Comparison of the Anion Inhibition Profiles of the α-CA Isoforms (SpiCA1, SpiCA2 and SpiCA3) from the Scleractinian Coral Stylophora pistillata
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Enzyme Purification and Sequence Analysis
2.2. Kinetic Characterization
2.3. Enzyme Protonography
2.4. Inhibition with Anions
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemistry
4.2. Gene Identification, Cloning, Expression and Purification
4.3. SDS-PAGE
4.4. Western Blotting
4.5. Protonography
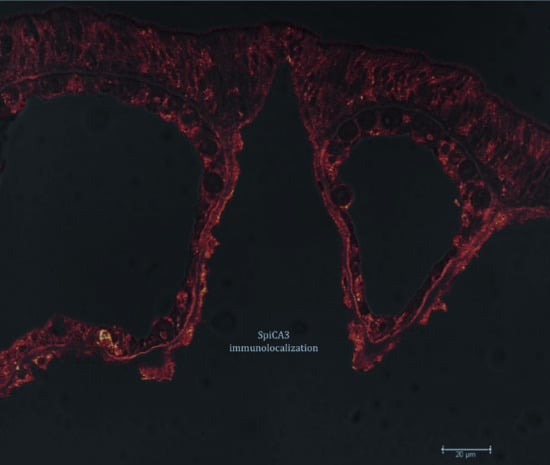
4.6. Immunolocalization with Anti-SpiCA3
4.7. Enzyme Kinetic and Inhibition
4.8. Primary Structure Analysis
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nishimori, I.; Onishi, S.; Takeuchi, H.; Supuran, C.T. The alpha and beta classes carbonic anhydrases from Helicobacter pylori as novel drug targets. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Morishita, S.; Nishimori, I.; Minakuchi, T.; Onishi, S.; Takeuchi, H.; Sugiura, T.; Vullo, D.; Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C.T. Cloning, polymorphism, and inhibition of beta-carbonic anhydrase of Helicobacter pylori. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 43, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomelino, C.L.; Supuran, C.T.; McKenna, R. Non-Classical Inhibition of Carbonic Anhydrase. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supuran, C.T. Structure and function of carbonic anhydrases. Biochem. J. 2016, 473, 2023–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supuran, C.T. How many carbonic anhydrase inhibition mechanisms exist? J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capasso, C.; Supuran, C.T. An Overview of the Selectivity and Efficiency of the Bacterial Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors. Curr. Med. Chem. 2015, 22, 2130–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Simone, G.; Monti, S.M.; Alterio, V.; Buonanno, M.; De Luca, V.; Rossi, M.; Carginale, V.; Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C.; Di Fiore, A. Crystal structure of the most catalytically effective carbonic anhydrase enzyme known, SazCA from the thermophilic bacterium Sulfurihydrogenibium azorense. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 2002–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capasso, C.; Supuran, C.T. An Overview of the Carbonic Anhydrases from Two Pathogens of the Oral Cavity: Streptococcus mutans and Porphyromonas gingivalis. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 2359–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Goff, C.; Ganot, P.; Zoccola, D.; Caminiti-Segonds, N.; Allemand, D.; Tambutte, S. Carbonic Anhydrases in Cnidarians: Novel Perspectives from the Octocorallian Corallium rubrum. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozensoy Guler, O.; Capasso, C.; Supuran, C.T. A magnificent enzyme superfamily: carbonic anhydrases, their purification and characterization. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capasso, C.; Supuran, C.T. Bacterial, fungal and protozoan carbonic anhydrases as drug targets. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2015, 19, 1689–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alafeefy, A.M.; Abdel-Aziz, H.A.; Vullo, D.; Al-Tamimi, A.M.; Al-Jaber, N.A.; Capasso, C.; Supuran, C.T. Inhibition of carbonic anhydrases from the extremophilic bacteria Sulfurihydrogenibium yellostonense (SspCA) and S. azorense (SazCA) with a new series of sulfonamides incorporating aroylhydrazone-, [1,2,4]triazolo[3,4-b][1,3,4]thiadiazinyl- or 2-(cyanophenylmethylene)-1,3,4-thiadiazol-3(2H)-yl moieties. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Supuran, C.T. Advances in structure-based drug discovery of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2017, 12, 61–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. An Overview of the Bacterial Carbonic Anhydrases. Metabolites 2017, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. Carbonic Anhydrase from Porphyromonas Gingivalis as a Drug Target. Pathogens 2017, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capasso, C.; Supuran, C.T. Inhibition of Bacterial Carbonic Anhydrases as a Novel Approach to Escape Drug Resistance. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 1237–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. The eta-class carbonic anhydrases as drug targets for antimalarial agents. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2015, 19, 551–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Roy, N.; Jackson, D.J.; Marie, B.; Ramos-Silva, P.; Marin, F. The evolution of metazoan α-carbonic anhydrases and their roles in calcium carbonate biomineralization. Front. Zool. 2014, 11, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mass, T.; Giuffre, A.J.; Sun, C.Y.; Stifler, C.A.; Frazier, M.J.; Neder, M.; Tamura, N.; Stan, C.V.; Marcus, M.A.; Gilbert, P. Amorphous calcium carbonate particles form coral skeletons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E7670–E7678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoccola, D.; Innocenti, A.; Bertucci, A.; Tambutte, E.; Supuran, C.T.; Tambutte, S. Coral Carbonic Anhydrases: Regulation by Ocean Acidification. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertucci, A.; Moya, A.; Tambutte, S.; Allemand, D.; Supuran, C.T.; Zoccola, D. Carbonic anhydrases in anthozoan corals-A review. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 1437–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voolstra, C.R.; Li, Y.; Liew, Y.J.; Baumgarten, S.; Zoccola, D.; Flot, J.-F.; Tambutte, S.; Allemand, D.; Aranda, M. Comparative analysis of the genomes of Stylophora pistillata and Acropora digitifera provides evidence for extensive differences between species of corals. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moya, A.; Tambutte, S.; Bertucci, A.; Tambutte, E.; Lotto, S.; Vullo, D.; Supuran, C.T.; Allemand, D.; Zoccola, D. Carbonic anhydrase in the scleractinian coral Stylophora pistillata: characterization, localization, and role in biomineralization. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 25475–25484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertucci, A.; Tambutte, S.; Supuran, C.T.; Allemand, D.; Zoccola, D. A new coral carbonic anhydrase in Stylophora pistillata. Mar. Biotechnol. 2011, 13, 992–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drake, J.L.; Mass, T.; Haramaty, L.; Zelzion, E.; Bhattacharya, D.; Falkowski, P.G. Proteomic analysis of skeletal organic matrix from the stony coral Stylophora pistillata. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3788–3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertucci, A.; Innocenti, A.; Scozzafava, A.; Tambutte, S.; Zoccola, D.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Inhibition studies with anions and sulfonamides of a new cytosolic enzyme from the scleractinian coral Stylophora pistillata. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertucci, A.; Innocenti, A.; Zoccola, D.; Scozzafava, A.; Allemand, D.; Tambutte, S.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: Inhibition studies of a coral secretory isoform with inorganic anions. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 650–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertucci, A.; Innocenti, A.; Zoccola, D.; Scozzafava, A.; Tambutte, S.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Inhibition studies of a coral secretory isoform by sulfonamides. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 5054–5058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrases-an overview. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 3467–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: An editorial. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2013, 23, 677–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase activators. Future Med. Chem. 2018, 10, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Fiore, A.; Capasso, C.; De Luca, V.; Monti, S.M.; Carginale, V.; Supuran, C.T.; Scozzafava, A.; Pedone, C.; Rossi, M.; De Simone, G. X-ray structure of the first ‘extremo-alpha-carbonic anhydrase‘, a dimeric enzyme from the thermophilic bacterium Sulfurihydrogenibium yellowstonense YO3AOP1. Acta. Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2013, 69, 1150–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrases: novel therapeutic applications for inhibitors and activators. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Simone, G.; Supuran, C.T. (In)organic anions as carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2012, 111, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Hainzl, T.; Grundstrom, C.; Forsman, C.; Samuelsson, G.; Sauer-Eriksson, A.E. Structural studies of beta-carbonic anhydrase from the green alga Coccomyxa: Inhibitor complexes with anions and acetazolamide. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalifah, R.G. The carbon dioxide hydration activity of carbonic anhydrase. I. Stop-flow kinetic studies on the native human isoenzymes B and C. J. Biol. Chem. 1971, 246, 2561–2573. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Innocenti, A.; Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C.T. Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Inhibition of cytosolic isoforms I, II, III, VII and XIII with less investigated inorganic anions. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 1855–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, V.; Del Prete, S.; Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. Protonography, a new technique for the analysis of carbonic anhydrase activity. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2015, 30, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Prete, S.; De Luca, V.; Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. Protonography, a technique applicable for the analysis of eta-carbonic anhydrase activity. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2015, 30, 920–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Prete, S.; De Luca, V.; Iandolo, E.; Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. Protonography, a powerful tool for analyzing the activity and the oligomeric state of the gamma-carbonic anhydrase identified in the genome of Porphyromonas gingivalis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 3747–3750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vullo, D.; De Luca, V.; Del Prete, S.; Carginale, V.; Scozzafava, A.; Capasso, C.; Supuran, C.T. Sulfonamide inhibition studies of the gamma-carbonic anhydrase from the Antarctic bacterium Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 3550–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganot, P.; Zoccola, D.; Tambutte, E.; Voolstra, C.R.; Aranda, M.; Allemand, D.; Tambutte, S. Structural Molecular Components of Septate Junctions in Cnidarians Point to the Origin of Epithelial Junctions in Eukaryotes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 44–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Prete, S.; Vullo, D.; De Luca, V.; Carginale, V.; di Fonzo, P.; Osman, S.M.; AlOthman, Z.; Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. Anion inhibition profiles of alpha-, beta- and gamma-carbonic anhydrases from the pathogenic bacterium Vibrio cholerae. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 3413–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Prete, S.; Vullo, D.; De Luca, V.; Carginale, V.; di Fonzo, P.; Osman, S.M.; AlOthman, Z.; Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. Anion inhibition profiles of the complete domain of the eta-carbonic anhydrase from Plasmodium falciparum. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 4410–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, V.; Vullo, D.; Del Prete, S.; Carginale, V.; Osman, S.M.; AlOthman, Z.; Supuran, C.T.; Capasso, C. Cloning, characterization and anion inhibition studies of a gamma-carbonic anhydrase from the Antarctic bacterium Colwellia psychrerythraea. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Isozyme | Activity Level | kcat (s−1) | Kcat/KM (M−1 s−1) | KI (Acetazolamide) (nM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hCAI | Moderate | 2.0 × 105 | 5.0 × 107 | 250 |
