Heterogeneity of γH2AX Foci Increases in Ex Vivo Biopsies Relative to In Vivo Tumors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Impact of Extrinsic Influences on Cellular Geometry
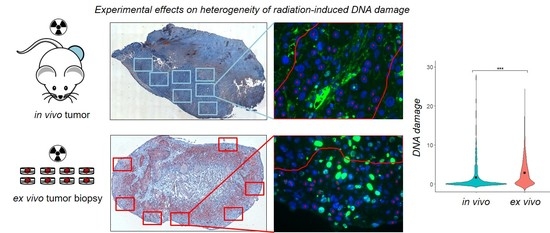
2.2. Heterogeneity of γH2AX Foci in Two Experimental Settings
2.2.1. In Vivo Cohort
2.2.2. Ex Vivo Cohort
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Tumor Handling and Data Acquisition
4.2. Data Processing
4.3. Statistical Analysis
4.3.1. Analysis on Cellular Geometry and Foci Number
4.3.2. Heterogeneity of γH2AX Foci
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| γH2AX | Gamma H2AX |
| hHNSCC | Human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma |
| LMEM | Linear mixed effects model |
| ROI | Region of interest |
| REML | Restricted maximum likelihood estimation |
| ML | Maximum likelihood estimation |
| BrdU | Bromodeoxyuridine |
| cfoci | Corrected foci |
| nfoci | Normalized foci |
References
- Bonassi, S.; Ugolini, D.; Kirsch-Volders, M.; Strömberg, U.; Vermeulen, R.; Tucker, J.D. Human population studies with cytogenetic biomarkers: Review of the literature and future prospectives. Environ. Mol. Mutagen. 2005, 45, 258–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willitzki, A.; Lorenz, S.; Hiemann, R.; Guttek, K.; Goihl, A.; Hartig, R.; Conrad, K.; Feist, E.; Sack, U.; Schierack, P.; et al. Fully automated analysis of chemically induced γH2AX foci in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells by indirect immunofluorescence. Cytom. Part A 2013, 83, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Van Oorschot, B.; Uitterhoeve, L.; Oomen, I.; Ten Cate, R.; Medema, J.P.; Vrieling, H.; Stalpers, L.J.A.; Moerland, P.D.; Franken, N.A.P. Prostate cancer patients with late radiation toxicity exhibit reduced expression of genes involved in DNA double-strand break repair and homologous recombination. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 1485–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, M.; Krause, M.; Overgaard, J.; Debus, J.; Bentzen, S.M.; Daartz, J.; Richter, C.; Zips, D.; Bortfeld, T. Radiation oncology in the era of precision medicine. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 234–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rassamegevanon, T.; Löck, S.; Range, U.; Krause, M.; Baumann, M.; von Neubeck, C. Tumor heterogeneity determined with a γH2AX foci assay: A study in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (hHNSCC) models. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 124, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willers, H.; Gheorghiu, L.; Liu, Q.; Efstathiou, J.A.; Wirth, L.J.; Krause, M.; von Neubeck, C. DNA Damage Response Assessments in Human Tumor Samples Provide Functional Biomarkers of Radiosensitivity. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2015, 25, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Riesterer, O.; Milas, L.; Ang, K.K. Use of molecular biomarkers for predicting the response to radiotherapy with or without chemotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 4075–4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddig, A.; Rübe, C.E.; Rödiger, S.; Schierack, P.; Reinhold, D.; Roggenbuck, D. DNA damage assessment and potential applications in laboratory diagnostics and precision medicine. J. Lab. Precis. Med. 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caudell, J.J.; Torres-Roca, J.F.; Gillies, R.J.; Enderling, H.; Kim, S.; Rishi, A.; Moros, E.G.; Harrison, L.B. The future of personalised radiotherapy for head and neck cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, e266–e273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, J.G.; Berglund, A.; Schell, M.J.; Mihaylov, I.; Fulp, W.J.; Yue, B.; Welsh, E.; Caudell, J.J.; Ahmed, K.; Strom, T.S.; et al. A genome-based model for adjusting radiotherapy dose (GARD): A retrospective, cohort-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinner, A.; Wu, W.; Staudt, C.; Iliakis, G. Gamma-H2AX in recognition and signaling of DNA double-strand breaks in the context of chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 