Recent Advances in Laser-Ablative Synthesis of Bare Au and Si Nanoparticles and Assessment of Their Prospects for Tissue Engineering Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Pulsed Laser Ablation in Liquids (PLAL) for the Synthesis of Colloidal Nanomaterials
3. PLAL Synthesis of Bare Nanomaterials for Biomedical Applications
3.1. Bare Laser-Synthesized Si Nanoparticles
3.2. Bare Laser-Synthesized Au Nanoparticles
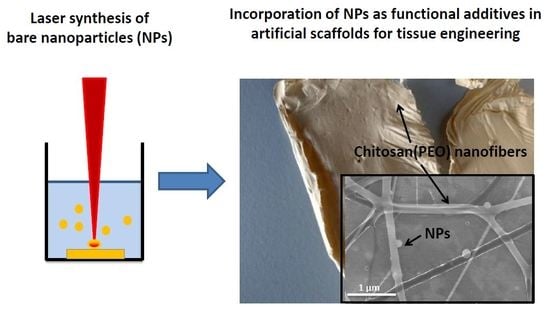
4. Potential Applications of BLS-NPs in Tissue Engineering
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NPs | Nanoparticles |
| PLAL | Pulsed Laser Ablation in Liquid |
References
- Amini, A.R.; Laurencin, C.T.; Nukavarapu, S.P. Bone Tissue Engineering: Recent Advances and Challenges. Crit. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 40, 363–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langer, R.; Vacanti, J. Advances in Tissue Engineering. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2018, 51, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wobma, H.; Vunjak-Novakovic, G. Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine 2015: A Year in Review. Tissue Eng. Part B. Rev. 2016, 22, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salgado, A.J.; Oliveira, J.M.; Martins, A.; Teixeira, F.G.; Silva, N.A.; Neves, N.M.; Sousa, N.; Reis, R.L. Chapter One—Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine: Past, Present, and Future. In Tissue Engineering of the Peripheral Nerve: Stem Cells and Regeneration Promoting Factors; International Review of Neurobiology; Geuna, S., Perroteau, I., Tos, P., Battiston, B., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013; Volume 108, pp. 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Webster, T.J. Nanotechnology and Nanomaterials: Promises for Improved Tissue Regeneration. Nano Today 2009, 4, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouten, C.V.C.; Driessen-Mol, A.; Baaijens, F.P.T. In Situ Heart Valve Tissue Engineering: Simple Devices, Smart Materials, Complex Knowledge. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2012, 9, 453–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreas, K.; Sittinger, M.; Ringe, J. Toward in Situ Tissue Engineering: Chemokine-Guided Stem Cell Recruitment. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 32, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, Y.; Yaszemski, M.J.; Mikos, A.G.; Laurencin, C.T. Tissue Engineering of Bone: Material and Matrix Considerations. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2008, 90 (Suppl. 1), 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoulas, E.; Manousaki, A.; Fotakis, C.; Stratakis, E. Biomimetic Surface Structuring Using Cylindrical Vector Femtosecond Laser Beams. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Y.; Wu, H.; Yu, A.; Wen, D. Biodegradable Polylactide/chitosan Blend Membranes. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 1362–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezwan, K.; Chen, Q.Z.; Blaker, J.J.; Boccaccini, A.R. Biodegradable and Bioactive Porous Polymer/inorganic Composite Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 3413–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Gao, C.; Mao, Z.; Zhou, J.; Shen, J.; Hu, X.; Han, C. Collagen/chitosan Porous Scaffolds with Improved Biostability for Skin Tissue Engineering. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 4833–4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppuswamy, P.; Venugopal, J.R.; Navaneethan, B.; Laiva, A.L.; Sridhar, S.; Ramakrishna, S. Functionalized Hybrid Nanofibers to Mimic Native ECM for Tissue Engineering Applications. Appl. Surface Sci. 2014, 322, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosellini, E.; Zhang, Y.S.; Migliori, B.; Barbani, N.; Lazzeri, L.; Shin, S.R.