Sesamol Inhibited Melanogenesis by Regulating Melanin-Related Signal Transduction in B16F10 Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. B16F10 Cell Viability with Sesamol Treatment
2.2. Sesamol Inhibited Melanin Biosynthesis in B16F10 Cells
2.3. Sesamol Inhibited Tyrosinase Activity in B16F10 Cells
2.4. Sesamol Inhibited Tyrosinase and TRP-1 Protein Expression in B16F10 Cells
2.5. Sesamol Downregulated MC1R and MITF Expression
2.6. Sesamol Inhibited Melanogenesis by Upregulating p-AKT and p-GSK3β Expression
2.7. Sesamol Upregulated p-ERK Expression
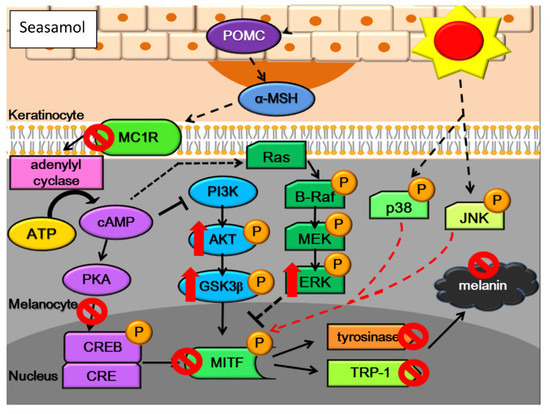
2.8. Effects of Sesamol on the Melanogenesis Signalling Pathway
2.8.1. Inhibition of Melanogenesis by Sesamol was Associated with PKA/MSK Regulation
2.8.2. Sesamol Inhibited Melanogenesis by Inhibiting PI3K
2.8.3. Sesamol Inhibited Melanogenesis by Inhibiting ERK
2.8.4. Sesamol Inhibited Melanogenesis by Inhibiting p38
2.8.5. Sesamol Inhibited Melanogenesis by Inhibiting JNK
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Materials
4.2. Cell Cultures and Cell Viability Assay
4.3. Melanin Content and Tyrosinase Activity Assay in B16F10 Cells
4.4. Western Blotting
4.5. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of interest
Abbreviations
| α-MSH | α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone |
| cAMP | cyclic adenosine monophosphate |
| CAPE | caffeic acid phenethyl ester |
| CREB | cAMP response element binding protein |
| p-CREB | phospho-cAMP response element binding protein |
| DHICA | 5,6-dihydroxyindole-2-carboxylic acid |
| l-DOPA | l-dihydroxyphenylalanine |
| DMSO | dimethyl sulfoxide |
| FBS | fetal bovine serum |
| GSK3β | glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta |
| MC1R | melanocortin 1 receptor |
| MITF | microphthalmia-associated transcription factor |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| PKA | protein kinase A |
| TRP-1 | tyrosinase-related protein-1 |
| TRP-2 | tyrosinase-related protein-2 |
References
- Brenner, M.; Hearing, V.J. The protective role of melanin against UV damage in human skin. Photochem. Photobiol. 2008, 84, 539–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Orazio, J.; Jarrett, S.; Amaro-Ortiz, A.; Scott, T. UV radiation and the skin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 12222–12248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, T.H.; Ding, H.Y.; Lin, R.J.; Liang, J.Y.; Liang, C.H. Inhibition of melanogenesis and oxidation by protocatechuic acid from Origanum vulgare (oregano). J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1767–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meira, W.V.; Heinrich, T.A.; Cadena, S.M.; Martinez, G.R. Melanogenesis inhibits respiration in B16-F10 melanoma cells whereas enhances mitochondrial cell content. Exp. Cell Res. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costin, G.E.; Hearing, V.J. Human skin pigmentation: Melanocytes modulate skin color in response to stress. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 976–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.; Tobin, D.J.; Shibahara, S.; Wortsman, J. Melanin pigmentation in mammalian skin and its hormonal regulation. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 1155–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.; Wortsman, J.; Luger, T.; Paus, R.; Solomon, S. Corticotropin releasing hormone and proopiomelanocortin involvement in the cutaneous response to stress. Physiol. Rev. 2000, 80, 979–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hearing, V.J. Determination of melanin synthetic pathways. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, E8–E11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Mello, S.A.; Finlay, G.J.; Baguley, B.C.; Askarian-Amiri, M.E. Signaling Pathways in Melanogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillaiyar, T.; Manickam, M.; Jung, S.H. Recent development of signaling pathways inhibitors of melanogenesis. Cell. Signal. 