Indications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(4), 1006. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041006