Treatment with Obestatin—A Ghrelin Gene-Encoded Peptide—Reduces the Severity of Experimental Colitis Evoked by Trinitrobenzene Sulfonic Acid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
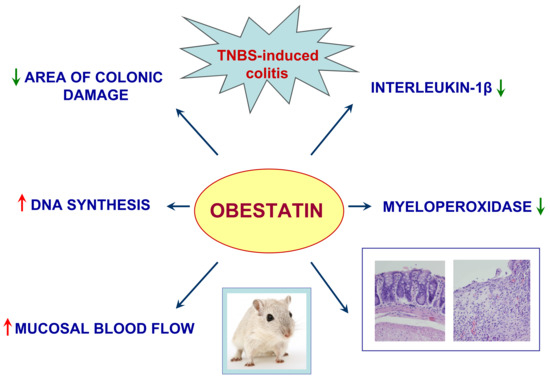
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Treatment
4.2. Measurement of Colonic Blood Flow, Leukocytes in the Blood, and Colonic Damage
4.3. Biochemical Analysis
4.3.1. Determination of DNA Synthesis in Colonic Mucosa
4.3.2. Determination of Interleukin-1β Concentration in Colonic Mucosa
4.3.3. Determination of Myeloperoxidase Activity in Colonic Mucosa
4.4. Histological Examination of the Colon
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, J.V.; Ren, P.-G.; Avsian-Kretchmer, O.; Luo, C.-W.; Rauch, R.; Klein, C.; Hsueh, A.J.W. Obestatin, a Peptide Encoded by the Ghrelin Gene, Opposes Ghrelin’s Effects on Food Intake. Science 2005, 310, 996–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Asakawa, A.; Fujimiya, M.; Lee, S.-D.; Inui, A. Ghrelin Gene Products and the Regulation of Food Intake and Gut Motility. Pharmacol. Rev. 2009, 61, 430–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ceranowicz, P.; Warzecha, Z.; Dembinski, A. Peptidyl Hormones of Endocrine Cells Origin in the Gut—Their Discovery and Physiological Relevance. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2015, 66, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Furnes, M.W.; Stenstrom, B.; Tømmerås, K.; Skoglund, T.; Dickson, S.L.; Kulseng, B.; Zhao, C.-M.; Chen, D. Feeding Behavior in Rats Subjected to Gastrectomy or Gastric Bypass Surgery. Eur. Surg. Res. 2008, 40, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanoine, J.-P.; Wong, A.C.K.; Barrios, V. Obestatin, Acylated and Total Ghrelin Concentrations in the Perinatal Rat Pancreas. Horm. Res. 2006, 66, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, A.S.; Soule, S.G.; Yandle, T.G.; Richards, A.M.; Pemberton, C.J. Characterisation of Proghrelin Peptides in Mammalian Tissue and Plasma. J. Endocrinol. 2007, 192, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granata, R.; Baragli, A.; Settanni, F.; Scarlatti, F.; Ghigo, E. Unraveling the Role of the Ghrelin Gene Peptides in the Endocrine Pancreas. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 45, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granata, R.; Settanni, F.; Gallo, D.; Trovato, L.; Biancone, L.; Cantaluppi, V.; Nano, R.; Annunziata, M.; Campiglia, P.; Arnoletti, E.; et al. Obestatin Promotes Survival of Pancreatic Beta-Cells and Human Islets and Induces Expression of Genes Involved in the Regulation of Beta-Cell Mass and Function. Diabetes 2008, 57, 967–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dun, S.L.; Brailoiu, G.C.; Brailoiu, E.; Yang, J.; Chang, J.K.; Dun, N.J. Distribution and Biological Activity of Obestatin in the Rat. J. Endocrinol. 2006, 191, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grönberg, M.; Tsolakis, A.V.; Magnusson, L.; Janson, E.T.; Saras, J. Distribution of Obestatin and Ghrelin in Human Tissues: Immunoreactive Cells in the Gastrointestinal Tract, Pancreas, and Mammary Glands. J. Histochem. Cytochem. Off. J. Histochem. Soc. 2008, 56, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volante, M.; Rosas, R.; Ceppi, P.; Rapa, I.; Cassoni, P.; Wiedenmann, B.; Settanni, F.; Granata, R.; Papotti, M. Obestatin in Human Neuroendocrine Tissues and Tumours: Expression and Effect on Tumour Growth. J. Pathol. 2009, 218, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.-M.; Furnes, M.W.; Stenström, B.; Kulseng, B.; Chen, D. Characterization of Obestatin- and Ghrelin-Producing Cells in the Gastrointestinal Tract and Pancreas of Rats: An Immunohistochemical and Electron-Microscopic Study. Cell Tissue Res. 2008, 331, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurriarán-Rodríguez, U.; Santos-Zas, I.; Al-Massadi, O.; Mosteiro, C.S.; Beiroa, D.; Nogueiras, R.; Crujeiras, A.B.; Seoane, L.M.; Señarís, J.; García-Caballero, T.; et al. The Obestatin/GPR39 System Is up-Regulated by Muscle Injury and Functions as an Autocrine Regenerative System. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 38379–38389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moretti, E.; Vindigni, C.; Tripodi, S.A.; Mazzi, L.; Nuti, R.; Figura, N.; Collodel, G. Immunolocalisation of Ghrelin and Obestatin in Human Testis, Seminal Vesicles, Prostate and Spermatozoa. Andrologia 2014, 46, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.V.; Jahr, H.; Luo, C.-W.; Klein, C.; Van Kolen, K.; Ver Donck, L.; De, A.; Baart, E.; Li, J.; Moechars, D.; et al. Obestatin Induction of Early-Response Gene Expression in Gastrointestinal and Adipose Tissues and the Mediatory Role of G Protein-Coupled Receptor, GPR39. Mol. Endocrinol. 2008, 22, 1464–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.V.; Li, L.; Huang, Q.; Ren, P.-G. Obestatin Receptor in Energy Homeostasis and Obesity Pathogenesis. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2013, 114, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, G.; He, Z.; Cong, P.; Chen, H.; Guo, Y.; Yu, J.; Liu, Z.; Ji, Q.; Song, Z.; Chen, Y. Peripheral Administration of TAT-Obestatin Can Influence the Expression of Liporegulatory Genes but Fails to Affect Food Intake in Mice. Peptides 2013, 42, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.-Y.; He, J.-M.; Tang, S.-Q.; Li, H.-Y.; Jiang, Q.-Y.; Zou, X.-T. Is GPR39 the Natural Receptor of Obestatin? Peptides 2009, 30, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chartrel, N.; Alvear-Perez, R.; Leprince, J.; Iturrioz, X.; Reaux-Le Goazigo, A.; Audinot, V.; Chomarat, P.; Coge, F.; Nosjean, O.; Rodriguez, M.; et al. Comment on “Obestatin, a Peptide Encoded by the Ghrelin Gene, Opposes Ghrelin’s Effects on Food Intake”. Science 2007, 315, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauwers, E.; Landuyt, B.; Arckens, L.; Schoofs, L.; Luyten, W. Obestatin Does Not Activate Orphan G Protein-Coupled Receptor GPR39. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 351, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granata, R.; Gallo, D.; Luque, R.M.; Baragli, A.; Scarlatti, F.; Grande, C.; Gesmundo, I.; Córdoba-Chacón, J.; Bergandi, L.; Settanni, F.; et al. Obestatin Regulates Adipocyte Function and Protects against Diet-Induced Insulin Resistance and Inflammation. FASEB J. 2012, 26, 3393–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alloatti, G.; Arnoletti, E.; Bassino, E.; Penna, C.; Perrelli, M.G.; Ghé, C.; Muccioli, G. Obestatin Affords Cardioprotection to the Ischemic-Reperfused Isolated Rat Heart and Inhibits Apoptosis in Cultures of Similarly Stressed Cardiomyocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2010, 299, H470–H481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Dong, X.-W.; Xia, J.-Y.; Xu, K.-Y.; Xu, Z.-R. Obestatin Plays Beneficial Role in Cardiomyocyte Injury Induced by Ischemia-Reperfusion in Vivo and in Vitro. Med. Sci. Monit. 2017, 23, 2127–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penna, C.; Tullio, F.; Femminò, S.; Rocca, C.; Angelone, T.; Cerra, M.C.; Gallo, M.P.; Gesmundo, I.; Fanciulli, A.; Brizzi, M.F.; et al. Obestatin Regulates Cardiovascular Function and Promotes Cardioprotection through the Nitric Oxide Pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 3670–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Wei, L.; Wu, J.; Wei, N.; Kong, X.; Tian, Z. Association of gastric emptying with ghrelin, obestatin and receptor (GHSR, GPR-39) in hypothalamus of diabetic rats. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2010, 90, 1137–1140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ataka, K.; Inui, A.; Asakawa, A.; Kato, I.; Fujimiya, M. Obestatin Inhibits Motor Activity in the Antrum and Duodenum in the Fed State of Conscious Rats. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 294, G1210–G1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimiya, M.; Asakawa, A.; Ataka, K.; Kato, I.; Inui, A. Different Effects of Ghrelin, Des-Acyl Ghrelin and Obestatin on Gastroduodenal Motility in Conscious Rats. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2008, 14, 6318–6326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qader, S.S.; Håkanson, R.; Rehfeld, J.F.; Lundquist, I.; Salehi, A. Proghrelin-Derived Peptides Influence the Secretion of Insulin, Glucagon, Pancreatic Polypeptide and Somatostatin: A Study on Isolated Islets from Mouse and Rat Pancreas. Regul. Pept. 2008, 146, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippl, F.; Erdmann, J.; Lichter, N.; Tholl, S.; Wagenpfeil, S.; Adam, O.; Schusdziarra, V. Relation of Plasma Obestatin Levels to BMI, Gender, Age and Insulin. Horm. Metab. Res. 2008, 40, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, L.; Zhao, Y.-T.; Teng, L.-L.; Li, M.-Z.; Jiang, H. Circulating Obestatin Levels Correlate with Fasting Insulin and HOMA-IR but Not with Hypertension in Elderly Men. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 69, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, A.-J.; Guo, Z.-F.; Wang, Y.-K.; Wang, L.-G.; Wang, W.-Z.; Lin, L.; Zheng, X.; Yuan, W.-J. Inhibitory Effect of Obestatin on Glucose-Induced Insulin Secretion in Rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 369, 969–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Şen, L.S.; Karakoyun, B.; Yeğen, C.; Akkiprik, M.; Yüksel, M.; Ercan, F.; Özer, A.; Yeğen, B.Ç. Treatment with Either Obestatin or Ghrelin Attenuates Mesenteric Ischemia-Reperfusion-Induced Oxidative Injury of the Ileum and the Remote Organ Lung. Peptides 2015, 71, 8–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khirazova, E.E.; Golubeva, M.G.; Maslova, M.V.; Graf, A.V.; Maklakova, A.S.; Baizhumanov, A.A.; Trofimova, L.K.; Sokolova, N.A.; Kamenskii, A.A. Effect of Anorexigenic Peptide Obestatin on Platelet Aggregation and Osmotic Resistance of Erythrocytes. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2013, 155, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Xing, Y.-X.; Gao, X.-Y.; Kuang, H.-Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, R. Obestatin Prevents H2O2-Induced Damage through Activation of TrkB in RGC-5 Cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 1061–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Słupecka, M.; Woliński, J.; Herman, A.P.; Ochniewicz, P.; Kornacka, M.K. Biological role of obestatin in physiology and pathophysiology. Med. Wieku Rozw. 2012, 16, 47–52. [Google Scholar]
- Trovato, L.; Gallo, D.; Settanni, F.; Gesmundo, I.; Ghigo, E.; Granata, R. Obestatin: Is It Really Doing Something? Front. Horm. Res. 2014, 42, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.-X.; Yang, L.; Kuang, H.-Y.; Gao, X.-Y.; Liu, H.-L. Function of Obestatin in the Digestive System. Nutrition 2017, 34, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, A.-J.; Guo, Z.-F.; Wang, Y.-K.; Lin, L.; Zheng, X.; Yuan, W.-J. Obestatin, Obesity and Diabetes. Peptides 2009, 30, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Yuan, C.; Li, Z.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Li, C.; Li, R.; Wang, S.-R. Meta-Analysis of the Relationship between Obestatin and Ghrelin Levels and the Ghrelin/Obestatin Ratio with Respect to Obesity. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2011, 341, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, C.C.; Liang, L.; Wang, C.L.; Fu, J.F.; Zhao, Z.Y. The Change in Ghrelin and Obestatin Levels in Obese Children after Weight Reduction. Acta Paediatr. 2009, 98, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wali, P.; King, J.; He, Z.; Tonb, D.; Horvath, K. Ghrelin and Obestatin Levels in Children with Failure to Thrive and Obesity. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2014, 58, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harsch, I.A.; Koebnick, C.; Tasi, A.M.; Hahn, E.G.; Konturek, P.C. Ghrelin and Obestatin Levels in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with and without Delayed Gastric Emptying. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2009, 54, 2161–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.; Li, L.; Yang, G.; Liu, J.; Li, K.; Tang, Y.; Liou, H.; Boden, G. Circulating Obestatin Levels in Normal Subjects and in Patients with Impaired Glucose Regulation and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Clin. Endocrinol. 2007, 66, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, M.G.; Bittel, D.C. Plasma Obestatin and Ghrelin Levels in Subjects with Prader-Willi Syndrome. Am. J. Med. Genet. 