CA 19-9 Pancreatic Tumor Marker Fluorescence Immunosensing Detection via Immobilized Carbon Quantum Dots Conjugated Gold Nanocomposite
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Characterization of CQDs
2.2. Characterization of CQDs/Au Nanocomposite
2.3. Optimization of Fluorescence Immunoassay Detection Conditions
2.4. Analytical Figures of Merit
2.5. Suitability of CQDs/Au–Ab–HRP Immunoassay Technique
2.6. Accuracy and Precision of CQDs/Au–Ab–HRP Immunoassay Technique
2.7. Study of Possible Interferences
2.8. Analysis of Real Samples
3. Experimental
3.1. Instrumentation
3.2. Chemicals and Reagents
3.3. Synthesis of CQDs
3.4. Preparation of CQDs/Au Nanocomposite
3.5. Spectroscopic and Microscopic Analysis of the CQDs/Au Nanocomposite
3.6. Immobilization of CA19-9 Ab–HRP Enzyme on CQDs/Au Nanocomposite
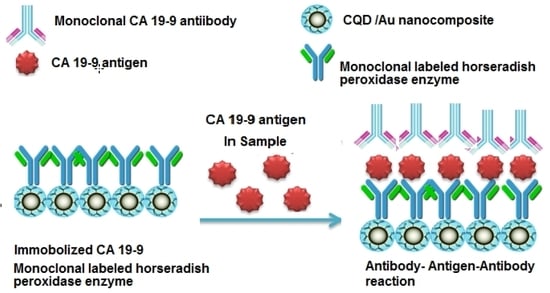
3.7. General Principle of the Immunoassay Method
3.8. The Immunoassay Procedure
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics 2017. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauter, E. Reliable biomarkers to identify new and recurrent cancer. Eur. J. Breast Health 2017, 13, 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mordente, A.; Meucci, E.; Martorana, G.; Silvestrini, A. Cancer biomarkers discovery and validation: State of the art, problems and future perspectives. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 867, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mayeux, R. Biomarkers: Potential uses and limitations. NeuroRx 2004, 1, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J; Shi, Q.; Mirza, W.; Jecmenica, M.; Yoder, M.; Mulloth, R.; Gordon, E.; Sothwal, A.; Thanneer, S.; Dharmapuri, S. Extremely high serum level of carbohydrate antigen 19-9 in a patient with colon adenocarcinoma. Cancer Rep. Rev. 2007, 1, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baryeh, K.; Takalkar, S.; Lund, M.; Liu, G. Development of quantitative immune chromatographic assay for rapid and sensitive detection of carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA 19-9) in human plasma. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 146, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazelton, W.; Luebeck, E. Biomarker-based early cancer detection: Is it achievable? Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 109fs9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohkura, H.; Sakawaki, O.; Ozaki, H. Enzyme immunoassay of CA19-9. Enzyme immunoassay and its clinical application. Kan Tan Sui 1985, 11, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Nishizono, I.; Uda, S.; Suzuki, N.; Kawada, H.; Murakami, H.; Ashihara, Y.; Okada, M. Rapid and sensitive chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassay for measuring tumor markers. Clin. Chem. 1991, 37, 1639–1644. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Du, D.; Yan, F.; Liu, S.; Ju, H. Electrochemical immunosensor for carbohydrate antigen 19-9 based on immunological reaction and its immobilization in titania sol–gel matrix. J. Immunol. Methods 2003, 283, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Yan, F.; Hu, X.; Ju, H. Chemiluminescent immunosensor for CA19-9 based on antigen immobilization on a cross-linked chitosan membrane. J. Immunol. Methods 2004, 291, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, B.; Xu, C.; Yang, C.; Liu, S.; Wang, M. ZnO quantum dot labeled immunosensor for carbohydrate antigen 19-9. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 2720–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.; Tang, Y.; Ge, L.; Guo, B.; Yao, C. Amperometric carbohydrate antigen 19-9 immunosensor based on three dimensional ordered macroporous magnetic Au film coupling direct electrochemistry of horseradish peroxidase. Anal. Chem. Acta 2014, 815, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Zhao, C.; Han, W.; Lin, L.; Liu, A.; Weng, S.; Lin, X. Simple and effective label-free electrochemical immunoassay for carbohydrate antigen 19-9 based on polythionine-Au composites as enhanced sensing signals for detecting different clinical samples. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 3049–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, T.H.; Cheon, J. Synergism of nanomaterials with physical stimuli for biology and medicine. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017, 50, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Gu, H. Novel metal nanomaterials and their catalytic applications. Molecules 2015, 20, 17070–17092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallakpour, S.; Khadadazadeh, L. Ultrasonic-assisted fabrication of starch/MWCNT-glucose nanocomposites for drug delivery. