Molecular and Ultrastructural Mechanisms Underlying Yellow Dwarf Symptom Formation in Wheat after Infection of Barley Yellow Dwarf Virus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. BYDV-GAV and Chlorophyll Contents Were Changed after BYDV-GAV Inoculated Zhong8601
2.2. The Chloroplasts in Zhong8601 Were Influenced after BYDV Inoculation
2.3. Global Transcripts Were Altered in BYDV-Infected Zhong8601 through Comparative Transcriptome
2.4. Chlorophyll Biosynthesis and Chloroplast Related Transcripts Were Down-Regulated after BYDV Infection
2.5. Phytohormone Signaling Related Transcripts Were Differentially Regulated in BYDV-Infected Zhong8601
2.6. ROS-Related Transcripts and H2O2 Accumulation also Participated in BYDV Symptom Formation in Zhong8601
2.7. The Microarray Data Confirmation by RT-qPCR
3. Discussion
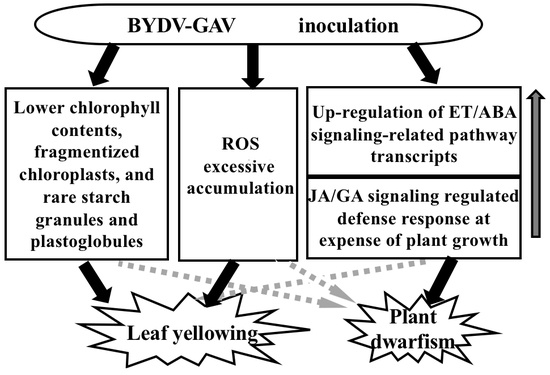
3.1. Major Mechanism for Yellowing Symptom Formation after BYDV-GAV Inoculation
3.2. Major Cause for Plant Dwarfism Formation after BYDV Inoculation
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials, BYDV-GAVIsolate, and Treatments
4.2. RNA Extraction and the First-Strand cDNA Synthesis
4.3. Virus Diagnostics by ELISA in Zhong8601 Leaves with BYDV-GAV and Mock Inoculation
4.4. Examination of Chlorophyll and H2O2 Contents in Zhong8601
4.5. TEM Assay for Samples of Zhong8601
4.6. Microarray Analysis
4.7. Real-Time Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miller, W.A.; Rasochova, L. Barley yellow dwarf virues. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 1997, 35, 167–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, A.M.Q.; Adams, M.J.; Carstens, E.B.; Lefkowitz, E.J. “Family Luteoviridae” in: Virus Taxonomy: Ninth Report of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses; Elsevier Academic Press: London, UK, 2012; pp. 1045–1053. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.; Zhang, S. Identification and application of four strains of wheat yellow dwarf virus. Sci. Agric. Sin. 1987, 298, 434–440. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Xie, J.; Gray, S.M.; Zhou, G.; Gao, B. A Chinese isolate of barley yellow dwarf virus-PAV represents a third distinct species within the PAV serotype. Arch. Virol. 2007, 152, 1365–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Z.; Wang, X.; Chang, S.; Zhou, G. The complete nucleotide sequence and its organization of the genome of Barley yellow dwarf virus-GAV. Sci. China Ser. C Life Sci. 2004, 47, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, F.; Rebekah, O.; Eric, J.; Shiaoman, C.; Marcio, A.; Frederic, K. Genome-wide association mapping of barley yellow dwarf virus tolerance in spring oat (Avena sativa L.). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155376. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Lin, Z.S.; Xin, Z.Y. Research progress in BYDV resistance genes derived from wheat and its wild relatives. J. Genet. Genom. 2009, 36, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, P.M.; Davidson, J.L.; Bariana, H.; Larkin, P.J. Effects of barley yellow dwarf virus on the yield of winter wheat. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1995, 46, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.; Ohm, H.; Goulart, L.; Lister, R.; Appels, R.; Benlhabib, O. Introgression and characterization of barley yellow dwarf virus resistance from Thinopyrum intermedium into wheat. Genome 1995, 38, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crasta, O.R.; Francki, M.G.; Buchoitz, D.B.; Sharma, H.C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, R.C.; Ohm, H.W.; Anderson, J.M. Identification and characterization of wheat-wheatgrass translocation lines and localization of barley yellow dwarf virus resistance. Genome 2000, 43, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayala, L.; Henry, M.; Gonzalez-de-Leon, D.; Ginkel, M.; Mujeeb-Kazi, A.; Keller, B.; Khairallah, M. A diagnostic molecular marker allowing the study of Th. intermedium-derived resistance to BYDV in bread wheat segregating populations. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2001, 102, 942–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Xu, H.J.; Xu, Q.F.; Larkin, P.; Xin, Z.Y. Development of novel PCR markers linked to the BYDV resistance gene Bdv2 useful in wheat for marker-assisted selection. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 109, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.D.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhao, D.; Wang, X.F.; Zhang, Z.Y. Wheat resistome in response to barley yellow dwarf virus infection. Funct. Integer. Genom. 2013, 13, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehto, K.; Tikkanen, M.; Hiriart, J.B.; Paakkarinen, V.; Aro, E.M. Depletion of the photosystem II core complex in mature tobacco leaves infected by the flavum strain of tobacco mosaic virus. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2003, 16, 1135–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Hajano, J.U.D.; Ren, Y.D.; Lu, C.T.; Wang, X.F. iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomics analysis of rice leaves infected by Rice stripe virus reveals several proteins involved in symptom formation. Virol. J. 2015, 12, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Yang, J.; Bi, H.; Zhang, P. Why mosaic? Gene expression profiling of African cassava mosaic virus-infected cassava reveals the effect of chlorophyll degradation on symptom development. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2014, 56, 122–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Vivancos, P.; Rubio, M.; Mesonero, V.; Periago, P.M.; Barceló, A.R.; Martínez-Gómez, P.; Hernández, J.A. The apoplastic antioxidant system in Prunus: Response to long-term plum pox virus infection. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 3813–3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, J.A.; Diaz-Vivancos, P.; Rubio, M.; Olmos, E.; Ros-Barceló, A.; Martínez-Gómez, P. Long-term PPV infection produces an oxidative stress in a susceptible apricot cultivar but not in a resistant cultivar. Physiol. Plant. 2006, 126, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Vivancos, P.; Clemente-Moreno, M.J.; Rubio, M.; Olmos, E.; García, J.A.; Martínez-Gómez, P.; Hernández, J.A. Alteration in the chloroplastic metabolism leads to ROS accumulation in pea plants in response to plum pox virus. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 2147–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.J.; Zhao, J.; Lu, W.J.; Deng, D.X. Gibberellin in plant height control: Old player, new story. Plant Cell Rep. 2017, 36, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayan, J.; Voronin, N.; Gong, F.; Sun, T.P.; Hedden, P.; Formm, H.; Aloni, R. Leaf-induced gibberellin signaling is essential for internode elongation, cambial activity, and fiber differentiation in tobacco stems. Plant Cell 2012, 24, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedel, C.; Habekuss, A.; Schliephake, E.; Niks, R.; Broer, I.; Ordon, F. Pyramiding of Ryd2 and Ryd3 conferring tolerance to a German isolate of Barley yellow dwarf virus-PAV (BYDV-PAV-ASL-1) leads to quantitative resistance against this isolate. Thero. Appl. Genet. 2011, 123, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, W.O. Tobamovirus-plant interactions. Virology 1992, 186, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.D.; Worley, E.; Udvardi, M. A NAP-AAO3 regulatory module promotes chlorophyll degradation via ABA biosynthesis in Arabidopsis leaves. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 4862–4874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zacarias, L.; Reid, M.S. Role of growth regulators in the senescence of Arabidopsis thaliana leaves. Physiol. Plant 1990, 80, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, H.H.; Häusler, R.E.; Fettke, J.; Herbst, K.; Niewiadomski, P.; Gierth, M.; Bell, K.; Steup, M.; Flügge, U.I.; Schneider, A. The role of plastidial glucose-6-phosphate/phosphate translocators in vegetative tissues of Arabidopsis thaliana mutants impaired in starch biosynthesis. Plant Biol. 2010, 12, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.M.; Söll, D. Antisense HEMA1 RNA expression inhibits heme and chlorophyll biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2000, 122, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, S.; Gilroy, S. Abscisic acid signal transduction in the barley aleurone is mediated by phospholipase D activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 2697–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, G.K.; Cheong, Y.H.; Kim, K.N.; Grant, J.J.; Huang, W.; D’Angelo, C.; Weinl, S.; Kudla, J.; Luan, S. The calcium sensor calcineurin B-like protein 9 modulates abscisic acid sensitivity and biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 1912–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yuan, G.; Yuan, S.; Duan, W.; Wang, P.; Bai, J.; Zhang, F.; Gao, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, C. TaOPR2 encodes a 12-oxo-phytodienoic acid reductase involved in the biosynthesis of jasmonic acid in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 29, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Deng, D. Molecular basis and evolutionary pattern of GA-GID1-DELLA regulatory module. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2014, 289, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.L.; Ding, L.H.; Yu, H. Crosstalk between GA and JA signaling mediates plant growth and defense. Plant Cell Rep. 2013, 32, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, R.A.R.; Baldwin, I.T.; Erb, M. Herbivory-induced jasmonates constrain plant sugar accumulation and growth by antagonizing gibberellin signaling and not by promoting secondary metabolite production. New Phytol. 2017, 215, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Martret, B.; Poage, M.; Shiel, K.; Nugent, G.D.; Dix, P.J. Tobacco chloroplast transformants expressing genes encoding dehudroascorbate reductase, glutathione reductase, and glutathione-S-transferase, exhibit altered anti-oxidant metabolism and improved abiotic stress tolerance. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2011, 9, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beracochea, V.C.; Almasia, N.I.; Peluffo, L.; Nahirñak, V.; Hopp, E.H.; Paniego, N.; Heinz, R.A.; Vazquez-Rovere, C.; Lia, V.V. Sunflower germin-like protein HaGLP1 promotes ROS accumulation and enhances protection against fungal pathogens in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Rep. 2015, 34, 1717–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, T.; Shen, J.; Fa, Y.; Su, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, H. Resistance-breaking population of Meloidogyne incognita utilizes plant peroxidase to scavenge reactive oxygen species, thereby promoting parasitism on tomato carrying Mi-1 gene. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 482, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, R.; Sugino, M.; Hatanaka, T.; Misoo, S.; Fukayama, H. CO2-responsive CONSTANS, CONSTANS-like, and time of chlorophyll a/b binding protein Expression 1 protein is a positive regulator of starch synthesis in vegetative organs of rice. Plant Physiol. 2015, 167, 1321–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, M.Q.; Gao, S.H.; Ren, J.L.; Yang, Q.H.; Li, H.X.; Yang, C.X.; Ye, Z. Overexpression of SlRBZ results in chlorosis and dwarfism through impairing chlorophyll, carotenoid, and gibberellin biosynthesis in tomato. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abeles, F.B.; Dunn, L.J.; Morgens, P.; Callahan, A.; Dinterman, R.E.; Schmidt, J. Induction of 33-kD and 60-kD peroxidases during ethylene-induced senescence of cucumber cotyledons. Plant Physiol. 1988, 87, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, B.L.; Sun, S.; Xing, G.M.; Wang, F.; Li, M.Y.; Tian, Y.S.; Xiong, A. S AP2/ERF transcription factors involved in response to tomato yellow leaf curly virus in tomato. Plant Genome 2016, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marieke, D.; Lisa Van den, B.; Hannes, C.; Kaatje Van, V.; Minami, M.; Dirk, I. The ETHYLENE RESPONSE FACTORs ERF6 and ERF11 anatagonistically regulate mannitol-induced growth inhibition in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 166–179. [Google Scholar]
- Mauri, N.; Fernández-Marcos, M.; Costas, C.; Desvoyes, B.; Pichel, A.; Caro, E.; Gutierrez, C. GEM, a member of the GRAM domain family of proteins, is part of the ABA signaling pathway. Sci. Rep. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Gao, Z.Q.; An, W.; Li, Y.L.; Jiao, X.F.; Wang, C.Y. Flag leaf photosynthetic characteristics, change in chlorophyll fluorescence parameters, and their relationships with yield of winter wheat sowed in spring. Ying Yong Shen Tai Xue Bao 2016, 27, 133–142. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Neill, S.; Cai, W.; Tang, Z. Hydrogen peroxide and jasmonic acid mediate oligogalacturonic acid-induced saponin accumulation in suspension-cultured cells of Panax ginseng. Physiol. Plant 2003, 118, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.Y.; Tian, S.K.; Yang, X.E. Changes of root morphology and Pb uptake by two species of Elsholtzia under Pb toxicity. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2005, 6, 546–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolton, M.D.; Kolmer, J.A.; Xu, W.W.; Garvin, D.F. Lr34-mediated leaf rust resistance in wheat: Transcript profiling reveals a high energetic demand supported by transient recruitment of multiple metabolic pathways. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2008, 21, 1515–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCt method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rong, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Massart, S.; Zhang, Z. Molecular and Ultrastructural Mechanisms Underlying Yellow Dwarf Symptom Formation in Wheat after Infection of Barley Yellow Dwarf Virus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041187
Rong W, Wang X, Wang X, Massart S, Zhang Z. Molecular and Ultrastructural Mechanisms Underlying Yellow Dwarf Symptom Formation in Wheat after Infection of Barley Yellow Dwarf Virus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(4):1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041187
Chicago/Turabian StyleRong, Wei, Xindong Wang, Xifeng Wang, Sebastien Massart, and Zengyan Zhang. 2018. "Molecular and Ultrastructural Mechanisms Underlying Yellow Dwarf Symptom Formation in Wheat after Infection of Barley Yellow Dwarf Virus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 4: 1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041187
APA StyleRong, W., Wang, X., Wang, X., Massart, S., & Zhang, Z. (2018). Molecular and Ultrastructural Mechanisms Underlying Yellow Dwarf Symptom Formation in Wheat after Infection of Barley Yellow Dwarf Virus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(4), 1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041187