5678–5694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; MacPhail, S.H.; Banáth, J.P.; Klokov, D.; Olive, P.L. Endogenous expression of phosphorylated histone H2AX in tumors in relation to DNA double-strand breaks and genomic instability. DNA Repair 2006, 5, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzayans, R.; Andrais, B.; Scott, A.; Wang, Y.; Weiss, R.; Murray, D. Spontaneous γH2AX Foci in Human Solid Tumor-Derived Cell Lines in Relation to p21WAF1 and WIP1 Expression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 11609–11628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koch, U.; Höhne, K.; Von Neubeck, C.; Thames, H.D.; Yaromina, A.; Dahm-Daphi, J.; Baumann, M.; Krause, M. Residual γh2AX foci predict local tumour control after radiotherapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2013, 108, 434–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menegakis, A.; Eicheler, W.; Yaromina, A.; Thames, H.D.; Krause, M.; Baumann, M. Residual DNA double strand breaks in perfused but not in unperfused areas determine different radiosensitivity of tumours. Radiother. Oncol. 2011, 100, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menegakis, A.; Von Neubeck, C.; Yaromina, A.; Thames, H.; Hering, S.; Hennenlotter, J.; Scharpf, M.; Noell, S.; Krause, M.; Zips, D.; et al. γh2AX assay in ex vivo irradiated tumour specimens: A novel method to determine tumour radiation sensitivity in patient-derived material. Radiother. Oncol. 2015, 116, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De-Colle, C.; Yaromina, A.; Hennenlotter, J.; Thames, H.; Mueller, A.-C.; Neumann, T.; Stenzl, A.; Scharpf, M.; Fend, F.; Ricardi, U.; et al. Ex vivo γH2AX radiation sensitivity assay in prostate cancer: Inter-patient and intra-patient heterogeneity. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 124, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menegakis, A.; De Colle, C.; Yaromina, A.; Hennenlotter, J.; Stenzl, A.; Scharpf, M.; Fend, F.; Noell, S.; Tatagiba, M.; Brucker, S.; et al. Residual γh2AX foci after ex vivo irradiation of patient samples with known tumour-type specific differences in radio-responsiveness. Radiother. Oncol. 2015, 116, 480–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marusyk, A.; Almendro, V.; Polyak, K. Intra-tumour heterogeneity: A looking glass for cancer? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meacham, C.E.; Morrison, S.J. Tumour heterogeneity and cancer cell plasticity. Nature 2013, 501, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cassidy, J.W.; Caldas, C.; Bruna, A. Maintaining tumor heterogeneity in patient-derived tumor xenografts. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 2963–2968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einbeck, J.; Ainsbury, E.; Barnard, S.; Oliveira, M.; Manning, G.; Puig, P.; Badie, C. On the Use of Random Effect Models for Radiation Biodosimetry. In Extended Abstracts Fall 2015. Trends in Mathematics; Ainsbury, E.A., Calle, L.M., Cardis, E., Einbeck, J., Gómez, G., Puig, P., Eds.; Birkhäuser: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 7, pp. 89–94. ISBN 978-3-319-55638-3. [Google Scholar]
- Oberg, A.L.; Mahoney, D.W. Linear Mixed Effects Models. In Methods in Molecular Biology: Topics in Biostatistics; Ambrosius, W.T., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2007; Volume 404, pp. 213–234. ISBN 0-387-27197-X. [Google Scholar]
- Duricki, D.A.; Soleman, S.; Moon, L.D.F. Analysis of longitudinal data from animals with missing values using SPSS. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 1112–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rothkamm, K.; Barnard, S.; Ainsbury, E.A.; Al-hafidh, J.; Barquinero, J.F.; Lindholm, C.; Moquet, J.; Perälä, M.; Roch-Lefèvre, S.; Scherthan, H.; et al. Manual versus automated γ-H2AX foci analysis across five European laboratories: Can this assay be used for rapid biodosimetry in a large scale radiation accident? Mutat. Res. 2013, 756, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redon, C.E.; Nakamura, A.J.; Gouliaeva, K.; Rahman, A.; Blakely, W.F.; Bonner, W.M. The use of gamma-H2AX as a biodosimeter for total-body radiation exposure in non-human primates. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; He, L.; Fan, D.; Ding, D.; Wang, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Chen, H. Establishment of a γ-H2AX foci-based assay to determine biological dose of radon to red bone marrow in rats. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goutham, H.V.; Mumbrekar, K.D.; Vadhiraja, B.M.; Fernandes, D.J.; Sharan, K.; Kanive Parashiva, G.; Kapaettu, S.; Bola Sadashiva, S.R. DNA double-strand break analysis by γ-H2AX foci: A useful method for determining the overreactors to radiation-induced acute reactions among head-and-neck cancer patients. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 84, e607–e612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gengenbacher, N.; Singhal, M.; Augustin, H.G. Preclinical mouse solid tumour models: Status quo, challenges and perspectives. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 751–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.Y.C.; Lin, D.; Gout, P.W.; Collins, C.C.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y. Lessons from patient-derived xenografts for better in vitro modeling of human cancer. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 79, 222–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, M.; Witkin, K.L.; Cohen-Fix, O. Sizing up the nucleus: Nuclear shape, size and nuclear-envelope assembly. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 1477–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgescu, W.; Osseiran, A.; Rojec, M.; Liu, Y.; Bombrun, M.; Tang, J.; Costes, S.V. Characterizing the DNA damage response by cell tracking algorithms and cell features classification using high-content time-lapse analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeshima, K.; Iino, H.; Hihara, S.; Imamoto, N. Nuclear size, nuclear pore number and cell cycle. Nucleus 2011, 2, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murga, M.; Jaco, I.; Fan, Y.; Soria, R.; Martinez-Pastor, B.; Cuadrado, M.; Yang, S.-M.; Blasco, M.A.; Skoultchi, A.I.; Fernandez-Capetillo, O. Global chromatin compaction limits the strength of the DNA damage response. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 178, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Löbrich, M.; Shibata, A.; Beucher, A.; Fisher, A.; Ensminger, M.; Goodarzi, A.A.; Barton, O.; Jeggo, P.A. γH2AX foci analysis for monitoring DNA double-strand break repair: Strengths, limitations and optimization. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cowell, I.G.; Sunter, N.J.; Singh, P.B.; Austin, C.A.; Durkacz, B.W.; Tilby, M.J. γH2AX Foci Form Preferentially in Euchromatin after Ionising-Radiation. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Gao, Y.; Yin, L.; Li, Q.; Li, J.; Chen, H. Induction and inhibition of the pan-nuclear gamma-H2AX response in resting human peripheral blood lymphocytes after X-ray irradiation. Cell Death Discov. 2016, 2, 16011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Solier, S.; Pommier, Y. The apoptotic ring: A novel entity with phosphorylated histones H2AX and H2B, and activated DNA damage response kinases. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 1853–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Solier, S.; Pommier, Y. The nuclear γ-H2AX apoptotic ring: Implications for cancers and autoimmune diseases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 2289–2297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edens, L.J.; White, K.H.; Jevtic, P.; Li, X.; Levy, D.L. Nuclear size regulation: From single cells to development and disease. Trends Cell Biol. 2013, 23, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jevtić, P.; Levy, D.L. Mechanisms of Nuclear Size Regulation in Model Systems and Cancer. In Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 773, pp. 537–569. ISBN 978-1-4899-8031-1. [Google Scholar]