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2018, 40, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghdisi, S.M.; Danesh, N.M.; Ramezani, M.; Yazdian-Robati, R.; Abnous, K. An amplified fluorescent aptasensor based on single-stranded DNA binding protein, copper and silica nanoparticles for sensitive detection of interferon-gamma. Anal. Chem. Acta 2017, 984, 62–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Ding, R.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Qu, L.; Pei, H.; Yildirimer, L.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, W. Graphene-based nanomaterials for drug and/or gene delivery, bioimaging and tissue engineering. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 1302–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryvolova, M.; Chomoucka, J.; Drbohlavova, J.; Kopel, P.; Babula, P.; Hynek, D.; Adam, V.; Eckschlager, T.; Hubalek, J.; Stiborova, M.; Kaiser, J.; et al. Modern micro and nanoparticle-based imaging techniques. Sensors 2012, 12, 14792–14820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Baldo, M.A.; Oetega, F.G.; Pareira, S.V.; Bertolino, F.A.; Serrano, M.J.; Lorente, J.A.; Raba, J.; Messina, G.A. Nanostructured platform integrated into a microfluidic immunosensor coupled to laser-induced fluorescence for the epithelial cancer biomarker determination. Michrochem. J. 2016, 128, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlo, G.D.; Curulli, A.; Toro, R.G.; Bianchini, C.; De Caro, T.; Padeletti, G.; Zane, D.; Ingo, G.M. Green synthesis of gold–chitosan nanocomposites for caffeic acid sensing. Langmuir 2012, 28, 5471–5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, W.; Gu, Y.; Li, L. Green synthesis of graphene/Ag nanocomposites. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 261, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thambiraj, S.; Shankaran, D. Green synthesis of highly fluorescent carbon quantum dots from sugarcane bagasse pulp. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 390, 435–443. [Google Scholar]
- Samal, M.; Mohapatra, P.; Subbiah, R.; Lee, C.; Anass, B.; Kim, J.; Kim, T.; Yi, D. InP/ZnS-graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites as fascinating materials for potential optoelectronic applications. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 9793–97805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, M.; Zhao, Z.; Hu, Z.; Liu, L.; Ji, H.; Shen, Z.; Ma, T. 0D/2D Heterojunctions of vanadate quantum dots/graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets for enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2017, 56, 8407–8411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javanbakht, S.; Namazi, H. Solid state photoluminescence thermoplastic starch film containing graphene quantum dots. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 176, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Li, S.; Yuan, F.; Fan, L. Fluorescent graphene quantum dots for biosensing and bioimaging. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 19773–19789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beloglazova, N.V.; Shmelin, P.S.; Speranaskaya, E.S.; Lucas, B.; Helmbrecht, C.; Knopp, D.; Niessner, R.; De Saeger, S.; Yu, I. Quantum dot loaded liposomes as fluorescent labels for immunoassay. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 7197–7204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Wei, P.; pengpumkiat, S.; Schumacher, E.A.; Remcho, V.T. Development of a carbon dot (C-dot)-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of human α-fetoprotein. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 8510–8516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Essner, J.B.; Laber, C.H.; Baker, G.A. Carbon dot reduced bimetallic nanoparticles: Size and surface plasmon resonance tunability for enhanced catalytic applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 16354–16360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Cui, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, P.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Z.; Dong, Y. A novel label-free electrochemical immunosensor based on functionalized nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots for carcinoembryonic antigen detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 90, 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Camargo, P.H.C.; Satyanarayana, K.G.; Wypych, F. Nanocomposites: Synthesis, structure, properties and new application opportunities. Mater. Res. 2009, 12, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zheng, J.; Yang, S.; Wu, C.; Liu, C.; Xiao, Y.; Li, Y.; Qing, Z.; Yang, R. Two-Photon Sensing and Imaging of Endogenous Biological Cyanide in Plant Tissues Using Graphene Quantum Dot/Gold Nanoparticle Conjugate. