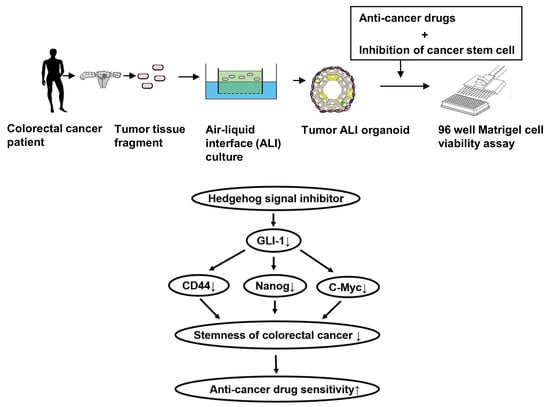
Hedgehog Signals Mediate Anti-Cancer Drug Resistance in Three-Dimensional Primary Colorectal Cancer Organoid Culture
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of Stem Cell-Related Signal Inhibitors on Cell Viability of Tumor Organoids
2.2. Effects of Hedgehog Signal Inhibitors on the Sensitivity for Anti-Cancer Drugs in Tumor Organoids
2.3. Effects of Hedgehog Signal Inhibitors on Expression of Stem Cell Marker Proteins in Tumor Organoids
2.4. Effects of Co-Treatment with Hedgehog Signal Inhibitors and Anti-Cancer Drugs on Colony Formation in Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Colorectal Tumor Tissues
4.4. Generation of Three-Dimensional ALI Tumor Colorectal Organoids
4.5. Cell Viability Assay of Organoids
4.6. Western Blotting
4.7. Colony Formation Assay
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Shin, H.R.; Bray, F.; Forman, D.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: Globocan 2008. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 2893–2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Siegel, R.L.; Ferlay, J.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordlinger, B.; Rougier, P. Liver metastases from colorectal cancer: The turning point. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 1442–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenz, H.J. First-line combination treatment of colorectal cancer with hepatic metastases: Choosing a targeted agent. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2008, 34 (Suppl. 2), S3–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croker, A.K.; Allan, A.L. Cancer stem cells: Implications for the progression and treatment of metastatic disease. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2008, 12, 374–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, E.H.; Wicha, M.S. Colon cancer stem cells: Implications for prevention and therapy. Trends Mol. Med. 2008, 14, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todaro, M.; Francipane, M.G.; Medema, J.P.; Stassi, G. Colon cancer stem cells: Promise of targeted therapy. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 2151–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepourcelet, M.; Chen, Y.N.; France, D.S.; Wang, H.; Crews, P.; Petersen, F.; Bruseo, C.; Wood, A.W.; Shivdasani, R.A. Small-molecule antagonists of the oncogenic Tcf/β-catenin protein complex. Cancer Cell 2004, 5, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoey, T.; Yen, W.C.; Axelrod, F.; Basi, J.; Donigian, L.; Dylla, S.; Fitch-Bruhns, M.; Lazetic, S.; Park, I.K.; Sato, A.; et al. Dll4 blockade inhibits tumor growth and reduces tumor-initiating cell frequency. Cell Stem Cell 2009, 5, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usui, T.; Sakurai, M.; Enjoji, S.; Kawasaki, H.; Umata, K.; Ohama, T.; Fujiwara, N.; Yabe, R.; Tsuji, S.; Yamawaki, H.; et al. Establishment of a novel model for anticancer drug resistance in three-dimensional primary culture of tumor microenvironment. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 7053872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingham, P.W.; McMahon, A.P. Hedgehog signaling in animal development: Paradigms and principles. Genes Dev. 2001, 15, 3059–3087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batsaikhan, B.E.; Yoshikawa, K.; Kurita, N.; Iwata, T.; Takasu, C.; Kashihara, H.; Shimada, M. Cyclopamine decreased the expression of sonic hedgehog and its downstream genes in colon cancer stem cells. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 6339–6344. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nagare, R.P.; Sneha, S.; Priya, S.K.; Ganesan, T.S. Cancer Stem Cells—Are Surface Markers Alone Sufficient? Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 12, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palle, K.; Mani, C.; Tripathi, K.; Athar, M. Aberrant gli1 activation in DNA damage response, carcinogenesis and chemoresistance. Cancers 2015, 7, 2330–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Cui, Y.; Ni, W.; Kim, S.; Xuan, Y. Gli1, a potential regulator of esophageal cancer stem cell, is identified as an independent adverse prognostic factor in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 143, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolba, M.F.; Abdel-Rahman, S.Z. Pterostilbine, an active component of blueberries, sensitizes colon cancer cells to 5-fluorouracil cytotoxicity. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Song, R.; Gu, D.; Zhang, X.; Yu, B.; Liu, B.; Xie, J. The role of gli1 for 5-fu resistance in colorectal cancer. Cell Biosci. 2017, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, B.A.; Vega, K.J.; Houchen, C.W. Intestinal stem cells and the colorectal cancer microenvironment. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 1898–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, R.F.; Moore, T.T.; Hattersley, M.M.; Scarpitti, M.; Yang, B.; Devereaux, E.; Ramachandran, V.; Arumugam, T.; Ji, B.; Logsdon, C.D.; et al. Inhibition of the hedgehog pathway targets the tumor-associated stroma in pancreatic cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2012, 10, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Callahan, C.A.; DuPree, K.J.; Darbonne, W.C.; Ahn, C.P.; Scales, S.J.; de Sauvage, F.J. Hedgehog signaling is restricted to the stromal compartment during pancreatic carcinogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 4254–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olive, K.P.; Jacobetz, M.A.; Davidson, C.J.; Gopinathan, A.; McIntyre, D.; Honess, D.; Madhu, B.; Goldgraben, M.A.; Caldwell, M.E.; Allard, D.; et al. Inhibition of hedgehog signaling enhances delivery of chemotherapy in a mouse model of pancreatic cancer. Science 2009, 324, 1457–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buller, N.V.; Rosekrans, S.L.; Metcalfe, C.; Heijmans, J.; van Dop, W.A.; Fessler, E.; Jansen, M.; Ahn, C.; Vermeulen, J.L.; Westendorp, B.F.; et al. Stromal indian hedgehog signaling is required for intestinal adenoma formation in mice. Gastroenterology 2015, 148, 170–180.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirschmann-Jax, C.; Foster, A.E.; Wulf, G.G.; Nuchtern, J.G.; Jax, T.W.; Gobel, U.; Goodell, M.A.; Brenner, M.K. A distinct “side population” of cells with high drug efflux capacity in human tumor cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14228–14233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rich, J.N. Cancer stem cells in radiation resistance. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 8980–8984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockler, M.; Wilcken, N.R.; Ghersi, D.; Simes, R.J. Systematic reviews of chemotherapy and endocrine therapy in metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2000, 26, 151–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, T.; Xu, J.; Zhu, Y. Self-renewal molecular mechanisms of colorectal cancer stem cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 39, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, M.T.; Hermann, P.C.; Witthauer, J.; Rubio-Viqueira, B.; Leicht, S.F.; Huber, S.; Ellwart, J.W.; Mustafa, M.; Bartenstein, P.; D’Haese, J.G.; et al. Combined targeted treatment to eliminate tumorigenic cancer stem cells in human pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology 2009, 137, 1102–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Li, C.; He, F.; Cai, Y.; Yang, H. Identification of CD44+CD24+ gastric cancer stem cells. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 137, 1679–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varnat, F.; Duquet, A.; Malerba, M.; Zbinden, M.; Mas, C.; Gervaz, P.; Ruiz i Altaba, A. Human colon cancer epithelial cells harbour active hedgehog-gli signalling that is essential for tumour growth, recurrence, metastasis and stem cell survival and expansion. EMBO Mol. Med. 2009, 1, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galimberti, F.; Busch, A.M.; Chinyengetere, F.; Ma, T.; Sekula, D.; Memoli, V.A.; Dragnev, K.H.; Liu, F.; Johnson, K.C.; Guo, Y.; et al. Response to inhibition of smoothened in diverse epithelial cancer cells that lack smoothened or patched 1 mutations. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 41, 1751–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, J.A.; de Sauvage, F.J. Clinical experience with hedgehog pathway inhibitors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 5321–5326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMillan, R.; Matsui, W. Molecular pathways: The hedgehog signaling pathway in cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4883–4888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yauch, R.L.; Dijkgraaf, G.J.; Alicke, B.; Januario, T.; Ahn, C.P.; Holcomb, T.; Pujara, K.; Stinson, J.; Callahan, C.A.; Tang, T.; et al. Smoothened mutation confers resistance to a hedgehog pathway inhibitor in medulloblastoma. Science 2009, 326, 572–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agyeman, A.; Mazumdar, T.; Houghton, J.A. Regulation of DNA damage following termination of hedgehog (hh) survival signaling at the level of the gli genes in human colon cancer. Oncotarget 2012, 3, 854–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Nadauld, L.; Ootani, A.; Corney, D.C.; Pai, R.K.; Gevaert, O.; Cantrell, M.A.; Rack, P.G.; Neal, J.T.; Chan, C.W.; et al. Oncogenic transformation of diverse gastrointestinal tissues in primary organoid culture. Nat. Med. 2014, 20, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ootani, A.; Li, X.; Sangiorgi, E.; Ho, Q.T.; Ueno, H.; Toda, S.; Sugihara, H.; Fujimoto, K.; Weissman, I.L.; Capecchi, M.R.; et al. Sustained in vitro intestinal epithelial culture within a wnt-dependent stem cell niche. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 701–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kake, S.; Usui, T.; Ohama, T.; Yamawaki, H.; Sato, K. Death-associated protein kinase 3 controls the tumor progression of a549 cells through erk mapk/c-myc signaling. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 1100–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, N.; Usui, T.; Ohama, T.; Sato, K. Regulation of beclin 1 protein phosphorylation and autophagy by protein phosphatase 2a (pp2a) and death-associated protein kinase 3 (dapk3). J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 10858–10866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yabe, R.; Miura, A.; Usui, T.; Mudrak, I.; Ogris, E.; Ohama, T.; Sato, K. Protein phosphatase methyl-esterase pme-1 protects protein phosphatase 2a from ubiquitin/proteasome degradation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Usui, T.; Sakurai, M.; Umata, K.; Elbadawy, M.; Ohama, T.; Yamawaki, H.; Hazama, S.; Takenouchi, H.; Nakajima, M.; Tsunedomi, R.; et al. Hedgehog Signals Mediate Anti-Cancer Drug Resistance in Three-Dimensional Primary Colorectal Cancer Organoid Culture. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041098
Usui T, Sakurai M, Umata K, Elbadawy M, Ohama T, Yamawaki H, Hazama S, Takenouchi H, Nakajima M, Tsunedomi R, et al. Hedgehog Signals Mediate Anti-Cancer Drug Resistance in Three-Dimensional Primary Colorectal Cancer Organoid Culture. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(4):1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041098
Chicago/Turabian StyleUsui, Tatsuya, Masashi Sakurai, Koji Umata, Mohamed Elbadawy, Takashi Ohama, Hideyuki Yamawaki, Shoichi Hazama, Hiroko Takenouchi, Masao Nakajima, Ryouichi Tsunedomi, and et al. 2018. "Hedgehog Signals Mediate Anti-Cancer Drug Resistance in Three-Dimensional Primary Colorectal Cancer Organoid Culture" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 4: 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041098
APA StyleUsui, T., Sakurai, M., Umata, K., Elbadawy, M., Ohama, T., Yamawaki, H., Hazama, S., Takenouchi, H., Nakajima, M., Tsunedomi, R., Suzuki, N., Nagano, H., Sato, K., Kaneda, M., & Sasaki, K. (2018). Hedgehog Signals Mediate Anti-Cancer Drug Resistance in Three-Dimensional Primary Colorectal Cancer Organoid Culture. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(4), 1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041098