Involvement of Melatonin in the Regulation of the Circadian System in Crayfish
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Circadian System Generalities
3. Circadian System in the Crayfish
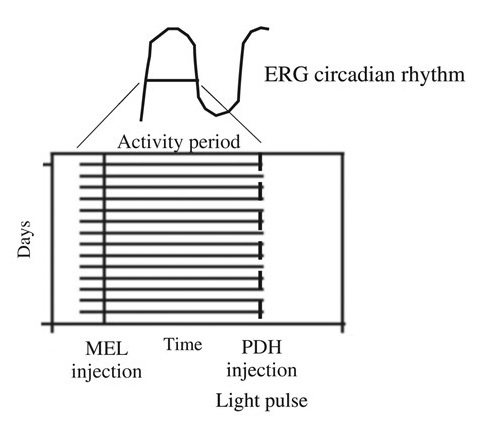
4. Synchronization in Crayfish: Involvement of Pigment Dispersing Hormone and Melatonin
5. Circadian System Coupling: Possible Role of MEL in Behaviors
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reiter, R.J.; Rosales-Corral, S.; Tan, D.X.; Jou, M.J.; Galano, A.; Xu, B. Melatonin as a mitochondria-targeted antioxidant: One of evolution’s best ideas. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 3863–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manchester, L.C.; Coto-Montes, A.; Boga, J.A.; Andersen, L.P.; Zhou, Z.; Galano, A.; Vriend, J.; Tan, D.X.; Reiter, R.J. Melatonin: An ancient molecule that makes oxygen metabolically tolerable. J. Pineal Res. 2015, 59, 403–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.X.; Hardeland, R.; Back, K.; Manchester, L.C.; Alatorre-Jimenez, M.A.; Reiter, R.J. On the significance of an alternate pathway of melatonin synthesis via 5-methoxytryptamine: Comparisons across species. J. Pineal Res. 2016, 61, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.X.; Manchester, L.C.; Esteban-Zubero, E.; Zhou, Z.; Reiter, R.J. Melatonin as a Potent and Inducible Endogenous Antioxidant: Synthesis and Metabolism. Molecules 2015, 20, 18886–18906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.; Dickson, E.J.; Jung, S.R.; Koh, D.S.; Hille, B. High membrane permeability for melatonin. J. Gen. Physiol. 2016, 147, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, E.J.; Lopes, R.H.; Lamy-Freund, M.T. Permeability of pure lipid bilayers to melatonin. J. Pineal Res. 1995, 19, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayo, J.C.; Sainz, R.M.; González-Menéndez, P.; Hevia, D.; Cernuda-Cernuda, R. Melatonin transport into mitochondria. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 3927–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, X.; Wang, C.; Yu, Z.; Peng, Y.; Wang, S.; Feng, S.; Zhang, S.; Tian, X.; Sun, C.; Liu, K.; et al. Human transporters, PEPT1/2, facilitate melatonin transportation into mitochondria of cancer cells: An implication of the therapeutic potential. J. Pineal Res. 2017, 62, e12390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.X.; Manchester, L.C.; Qin, L.; Reiter, R.J. Melatonin: A Mitochondrial Targeting Molecule Involving Mitochondrial Protection and Dynamics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pévet, P. The internal time-giver role of melatonin. A key for our health. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 170, 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrillo-Vico, A.; Calvo, J.R.; Abreu, P.; Lardone, P.J.; García-Mauriño, S.; Reiter, R.J.; Guerrero, J.M. Evidence of melatonin synthesis by human lymphocytes and its physiological significance: Possible role as intracrine, autocrine, and/or paracrine substance. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 537–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredrich, M.; Hampel, M.; Seidel, K.; Christ, E.; Korf, H.W. Impact of melatonin receptor-signaling on Zeitgeber time-dependent changes in cell proliferation and apoptosis in the adult murine hippocampus. Hippocampus 2017, 27, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeffer, M.; Korf, H.W.; Wicht, H. Synchronizing effects of melatonin on diurnal and circadian rhythms. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2018, 258, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabecka-Lonczynska, A.; Mytych, J.; Solek, P.; Kulpa, M.; Koziorowski, M. New insight on the role of melatonin receptors in reproductive processes of seasonal breeders on the example of mature male European bison (Bison bonasus, Linnaeus 1758). J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2017, 173, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavroudis, P.D.; DuBois, D.C.; Almon, R.R.; Jusko, W.J. Daily variation of gene expression in diverse rat tissues. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhadra, U.; Thakkar, N.; Das, P.; Pal Bhadra, M. Evolution of circadian rhythms: From bacteria to human. Sleep Med. 2017, 35, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honma, S. The mammalian circadian system: A hierarchical multi-oscillator structure for generating circadian rhythm. J. Physiol. Sci. 2018, 68, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilorz, V.; Helfrich-Förster, C.; Oster, H. The role of the circadian clock system in physiology. Pflugers Arch. 2018, 470, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heyde, I.; Kiehn, J.T.; Oster, H. Mutual influence of sleep and circadian clocks on physiology and cognition. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 119, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, R.J.; Chbeir, S. Dark matters: Effects of light at night on metabolism. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2018, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero-Vargas, N.N.; Salgado-Delgado, R.; del Carmen Basualdo, M.; García, J.; Guzmán-Ruiz, M.; Carrero, J.C.; Escobar, C.; Buijs, R.M. Reciprocal interaction between the suprachiasmatic nucleus and the immune system tunes down the inflammatory response to lipopolysaccharide. J. Neuroimmunol. 2014, 273, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadenas, C.; van de Sandt, L.; Edlund, K.; Lohr, M.; Hellwig, B.; Marchan, R.; Schmidt, M.; Rahnenführer, J.; Oster, H.; Hengstler, J.G. Loss of circadian clock gene expression is associated with tumor progression in breast cancer. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 3282–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Helm, B.; Visser, M.E.; Schwartz, W.; Kronfeld-Schor, N.; Gerkema, M.; Piersma, T.; Bloch, G. Two sides of a coin: Ecological and chronobiological perspectives of timing in the wild. Philos. Trans. R Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2017, 372, 20160246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramkisoensing, A.; Meijer, J.H. Synchronization of Biological Clock Neurons by Light and Peripheral Feedback Systems Promotes Circadian Rhythms and Health. Front. Neurol. 2015, 6, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aschoff, J. (Ed.) Freerunning and entrained circadian rhythms. In Handbook of Behavioral Neurology. Biological Rhythms; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1981; Volume 4, pp. 81–93. ISBN 0306405857. [Google Scholar]
- Mohawk, J.A.; Takahashi, J.S. Cell autonomy and synchrony of suprachiasmatic nucleus circadian oscillators. Trends Neurosci. 2011, 34, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pittendrigh, C.S. Circadian systems: General perspective. In Handbook of Behavioral Neurology. Biological Rhythms; Aschoff, J., Ed.; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1981; Volume 4, pp. 57–80. ISBN 0306405857. [Google Scholar]
- Panda, S.; Hogenesch, J.B. It’s all in the timing: Many clocks, many outputs. J. Biol. Rhythms 2004, 19, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buijs, F.N.; León-Mercado, L.; Guzmán-Ruiz, M.; Guerrero-Vargas, N.N.; Romo-Nava, F.; Buijs, R.M. The Circadian System: A Regulatory Feedback Network of Periphery and Brain. Physiology 2016, 31, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Acuña-Castroviejo, D.; Escames, G.; Venegas, C.; Díaz-Casado, M.E.; Lima-Cabello, E.; López, L.C.; Rosales-Corral, S.; Tan, D.X.; Reiter, R.J. Extrapineal melatonin: Sources, regulation, and potential functions. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 2997–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Clough, S.J.; Hutchinson, A.J.; Adamah-Biassi, E.B.; Popovska-Gorevski, M.; Dubocovich, M.L. MT1 and MT2 Melatonin Receptors: A Therapeutic Perspective. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2016, 56, 361–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, L.; Gao, L.; Su, Y.; Lin, N.; Pu, J. The nuclear melatonin receptor RORα is a novel endogenous defender against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. J. Pineal Res. 2016, 60, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez-Alonso, A.; Valdés-Tovar, M.; Solís-Chagoyán, H.; Benítez-King, G. Melatonin stimulates dendrite formation and complexity in the hilar zone of the rat hippocampus: Participation of the Ca++/Calmodulin complex. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 1907–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hablitz, L.M.; Molzof, H.E.; Abrahamsson, K.E.; Cooper, J.M.; Prosser, R.A.; Gamble, K.L. GIRK Channels Mediate the Nonphotic Effects of Exogenous Melatonin. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 14957–14965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hou, S.W.; Zheng, P.; Sun, F.Y. Melatonin inhibits outward delayed rectifier potassium currents in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neuron via intracellular indole-related domains. J. Pineal Res. 2004, 36, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galván-Arrieta, T.; Trueta, C.; Cercós, M.G.; Valdés-Tovar, M.; Alarcón, S.; Oikawa, J.; Zamudio-Meza, H.; Benítez-King, G. The role of melatonin in the neurodevelopmental etiology of schizophrenia: A study in human olfactory neuronal precursors. J. Pineal Res. 2017, 63, e12421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Shen, S.Q.; Corbo, J.C.; Kefalov, V.J. Circadian and light-driven regulation of rod dark adaptation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hiragaki, S.; Baba, K.; Coulson, E.; Kunst, S.; Spessert, R.; Tosini, G. Melatonin signaling modulates clock genes expression in the mouse retina. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson-Mora, J.; Prieto-Sagredo, J.; Loredo-Ranjel, R.; Fanjul-Moles, M.L. Putative pacemakers in the eyestalk and brain of the crayfish Procambarus clarkii show circadian oscillations in levels of mRNA for crustacean hyperglycemic hormone. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanjul-Moles, M.L.; Prieto-Sagredo, J. The circadian system of crayfish: A developmental approach. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2003, 60, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrera-Mera, B. Visual circadian rhythmicity in split brain crayfish: A plastic behavioral expression of symmetric circadian pacemakers. Brain Res. Bull. 1985, 15, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solís-Chagoyán, H.; Alvarado, R.; Figueroa, A.; Mendoza-Vargas, L.; Fuentes-Pardo, B. Pigment dispersing hormone modulates spontaneous electrical activity of the cerebroid ganglion and synchronizes electroretinogram circadian rhythm in crayfish Procambarus clarkii. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A 2012, 161, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza-Vargas, L.; Ortega, P.; Fuentes-Pardo, B.; Viccon-Pale, J.A. Circadian rhythm in locomotor activity in the burrower crayfish Procambarus acanthophorus (Villalobos 1948). Biol. Rhythm Res. 2016, 47, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Mahesh, G.; Houl, J.H.; Hardin, P.E. Circadian Activators Are Expressed Days before They Initiate Clock Function in Late Pacemaker Neurons from Drosophila. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 8662–8671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Homberg, U.; Reischig, T.; Stengl, M. Neural organization of the circadian system of the cockroach Leucophaea maderae. Chronobiol. Int. 2003, 20, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ushirogawa, H.; Abe, Y.; Tomioka, K. Circadian locomotor rhythms in the cricket, Gryllodes sigillatus. II. Interactions between bilaterally paired circadian pacemakers. Zool. Sci. 1997, 14, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albers, H.E.; Walton, J.C.; Gamble, K.L.; McNeill, J.K., 4th; Hummer, D.L. The dynamics of GABA signaling: Revelations from the circadian pacemaker in the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2017, 44, 35–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tso, C.F.; Simon, T.; Greenlaw, A.C.; Puri, T.; Mieda, M.; Herzog, E.D. Astrocytes Regulate Daily Rhythms in the Suprachiasmatic Nucleus and Behavior. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Landgraf, D.; Koch, C.E.; Oster, H. Embryonic development of circadian clocks in the mammalian suprachiasmatic nuclei. Front. Neuroanat 2014, 8, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escamilla-Chimal, E.G.; Velázquez-Amado, R.M.; Fiordelisio, T.; Fanjul-Moles, M.L. Putative pacemakers of crayfish show clock proteins interlocked with circadian oscillations. J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 213, 3723–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hernández, O.H.; Fuentes-Pardo, B. Cerebroid ganglion is the presumptive pacemaker of the circadian rhythm of electrical response to light in the crayfish. Biol. Rhythm Res. 2001, 32, 125–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera-Mera, B.; Block, G.D. Protocerebral circadian pacemakers in crayfish: Evidence for mutually coupled pacemakers. Brain Res. 1990, 522, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verde, M.A.; Barriga-Montoya, C.; Fuentes-Pardo, B. Pigment dispersing hormone generates a circadian response to light in the crayfish, Procambarus clarkii. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A 2007, 147, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Sosa, L.; Aréchiga, H. Range of modulation of light sensitivity by accessory pigments in the crayfish compound eye. Vis. Res. 1982, 22, 1515–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, J.A.; Fuentes-Pardo, B. Circadian rhythm in the amplitude of the electroretinogram in the isolated eyestalk of the crayfish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A 1977, 56, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aréchiga, H.; Rodríguez-Sosa, L. Circadian clock function in isolated eyestalk tissue of crayfish. Proc. Biol. Sci. 1998, 265, 1819–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanjul-Moles, M.L.; Miranda-Anaya, M.; Prieto, J. Circadian locomotor activity rhythm during ontogeny in crayfish Procambarus clarkii. Chronobiol. Int. 1996, 13, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De La O-Martínez, A.; Verde, M.A.; Valadez, R.L.; Viccon-Pale, J.; Fuentes-Pardo, B. About the existence of circadian activity in cave crayfish. Biol. Rhythm Res. 2004, 35, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Vargas, L.; Báez-Saldaña, A.; Alvarado, R.; Fuentes-Pardo, B.; Flores-Soto, E.; Solís-Chagoyán, H. Circadian rhythm in melatonin release as a mechanism to reinforce the temporal organization of the circadian system in crayfish. Invert. Neurosci. 2017, 17, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, T.L.; Larimer, J.L. Neural control of circadian rhythmicity in the crayfish. I. The locomotor activity rhythm. J. Comp. Physiol. 1975, 97, 59–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandeman, D.; Sandeman, R.; Derby, C.; Schmidt, M. Morphology of the Brain of Crayfish, Crabs, and Spiny Lobsters: A Common Nomenclature for Homologous Structures. Biol. Bull. 1992, 183, 304–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fanjul-Moles, M.L.; Durán-Lizarraga, M.E.; Gonsebatt, M.E.; Prieto-Sagredo, J. The effect of photoperiod and light irradiance on the antioxidant circadian system of two species of crayfish from different latitudes: Procambarus clarkii and P. digueti. Photochem. Photobiol. 2003, 77, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Sáenz, E.; Fuentes-Pardo, B.; Hernández-Falcón, J. Photoentrainment of the circadian rhythm in the electroretinogram of the crayfish and its dependence of the sinus gland. J. Exp. Zool. 1992, 264, 144–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfrin, C.; Tom, M.; de Moro, G.; Gerdol, M.; Giulianini, P.G.; Pallavicini, A. The eyestalk transcriptome of red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii. Gene 2015, 557, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulau, P.; Meisen, I.; Schmitz, T.; Keller, R.; Peter-Katalinić, J. Identification of neuropeptides from the sinus gland of the crayfish Orconectes limosus using nanoscale on-line liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2004, 3, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, U.; Aréchiga, H. Regulation of crustacean neurosecretory cell activity. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 1998, 18, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Falcón, J.; Moreno-Sáenz, E.; Farías, J.M.; Fuentes-Pardo, B. Role of the sinus gland in crayfish circadian rhythmicity—I. Pseudopupil circadian rhythm. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A 1987, 87, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solís-Chagoyán, H.; Figueroa, A.; Mendoza-Vargas, L.; Fuentes Pardo, B.; Jiménez-Rubio, G. Simultaneous effect of melatonin on supraoesophageal ganglion spontaneous electrical activity and photoreceptor electroretinogram amplitude in crayfish. Crustaceana 2012, 85, 1241–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solís-Chagoyán, H.; Mendoza-Vargas, L.; Fuentes-Pardo, B. Melatonin modulates the ERG circadian rhythm in crayfish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A 2008, 149, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, J.M.; Genco, M.C.; Marlow, E.D.; Benton, J.L.; Beltz, B.S.; Sandeman, D.C. Brain photoreceptor pathways contributing to circadian rhythmicity in crayfish. Chronobiol. Int. 2009, 26, 1136–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Sosa, L.; Calderón-Rosete, G.; Flores, G. Circadian and ultradian rhythms in the crayfish caudal photoreceptor. Synapse 2008, 62, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, J.D.; Baik, L.S.; Holmes, T.C.; Montell, C. A rhodopsin in the brain functions in circadian photoentrainment in Drosophila. Nature 2017, 545, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fuentes-Pardo, B.; Ramos-Carvajal, J. The phase response curve of electroretinographic circadian rhythm of crayfish. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A 1983, 74, 711–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Sáenz, E.; Hernández-Falcón, J.; Fuentes-Pardo, B. Role of the sinus gland in crayfish circadian rhythmicity—II. ERG circadian rhythm. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A 1987, 87, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balzer, I.; Espinola, I.R.; Fuentes-Pardo, B. Daily variations of immunoreactive melatonin in the visual system of crayfish. Biol. Cell 1997, 89, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barriga-Montoya, C.; Gómez-Lagunas, F.; Fuentes-Pardo, B. Effect of pigment dispersing hormone on the electrical activity of crayfish visual photoreceptors during the 24-h cycle. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A 2010, 157, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza-Vargas, L.; Solís-Chagoyán, H.; Benítez-King, G.; Fuentes-Pardo, B. MT2-like melatonin receptor modulates amplitude receptor potential in visual cells of crayfish during a 24-hour cycle. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A 2009, 154, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar Jha, P.; Challet, E.; Kalsbeek, A. Circadian rhythms in glucose and lipid metabolism in nocturnal and diurnal mammals. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015, 418, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kallen, J.L.; Rigiani, N.; Trompenaars, H.J.A.J. Aspects of entrainment of CHH cell activity and hemolymph glucose levels in crayfish. Biol. Bull. 1988, 175, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herberholz, J.; Swierzbinski, M.E.; Birke, J.M. Effects of Different Social and Environmental Conditions on Established Dominance Relationships in Crayfish. Biol. Bull. 2016, 230, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergman, D.A.; Moore, P.A. The role of chemical signals in the social behavior of crayfish. Chem. Senses 2005, 30, i305–i306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momohara, Y.; Aonuma, H.; Nagayama, T. Tyraminergic modulation of agonistic outcomes in crayfish. J. Comp. Physiol. A 2018, 204, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momohara, Y.; Kanai, A.; Nagayama, T. Aminergic control of social status in crayfish agonistic encounters. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomaa, A.M.; Galal, H.M.; Abou-Elgait, A.T. Neuroprotective effects of melatonin administration against chronic immobilization stress in rats. Int. J. Physiol. Pathophysiol. Pharmacol. 2017, 9, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tilden, A.R.; Brauch, R.; Ball, R.; Janze, A.M.; Ghaffari, A.H.; Sweeney, C.T.; Yurek, J.C.; Cooper, R.L. Modulatory effects of melatonin on behavior, hemolymph metabolites, and neurotransmitter release in crayfish. Brain Res. 2003, 992, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdés-Tovar, M.; Estrada-Reyes, R.; Solís-Chagoyán, H.; Argueta, J.; Dorantes-Barrón, A.M.; Quero-Chávez, D.; Cruz-Garduño, R.; Cercós, M.G.; Trueta, C.; Oikawa-Sala, J.; et al. Circadian modulation of neuroplasticity by melatonin: A target in the treatment of depression. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mendoza-Vargas, L.; Guarneros-Bañuelos, E.; Báez-Saldaña, A.; Galicia-Mendoza, F.; Flores-Soto, E.; Fuentes-Pardo, B.; Alvarado, R.; Valdés-Tovar, M.; Sommer, B.; Benítez-King, G.; et al. Involvement of Melatonin in the Regulation of the Circadian System in Crayfish. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072147
Mendoza-Vargas L, Guarneros-Bañuelos E, Báez-Saldaña A, Galicia-Mendoza F, Flores-Soto E, Fuentes-Pardo B, Alvarado R, Valdés-Tovar M, Sommer B, Benítez-King G, et al. Involvement of Melatonin in the Regulation of the Circadian System in Crayfish. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(7):2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072147
Chicago/Turabian StyleMendoza-Vargas, Leonor, Elizabeth Guarneros-Bañuelos, Armida Báez-Saldaña, Fabiola Galicia-Mendoza, Edgar Flores-Soto, Beatriz Fuentes-Pardo, Ramón Alvarado, Marcela Valdés-Tovar, Bettina Sommer, Gloria Benítez-King, and et al. 2018. "Involvement of Melatonin in the Regulation of the Circadian System in Crayfish" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 7: 2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072147
APA StyleMendoza-Vargas, L., Guarneros-Bañuelos, E., Báez-Saldaña, A., Galicia-Mendoza, F., Flores-Soto, E., Fuentes-Pardo, B., Alvarado, R., Valdés-Tovar, M., Sommer, B., Benítez-King, G., & Solís-Chagoyán, H. (2018). Involvement of Melatonin in the Regulation of the Circadian System in Crayfish. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(7), 2147. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072147