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 19509–19515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Chan, C.; Pang, Y.; Ye, W.; Tian, F.; Lyu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M. A fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) biosensor based on graphene quantum dots (GQDs) and gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) for the detection of mecA gene sequence of Staphylococcus aureus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 67, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; He, X.; Wang, K.; He, D.; Wang, Y.; Mao, Y.; Shi, H.; Wen, L. A highly sensitive electrochemiluminescence assay for protein kinase based on double-quenching of graphene quantum dots by G-quadruplex-hemin and gold nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 70, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ting, S.L.; Ee, S.J.; Ananthanarayanan, A.; Leong, K.C.; Chen, P. Graphene quantum dots functionalized gold nanoparticles for sensitive electrochemical detection of heavy metal ions. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 172, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Wei, W.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S. Electrochemiluminescence resonance energy transfer between graphene quantum dots and gold nanoparticles for DNA damage detection. Analyst 2014, 139, 2404–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, J.; Wang, K.C.; Wang, C.; Hua, M.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Mao, H.; Wang, K. A FRET-based ratiometric fluorescent aptasensor for rapid and onsite visual detection of ochratoxin A. Analyst 2015, 140, 7434–7442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Wu, H.; Shang, P.; Zeng, X.; Chi, Y. immobilizing water-soluble graphene quantum dots with gold nanoparticles for a low potential electrochemiluminescence immunosensor. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 16366–16371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazloum-Ardakani, M.; Aghaei, R.; Abdollahi-Alibeik, M.; Moaddeli, A. Fabrication of modified glassy carbon electrode using graphene quantum dot, gold nanoparticles and 4-(((4-mercaptophenyl) imino) methyl) benzene-1,2-diol by self-assembly methodand investigation of their electrocatalytic activities. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2015, 738, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Tian, F.; Lyu, J.; Yang, M. Nanoparticle based fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) for biosensing applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 6989–7005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthurasu, A.; Ganesh, V. Horseradish peroxidase enzyme immobilized graphene quantum dots as electrochemical biosensors. Appl. Biotechem. Biotechnol. 2014, 174, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, J.; Huang, X.; Liu, H.; Guo, S.; Zhang, J. Horseradish peroxidase immobilized on graphene oxide: Physical properties and applications in phenolic compound removal. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 8469–8473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tertis, M.; Florea, A.; Sandulescu, R.; Cristea, C. Carbon based electrodes modified with horseradish peroxidase immobilized in conducting polymers for acetaminophen Analysis. Sensors 2013, 13, 4841–4854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amjadi, M.; Hallaj, T.; Asadollahi, H.; Song, Z.; de Frutos, M.; Hildebrandt, N. Facile synthesis of Carbon quantum dot/Ag nanocomposite and its application for colorimetric detection of methimazole. Sens. Actuators B 2017, 244, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Technique | Principle | Linear Concentration Range U mL−1 | Detection Limit U mL−1 | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrochemical immunoassay | Immobilization of CA 19-9 antigen with titania sol–gel on a graphite electrode | 3–20 | 2.68 | [10] |
| Chemiluminescent immunosensor assay | Immobilization of CA 19-9 antigen on the cross-linked membrane | 2.0–25 | 1.0 | [11] |
| Chemiluminescent enzyme immunoassay | Using a derivative of 1,2-dioxetane phosphate to measure alkaline phosphatase as a labeling enzyme for the detection of CA 19-9 | 6.0–520 | 0.26 | [9] |
