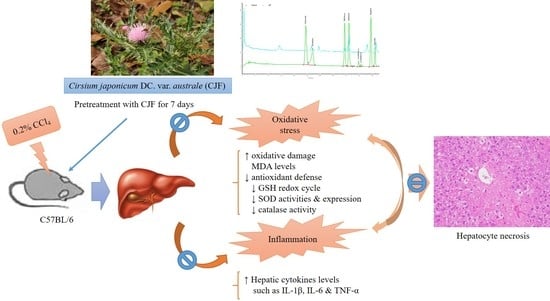
Comparison of the Hepatoprotective Effects of Four Endemic Cirsium Species Extracts from Taiwan on CCl4-Induced Acute Liver Damage in C57BL/6 Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. CCl4-Induced Acute Liver Damage in C57BL/6 Mice
2.1.1. Serum Biochemical Levels of CCl4-Induced Acute Liver Damage in C57BL/6 Mice
2.1.2. Hepatic Histopathology of CCl4-Induced Acute Liver Damage in C57BL/6 Mice
2.1.3. Hepatic Antioxidant Activities and MDA Levels of CCl4-Induced Acute Liver Damage in C57BL/6 Mice
2.1.4. Hepatic Cytokine Levels of CCl4-Induced Acute Liver Damage in C57BL/6 Mice
2.1.5. Antioxidant Protein Expression of CCl4-Induced Acute Liver Damage in C57BL/6 Mice
2.2. Antioxidant Ingredient Contents and Activities of Four Cirsium Species Extracts
2.2.1. Total Phenolics (TPs) Contents, Total Phenylpropanoid Glycosides (PPGs) Contents, and HPLC Analysis of Four Cirsium Species Extracts
2.2.2. Antioxidant Activities of Four Cirsium Species Extracts
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Collection and Preparation of Plant Materials
4.2. CCl4-Induced Acute Liver Damage in C57BL/6 Mice
4.2.1. Animals
4.2.2. CCl4-Induced Acute Liver Damage in C57BL/6 Mice
4.2.3. Assessment of Liver Function
4.2.4. Hepatic Antioxidant Defense System and MDA Levels
4.2.5. Hepatic Cytokines Levels
4.2.6. Histopathological Stain
4.2.7. Western Blot
4.3. Measurement of Antioxidant Phytoconstituent Contents and Activities
4.3.1. Measurement of Phytoconstituents Using a Spectrophotometric Reader
4.3.2. Determination of Phytoconstituents Using HPLC-DAD
4.3.3. Trolox Equivalent Antioxidant Capacity (TEAC) Assay
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABTS | 2,2′-Azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulphonic acid) |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| ANOVA | One-way analysis of variance |
| CAH | The aerial part of C. arisanense Kitam. |
| CAH-L | Low dose (5 mg/kg) of CAH |
| CAH-H | High dose (50 mg/kg) of CAH |
| CH | Cirsii Herba |
| CH-L | Low dose (5 mg/kg) of CH |
| CH-H | High dose (50 mg/kg) of CH |
| CJF | The flower part of C. japonicum DC. var. australe Kitam. |
| CJF-L | Low dose (0.5 mg/kg) of CJF |
| CJF-H | High dose (5 mg/kg) of CJF |
| CKH | The aerial part of C. kawakamii Hayata |
| CKH-L | Low dose (5 mg/kg) of CKH |
| CKH-H | High dose (50 mg/kg) of CKH |
| CMC | Carboxymethylcellulose |
| Cu/Zn-SOD | Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase |
| DAD | Photodiode array detector |
| DTNB | 5,5′-Dithio-bis-(2-nitrobenzoic acid) |
| GPx | Glutathione peroxidase |
| GR | Glutathione reductase |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| GST | Glutathione S-transferase |
| H&E | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| Mn-SOD | Mn-superoxide dismutase |
| NADPH | β-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate |
| PPGs | Phenylpropanoid glycosides |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RT | Room temperature |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| TBA | Thiobarbituric acid |
| TBARS | Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances |
| TEAC | Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| TPs | Total phenolics |
References
- Ostapowicz, G.; Fontana, R.J.; Schiodt, F.V.; Larson, A.; Davern, T.J.; Han, S.H.; McCashland, T.M.; Shakil, A.O.; Hay, J.E.; Hynan, L.; et al. Results of a prospective study of acute liver failure at 17 tertiary care centers in the United States. Ann. Intern. Med. 2002, 137, 947–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Dong, Z.; Chang, X.; Zhang, C.; Rong, G.; Gao, X.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; Rong, Y.; et al. Protective effect of the total flavonoids from Apocynum venetum L. on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in vitro and in vivo. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Li, L.; Ma, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Pang, W.; Xiong, M.; Fang, S.; Li, Y. Hepatoprotective effect of methyl ferulic acid against carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury in rats. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 2228–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadek, K.M.; Saleh, E.A.; Nasr, S.M. Molecular hepatoprotective effects of lipoic acid against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in rats: Hepatoprotection at molecular level. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2018, 37, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Dai, C.; Liu, Q.; Li, J.; Qiu, J. Curcumin attenuates on carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury in mice via modulation of the Nrf2/HO-1 and TGF-β1/Smad3 pathway. Molecules 2018, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recknagel, R.O.; Glende, E.A., Jr.; Dolak, J.A.; Waller, R.L. Mechanisms of carbon tetrachloride toxicity. Pharmacol. Ther. 1989, 43, 139–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, L.W.; Boll, M.; Stampfl, A. Hepatotoxicity and mechanism of action of haloalkanes: Carbon tetrachloride as a toxicological model. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2003, 33, 105–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Shao, H.; Chen, Y.; Ding, N.; Yang, A.; Tian, J.; Jiang, Y.; Li, G.; Jiang, Y. In renal hypertension, Cirsium japonicum strengthens cardiac function via the intermedin/nitric oxide pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 101, 787–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, N.; Li, Y.; Zhou, M.; Gao, J.; Hou, Y.; Jiang, M.; Bai, G. The hemostatic effect study of Cirsium setosum on regulating α1-ARs via mediating norepinephrine synthesis by enzyme catalysis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 87, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, O.K.; Choi, B.Y.; Park, J.O.; Lee, J.W.; Park, B.K.; Joo, C.G.; Heo, H.J.; Keum, Y.S. Ethanol extract of Cirsium japonicum var. ussuriense Kitamura exhibits the activation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2-dependent antioxidant response element and protects human keratinocyte HaCaT cells against oxidative DNA damage. J. Cancer Prev. 2016, 21, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Wang, L.H.; Jiang, J.G. Hepatoprotective effect of flavonoids from Cirsium japonicum DC on hepatotoxicity in comparison with silymarin. Food Funct. 2016, 7, 2179–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Guo, Y.; Luo, B.; Liu, W.; Wei, R.; Yang, C.; Ding, C.; Xu, X.; He, M. Hepatoprotective phenylethanoid glycosides from Cirsium setosum. Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 30, 1824–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Y.; Liu, L.Y.; Hong, Z.F.; Peng, J. Ethanol extract of Cirsium japonicum attenuates hepatic lipid accumulation via AMPK activation in human HepG2 cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2014, 8, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Pena, J.B.; Kim, C.A.; Lee, H.L.; Yoon, S.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Hong, E.Y.; Kim, G.H.; Ryu, J.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, K.M.; et al. Luteolin mediates the antidepressant-like effects of Cirsium japonicum in mice, possibly through modulation of the GABAA receptor. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2014, 37, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dela Pena, I.J.; Lee, H.L.; Yoon, S.Y.; Dela Pena, J.B.; Kim, H.K.; Hong, E.Y.; Cheong, J.H. The ethanol extract of Cirsium japonicum increased chloride ion influx through stimulating GABAA receptor in human neuroblastoma cells and exhibited anxiolytic-like effects in mice. Drug Discov. Ther. 2013, 7, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Heo, S.I.; Wang, M.H. Antioxidant and antidiabetic activities of extracts from Cirsium japonicum roots. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2008, 2, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wellington, K.; Jarvis, B. Silymarin: A review of its clinical properties in the management of hepatic disorders. BioDrugs 2001, 15, 465–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saller, R.; Meier, R.; Brignoli, R. The use of silymarin in the treatment of liver diseases. Drugs 2001, 61, 2035–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abenavoli, L.; Milic, N.; Capasso, F. Anti-oxidant therapy in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: The role of silymarin. Endocrine 2012, 42, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieber, C.S.; Leo, M.A.; Cao, Q.; Ren, C.; DeCarli, L.M. Silymarin retards the progression of alcohol-induced hepatic fibrosis in baboons. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2003, 37, 336–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.P.; Lu, S.Y. Cirsium. In Flora of Taiwan, 2nd ed.; Huang, T.C., Ed.; Editorial Committee of the Flora of Taiwan, Department of Botany, National Taiwan University: Taipei, Taiwan, 2000; Volume 4, pp. 903–911. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Sun, Z.; Shang, X.; Li, J.; Wang, R.; Zhu, J. Triterpene compounds from Cirsium setosum. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2012, 37, 951–955. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ganzera, M.; Pocher, A.; Stuppner, H. Differentiation of Cirsium japonicum and C. setosum by TLC and HPLC-MS. Phytochem. Anal. 2005, 16, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, D.L.; Ma, Q.G.; Wei, R.R. Cytotoxic phenylpropanoid glycosides from Cirsium japonicum. J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 2016, 18, 1122–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, W.C.; Wu, Y.C.; Danko, B.; Cheng, Y.B.; Hsieh, T.J.; Hsieh, C.T.; Tsai, Y.C.; El-Shazly, M.; Martins, A.; Hohmann, J.; et al. Bioactive constituents of Cirsium japonicum var. australe. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 1624–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Lausted, C.; Yoo, H.; Yan, X.; Brightman, A.; Chen, J.; Wang, W.; Bu, X.; Hood, L. Quantitative liver-specific protein fingerprint in blood: A signature for hepatotoxicity. Theranostics 2014, 4, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, K.L.; Tsai, C.T.; Chang, W.M.; Shen, M.L.; Wu, C.T.; Liao, H.F. Hepatoprotective effect of Cirsium arisanense Kitamura in tacrine-treated hepatoma Hep 3B cells and C57BL mice. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2008, 36, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.R.; Lin, W.H.; Hseu, Y.C.; Lien, J.C.; Lin, Y.T.; Kuo, T.P.; Ching, H. Evaluation of the antioxidant activity of five endemic Ligustrum species leaves from Taiwan flora in vitro. Food Chem. 2011, 127, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Z.; Deaciuc, I.; Song, M.; Lee, D.Y.; Liu, Y.; Ji, X.; McClain, C. Silymarin protects against acute ethanol-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2006, 30, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papackova, Z.; Heczkova, M.; Dankova, H.; Sticova, E.; Lodererova, A.; Bartonova, L.; Poruba, M.; Cahova, M. Silymarin prevents acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity in mice. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letteron, P.; Labbe, G.; Degott, C.; Berson, A.; Fromenty, B.; Delaforge, M.; Larrey, D.; Pessayre, D. Mechanism for the protective effects of silymarin against carbon tetrachloride-induced lipid peroxidation and hepatotoxicity in mice. Evidence that silymarin acts both as an inhibitor of metabolic activation and as a chain-breaking antioxidant. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1990, 39, 2027–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, P.; Head, K. A review of the bioavailability and clinical efficacy of milk thistle phytosome: A silybin-phosphatidylcholine complex (Siliphos). Altern. Med. Rev. 2005, 10, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arauz, J.; Ramos-Tovar, E.; Muriel, P. Redox state and methods to evaluate oxidative stress in liver damage: From bench to bedside. Ann. Hepatol. 2016, 15, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feher, J.; Lang, I.; Deak, G.; Cornides, A.; Nekam, K.; Gergely, P. Free radicals in tissue damage in liver diseases and therapeutic approach. Tokai J. Exp. Clin. Med. 1986, 11 Suppl, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Townsend, D.M.; Tew, K.D. The role of glutathione-S-transferase in anti-cancer drug resistance. Oncogene 2003, 22, 7369–7375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukai, T.; Ushio-Fukai, M. Superoxide dismutases: Role in redox signaling, vascular function, and diseases. Antioxid. Redox. Signal. 