Design, Synthesis, Cytotoxic Evaluation and Molecular Docking of New Fluoroquinazolinones as Potent Anticancer Agents with Dual EGFR Kinase and Tubulin Polymerization Inhibitory Effects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
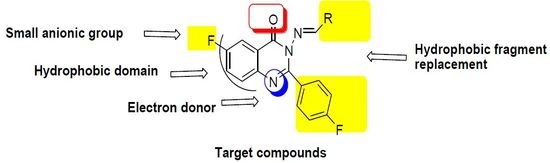
- Two fluoride substitutions. One of them attached directly at position 6 and the other one attached indirectly through 4-fluorophenyl at position 2 of quinazolinone.
- Different hydrophobic fragments with different electronic environment to enhance hydrophobic interactions, therefore obtaining better binding and better activity. This was done by joining the arylidene moiety at position 3 of quinazolinone. This moiety attached to different substituted aromatic rings. This configuration could target different areas of the EGFR protein kinase binding site to produce more selective molecules. Figure 1 shows the structural similarity of the reference anticancer quinazolines lapatinib, erlotinib, gefitinib, thymitaq and title compounds.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Cytotoxicity Screening
2.3. EGFR Assay
2.4. Tubulin Polymerization Inhibition Assay
2.5. Molecular Docking Study into the EGFR Binding Site
2.6. Molecular Docking Study into the Tubulin Binding Site
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.2. Synthesis of 6-Fluoro 2-(4-fluorophenyl)-benzo[d] [1,3] oxazine-4-one (3)
3.3. Synthesis of Isomers of 2-(4-Fluorobenzamido)-5-fluorobenzohydrazide (4) and 3-Ami.no-6-fluoro-2-(4-fluorophenyl)quinazolin-4(3H)-one (5)
3.3.1. 2-(4-Fluorobenzamido)-5-fluorobenzohydrazide (4)
3.3.2. Synthesis of 3-Amino-6-fluoro-2-(4-fluorophenyl)quinazolin-4(3H)-one (5)
3.4. Synthesis of 3-(Substituted benzylideneamino)-6-fluoro-2-(4-fluorophenyl)quinazolin-4(3H)-ones (6–8) and (10a–g)
3.4.1. 3-(3-Iminoindolin-2-one)-6-fluoro-2-(4-flurophenyl)quinazoline-4(3H)-one (6)
3.4.2. 3-((Furan-2-yl)methyleneamino)-6-fluoro-2-(4-fluorophenyl)quinazolin-4(3H)-one (7)
3.4.3. 3-(3-Phenylallylideneamino)-6-fluoro-2-(4-fluorophenyl)quinazolin-4(3H)-one (8)
3.4.4. 3-(Benzylideneamino)-6-fluoro-2-(4-fluorophenyl)quinazolin-4(3H)-one (10a)
3.4.5. 3-(4-Methylbenzylideneamino)-6-fluoro-2-(4-fluorophenyl)quinazoline-4(3H)-one (10b)
3.4.6. 3-(4-Methoxybenzylideneamino)-6-fluoro-2-(4-fluorophenyl)quinazolin-4(3H)-one (10c)
3.4.7. 3-(4-Fluorobenzylideneamino)-6-fluoro-2-(4-fluorophenyl)quinazolin-4(3H)-one (10d)
3.4.8. 3-(4-Nitrobenzylideneamino)-6-fluoro-2-(4-fluorophenyl)quinazolin-4(3H)-one (10e)
3.4.9. 3-(4-Chlorobenzylideneamino)-6-fluoro-2-(4-fluorophenyl)quinazolin-4(3H)-one (10f)
3.4.10. 3-(4-Hydroxybenzylideneamino)-6-fluoro-2-(4-fluorophenyl) quinazolin-4(3H)-one (10g)
3.5. In Vitro Cytotoxic Screening
3.6. EGFR Inhibition Assay
3.7. Tubulin Polymerization Inhibition Assay
3.8. Statistical Analysis
3.9. Molecular Docking
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zayed, M.F.; Ahmed, H.E.A.; Omar, A.M.; Abdelrahim, A.S.; El-Adl, K. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation studies of novel quinazolinone derivatives as anticonvulsant agents. Med. Chem. Res. 2013, 22, 5823–5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, J.D.; Cusack, D.; Sullivan, P.T.; Guiry, P.J. Synthesis of quinazolinones and quinazolines. ChemInform 2005, 61, 10153–10202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, S.R.; Malhotra, V.; Nath, R.; Shanker, K. Synthesis and Antihypertensive Activity of Novel Quinazolin-4(3H)-one Derivatives. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Agents Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zayed, M.F.; Hassan, M.H. Synthesis and biological evaluation studies of novel quinazolinone derivatives as antibacterial and anti-inflammatory agents. Saudi Pharm. J. 2014, 22, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sharief, M.A.; Ahmed, Z.M.; El-Sharief, M.S. Synthesis, characterization, and derivatization of some novel types of fluorinated mono- and bis-imidazolidineiminothiones with antitumor, antiviral, antibacterial, and antifungal activities. J. Fluor. Chem. 2011, 132, 596–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.S.; Ganguly, S.; Veerasamy, R.; Clercq, E. Synthesis, antiviral activity and cytotoxicity evaluation of Schiff bases of some 2-phenyl quinazoline-4(3)H-ones. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 5474–5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, E.S.; Awadallah, M.F.; Ibrahim, A.; Said, E.G.; Kamel, G.M. New quinazolinone–pyrimidine hybrids: Synthesis, anti-infl ammatory, and ulcerogenicity studies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 53, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, Z.; Akhtar, M.J.; Haider, M.R.; Khan, A.A.; Siddiqui, A.A.; Yar, M.S. Design and synthesis of quinazoline-3,4-(4H)-diamine endowed with thiazoline moiety as new class for DPP-4 and DPPH inhibitor. Bioorg. Chem. 2017, 71, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ram, V.J.; Farhanullah, B.K.; Srivastava, A.K. Synthesis and antihyperglycemic activity of suitably functionalized 3H-quinazolin-4-ones. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2003, 1, 2439–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M.; Mohamed, A.Y.; El-Bayouki, M.A.; Basyouni, W.M.; Abbas, S.Y. Synthesis of some new 4(3H)-quinazolinone-2-carboxaldehyde thiosemicarbazones and their metal complexes and a study on their anticonvulsant, analgesic, cytotoxic and antimicrobial activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 45, 3365–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Rashood, S.T.; Aboldahab, I.A.; Nagi, M.N.; Abouzeid, L.A.; Abdel-Aziz, A.A.; Abdel-Hamide, S.G.; Youssef, K.M.; Al-Obaid, A.M.; El-Subbagh, H.I. Synthesis, dihydrofolate reductase inhibition, antitumor testing, and molecular modeling study of some new 4(3H)-quinazolinone analogs. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2006, 14, 8608–86021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zayed, M.F.; Hassan, M.H. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation studies of novel quinazoline derivatives as cytotoxic agents. Drug Res. 2013, 63, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Obaid, A.M.; Abdel-Hamide, S.G.; El-Kashef, H.A.; Abdel-Aziz, A.A.M.; El-Azab, A.S.; Al-Khamees, H.A.; El-Subbagh, H.I. Substituted quinazolines, part 3. Synthesis, in vitro antitumor activity and molecular modeling study of certain 2-thieno-4(3H)-quinazolinone analogs. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 44, 2379–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zayed, M.F.; Ahmed, H.E.A.; Ihmaid, S.; Omar, A.M.; Abdelrahim, A.S. Synthesis and screening of some new fluorinated quinazolinone-sulphonamide hybrids as anticancer agents. J. Taibah Univ. Med. Sci. 2015, 10, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isanbor, C.; O’Hagan, D. Fluorine in medicinal chemistry: A review of anti-cancer agents. J. Fluor. Chem. 2006, 127, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layevaa, A.A.; Nosovaa, E.V.; Lipunovaa, G.N.; Trashakhovaa, T.V.; Charushinb, V.N. A new approach to fluorinated 4(3H)-quinazolinones. J. Fluor. Chem. 2007, 128, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.R.M.; Mohamed, G.A.; Al Haidari, R.A.; Zayed, M.F.; El-Kholy, A.A.; Elkhayat, E.S.; Ross, S.A. Fusarithioamide B, a new benzamide derivative from the endophytic fungus Fusarium chlamydosporium with potent cytotoxic and antimicrobial activities. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 786–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, H.E.A.; Ihmaid, S.K.; Omar, A.m.; Shehata, A.M.; Rateb, H.S.; Zayed, M.F.; Ahmed, S.; Elaasser, M.M. Design, synthesis, molecular docking of new lipophilic acetamide derivatives affording potential anticancer and antimicrobial agents. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 76, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihmaid, S.; Ahmed, H.E.A.; Zayed, M.F. The Design and Development of Potent Small Molecules as Anticancer Agents Targeting EGFR TK and Tubulin Polymerization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Congiu, C.; Cocco, M.T.; Lilliu, V.; Onnis, V. New potential anticancer agents based on the anthranilic acid scaffold: Synthesis and evaluation of biological activity. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 8245–8252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The protein data bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, G.M.; Goodsell, D.S.; Halliday, R.S.; Huey, R.; Hart, W.E.; Belew, R.K. Automated docking using a Lamarckian genetic algorithm and an empirical binding free energy function. J. Comput. Chem. 1998, 19, 1639–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chemical Computing Group. Molecular Operating Environment (MOE); Chemical Computing Group: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2013; Available online: http://www.chemcomp.com (accessed on 7 February 2013).