2017, 40, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, T.; Hearing, V.J. Update on the regulation of mammalian melanocyte function and skin pigmentation. Expert Rev. Dermatol. 2011, 6, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.; Zmijewski, M.A.; Pawelek, J. l-tyrosine and l-dihydroxyphenylalanine as hormone-like regulators of melanocyte functions. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2012, 25, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slominski, A.T.; Zmijewski, M.A.; Zbytek, B.; Tobin, D.J.; Theoharides, T.C.; Rivier, J. Key role of CRF in the skin stress response system. Endocr. Rev. 2013, 34, 827–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hearing, V.J. Milestones in melanocytes/melanogenesis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, E1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhuang, Y. Antioxidant and Anti-tyrosinase Activities of Phenolic Extracts from Rape Bee Pollen and Inhibitory Melanogenesis by cAMP/MITF/TYR Pathway in B16 Mouse Melanoma Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, F.L.; Wang, M.C.; Liang, C.J.; Ko, H.H.; Lee, C.W. Melanogenesis Inhibitor(s) from Phyla nodiflora Extract. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 867494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanimozhi, P.; Prasad, N.R. Antioxidant potential of sesamol and its role on radiation-induced DNA damage in whole-body irradiated Swiss albino mice. Perumal Kanimozhi, Nagarajan Rajendra Prasad 2009, 28, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geetha, T.; Rohit, B.; Pal, K.I. Sesamol: An efficient antioxidant with potential therapeutic benefits. Med. Chem. 2009, 5, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Xiang, Q.; Du, L.; Song, G.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X. The interaction of sesamol with DNA and cytotoxicity, apoptosis, and localization in HepG2 cells. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, N.; Rai, A.K.; Kumari, R.; Bhat, K.V. Value addition in sesame: A perspective on bioactive components for enhancing utility and profitability. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2014, 8, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, Y.; Hearing, V.J. Physiological factors that regulate skin pigmentation. BioFactors 2009, 35, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oka, M.; Nagai, H.; Ando, H.; Fukunaga, M.; Matsumura, M.; Araki, K.; Ogawa, W.; Miki, T.; Sakaue, M.; Tsukamoto, K.; et al. Regulation of melanogenesis through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt pathway in human G361 melanoma cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2000, 115, 699–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, K.S.; Yang, J.Y.; Lee, J.; Lee, Y.R.; Kim, S.S.; Kim, G.R.; Chae, J.S.; Ahn, J.H.; Shin, D.S.; Choi, T.Y.; et al. A novel anti-melanogenic agent, KDZ-001, inhibits tyrosinase enzymatic activity. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaei, M.; Mohammadi, H.T.; Mahdavi, A.; Shourian, M.; Ghafouri, H. Evaluation of thiazolidinone derivatives as a new class of mushroom tyrosinase inhibitors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 108, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, C.M.; Sathisha, U.V.; Dharmesh, S.; Rao, A.G.; Singh, S.A. Interaction of sesamol (3,4-methylenedioxyphenol) with tyrosinase and its effect on melanin synthesis. Biochimie 2011, 93, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Imokawa, G.; Bennett, D.C.; Hearing, V.J. Tyrosinase stabilization by Tyrp1 (the brown locus protein). J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 31801–31805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, S.H.; Lee, S.H. Sesamol decreases melanin biosynthesis in melanocyte cells and zebrafish: Possible involvement of MITF via the intracellular cAMP and p38/JNK signalling pathways. Exp. Dermatol. 