2007, 143A, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Yue, H.; Zhang, J.; Pu, J.; Yu, Q. Effects of Plasma Ghrelin, Obestatin, and Ghrelin/Obestatin Ratio on Blood Pressure Circadian Rhythms in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome. Chin. Med. J. 2014, 127, 850–855. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sibilia, V.; Rindi, G.; Pagani, F.; Rapetti, D.; Locatelli, V.; Torsello, A.; Campanini, N.; Deghenghi, R.; Netti, C. Ghrelin Protects against Ethanol-Induced Gastric Ulcers in Rats: Studies on the Mechanisms of Action. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brzozowski, T.; Konturek, P.C.; Konturek, S.J.; Kwiecień, S.; Drozdowicz, D.; Bielanski, W.; Pajdo, R.; Ptak, A.; Nikiforuk, A.; Pawlik, W.W.; et al. Exogenous and Endogenous Ghrelin in Gastroprotection against Stress-Induced Gastric Damage. Regul. Pept. 2004, 120, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konturek, P.C.; Brzozowski, T.; Walter, B.; Burnat, G.; Hess, T.; Hahn, E.G.; Konturek, S.J. Ghrelin-Induced Gastroprotection against Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury Involves an Activation of Sensory Afferent Nerves and Hyperemia Mediated by Nitric Oxide. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 536, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brzozowski, T.; Konturek, P.C.; Sliwowski, Z.; Drozdowicz, D.; Kwiecien, S.; Pawlik, M.; Pajdo, R.; Konturek, S.J.; Pawlik, W.W.; Hahn, E.G. Neural Aspects of Ghrelin-Induced Gastroprotection against Mucosal Injury Induced by Noxious Agents. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2006, 57 (Suppl. 6), 63–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Işeri, S.O.; Sener, G.; Yüksel, M.; Contuk, G.; Cetinel, S.; Gedik, N.; Yegen, B.C. Ghrelin against Alendronate-Induced Gastric Damage in Rats. J. Endocrinol. 2005, 187, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dembinski, A.; Warzecha, Z.; Ceranowicz, P.; Tomaszewska, R.; Stachura, J.; Konturek, S.J.; Konturek, P.C. Ghrelin Attenuates the Development of Acute Pancreatitis in Rat. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2003, 54, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dembiński, A.; Warzecha, Z.; Ceranowicz, P.; Cieszkowski, J.; Pawlik, W.W.; Tomaszewska, R.; Kuśnierz-Cabala, B.; Naskalski, J.W.; Kuwahara, A.; Kato, I. Role of Growth Hormone and Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 in the Protective Effect of Ghrelin in Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Acute Pancreatitis. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 2006, 16, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonior, J.; Warzecha, Z.; Ceranowicz, P.; Gajdosz, R.; Pierzchalski, P.; Kot, M.; Leja-Szpak, A.; Nawrot-Porąbka, K.; Link-Lenczowski, P.; Pędziwiatr, M.; et al. Capsaicin-Sensitive Sensory Nerves Are Necessary for the Protective Effect of Ghrelin in Cerulein-Induced Acute Pancreatitis in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warzecha, Z.; Dembinski, A. Protective and Therapeutic Effects of Ghrelin in the Gut. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warzecha, Z.; Kownacki, P.; Ceranowicz, P.; Dembinski, M.; Cieszkowski, J.; Dembinski, A. Ghrelin Accelerates the Healing of Oral Ulcers in Non-Sialoadenectomized and Sialoadenectomized Rats. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2013, 64, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cieszkowski, J.; Warzecha, Z.; Ceranowicz, P.; Ceranowicz, D.; Kusnierz-Cabala, B.; Pedziwiatr, M.; Dembinski, M.; Ambrozy, T.; Kaczmarzyk, T.; Pihut, M.; et al. Therapeutic Effect of Exogenous Ghrelin in the Healing of Gingival Ulcers Is Mediated by the Release of Endogenous Growth Hormone and Insulin-like Growth Factor-1. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2017, 68, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ceranowicz, P.; Warzecha, Z.; Dembinski, A.; Sendur, R.; Cieszkowski, J.; Ceranowicz, D.; Pawlik, W.W.; Kuwahara, A.; Kato, I.; Konturek, P.C. Treatment with Ghrelin Accelerates the Healing of Acetic Acid-Induced Gastric and Duodenal Ulcers in Rats. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. Off. J. Pol. Physiol. Soc. 2009, 60, 87–98. [Google Scholar]