- Jevtić, P.; Edens, L.J.; Vuković, L.D.; Levy, D.L. Sizing and shaping the nucleus: Mechanisms and significance. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2014, 28, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costes, S.V.; Boissière, A.; Ravani, S.; Romano, R.; Parvin, B.; Barcellos-Hoff, M.H. Imaging Features that Discriminate between Foci Induced by High- and Low-LET Radiation in Human Fibroblasts. Radiat. Res. 2006, 165, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reindl, J.; Girst, S.; Walsh, D.W.M.; Greubel, C.; Schwarz, B.; Siebenwirth, C.; Drexler, G.A.; Friedl, A.A.; Dollinger, G. Chromatin organization revealed by nanostructure of irradiation induced γH2AX, 53BP1 and Rad51 foci. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eryilmaz, M.; Schmitt, E.; Krufczik, M.; Theda, F.; Lee, J.-H.; Cremer, C.; Bestvater, F.; Schaufler, W.; Hausmann, M.; Hildenbrand, G. Localization Microscopy Analyses of MRE11 Clusters in 3D-Conserved Cell Nuclei of Different Cell Lines. Cancers 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagiwara, Y.; Niimi, A.; Isono, M.; Yamauchi, M.; Yasuhara, T.; Limsirichaikul, S.; Oike, T.; Sato, H.; Held, K.D.; Nakano, T.; et al. 3D-structured illumination microscopy reveals clustered DNA double-strand break formation in widespread γH2AX foci after high LET heavy-ion particle radiation. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 109370–109381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Redon, C.E.; Dickey, J.S.; Bonner, W.M.; Sedelnikova, O.A. γ-H2AX as a biomarker of DNA damage induced by ionizing radiation in human peripheral blood lymphocytes and artificial skin. Adv. Sp. Res. 2009, 43, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mah, L.-J.; El-Osta, A.; Karagiannis, T.C. γH2AX: A sensitive molecular marker of DNA damage and repair. Leukemia 2010, 24, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majumder, B.; Baraneedharan, U.; Thiyagarajan, S.; Radhakrishnan, P.; Narasimhan, H.; Dhandapani, M.; Brijwani, N.; Pinto, D.D.; Prasath, A.; Shanthappa, B.U.; et al. Predicting clinical response to anticancer drugs using an ex vivo platform that captures tumour heterogeneity. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coleman, C.N.; Higgins, G.S.; Brown, J.M.; Baumann, M.; Kirsch, D.G.; Willers, H.; Prasanna, P.G.S.; Dewhirst, M.W.; Bernhard, E.J.; Ahmed, M.M. Improving the Predictive Value of Preclinical Studies in Support of Radiotherapy Clinical Trials. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 3138–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shamir, E.R.; Ewald, A.J. Three-dimensional organotypic culture: Experimental models of mammalian biology and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 647–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidalgo, M.; Amant, F.; Biankin, A.V.; Budinská, E.; Byrne, A.T.; Caldas, C.; Clarke, R.B.; de Jong, S.; Jonkers, J.; Mælandsmo, G.M.; et al. Patient-derived Xenograft models: An emerging platform for translational cancer research. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 998–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rassamegevanon, T.; Löck, S.; Baumann, M.; Krause, M.; Von Neubeck, C. Heterogeneity of γH2AX Foci Increases in Ex Vivo Biopsies Relative to In Vivo Tumors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2616. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092616
Rassamegevanon T, Löck S, Baumann M, Krause M, Von Neubeck C. Heterogeneity of γH2AX Foci Increases in Ex Vivo Biopsies Relative to In Vivo Tumors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(9):2616. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092616
Chicago/Turabian StyleRassamegevanon, Treewut, Steffen Löck, Michael Baumann, Mechthild Krause, and Cläre Von Neubeck. 2018. "Heterogeneity of γH2AX Foci Increases in Ex Vivo Biopsies Relative to In Vivo Tumors" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 9: 2616. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092616
APA StyleRassamegevanon, T., Löck, S., Baumann, M., Krause, M., & Von Neubeck, C. (2018). Heterogeneity of γH2AX Foci Increases in Ex Vivo Biopsies Relative to In Vivo Tumors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(9), 2616. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092616