2015, 24, 761–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, C.T.; Kwon, T.R.; Jang, Y.J.; Yoo, K.H.; Kim, B.J.; Kim, H. Inhibitory effects of Stichopus japonicus extract on melanogenesis of mouse cells via ERK phosphorylation. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 1079–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, C.Y.; You, S.T.; Kim, J.H.; Chung, J.H.; Han, S.B.; Shin, E.Y.; Kim, E.G. p21-Activated Kinase 4 Critically Regulates Melanogenesis via Activation of the CREB/MITF and β-Catenin/MITF Pathways. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagashira, H.; Miyamoto, A.; Kitamura, S.; Tsubata, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Takagaki, K.; Imokawa, G. UVB Stimulates the Expression of Endothelin B Receptor in Human Melanocytes via a Sequential Activation of the p38/MSK1/CREB/MITF Pathway Which Can Be Interrupted by a French Maritime Pine Bark Extract through a Direct Inactivation of MSK1. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, Y.T.; Kuo, C.Y.; Kuan, Y.D.; Lin, H.C.; Wu, L.H.; Lee, C.H. The Extracts of Astragalus membranaceus Inhibit Melanogenesis through the ERK Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 14, 1049–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.C.; Lin, Y.Y.; Yang, S.Y.; Weng, Y.T.; Tsai, Y.T. Antimelanogenic effect of c-phycocyanin through modulation of tyrosinase expression by upregulation of ERK and downregulation of p38 MAPK signaling pathways. J. Biomed. Sci. 2011, 18, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, H.M.; Chien, Y.C.; Wu, C.H.; Kuo, Y.H.; Wu, W.C.; Pan, Y.Y.; Su, Y.H.; Wen, K.C. Hydroalcoholic extract of Rhodiola rosea L. (Crassulaceae) and its hydrolysate inhibit melanogenesis in B16F0 cells by regulating the CREB/MITF/tyrosinase pathway. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 65, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, Y.H.; Chen, C.C.; Lin, P.; You, Y.J.; Chiang, H.M. N-(4-bromophenethyl) Caffeamide Inhibits Melanogenesis by Regulating AKT/Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 Beta/Microphthalmia-associated Transcription Factor and Tyrosinase-related Protein 1/Tyrosinase. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2015, 16, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, K.C.; Chang, C.S.; Chien, Y.C.; Wang, H.W.; Wu, W.C.; Wu, C.S.; Chiang, H.M. Tyrosol and its analogues inhibit α-melanocyte-stimulating hormone induced melanogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 23420–23440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]











© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, P.-Y.; You, Y.-J.; Liu, Y.-J.; Hou, C.-W.; Wu, C.-S.; Wen, K.-C.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chiang, H.-M. Sesamol Inhibited Melanogenesis by Regulating Melanin-Related Signal Transduction in B16F10 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1108. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041108
Wu P-Y, You Y-J, Liu Y-J, Hou C-W, Wu C-S, Wen K-C, Lin C-Y, Chiang H-M. Sesamol Inhibited Melanogenesis by Regulating Melanin-Related Signal Transduction in B16F10 Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(4):1108. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041108
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Po-Yuan, Ya-Jhen You, Yi-Jung Liu, Chien-Wei Hou, Chin-Sheng Wu, Kuo-Ching Wen, Chien-Yih Lin, and Hsiu-Mei Chiang. 2018. "Sesamol Inhibited Melanogenesis by Regulating Melanin-Related Signal Transduction in B16F10 Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 4: 1108. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041108
APA StyleWu, P. -Y., You, Y. -J., Liu, Y. -J., Hou, C. -W., Wu, C. -S., Wen, K. -C., Lin, C. -Y., & Chiang, H. -M. (2018). Sesamol Inhibited Melanogenesis by Regulating Melanin-Related Signal Transduction in B16F10 Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(4), 1108. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041108