| hCAII | Very high | 1.4 × 106 | 1.5 × 108 | 12 |
| SpiCA1 | Moderate | 3.1 × 105 | 4.6 × 107 | 16 |
| SpiCA2 | High | 5.6 × 105 | 8.3 × 107 | 74 |
| SpiCA3 | Very high | 1.6 × 106 | 1.5 × 108 | 737 |
| Inhibitor | KI [mM] # | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hCA I a | hCA II a | SpiCA1 b | SpiCA2 b | SpiCA3 c | |
| F− | >300 | >300 | 0.62 | 0.92 | 0.48 |
| Cl− | 6 | 200 | 0.50 | 0.53 | 0.51 |
| Br− | 4 | 63 | 0.0097 | 0.96 | 0.23 |
| I− | 0.3 | 26 | 0.0090 | 33.0 | 0.56 |
| CNO− | 0.0007 | 0.03 | 0.59 | 0.69 | 2.41 |
| SCN− | 0.2 | 1.6 | 0.68 | 0.51 | 2.53 |
| CN− | 0.0005 | 0.02 | 0.58 | 0.86 | 0.050 |
| N3− | 0.0012 | 1.5 | 0.52 | 4.68 | 0.080 |
| HCO3− | 12 | 85 | 0.45 | 7.81 | 0.40 |
| CO32− | 15 | 73 | 0.010 | 0.24 | 5.66 |
| NO3− | 7 | 35 | 0.56 | 0.99 | 12.8 |
| NO2− | 8.4 | 63 | 0.77 | 3.15 | 0.45 |
| HS− | 0.0006 | 0.04 | 0.58 | 3.94 | 0.34 |
| HSO3− | 18 | 89 | 0.41 | 0.43 | 5.20 |
| SO42− | 63 | >200 | 0.91 | 0.33 | 0.61 |
| SnO32− | 0.57 | 0.83 | nt | nt | 2.96 |
| SeO42− | 118 | 112 | nt | nt | 5.14 |
| TeO42− | 0.66 | 0.92 | nt | nt | >100 |
| P2O74− | 25.8 | 48.5 | nt | nt | >100 |
| V2O74− | 0.54 | 0.57 | nt | nt | >100 |
| B4O72− | 0.64 | 0.95 | nt | nt | 0.84 |
| ReO4− | 0.11 | 0.75 | nt | nt | >100 |
| RuO4 | 0.10 | 0.69 | nt | nt | 0.76 |
| S2O82− | 0.11 | 0.084 | nt | nt | >100 |
| SeCN− | 0.085 | 0.086 | nt | nt | 0.15 |
| CS32− | 0.0087 | 0.0088 | nt | nt | 0.47 |
| Et2NCS2− | 0.00079 | 3.1 | nt | nt | 0.044 |
| Triflate | nt | nt | nt | nt | 0.29 |
| BF4− | >200 | >200 | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| ClO4− | >200 | >200 | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| FSO3− | nt | nt | nt | nt | 0.55 |
| NH(SO3)22− | nt | 0.76 | nt | nt | 0.48 |
| H2NSO2NH2 | 0.31 | 1.13 | 0.010 | 0.057 | 0.0007 |
| H2NSO3H | 0.021 | 0.39 | 0.81 | 0.085 | >100 |
| Ph-B(OH)2 | 58.6 | 23.1 | 0.68 | 0.081 | >100 |
| Ph-AsO3H2 | 31.7 | 49.2 | 0.78 | 0.067 | >100 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Del Prete, S.; Bua, S.; Zoccola, D.; Alasmary, F.A.S.; AlOthman, Z.; Alqahtani, L.S.; Techer, N.; Supuran, C.T.; Tambutté, S.; Capasso, C. Comparison of the Anion Inhibition Profiles of the α-CA Isoforms (SpiCA1, SpiCA2 and SpiCA3) from the Scleractinian Coral Stylophora pistillata. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2128. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072128
Del Prete S, Bua S, Zoccola D, Alasmary FAS, AlOthman Z, Alqahtani LS, Techer N, Supuran CT, Tambutté S, Capasso C. Comparison of the Anion Inhibition Profiles of the α-CA Isoforms (SpiCA1, SpiCA2 and SpiCA3) from the Scleractinian Coral Stylophora pistillata. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(7):2128. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072128
Chicago/Turabian StyleDel Prete, Sonia, Silvia Bua, Didier Zoccola, Fatmah A.S. Alasmary, Zeid AlOthman, Linah S. Alqahtani, Nathalie Techer, Claudiu T. Supuran, Sylvie Tambutté, and Clemente Capasso. 2018. "Comparison of the Anion Inhibition Profiles of the α-CA Isoforms (SpiCA1, SpiCA2 and SpiCA3) from the Scleractinian Coral Stylophora pistillata" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 7: 2128. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072128
APA StyleDel Prete, S., Bua, S., Zoccola, D., Alasmary, F. A. S., AlOthman, Z., Alqahtani, L. S., Techer, N., Supuran, C. T., Tambutté, S., & Capasso, C. (2018). Comparison of the Anion Inhibition Profiles of the α-CA Isoforms (SpiCA1, SpiCA2 and SpiCA3) from the Scleractinian Coral Stylophora pistillata. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(7), 2128. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072128