- Konturek, P.C.; Brzozowski, T.; Engel, M.; Burnat, G.; Gaca, P.; Kwiecien, S.; Pajdo, R.; Konturek, S.J. Ghrelin Ameliorates Colonic Inflammation. Role of Nitric Oxide and Sensory Nerves. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2009, 60, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maduzia, D.; Matuszyk, A.; Ceranowicz, D.; Warzecha, Z.; Ceranowicz, P.; Fyderek, K.; Galazka, K.; Dembinski, A. The Influence of Pretreatment with Ghrelin on the Development of Acetic-Acid-Induced Colitis in Rats. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2015, 66, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matuszyk, A.; Ceranowicz, D.; Warzecha, Z.; Ceranowicz, P.; Fyderek, K.; Gałązka, K.; Cieszkowski, J.; Bonior, J.; Jaworek, J.; Pihut, M.; et al. The Influence of Ghrelin on the Development of Dextran Sodium Sulfate-Induced Colitis in Rats. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 718314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matuszyk, A.; Ceranowicz, P.; Warzecha, Z.; Cieszkowski, J.; Ceranowicz, D.; Gałązka, K.; Bonior, J.; Jaworek, J.; Bartuś, K.; Gil, K.; et al. Exogenous Ghrelin Accelerates the Healing of Acetic Acid-Induced Colitis in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceranowicz, P.; Warzecha, Z.; Cieszkowski, J.; Ceranowicz, D.; Kuśnierz-Cabala, B.; Bonior, J.; Jaworek, J.; Ambroży, T.; Gil, K.; Olszanecki, R.; et al. Essential Role of Growth Hormone and IGF-1 in Therapeutic Effect of Ghrelin in the Course of Acetic Acid-Induced Colitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warzecha, Z.; Ceranowicz, P.; Dembinski, A.; Cieszkowski, J.; Kusnierz-Cabala, B.; Tomaszewska, R.; Kuwahara, A.; Kato, I. Therapeutic Effect of Ghrelin in the Course of Cerulein-Induced Acute Pancreatitis in Rats. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2010, 61, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceranowicz, D.; Warzecha, Z.; Dembinski, A.; Ceranowicz, P.; Cieszkowski, J.; Kusnierz-Cabala, B.; Tomaszewska, R.; Kuwahara, A.; Kato, I. Role of Hormonal Axis, Growth Hormone—IGF-1, in the Therapeutic Effect of Ghrelin in the Course of Cerulein-Induced Acute Pancreatitis. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2010, 61, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bukowczan, J.; Warzecha, Z.; Ceranowicz, P.; Kusnierz-Cabala, B.; Tomaszewska, R.; Dembinski, A. Therapeutic Effect of Ghrelin in the Course of Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Acute Pancreatitis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2015, 21, 2284–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonior, J.; Ceranowicz, P.; Gajdosz, R.; Kuśnierz-Cabala, B.; Pierzchalski, P.; Warzecha, Z.; Dembiński, A.; Pędziwiatr, M.; Kot, M.; Leja-Szpak, A.; et al. Molecular Ghrelin System in the Pancreatic Acinar Cells: The Role of the Polypeptide, Caerulein and Sensory Nerves. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceranowicz, P.; Warzecha, Z.; Dembinski, A.; Cieszkowski, J.; Dembinski, M.; Sendur, R.; Kusnierz-Cabala, B.; Tomaszewska, R.; Kuwahara, A.; Kato, I. Pretreatment with Obestatin Inhibits the Development of Cerulein-Induced Pancreatitis. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2009, 60, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bukowczan, J.; Warzecha, Z.; Ceranowicz, P.; Kuśnierz-Cabala, B.; Tomaszewska, R.; Dembinski, A. Pretreatment with Obestatin Reduces the Severity of Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Acute Pancreatitis in Rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 760, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukowczan, J.; Warzecha, Z.; Ceranowicz, P.; Kuśnierz-Cabala, B.; Tomaszewska, R. Obestatin Accelerates the Recovery in the Course of Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Acute Pancreatitis in Rats. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dembiński, A.; Warzecha, Z.; Ceranowicz, P.; Cieszkowski, J.; Dembiński, M.; Ptak-Belowska, A.; Kuwahara, A.; Kato, I. Administration of Obestatin Accelerates the Healing of Chronic Gastric Ulcers in Rats. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. 2011, 17, BR196–BR200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandridis, E.; Zisimopoulos, A.; Liratzopoulos, N.; Katsos, I.; Manolas, K.; Kouklakis, G. Obestatin/Ghrelin Ratio: A New Activity Index in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2009, 15, 1557–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.Y.; Jeong, J.B.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, S.H.; Koh, S.-J.; Kim, B.G.; Lee, K.L. Circulating Ghrelin Levels and Obestatin/Ghrelin Ratio as a Marker of Activity in Ulcerative Colitis. Intest. Res. 2015, 13, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, F.; Chimienti, G.; Linsalata, M.; Clemente, C.; Orlando, A.; Riezzo, G. The Obestatin/Ghrelin Ratio and Ghrelin Genetics in Adult Celiac Patients before and after a Gluten-Free Diet, in Irritable Bowel Syndrome Patients and Healthy Individuals. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 29, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matuszyk, A.; Ceranowicz, P.; Warzecha, Z.; Cieszkowski, J.; Bonior, J.; Jaworek, J.; Kuśnierz-Cabala, B.; Konturek, P.; Ambroży, T.; Dembiński, A. Obestatin Accelerates the Healing of Acetic Acid-Induced Colitis in Rats. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 2834386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pamukcu, O.; Kumral, Z.N.O.; Ercan, F.; Yegen, B.C.; Ertem, D. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Obestatin and Ghrelin in Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Colitis in Rats. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2013, 57, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brenna, Ø.; Furnes, M.W.; Drozdov, I.; van Beelen Granlund, A.; Flatberg, A.; Sandvik, A.K.; Zwiggelaar, R.T.M.; Mårvik, R.; Nordrum, I.S.; Kidd, M.; et al. Relevance of TNBS-Colitis in Rats: A Methodological Study with Endoscopic, Histologic and Transcriptomic Characterization and Correlation to IBD. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te Velde, A.A.; de Kort, F.; Sterrenburg, E.; Pronk, I.; ten Kate, F.J.W.; Hommes, D.W.; van Deventer, S.J.H. Comparative Analysis of Colonic Gene Expression of Three Experimental Colitis Models Mimicking Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2007, 13, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoniou, E.; Margonis, G.A.; Angelou, A.; Pikouli, A.; Argiri, P.; Karavokyros, I.; Papalois, A.; Pikoulis, E. The TNBS-Induced Colitis Animal Model: An Overview. Ann. Med. Surg. 2016, 11, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neurath, M.F.; Fuss, I.; Kelsall, B.L.; Stüber, E.; Strober, W. Antibodies to Interleukin 12 Abrogate Established Experimental Colitis in Mice. J. Exp. Med. 1995, 182, 1281–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawada, M.; Arihiro, A.; Mizoguchi, E. Insights from Advances in Research of Chemically Induced Experimental Models of Human Inflammatory Bowel Disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 5581–5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, G.P.; Beck, P.L.; Herridge, M.S.; Depew, W.T.; Szewczuk, M.R.; Wallace, J.L. Hapten-Induced Model of Chronic Inflammation and Ulceration in the Rat Colon. Gastroenterology 1989, 96 Pt 2, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elson, C.O.; Beagley, K.W.; Sharmanov, A.T.; Fujihashi, K.; Kiyono, H.; Tennyson, G.S.; Cong, Y.; Black, C.A.; Ridwan, B.W.; McGhee, J.R. Hapten-Induced Model of Murine Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Mucosa Immune Responses and Protection by Tolerance. J. Immunol. 1996, 157, 2174–2185. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fitzpatrick, L.R.; Meirelles, K.; Small, J.S.; Puleo, F.J.; Koltun, W.A.; Cooney, R.N. A New Model of Chronic Hapten-Induced Colitis in Young Rats. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2010, 50, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaxman, B.A.; Harper, R.A. Primary Cell Culture for Biochemical Studies of Human Keratinocytes. A Method for Production of Very Large Numbers of Cells without the Necessity of Subculturing Techniques. Br. J. Dermatol. 