| ZnO quantum dots immunoassay | Employing ZnO quantum dots as an electrochemical and luminescent immunoassay | 0.1–180 1.0–180 | 0.04 0.25 | [12] |
| Amperometric electrochemical immunoassay | Immobilization of CA 19-9 antibody on three-dimensional ordered macroporous magnetic sensors | 0.05–15.65 | 0.01 | [13] |
| Proposed CQDs/Au nanocomposite immunoassay method | Using CQDs/Au nanocomposite in the detection of CA 19-9 by a solid- phase immunoassay | 0.01–350 | 0.007 | Present study |
| Samples | Immobilized CQDs/Au/HRP Method | Immobilized Chemiluminscence Cross-Linked Chitosan Method [11] | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Found U mL−1 | % RSD (n = 6) | Found U mL−1 | % RSD (n = 6) |
| 1 | 5.9 | ±0.2 | 5.4 | ±0.7 |
| 2 | 10.5 | ±1.1 | 9.5 | ±1.2 |
| 3 | 22.1 | ±0.9 | 20.3 | ±1.1 |
| 4 | 20.3 | ±1.4 | 19.3 | ±0.9 |
| 5 | 12.8 | ±0.6 | 14.3 | ±0.7 |
| 6 | 25.0 | ±1.2 | 23.2 | ±1.5 |
| 7 | 18.2 | ±1.5 | 16.4 | ±0.8 |
| 8 | 24.1 | ±0.8 | 22.5 | ±0.7 |
| 9 | 13.6 | ±0.3 | 15.8 | ±0.1 |
| 10 | 10.8 | ±1.4 | 11.6 | ±1.6 |
| 11 | 14.0 | ±0.4 | 14.1 | ±0.9 |
| 12 | 6.3 | ±0.8 | 5.8 | ±1.3 |
| 13 | 17.4 | ±1.1 | 16.2 | ±1.2 |
| 14 | 8.3 | ±2.1 | 9.5 | ±0.9 |
| 15 | 12.5 | ±0.9 | 13.8 | ±0.5 |
| Immobilized CQDs/Au/HRP Method | |
|---|---|
| Interfering species (10 ng mL−1) | Tolerable value |
| Na+, K+, Ca2+, Mg2+, Zn2+, Ag+, Ba2+ | 1000 |
| Glucose, sucrose, lactose | 650 |
| Glycine, alanine, histidine, valine | 420 |
| Uric acid, ascorbic acid, caffeine | 250 |
| CA 27-29, CA 15-3, CA 125, and PSA | 510 |
| Initial CA 19-9 Conc. (U mL−1) | Added CA 19-9 (U mL−1) | Immobilized CQDs/Au/HRP Method | Immobilized-CL Cross-Linked Chitosan Method [11] | t = (2.228) * | F = (5.05) * | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detected CA 19-9 (U mL−1) | % Recovery (n = 6) | % RSD (n = 6) | Detected CA 19-9 (U mL−1) | % Recovery (n = 6) | % RSD (n = 6) | t-Test | F-Test | ||
| 0.6 | 0.5 5.0 10.0 | 1.09 5.58 10.54 | 99.1 99.6 99.4 | 1.2 1.4 1.6 | 1.08 5.54 10.56 | 98.2 98.9 99.6 | 1.5 1.6 1.7 | 1.248 0.809 0.210 | 1.56 1.31 1.12 |
| 1.7 | 0.5 5.0 10.0 | 2.19 6.58 11.47 | 99.5 98.2 98.0 | 1.5 0.9 1.1 | 2.17 6.56 11.44 | 98.6 97.9 97.8 | 2.1 1.2 1.8 | 0.860 0.495 0.233 | 1.96 1.77 2.68 |
| 5.9 | 0.5 5.0 10.0 | 6.39 10.87 15.46 | 99.8 99.7 97.2 | 0.6 0.9 1.3 | 6.37 10.82 15.43 | 99.5 99.2 97.0 | 0.4 1.5 1.8 | 1.040 0.706 0.222 | 2.25 2.77 1.92 |
| 8.7 | 0.5 5.0 10.0 | 9.17 13.55 18.69 | 99.7 98.9 99.9 | 0.6 1.5 0.5 | 9.14 13.51 18.66 | 99.3 98.6 99.8 | 1.0 0.9 0.8 | 0.842 0.424 0.259 | 2.78 2.77 2.56 |
| 10.3 | 0.5 5.01 0.0 | 10.75 15.17 19.99 | 99.5 99.2 98.5 | 1.3 0.9 1.8 | 10.69 15.00 19.87 | 98.9 98.0 97.8 | 1.2 0.7 2.4 | 0.831 2.553 0.573 | 1.17 1.65 1.78 |
| 3.5 | 0.5 5.0 10.0 | 3.98 8.47 13.42 | 99.5 99.6 99.4 | 1.7 1.1 1.3 | 3.92 8.45 13.34 | 98.0 99.5 98.8 | 1.5 0.7 1.4 | 1.629 0.187 0.771 | 1.28 2.47 1.16 |
| 12.7 | 0.5 5.0 10.0 | 13.02 17.63 22.20 | 98.6 99.6 97.8 | 0.9 1.2 1.6 | 12.98 17.59 22.24 | 98.3 99.4 97.9 | 1.1 0.6 2.1 | 0.515 0.367 0.093 | 1.49 4.00 1.72 |
| 14.0 | 0.5 5.0 10.0 | 13.98 18.95 23.84 | 96.4 99.7 99.3 | 2.1 0.7 1.1 | 13.99 18.92 23.81 | 96.5 99.6 99.2 | 1.7 0.8 1.3 | 0.091 0.227 0.144 | 1.53 1.31 1.39 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alarfaj, N.A.; El-Tohamy, M.F.; Oraby, H.F. CA 19-9 Pancreatic Tumor Marker Fluorescence Immunosensing Detection via Immobilized Carbon Quantum Dots Conjugated Gold Nanocomposite. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041162
Alarfaj NA, El-Tohamy MF, Oraby HF. CA 19-9 Pancreatic Tumor Marker Fluorescence Immunosensing Detection via Immobilized Carbon Quantum Dots Conjugated Gold Nanocomposite. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(4):1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041162
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlarfaj, Nawal Ahmad, Maha Farouk El-Tohamy, and Hesham Farouk Oraby. 2018. "CA 19-9 Pancreatic Tumor Marker Fluorescence Immunosensing Detection via Immobilized Carbon Quantum Dots Conjugated Gold Nanocomposite" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 4: 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041162
APA StyleAlarfaj, N. A., El-Tohamy, M. F., & Oraby, H. F. (2018). CA 19-9 Pancreatic Tumor Marker Fluorescence Immunosensing Detection via Immobilized Carbon Quantum Dots Conjugated Gold Nanocomposite. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(4), 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041162