- Raffa, D.; Edler, M.C.; Daidone, G.; Daidone, G.; Maggio, B.; Merickech, M.; Plescia, S.; Schillaci, D.; Bai, R.; Hamel, E. Synthesis, cytotoxicity, and inhibitory effects on tubulin polymerization of a new 3-heterocyclo substituted 2-styrylquinazolinones. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 39, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayoumi, A.H.; Elgamal, K.; Elmorsy, A.; Ihmaid, S.; Ahmed, H.E.A. Triazolo[4,3-a]-quinoxaline Moieties as Potent Anticancer Agents with Dual EGFR Kinase and Tubulin Polymerization Inhibitory Effects. Molecules 2018, 23, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Compound | IC50 µM | 3rd Position Substitution | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MCF-7 | MDA-MBA-231 | ||
| 6 | 0.35 ± 0.01 | 1.38 ± 0.14 | 3-iminoindolin-2-one |
| 7 | 1.06 ± 0.03 | 0.94 ± 0.07 | (furan-2-yl)methylene amine |
| 8 | 36.57 ± 1.81 | 21.64 ± 1.4 | Phenylallylidene amine |
| 10a | 0.95 ± 0.01 | 2.48 ± 0.17 | Substituted benzylidene amine |
| 10b | 5.07 ± 0.33 | 3.09 ± 0.08 | |
| 10c | 10.43 ± 1.14 | 1.09 ± 0.01 | |
| 10d | 0.89 ± 0.02 | 0.38 ± 0.01 | |
| 10e | 2.61 ± 0.14 | 0.28 ± 0.02 | |
| 10f | 0.71 ± 0.01 | 3.76 ± 0.22 | |
| 10g | 1.32 ± 0.08 | 2.54 ± 0.23 | |
| Gefitinib | 0.9 ± 0.02 | 1.30 ± 0.04 | |
| Compound | Selectivity Indices | Cell Line | |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | ||
| 10c | 9.57 ± 0.11 | 0.10 ± 0.13 | MDA-MBA-231 selective |
| 10e | 9.32 ± 0.08 | 0.11 ± 0.17 | |
| 10d | 2.34 ± 0.05 | 0.43 ± 0.09 | |
| 8 | 1.69 ± 0.15 | 0.59 ± 0.02 | |
| 10b | 1.64 ± 0.21 | 0.61 ± 0.06 | |
| 7 | 1.13 ± 0.09 | 0.89 ± 0.18 | |
| Gefitinib | 0.75 ± 0.18 | 1.34 ± 0.19 | MCF-7 selective |
| 10g | 0.52 ± 0.07 | 1.92 ± 0.05 | |
| 10a | 0.39 ± 0.01 | 2.61 ± 0.09 | |
| 6 | 0.25 ± 0.06 | 3.94 ± 0.26 | |
| 10f | 9.57 ± 0.22 | 5.29 ± 0.31 | |
| Compound | IC50 (nM) | |
|---|---|---|
| MCF-7 | MDA-MBA-231 | |
| 6 | 75.2 ± 0.08 | - |
| 10e | - | 170.08 ± 0.02 |
| Gefitinib | 78.04 ± 0.11 | 299 ± 0.12 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zayed, M.F.; Ahmed, S.; Ihmaid, S.; Ahmed, H.E.A.; Rateb, H.S.; Ibrahim, S.R.M. Design, Synthesis, Cytotoxic Evaluation and Molecular Docking of New Fluoroquinazolinones as Potent Anticancer Agents with Dual EGFR Kinase and Tubulin Polymerization Inhibitory Effects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061731
Zayed MF, Ahmed S, Ihmaid S, Ahmed HEA, Rateb HS, Ibrahim SRM. Design, Synthesis, Cytotoxic Evaluation and Molecular Docking of New Fluoroquinazolinones as Potent Anticancer Agents with Dual EGFR Kinase and Tubulin Polymerization Inhibitory Effects. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(6):1731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061731
Chicago/Turabian StyleZayed, Mohamed F., Sahar Ahmed, Saleh Ihmaid, Hany E. A. Ahmed, Heba S. Rateb, and Sabrin R. M. Ibrahim. 2018. "Design, Synthesis, Cytotoxic Evaluation and Molecular Docking of New Fluoroquinazolinones as Potent Anticancer Agents with Dual EGFR Kinase and Tubulin Polymerization Inhibitory Effects" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 6: 1731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061731
APA StyleZayed, M. F., Ahmed, S., Ihmaid, S., Ahmed, H. E. A., Rateb, H. S., & Ibrahim, S. R. M. (2018). Design, Synthesis, Cytotoxic Evaluation and Molecular Docking of New Fluoroquinazolinones as Potent Anticancer Agents with Dual EGFR Kinase and Tubulin Polymerization Inhibitory Effects. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(6), 1731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061731