2011, 15, 1583–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhi, H.; Guicciardi, M.E.; Gores, G.J. Hepatocyte death: A clear and present danger. Physiol. Rev. 2010, 90, 1165–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.J.; Zhang, J.X.; Zhang, X.Q.; Qi, M.J.; Shi, M.Z.; Yang, J.; Zhang, K.Z.; Guo, C.; Han, Y.L. Effects of diosmetin on nine cytochrome P450 isoforms, UGTs and three drug transporters in vitro. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 334, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Gong, X.B.; Huang, L.G.; Wang, Z.X.; Wan, R.Z.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, B.S. Diosmetin exerts anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects to protect against endotoxin-induced acute hepatic failure in mice. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 30723–30733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Gao, M.; Sun, S.; Bi, A.; Xin, Y.; Han, X.; Wang, L.; Yin, Z.; Luo, L. Protective effect of l-theanine on carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 422, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, H.C.; Chang, H.C.; Lan, W.C.; Tsai, F.H.; Liao, J.C.; Wu, C.R. Protective effects of Drynaria fortunei against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced oxidative damage in B35 cells via the PI3K/AKT pathway. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1956–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleh, I.A.; Vinatoru, M.; Mason, T.J.; Abdel-Azim, N.S.; Shams, K.A.; Aboutabl, E.; Hammouda, F.M. Extraction of silymarin from milk thistle (Silybum marianum) seeds—A comparison of conventional and microwave-assisted extraction methods. J. Microw. Power Electromagn. Energy 2017, 51, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Samples | Yields (%) | TPs (mg of Catechin/g) | PPGs (mg of Verbascoside/g) | Silydianin | Silibinin α | Silibinin β | Diosmetin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAH | 23.9 | 109.65 ± 0.57 | 175.20 ± 5.45 | 1.23 ± 0.06 | 2.53 ± 0.01 | - | - |
| CKH | 4.5 | 93.91 ± 1.07 | 2.30 ± 0.000 | - | 1.11 ± 0.02 | 25.14 ± 0.23 | - |
| CJF | 10 | 49.52 ± 2.11 | 28.64 ± 1.01 | 3.28 ± 0.04 | 0.88 ± 0.01 | 3.74 ± 0.01 | 8.66 ± 0.06 |
| CH | 15.1 | 44.86 ± 1.77 | 25.33 ± 1.24 | - | 0.38 ± 0.01 | 0.34 ± 0.01 | - |
| Time (min) | Solvent A (%) | Solvent B (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0–15 | 90 | 10 |
| 15–25 | 70 | 30 |
| 25–35 | 55 | 45 |
| 35–45 | 35 | 65 |
| 45–50 | 0 | 100 |
| 50–55 | 0 | 100 |
| 55–65 | 90 | 10 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Z.-W.; Chang, J.-C.; Lin, L.-W.; Tsai, F.-H.; Chang, H.-C.; Wu, C.-R. Comparison of the Hepatoprotective Effects of Four Endemic Cirsium Species Extracts from Taiwan on CCl4-Induced Acute Liver Damage in C57BL/6 Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1329. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051329
Zhao Z-W, Chang J-C, Lin L-W, Tsai F-H, Chang H-C, Wu C-R. Comparison of the Hepatoprotective Effects of Four Endemic Cirsium Species Extracts from Taiwan on CCl4-Induced Acute Liver Damage in C57BL/6 Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(5):1329. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051329
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Zi-Wei, Jen-Chih Chang, Li-Wei Lin, Fan-Hsuan Tsai, Hung-Chi Chang, and Chi-Rei Wu. 2018. "Comparison of the Hepatoprotective Effects of Four Endemic Cirsium Species Extracts from Taiwan on CCl4-Induced Acute Liver Damage in C57BL/6 Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 5: 1329. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051329
APA StyleZhao, Z. -W., Chang, J. -C., Lin, L. -W., Tsai, F. -H., Chang, H. -C., & Wu, C. -R. (2018). Comparison of the Hepatoprotective Effects of Four Endemic Cirsium Species Extracts from Taiwan on CCl4-Induced Acute Liver Damage in C57BL/6 Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(5), 1329. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051329