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Cascone, M.G. Protein/polysaccharide-Based Scaffolds Mimicking Native Extracellular Matrix for Cardiac Tissue Engineering Applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2018, 106, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webber, M.J.; Khan, O.F.; Sydlik, S.A.; Tang, B.C.; Langer, R. A Perspective on the Clinical Translation of Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 43, 641–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billström, G.H.; Blom, A.W.; Larsson, S.; Beswick, A.D. Application of Scaffolds for Bone Regeneration Strategies: Current Trends and Future Directions. Injury 2018, 44, S28–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, J.H.; Best, S.M. Calcium Phosphate Scaffolds for Bone Repair. JOM 2011, 63, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bassyouni, G.T.; Beherei, H.H.; Mohamed, K.R.; Kenawy, S.H. Fabrication and Bioactivity Behavior of HA/bioactive Glass Composites in the Presence of Calcium Hexaboride. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2016, 175, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, C.Q.; Zhou, Y. In Vitro Bioactivity of a Biocomposite Fabricated from HA and Ti Powders by Powder Metallurgy Method. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 2909–2915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M. Developing Bioactive Composite Materials for Tissue Replacement. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 2133–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle, S.D.; Miño, N.; Muñoz, F.; González, A.; Planell, J.A.; Ginebra, M.-P. In Vivo Evaluation of an Injectable Macroporous Calcium Phosphate Cement. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2007, 18, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tancred, D.C.; Carr, A.J.; McCormack, B.A.O. Development of a New Synthetic Bone Graft. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1998, 9, 819–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Place, E.S.; George, J.H.; Williams, C.K.; Stevens, M.M. Synthetic Polymer Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stratton, S.; Shelke, N.B.; Hoshino, K.; Rudraiah, S.; Kumbar, S.G. Bioactive Polymeric Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering. Bioact. Mater. 2016, 1, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakravan, M.; Heuzey, M.-C.; Ajji, A. A Fundamental Study of chitosan/PEO Electrospinning. Polymer Guildf. 2011, 52, 4813–4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeken, C.R.; Fox, D.B.; Bachman, S.L.; Ramshaw, B.J.; Grant, S.A. Characterization of Bionanocomposite Scaffolds Comprised of Amine-Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles and Silicon Carbide Nanowires Crosslinked to an Acellular Porcine Tendon. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2011, 97, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, S.; Vial, S.; Reis, R.L.; Oliveira, J.M. Nanoparticles for Bone Tissue Engineering. Biotechnol. Prog. 2017, 33, 590–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.Y.; Kumar, D.; Khang, G.; Lim, D.-K. Recent Advances in Gold Nanoparticle-Based Bioengineering Applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 8433–8444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vial, S.; Reis, R.L.; Oliveira, J.M. Recent Advances Using Gold Nanoparticles as a Promising Multimodal Tool for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2017, 21, 92–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.-S.; Ahn, E.H.; Dvir, T.; Kim, D.-H. Emerging Nanotechnology Approaches in Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9 (Suppl. 1), 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annur, D.; Wang, Z.K.; Liao, J.D.; Kuo, C. Plasma-Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles on Electrospun Chitosan Nanofiber Surfaces for Antibacterial Applications. Biomacromolecules 2015, 16, 3248–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.W.; Rajendran, S.; Joshi, M. Synthesis and Characterization of Chitosan and Silver Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles for Bioactive Polyester. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Carregal-Romero, S.; Casula, M.F.; Gutierrez, L.; Morales, M.P.; Bohm, I.B.; Heverhagen, J.T.; Prosperi, D.; Parak, W.J. Biological Applications of Magnetic Nanoparticles. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 4306–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sensenig, R.; Sapir, Y.; MacDonald, C.; Cohen, S.; Polyak, B. Magnetic Nanoparticle-Based Approaches to Locally Target Therapy and Enhance Tissue Regeneration in Vivo. Nanomedicine 2012, 7, 1425–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenholm, J.M.; Zhang, J.; Linden, M.; Sahlgren, C. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles in Tissue Engineering—A Perspective. Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canham, L.T. Bioactive Silicon Structure Fabrication Through Nanoetching Techniques. Adv. Mater. 1995, 7, 1033–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Gu, L.; von Maltzahn, G.; Ruoslahti, E.; Bhatia, S.N.; Sailor, M.J. Biodegradable Luminescent Porous Silicon Nanoparticles for in Vivo Applications. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erogbogbo, F.; Yong, K.-T.; Roy, I.; Xu, G.; Prasad, P.N.; Swihart, M.T. Biocompatible Luminescent Silicon Quantum Dots for Imaging of Cancer Cells. ACS Nano 2008, 2, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, L.; Hall, D.J.; Qin, Z.; Anglin, E.; Joo, J.; Mooney, D.J.; Howell, S.B.; Sailor, M.J. In Vivo Time-Gated Fluorescence Imaging with Biodegradable Luminescent Porous Silicon Nanoparticles. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gongalsky, M.B.; Osminkina, L.A.; Pereira, A.; Manankov, A.A.; Fedorenko, A.A.; Vasiliev, A.N.; Solovyev, V.V.; Kudryavtsev, A.A.; Sentis, M.; Kabashin, A.V.; et al. Laser-Synthesized Oxide-Passivated Bright Si Quantum Dots for Bioimaging. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timoshenko, V.Y.; Kudryavtsev, A.A.; Osminkina, L.A.; Vorontsov, A.S.; Ryabchikov, Y.V.; Belogorokhov, I.A.; Kovalev, D.; Kashkarov, P.K. Silicon Nanocrystals as Photosensitizers of Active Oxygen for Biomedical Applications. JETP Lett. 2006, 83, 423–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Kim, H.; Hong, C.; Kim, M.; Hong, S.S.; Lee, D.H.; Lee, W.I. Porous Silicon as an Agent for Cancer Thermotherapy Based on near-Infrared Light Irradiation. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 4790–4795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamarov, K.P.; Osminkina, L.A.; Zinovyev, S.V.; Maximova, K.A.; Kargina, J.V.; Gongalsky, M.B.; Ryabchikov, Y.; Al-Kattan, A.; Sviridov, A.P.; Sentis, M.; et al. Radio Frequency Radiation-Induced Hyperthermia Using Si Nanoparticle-Based Sensitizers for Mild Cancer Therapy. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sviridov, A.P.; Andreev, V.G.; Ivanova, E.M.; Osminkina, L.A.; Tamarov, K.P.; Timoshenko, V.Y. Porous Silicon Nanoparticles as Sensitizers for Ultrasonic Hyperthermia. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 193110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, S.K.; Yang, L.; Yung, L.-Y.L.; Ong, C.-N.; Ong, W.-Y.; Yu, L.E. Characterization, Purification, and Stability of Gold Nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 9023–9030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, C.M.; McCusker, C.D.; Yilmaz, T.; Rotello, V.M. Toxicity of Gold Nanoparticles Functionalized with Cationic and Anionic Side Chains. Bioconjug. Chem. 2004, 15, 897–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- English, D.S.; Pell, L.E.; Yu, Z.; Barbara, P.F.; Korgel, B.A. Size Tunable Visible Luminescence from Individual Organic Monolayer Stabilized Silicon Nanocrystal Quantum Dots. Nano Lett. 2002, 2, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, H.; Takahashi, K. Preparation of Silica Microcapsules by Sol-Gel Method in W/O Emulsion. J. Chem. Eng. Jpn. 1998, 31, 808–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Baldwin, R.K.; Pettigrew, K.A.; Kauzlarich, S.M. Solution Synthesis of Ultrastable Luminescent Siloxane-Coated Silicon Nanoparticles. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 1181–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabashin, A.V.; Delaporte, P.; Grojo, D.; Torres, R.; Sarnet, T.; Sentis, M. Nanofabrication with Pulsed Lasers. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 454–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marine, W.; Patrone, L.; Luk’yanchuk, B.; Sentis, M. Strategy of Nanocluster and Nanostructure Synthesis by Conventional Pulsed Laser Ablation. Appl. Surface Sci. 2000, 154–155, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geohegan, D.B.; Puretzky, A.A.; Duscher, G.; Pennycook, S.J. Time-Resolved Imaging of Gas Phase Nanoparticle Synthesis by Laser Ablation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 72, 2987–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrone, L.; Nelson, D.; Safarov, V.I.; Sentis, M.; Marine, W.; Giorgio, S. Photoluminescence of Silicon Nanoclusters with Reduced Size Dispersion Produced by Laser Ablation. J. Appl. Phys. 2000, 87, 3829–3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabashin, A.V.; Meunier, M.; Leonelli, R. Photoluminescence Characterization of Si-Based Nanostructured Films Produced by Pulsed Laser Ablation. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B Microelectron. Nanomed. Struct. Process. Meas. Phenom. 2001, 19, 2217–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabashin, A.V.; Meunier, M. Visible Photoluminescence from Nanostructured Si-Based Layers Produced by Air Optical Breakdown on Silicon. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 1619–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabashin, A.V.; Meunier, M. Laser-Induced Treatment of Silicon in Air and Formation of Si/SiOx Photoluminescent Nanostructured Layers. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2003, 101, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabashin, A.V.; Sylvestre, J.-P.; Patskovsky, S.; Meunier, M. Correlation between Photoluminescence Properties and Morphology of Laser-Ablated Si/SiOx Nanostructured Films. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 91, 3248–3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fojtik, A.; Henglein, A. Laser Ablation of Films and Suspended Particles in Solvent-Formation of Cluster and Colloid Solutions. Ber. Bunsenges. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 252. [Google Scholar]
- Sibbald, M.S.; Chumanov, G.; Cotton, T.M. Reduction of Cytochrome c by Halide-Modified, Laser-Ablated Silver Colloids. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 4672–4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafuné, F.; Kohno, J.; Takeda, Y.; Kondow, T.; Sawabe, H. Formation of Gold Nanoparticles by Laser Ablation in Aqueous Solution of Surfactant. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 5114–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgaev, S.I.; Sinakin, A.V.; Vornov, V.V.; Shafeev, G.A.; Bozon-Verduaz, F. Nanoparticles Produced by Laser Ablation of Solids in Liquid Environment. Appl. Surface Sci. 2002, 186, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabashin, V.K.; Meunier, M. Synthesis of Colloidal Nanoparticles during Femtosecond Laser Ablation of Gold in Water. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 94, 7941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabashin, V.K.; Meunier, M. Femtosecond Laser Ablation in Aqueous Solutions: A Novel Method to Synthesize Non-Toxic Metal Colloids with Controllable Size. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2007, 59, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besner, S.; Degorce, J.-Y.; Kabashin, A.V.; Meunier, M. Influence of Ambient Medium on Femtosecond Laser Processing of Silicon. Appl. Surface Sci. 2005, 247, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximova, K.; Aristov, A.; Sentis, M.; Kabashin, A.V. Size-Controllable Synthesis of Bare Gold Nanoparticles by Femtosecond Laser Fragmentation in Water. Nanotechnology 2015, 26, 065601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blandin, P.; Maximova, K.A.; Gongalsky, M.B.; Sanchez-Royo, J.F.; Chirvony, V.S.; Sentis, M.; Timoshenko, V.Y.; Kabashin, A.V. Femtosecond Laser Fragmentation from Water-Dispersed Microcolloids: Toward Fast Controllable Growth of Ultrapure Si-Based Nanomaterials for Biological Applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 2489–2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kattan, A.; Ryabchikov, Y.V.; Baati, T.; Chirvony, V.; Sánchez-Royo, J.F.; Sentis, M.; Braguer, D.; Timoshenko, V.Y.; Estève, M.