1975, 92, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigneri, S.; Scialabba, A.; Termini, R.; Germanà, B.; Vianello, F.; Grassi, S.A.; Plebani, M.; Di Mario, F. Pathophysiology of the Gastric Microcirculation. Ital. J. Gastroenterol. 1992, 24, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sørbye, H.; Svanes, K. The Role of Blood Flow in Gastric Mucosal Defence, Damage and Healing. Dig. Dis. 1994, 12, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlando, R.C. The Integrity of the Esophageal Mucosa. Balance between Offensive and Defensive Mechanisms. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2010, 24, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Salam, O.M.; Czimmer, J.; Debreceni, A.; Szolcsányi, J.; Mózsik, G. Gastric Mucosal Integrity: Gastric Mucosal Blood Flow and Microcirculation. An Overview. J. Physiol. Paris 2001, 95, 105–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warzecha, Z.; Ceranowicz, D.; Dembiński, A.; Ceranowicz, P.; Cieszkowski, J.; Kuwahara, A.; Kato, I.; Dembiński, M.; Konturek, P.C. Ghrelin Accelerates the Healing of Cysteamine-Induced Duodenal Ulcers in Rats. Med. Sci. Monit. 2012, 18, BR181–BR187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, F.W.; Su, K.C.; Pique, J.M.; Thiefin, G.; Passaro, E.; Guth, P.H. Superior Mesenteric Artery Is More Important than Inferior Mesenteric Artery in Maintaining Colonic Mucosal Perfusion and Integrity in Rats. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1992, 37, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osborn, L. Leukocyte Adhesion to Endothelium in Inflammation. Cell 1990, 62, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rich, R.; Fleisher, T.; Shearer, W.; Schroeder, H.; Frew, A.; Weyand, C. Clinical Immunology: Principles and Practice, 4th ed.; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Conlan, J.W.; North, R.J. Neutrophils Are Essential for Early Anti-Listeria Defense in the Liver, but Not in the Spleen or Peritoneal Cavity, as Revealed by a Granulocyte-Depleting Monoclonal Antibody. J. Exp. Med. 1994, 179, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daley, J.M.; Thomay, A.A.; Connolly, M.D.; Reichner, J.S.; Albina, J.E. Use of Ly6G-Specific Monoclonal Antibody to Deplete Neutrophils in Mice. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2008, 83, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reber, L.L.; Gillis, C.M.; Starkl, P.; Jönsson, F.; Sibilano, R.; Marichal, T.; Gaudenzio, N.; Bérard, M.; Rogalla, S.; Contag, C.H.; et al. Neutrophil Myeloperoxidase Diminishes the Toxic Effects and Mortality Induced by Lipopolysaccharide. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hock, H.; Hamblen, M.J.; Rooke, H.M.; Traver, D.; Bronson, R.T.; Cameron, S.; Orkin, S.H. Intrinsic Requirement for Zinc Finger Transcription Factor Gfi-1 in Neutrophil Differentiation. Immunity 2003, 18, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sugimoto, M.A.; Sousa, L.P.; Pinho, V.; Perretti, M.; Teixeira, M.M. Resolution of Inflammation: What Controls Its Onset? Front. Immunol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sebastian, S.; Ashton, K.; Houston, Y.; Diggory, T.M.; Dore, P. Anti-TNF Therapy Induced Immune Neutropenia in Crohns Disease-Report of 2 Cases and Review of Literature. J. Crohn’s Colitis 2012, 6, 713–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, F.G.; Dasilva, G.; Wexner, S.D. Neutropenic Enterocolitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A.; Wolff, S.M. The Role of Interleukin-1 in Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1993, 328, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A. Immunological and Inflammatory Functions of the Interleukin-1 Family. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 519–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garlanda, C.; Dinarello, C.A.; Mantovani, A. The Interleukin-1 Family: Back to the Future. Immunity 2013, 39, 1003–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lopez-Castejon, G.; Brough, D. Understanding the Mechanism of IL-1β Secretion. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2011, 22, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogquist, K.A.; Nett, M.A.; Unanue, E.R.; Chaplin, D.D. Interleukin 1 Is Processed and Released during Apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 8485–8489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A. A Clinical Perspective of IL-1β as the Gatekeeper of Inflammation. Eur. J. Immunol. 2011, 41, 1203–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A.; Simon, A.; van der Meer, J.W.M. Treating Inflammation by Blocking Interleukin-1 in a Broad Spectrum of Diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 633–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Randhawa, P.K.; Singh, K.; Singh, N.; Jaggi, A.S. A Review on Chemical-Induced Inflammatory Bowel Disease Models in Rodents. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2014, 18, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warzecha, Z.; Dembiński, A.; Brzozowski, T.; Ceranowicz, P.; Pajdo, R.; Niemiec, J.; Drozdowicz, D.; Mitis-Musioł, M.; Konturek, S.J. Gastroprotective Effect of Histamine and Acid Secretion on Ammonia-Induced Gastric Lesions in Rats. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 35, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, P.P.; Priebat, D.A.; Christensen, R.D.; Rothstein, G. Measurement of Cutaneous Inflammation: Estimation of Neutrophil Content with an Enzyme Marker. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1982, 78, 206–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilaseca, J.; Salas, A.; Guarner, F.; Rodríguez, R.; Martínez, M.; Malagelada, J.R. Dietary Fish Oil Reduces Progression of Chronic Inflammatory Lesions in a Rat Model of Granulomatous Colitis. Gut 1990, 31, 539–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Groups | Morphological Changes | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grading of Colonic Damage (0–2) | Inflammatory Infiltration (0–3) | Depth of Damage (0–3) | Fibrosis (0–3) | |
| Control (NaCl) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Obestatin 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Obestatin 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Obestatin 16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Colitis (TNBS) + NaCl | 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
| Colitis + Obestatin 4 | 1–2 | 1–2 | 1 | 2 |
| Colitis + Obestatin 8 | 0–1 | 1 | 0–1 | 1 |
| Colitis + Obestatin 16 | 0–1 | 1 | 0–1 | 1 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Konarska, K.; Cieszkowski, J.; Warzecha, Z.; Ceranowicz, P.; Chmura, A.; Kuśnierz-Cabala, B.; Gałązka, K.; Kowalczyk, P.; Miskiewicz, A.; Konturek, T.J.; et al. Treatment with Obestatin—A Ghrelin Gene-Encoded Peptide—Reduces the Severity of Experimental Colitis Evoked by Trinitrobenzene Sulfonic Acid. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061643
Konarska K, Cieszkowski J, Warzecha Z, Ceranowicz P, Chmura A, Kuśnierz-Cabala B, Gałązka K, Kowalczyk P, Miskiewicz A, Konturek TJ, et al. Treatment with Obestatin—A Ghrelin Gene-Encoded Peptide—Reduces the Severity of Experimental Colitis Evoked by Trinitrobenzene Sulfonic Acid. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(6):1643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061643
Chicago/Turabian StyleKonarska, Katarzyna, Jakub Cieszkowski, Zygmunt Warzecha, Piotr Ceranowicz, Anna Chmura, Beata Kuśnierz-Cabala, Krystyna Gałązka, Paweł Kowalczyk, Andrzej Miskiewicz, Thomas Jan Konturek, and et al. 2018. "Treatment with Obestatin—A Ghrelin Gene-Encoded Peptide—Reduces the Severity of Experimental Colitis Evoked by Trinitrobenzene Sulfonic Acid" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 6: 1643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061643
APA StyleKonarska, K., Cieszkowski, J., Warzecha, Z., Ceranowicz, P., Chmura, A., Kuśnierz-Cabala, B., Gałązka, K., Kowalczyk, P., Miskiewicz, A., Konturek, T. J., Pędziwiatr, M., & Dembiński, A. (2018). Treatment with Obestatin—A Ghrelin Gene-Encoded Peptide—Reduces the Severity of Experimental Colitis Evoked by Trinitrobenzene Sulfonic Acid. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(6), 1643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061643