-A.; Kabashin, A.V. Ultrapure Laser-Synthesized Si Nanoparticles with Variable Oxidation States for Biomedical Applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 7852–7858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebié, S.; Holade, Y.; Maximova, K.; Sentis, M.; Delaporte, P.; Kokoh, K.B.; Napporn, T.W.; Kabashin, A.V. Advanced Electrocatalysts on the Basis of Bare Au Nanomaterials for Biofuel Cell Applications. ACS Catal. 2015, 5, 6489–6496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvestre, J.P.; Kabashin, A.V.; Sacher, E.; Meunier, M.; Luong, J.H.T. Stabilization and Size Control of Gold Nanoparticles during Laser Ablation in Aqueous Cyclodextrins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 7176–7177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabashin, A.V.; Meunier, M.; Kingston, C.; Luong, J.H.T. Fabrication and Characterization of Gold Nanoparticles by Femtosecond Laser Ablation in an Aqueous Solution of Cyclodextrins. J. Chem. Phys. B 2003, 107, 4527–4531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvestre, J.; Poulin, S.; Kabashin, A.V.; Sacher, E.; Meunier, M.; Luong, J.H.T. Surface Chemistry of Gold Nanoparticles Produced by Laser Ablation in Aqueous Media. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 16864–16869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correard, F.; Maximova, K.; Estève, M.-A.; Villard, C.; Roy, M.; Al-Kattan, A.; Sentis, M.; Gingras, M.; Kabashin, A.V.; Braguer, D. Gold Nanoparticles Prepared by Laser Ablation in Aqueous Biocompatible Solutions: Assessment of Safety and Biological Identity for Nanomedicine Applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 5415–5430. [Google Scholar]
- Al-kattan, A.; Nirwan, V.P.; Munnier, E.; Chourpa, I. Toward Multifunctional Hybrid Platforms for Tissue Engineering Based on Chitosan ( PEO ) Nanofibers Functionalized by Bare Laser-Synthesized Au and Si Nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 31759–31766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Gökce, B.; Barcikowski, S. Laser Synthesis and Processing of Colloids: Fundamentals and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 3990–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dell’Aglio, M.; Gaudiuso, R.; Pascale, O.D.; Giacomo, A.D. Mechanisms and Processes of Pulsed Laser Ablation in Liquids during Nanoparticle Production. Appl. Surface Sci. 2015, 348, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlisle, E.M. Silicon: A Requirement in Bone Formation Independent of Vitamin D1. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1981, 33, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jugdaohsingh, R. Silicon and bone health. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2007, 11, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Emerick, R.J.; Kayongo-Male, H. Interactive Effects of Dietary Silicon, Copper, and Zinc in the Rat. J. Nutr. Biochem. 1990, 1, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neiner, D.; Chiu, H.W.; Kauzlarich, S.M. Low-Temperature Solution Route to Macroscopic Amounts of Hydrogen Terminated Silicon Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 11016–11017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilley, R.D.; Yamamoto, K. The Microemulsion Synthesis of Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic Silicon Nanocrystals. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 2053–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrera, Z.Y.; Aceves-Mijares, M.; Cabrera, M.A.I. Single Electron Charging and Transport in Silicon Rich Oxide. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 3962. [Google Scholar]
- Arul Dhas, N.; Raj, C.P.; Gedanken, A. Preparation of Luminescent Silicon Nanoparticles: A Novel Sonochemical Approach. Chem. Mater. 1998, 10, 3278–3281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baati, T.; Al-kattan, A.; Esteve, M.; Njim, L.; Ryabchikov, Y.; Chaspoul, F.; Hammami, M.; Sentis, M.; Kabashin, A.V.; Braguer, D. Ultrapure Laser-Synthesized Si- Based Nanomaterials for Biomedical Applications: In Vivo Assessment of Safety and Biodistribution. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Kou, X.; Yang, Z.; Ni, W.; Wang, J. Shape- and Size-Dependent Refractive Index Sensitivity of Gold Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2008, 24, 5233–5237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.-S.; El-Sayed, M.A. Gold and Silver Nanoparticles in Sensing and Imaging: Sensitivity of Plasmon Response to Size, Shape, and Metal Composition. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 19220–19225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liedberg, B.; Nylander, C.; Lundström, I. Biosensing with surface plasmon resonance—How it all started. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1995, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anker, J.N.; Hall, W.P.; Lyandres, O.; Shah, N.C.; Zhao, J.; Van Duyne, R.P. Biosensing with plasmonic nanosensors. Nat. Mater. 2008, 7, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patskovsky, S.; Kabashin, A.V.; Meunier, M.; Luong, J.H.T. Silicon-based surface plasmon resonance sensing with two surface plasmon polariton modes. Appl. Opt. 2003, 42, 6905–6909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemova, G.; Kabashin, A.V.; Kashyap, R. Surface plasmon-polariton Mach-Zehnder refractive index sensor. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 2008, 25, 1673–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, X.; Wang, X.; Ku, G.; Gill, K.L.; O’Neal, D.P.; Stoica, G.; Wang, L.V. Photoacoustic Tomography of a Nanoshell Contrast Agent in the in Vivo Rat Brain. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 1689–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yguerabide, J.; Yguerabide, E.E. Light-Scattering Submicroscopic Particles as Highly Fluorescent Analogs and Their Use as Tracer Labels in Clinical and Biological Applications. Anal. Biochem. 1998, 262, 137–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, L.R.; Stafford, R.J.; Bankson, J.A.; Sershen, S.R.; Rivera, B.; Price, R.E.; Hazle, J.D.; Halas, N.J.; West, J.L. Nanoshell-mediated near-infrared thermal therapy of tumors under magnetic resonance guidance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 13549–13554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loo, C.; Lowery, A.; Halas, N.J.; West, J.; Drezek, R. Immunotargeted nanoshells for integrated cancer imaging and therapy. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 709–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; El-Sayed, I.H.; Qian, W.; El-Sayed, M.A. Cancer cell imaging and photothermal therapy in near-infrared region by using gold nanorods. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 2115–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipka, J.; Semmler-Behnke, M.; Sperling, R.A.; Wenk, A.; Takenaka, S.; Schleh, C.; Kissel, T.; Parak, W.J.; Kreyling, W.G. Biodistribution of PEG-Modified Gold Nanoparticles Following Intratracheal Instillation and Intravenous Injection. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 6574–6581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, W.-S.; Cho, M.; Jeong, J.; Choi, M.; Han, B.S.; Shin, H.-S.; Hong, J.; Chung, B.H.; Jeong, J.; Cho, M.-H. Size-Dependent Tissue Kinetics of PEG-Coated Gold Nanoparticles. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2010, 245, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Bae, K.H.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, K.R.; Park, T.G. Amine-Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles as Non-Cytotoxic and Efficient Intracellular siRNA Delivery Carriers. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 364, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wangoo, N.; Bhasin, K.K.; Mehta, S.K.; Suri, C.R. Synthesis and Capping of Water-Dispersed Gold Nanoparticles by an Amino Acid: Bioconjugation and Binding Studies. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 323, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javier, D.J.; Nitin, N.; Levy, M.; Ellington, A.; Richards-Kortum, R. Aptamer-Targeted Gold Nanoparticles As Molecular-Specific Contrast Agents for Reflectance Imaging. Bioconjug. Chem. 2008, 19, 1309–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Liu, D.; Wang, Z. Functional Gold Nanoparticle−Peptide Complexes as Cell-Targeting Agents. Langmuir 2008, 24, 10293–10297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munday, R. Toxicity of Thiols and Disulphides: Involvement of Free-Radical Species. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1989, 7, 659–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernodet, N.; Fang, X.; Sun, Y.; Bakhtina, A.; Ramakrishnan, A.; Sokolov, J.; Ulman, A.; Rafailovich, M. Adverse Effects of Citrate/gold Nanoparticles on Human Dermal Fibroblasts. Small 2006, 2, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubin-Tam, M.-E.; Hamad-Schifferli, K. Gold Nanoparticle-Cytochrome C Complexes: The Effect of Nanoparticle Ligand Charge on Protein Structure. Langmuir 2005, 21, 12080–12084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etchegoin, P.G.; Le Ru, E.C. A Perspective on Single Molecule SERS: Current Status and Future Challenges. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2008, 10, 6079–6089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deyao, K.; Tao, P.; Goosen, M.F.A.; Min, J.M.; He, Y.Y. Ph-Sensitivity of Hydrogels Based on Complex-Forming Chitosan—Polyether Interpenetrating Polymer Network. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1993, 48, 343–354. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Kotaki, M.; Yong, T.; He, W.; Ramakrishna, S. Surface Engineering of Electrospun Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Nanofibers towards Development of a New Material for Blood Vessel Engineering. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 2527–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.; Wendorff, J.H.; Greiner, A. Use of Electrospinning Technique for Biomedical Applications. Polymer 2008, 49, 5603–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Patra, P.K.; Warner, S.B.; Bhowmick, S. Role of Fiber Diameter in Adhesion and Proliferation of NIH 3T3 Fibroblast on Electrospun Polycaprolactone Scaffolds. Tissue Eng. 2007, 13, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabashin, A.V.; Timoshenko, V.Y. What theranostic applications could ultrapure laser-synthesized Si nanoparticles have in cancer? Nanomedicine 2016, 11, 2247–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kögler, M.; Ryabchikov, Y.V.; Uusitalo, S.; Popov, A.; Popov, A.; Tselikov, G.; Välimaa, A.-L.; Al-Kattan, A.; Hiltunen, J.; Laitinen, R.; et al. Bare Laser-Synthesized Au-Based Nanoparticles as Non-Disturbing SERS Probes for Bacteria Identification. J. Biophotonics 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bibikova, O.; Haas, J.; Lopez-Lorente, A.; Popov, A.; Yury, R.; Kinnunen, M.; Kabashin, A.V.; Meglinski, I.; Mizaikoff, B. Surface enhanced infrared absorption spectroscopy based on gold nanostars and spherical nanoparticles. Anal. Chimica Acta 2017, 990, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Kattan, A.; Nirwan, V.P.; Popov, A.; Ryabchikov, Y.V.; Tselikov, G.; Sentis, M.; Fahmi, A.; Kabashin, A.V. Recent Advances in Laser-Ablative Synthesis of Bare Au and Si Nanoparticles and Assessment of Their Prospects for Tissue Engineering Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1563. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061563
Al-Kattan A, Nirwan VP, Popov A, Ryabchikov YV, Tselikov G, Sentis M, Fahmi A, Kabashin AV. Recent Advances in Laser-Ablative Synthesis of Bare Au and Si Nanoparticles and Assessment of Their Prospects for Tissue Engineering Applications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(6):1563. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061563
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Kattan, Ahmed, Viraj P. Nirwan, Anton Popov, Yury V. Ryabchikov, Gleb Tselikov, Marc Sentis, Amir Fahmi, and Andrei V. Kabashin. 2018. "Recent Advances in Laser-Ablative Synthesis of Bare Au and Si Nanoparticles and Assessment of Their Prospects for Tissue Engineering Applications" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 6: 1563. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061563
APA StyleAl-Kattan, A., Nirwan, V. P., Popov, A., Ryabchikov, Y. V., Tselikov, G., Sentis, M., Fahmi, A., & Kabashin, A. V. (2018). Recent Advances in Laser-Ablative Synthesis of Bare Au and Si Nanoparticles and Assessment of Their Prospects for Tissue Engineering Applications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(6), 1563. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061563