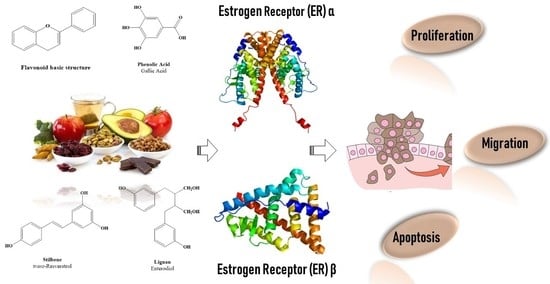
Beyond the Antioxidant Activity of Dietary Polyphenols in Cancer: the Modulation of Estrogen Receptors (ERs) Signaling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Dietary Polyphenols Structure and Source
2.1. Dietary Polyphenols’ Bioavailability and Metabolites
2.2. Polyphenols and Cancer
2.3. Polyphenols as Ligand of Estrogen Receptors
3. Estrogen Receptors: Structure and Molecular Mechanisms of Action
4. ERs-Based Polyphenol Effects on Cancer Hallmarks
4.1. Cancer Cell Proliferation
4.2. Cancer Cell Escape from Apoptosis
4.3. Cancer Migration and Metastasis
5. Conclusions and Perspective
Author Contributions
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kondratyuk, T.P.; Pezzuto, J.M. Natural product polyphenols of relevance to human health. Pharm. Biol. 2004, 42, 46–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, L. Polyphenols: Chemistry, dietary sources, metabolism, and nutritional significance. Nutr. Rev. 1998, 56, 317–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalbert, A.; Manach, C.; Morand, C.; Remesy, C.; Jimenez, L. Dietary polyphenols and the prevention of diseases. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2005, 45, 287–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virgili, F.; Marino, M. Regulation of cellular signals from nutritional molecules: A specific role for phytochemicals, beyond antioxidant activity. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 45, 1205–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vauzour, D.; Rodriguez-Mateos, A.; Corona, G.; Oruna-Concha, M.J.; Spencer, J.P. Polyphenols and human health: Prevention of disease and mechanisms of action. Nutrients 2010, 2, 1106–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zheng, J.; Li, Y.; Xu, D.P.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.M.; Li, H.B. Natural polyphenols for prevention and treatment of cancer. Nutrients 2016, 8, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paterni, I.; Granchi, C.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A.; Minutolo, F. Estrogen receptors alpha (eralpha) and beta (erbeta): Subtype-selective ligands and clinical potential. Steroids 2014, 90, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rietjens, I.M.; Sotoca, A.M.; Vervoort, J.; Louisse, J. Mechanisms underlying the dualistic mode of action of major soy isoflavones in relation to cell proliferation and cancer risks. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 100–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galluzzo, P.; Marino, M. Nutritional flavonoids impact on nuclear and extranuclear estrogen receptor activities. Genes Nutr. 2006, 1, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Michel, T.; Halabalaki, M.; Skaltsounis, A.L. New concepts, experimental approaches, and dereplication strategies for the discovery of novel phytoestrogens from natural sources. Planta Med. 2013, 79, 514–532. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, K.M. The shikimate pathway: Early steps in the biosynthesis of aromatic compounds. Plant Cell 1995, 7, 907–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, K.B.; Rizvi, S.I. Plant polyphenols as dietary antioxidants in human health and disease. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2009, 2, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecomte, S.; Demay, F.; Ferriere, F.; Pakdel, F. Phytochemicals targeting estrogen receptors: Beneficial rather than adverse effects? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manach, C.; Scalbert, A.; Morand, C.; Remesy, C.; Jimenez, L. Polyphenols: Food sources and bioavailability. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 79, 727–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Archivio, M.; Filesi, C.; Vari, R.; Scazzocchio, B.; Masella, R. Bioavailability of the polyphenols: Status and controversies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 1321–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DuPont, M.S.; Mondin, Z.; Williamson, G.; Price, K.R. Effect of variety, processing, and storage on the flavonoid glycoside content and composition of lettuce and endive. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 3957–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Sluis, A.A.; Dekker, M.; de Jager, A.; Jongen, W.M. Activity and concentration of polyphenolic antioxidants in apple: Effect of cultivar, harvest year, and storage conditions. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 3606–3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Archivio, M.; Filesi, C.; Di Benedetto, R.; Gargiulo, R.; Giovannini, C.; Masella, R. Polyphenols, dietary sources and bioavailability. Ann. Ist. Super. Sanita 2007, 43, 348–361. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, V.S. Bioavailability of nutrients: A practical approach to in vitro demonstration of the availability of nutrients in multivitamin-mineral combination products. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 1349S–1350S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duthie, G.G.; Pedersen, M.W.; Gardner, P.T.; Morrice, P.C.; Jenkinson, A.M.; McPhail, D.B.; Steele, G.M. The effect of whisky and wine consumption on total phenol content and antioxidant capacity of plasma from healthy volunteers. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 52, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Young, J.F.; Nielsen, S.E.; Haraldsdottir, J.; Daneshvar, B.; Lauridsen, S.T.; Knuthsen, P.; Crozier, A.; Sandstrom, B.; Dragsted, L.O. Effect of fruit juice intake on urinary quercetin excretion and biomarkers of antioxidative status. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1999, 69, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fito, M.; Guxens, M.; Corella, D.; Saez, G.; Estruch, R.; de la Torre, R.; Frances, F.; Cabezas, C.; Lopez-Sabater Mdel, C.; Marrugat, J.; et al. Effect of a traditional mediterranean diet on lipoprotein oxidation: A randomized controlled trial. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrugat, J.; Covas, M.I.; Fito, M.; Schroder, H.; Miro-Casas, E.; Gimeno, E.; Lopez-Sabater, M.C.; de la Torre, R.; Farre, M.; Investigators, S. Effects of differing phenolic content in dietary olive oils on lipids and ldl oxidation—A randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 43, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van het Hof, K.H.; Wiseman, S.A.; Yang, C.S.; Tijburg, L.B. Plasma and lipoprotein levels of tea catechins following repeated tea consumption. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1999, 220, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, A.A.; Edwards, C.A.; Lean, M.E.; Crozier, A. Absorption and excretion of conjugated flavonols, including quercetin-4’-o-beta-glucoside and isorhamnetin-4’-o-beta-glucoside by human volunteers after the consumption of onions. Free Radic. Res. 1998, 29, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollman, P.C.; van Trijp, J.M.; Buysman, M.N.; van der Gaag, M.S.; Mengelers, M.J.; de Vries, J.H.; Katan, M.B. Relative bioavailability of the antioxidant flavonoid quercetin from various foods in man. FEBS Lett. 1997, 418, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Day, A.J.; DuPont, M.S.; Ridley, S.; Rhodes, M.; Rhodes, M.J.; Morgan, M.R.; Williamson, G. Deglycosylation of flavonoid and isoflavonoid glycosides by human small intestine and liver beta-glucosidase activity. FEBS Lett. 1998, 436, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeth, K.; Plumb, G.W.; Berrin, J.G.; Juge, N.; Jacob, R.; Naim, H.Y.; Williamson, G.; Swallow, D.M.; Kroon, P.A. Deglycosylation by small intestinal epithelial cell beta-glucosidases is a critical step in the absorption and metabolism of dietary flavonoid glycosides in humans. Eur. J. Nutr. 2003, 42, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, A.J.; Williamson, G. Biomarkers for exposure to dietary flavonoids: A review of the current evidence for identification of quercetin glycosides in plasma. Br. J. Nutr. 2001, 86 (Suppl. 1), S105–S110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setchell, K.D.; Faughnan, M.S.; Avades, T.; Zimmer-Nechemias, L.; Brown, N.M.; Wolfe, B.E.; Brashear, W.T.; Desai, P.; Oldfield, M.F.; Botting, N.P.; et al. Comparing the pharmacokinetics of daidzein and genistein with the use of 13c-labeled tracers in premenopausal women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sesink, A.L.; O’Leary, K.A.; Hollman, P.C. Quercetin glucuronides but not glucosides are present in human plasma after consumption of quercetin-3-glucoside or quercetin-4’-glucoside. J. Nutr. 2001, 131, 1938–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setchell, K.D.; Brown, N.M.; Lydeking-Olsen, E. The clinical importance of the metabolite equol-a clue to the effectiveness of soy and its isoflavones. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 3577–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felgines, C.; Talavera, S.; Gonthier, M.P.; Texier, O.; Scalbert, A.; Lamaison, J.L.; Remesy, C. Strawberry anthocyanins are recovered in urine as glucuro- and sulfoconjugates in humans. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 1296–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regev-Shoshani, G.; Shoseyov, O.; Bilkis, I.; Kerem, Z. Glycosylation of resveratrol protects it from enzymic oxidation. Biochem. J. 2003, 374, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.J.; Anderson, K.E. Sex and long-term soy diets affect the metabolism and excretion of soy isoflavones in humans. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 68, 1500S–1504S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, G.L.; Tedesco, I.; Spagnuolo, C.; Russo, M. Antioxidant polyphenols in cancer treatment: Friend, foe or foil? Semin. Cancer Biol. 2017, 46, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomasset, S.C.; Berry, D.P.; Garcea, G.; Marczylo, T.; Steward, W.P.; Gescher, A.J. Dietary polyphenolic phytochemicals—Promising cancer chemopreventive agents in humans? A review of their clinical properties. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 120, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asensi, M.; Ortega, A.; Mena, S.; Feddi, F.; Estrela, J.M. Natural polyphenols in cancer therapy. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2011, 48, 197–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dashwood, R.H. Frontiers in polyphenols and cancer prevention. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 267S–269S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luqman, S.; Rizvi, S.I. Protection of lipid peroxidation and carbonyl formation in proteins by capsaicin in human erythrocytes subjected to oxidative stress. Phytother. Res. 2006, 20, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, K.B.; Mishra, N.; Rizvi, S.I. Protective role of myricetin on markers of oxidative stress in human erythrocytes subjected to oxidative stress. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2009, 4, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clifford, M.N. Chlorogenic acids and other cinnamates. Nature, occurence, dietary burden, absorptionand metabolism. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2000, 80, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergediene, E.; Jonsson, K.; Szymusiak, H.; Tyrakowska, B.; Rietjens, I.M.; Cenas, N. Prooxidant toxicity of polyphenolic antioxidants to hl-60 cells: Description of quantitative structure-activity relationships. FEBS Lett. 1999, 462, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, N.; Oda, O.; Nagao, S. Prooxidant activity of caffeic acid, dietary non-flavonoid phenolic acid, on cu2+-induced low density lipoprotein oxidation. FEBS Lett. 1997, 405, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, S. Cancer chemoprevention and chemotherapy: Dietary polyphenols and signalling pathways. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2008, 52, 507–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Corona, G.; Deiana, M.; Incani, A.; Vauzour, D.; Dessi, M.A.; Spencer, J.P. Inhibition of p38/creb phosphorylation and cox-2 expression by olive oil polyphenols underlies their anti-proliferative effects. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 362, 606–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guichard, C.; Pedruzzi, E.; Fay, M.; Marie, J.C.; Braut-Boucher, F.; Daniel, F.; Grodet, A.; Gougerot-Pocidalo, M.A.; Chastre, E.; Kotelevets, L.; et al. Dihydroxyphenylethanol induces apoptosis by activating serine/threonine protein phosphatase pp2a and promotes the endoplasmic reticulum stress response in human colon carcinoma cells. Carcinogenesis 2006, 27, 1812–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Munerol, B.; Pollard, S.; Youdim, K.A.; Pannala, A.S.; Kuhnle, G.G.; Debnam, E.S.; Rice-Evans, C.; Spencer, J.P. The reaction of flavanols with nitrous acid protects against n-nitrosamine formation and leads to the formation of nitroso derivatives which inhibit cancer cell growth. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2006, 40, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bin Hafeez, B.; Asim, M.; Siddiqui, I.A.; Adhami, V.M.; Murtaza, I.; Mukhtar, H. Delphinidin, a dietary anthocyanidin in pigmented fruits and vegetables: A new weapon to blunt prostate cancer growth. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 3320–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yun, J.M.; Afaq, F.; Khan, N.; Mukhtar, H. Delphinidin, an anthocyanidin in pigmented fruits and vegetables, induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in human colon cancer hct116 cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2009, 48, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulzomi, P.; Bolli, A.; Galluzzo, P.; Leone, S.; Acconcia, F.; Marino, M. Naringenin and 17 beta-estradiol coadministration prevents hormone-induced human cancer cell growth. IUBMB Life 2010, 62, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, H.M.; Park, G.H.; Eo, H.J.; Jeong, J.B. Naringenin-mediated atf3 expression contributes to apoptosis in human colon cancer. Biomol. Ther. 2016, 24, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arul, D.; Subramanian, P. Naringenin (citrus flavonone) induces growth inhibition, cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2013, 19, 763–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamoto, T.; Horiguchi, H.; Oguma, E.; Kayama, F. Effects of diverse dietary phytoestrogens on cell growth, cell cycle and apoptosis in estrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer cells. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2010, 21, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, M.; Pellegrini, M.; La Rosa, P.; Acconcia, F. Susceptibility of estrogen receptor rapid responses to xenoestrogens: Physiological outcomes. Steroids 2012, 77, 910–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mense, S.M.; Hei, T.K.; Ganju, R.K.; Bhat, H.K. Phytoestrogens and breast cancer prevention: Possible mechanisms of action. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirotkin, A.V.; Harrath, A.H. Phytoestrogens and their effects. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 741, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, S.; Whitehead, S.A. Phytoestrogens and breast cancer--promoters or protectors? Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2006, 13, 995–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, P.G.; Awad, A.B. Phytosterols as anticancer compounds. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarty, M.F. Isoflavones made simple-genistein’s agonist activity for the beta-type estrogen receptor mediates their health benefits. Med. Hypotheses 2006, 66, 1093–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Woude, H.; Ter Veld, M.G.; Jacobs, N.; van der Saag, P.T.; Murk, A.J.; Rietjens, I.M. The stimulation of cell proliferation by quercetin is mediated by the estrogen receptor. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2005, 49, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuiper, G.G.; Lemmen, J.G.; Carlsson, B.; Corton, J.C.; Safe, S.H.; van der Saag, P.T.; van der Burg, B.; Gustafsson, J.A. Interaction of estrogenic chemicals and phytoestrogens with estrogen receptor beta. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 4252–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escande, A.; Pillon, A.; Servant, N.; Cravedi, J.P.; Larrea, F.; Muhn, P.; Nicolas, J.C.; Cavailles, V.; Balaguer, P. Evaluation of ligand selectivity using reporter cell lines stably expressing estrogen receptor alpha or beta. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 71, 1459–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, S.O.; Simon, S.; Chae, K.; Metzler, M.; Korach, K.S. Phytoestrogens and their human metabolites show distinct agonistic and antagonistic properties on estrogen receptor alpha (eralpha) and erbeta in human cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2004, 80, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, J.F.; Page, J.E. Xanthohumol and related prenylflavonoids from hops and beer: To your good health! Phytochemistry 2004, 65, 1317–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonnell, D.P. The molecular determinants of estrogen receptor pharmacology. Maturitas 2004, 48 (Suppl. 1), S7–S12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, J.; Gustafsson, J.A. Estrogen signaling: A subtle balance between er alpha and er beta. Mol. Interv. 2003, 3, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ascenzi, P.; Bocedi, A.; Marino, M. Structure-function relationship of estrogen receptor alpha and beta: Impact on human health. Mol. Aspect. Med. 2006, 27, 299–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acconcia, F.; Marino, M. The effects of 17beta-estradiol in cancer are mediated by estrogen receptor signaling at the plasma membrane. Front. Physiol. 2011, 2, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiocchetti, M.; Ascenzi, P.; Marino, M. Neuroprotective effects of 17beta-estradiol rely on estrogen receptor membrane initiated signals. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkoyluoglu, E.; Madak-Erdogan, Z. Nuclear and extranuclear-initiated estrogen receptor signaling crosstalk and endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Steroids 2016, 114, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hamilton, K.J.; Hewitt, S.C.; Arao, Y.; Korach, K.S. Estrogen hormone biology. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2017, 125, 109–146. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Herynk, M.H.; Fuqua, S.A. Estrogen receptor mutations in human disease. Endocr. Rev. 2004, 25, 869–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metivier, R.; Penot, G.; Hubner, M.R.; Reid, G.; Brand, H.; Kos, M.; Gannon, F. Estrogen receptor-alpha directs ordered, cyclical, and combinatorial recruitment of cofactors on a natural target promoter. Cell 2003, 115, 751–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard, N.; Charbonneau, C.; Sanchez, M.; Licznar, A.; Busson, M.; Lazennec, G.; Tremblay, A. Phosphorylation of activation function-1 regulates proteasome-dependent nuclear mobility and e6-associated protein ubiquitin ligase recruitment to the estrogen receptor beta. Mol. Endocrinol. 2008, 22, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, G.; Hubner, M.R.; Metivier, R.; Brand, H.; Denger, S.; Manu, D.; Beaudouin, J.; Ellenberg, J.; Gannon, F. Cyclic, proteasome-mediated turnover of unliganded and liganded eralpha on responsive promoters is an integral feature of estrogen signaling. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 695–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriarty, K.; Kim, K.H.; Bender, J.R. Minireview: Estrogen receptor-mediated rapid signaling. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 5557–5563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, S.; Gustafsson, J.A. Estrogen receptors: Therapies targeted to receptor subtypes. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 89, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razandi, M.; Alton, G.; Pedram, A.; Ghonshani, S.; Webb, P.; Levin, E.R. Identification of a structural determinant necessary for the localization and function of estrogen receptor alpha at the plasma membrane. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 1633–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquez, D.C.; Chen, H.W.; Curran, E.M.; Welshons, W.V.; Pietras, R.J. Estrogen receptors in membrane lipid rafts and signal transduction in breast cancer. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 246, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acconcia, F.; Totta, P.; Ogawa, S.; Cardillo, I.; Inoue, S.; Leone, S.; Trentalance, A.; Muramatsu, M.; Marino, M. Survival versus apoptotic 17beta-estradiol effect: Role of er alpha and er beta activated non-genomic signaling. J. Cell. Physiol. 2005, 203, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galluzzo, P.; Caiazza, F.; Moreno, S.; Marino, M. Role of erbeta palmitoylation in the inhibition of human colon cancer cell proliferation. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2007, 14, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammes, S.R.; Levin, E.R. Extranuclear steroid receptors: Nature and actions. Endocr. Rev. 2007, 28, 726–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukocheva, O.; Wadham, C.; Holmes, A.; Albanese, N.; Verrier, E.; Feng, F.; Bernal, A.; Derian, C.K.; Ullrich, A.; Vadas, M.A.; et al. Estrogen transactivates egfr via the sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor edg-3: The role of sphingosine kinase-1. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 173, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maggiolini, M.; Picard, D. The unfolding stories of gpr30, a new membrane-bound estrogen receptor. J. Endocrinol. 2010, 204, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prossnitz, E.R.; Arterburn, J.B.; Smith, H.O.; Oprea, T.I.; Sklar, L.A.; Hathaway, H.J. Estrogen signaling through the transmembrane g protein-coupled receptor gpr30. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 2008, 70, 165–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, E.R. Plasma membrane estrogen receptors. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 20, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Otto, C.; Fuchs, I.; Kauselmann, G.; Kern, H.; Zevnik, B.; Andreasen, P.; Schwarz, G.; Altmann, H.; Klewer, M.; Schoor, M.; et al. Gpr30 does not mediate estrogenic responses in reproductive organs in mice. Biol. Reprod. 2009, 80, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deroo, B.J.; Korach, K.S. Estrogen receptors and human disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Colditz, G.A. Relationship between estrogen levels, use of hormone replacement therapy, and breast cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1998, 90, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hankinson, S.E.; Colditz, G.A.; Willett, W.C. Towards an integrated model for breast cancer etiology: The lifelong interplay of genes, lifestyle, and hormones. Breast Cancer Res. 2004, 6, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ellem, S.J.; Risbridger, G.P. Treating prostate cancer: A rationale for targeting local oestrogens. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musgrove, E.A.; Sutherland, R.L. Biological determinants of endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, C.; Gustafsson, J.A. The different roles of er subtypes in cancer biology and therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Shang, Y. Estrogen and cancer. Annual review of physiology. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2013, 75, 225–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.G.; Zeng, Q.; Tse, G.M. Estrogen and its receptors in cancer. Med. Res. Rev. 2008, 28, 954–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantinopoulos, P.A.; Kominea, A.; Vandoros, G.; Sykiotis, G.P.; Andricopoulos, P.; Varakis, I.; Sotiropoulou-Bonikou, G.; Papavassiliou, A.G. Oestrogen receptor beta (erbeta) is abundantly expressed in normal colonic mucosa, but declines in colon adenocarcinoma paralleling the tumour’s dedifferentiation. Eur. J. Cancer 2003, 39, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazennec, G. Estrogen receptor beta, a possible tumor suppressor involved in ovarian carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2006, 231, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Behrens, D.; Gill, J.H.; Fichtner, I. Loss of tumourigenicity of stably erbeta-transfected mcf-7 breast cancer cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2007, 274, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Razandi, M.; Pedram, A.; Greene, G.L.; Levin, E.R. Cell membrane and nuclear estrogen receptors (ers) originate from a single transcript: Studies of eralpha and erbeta expressed in chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 1999, 13, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Totta, P.; Pesiri, V.; Enari, M.; Marino, M.; Acconcia, F. Clathrin heavy chain interacts with estrogen receptor α and modulates 17β-estradiol signalling. Mol. Endocrinol. 2015, 29, 739–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castoria, G.; Migliaccio, A.; Bilancio, A.; Di Domenico, M.; de Falco, A.; Lombardi, M.; Fiorentino, R.; Varricchio, L.; Barone, M.V.; Auricchio, F. Pi3-kinase in concert with src promotes the s-phase entry of oestradiol-stimulated mcf-7 cells. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 6050–6059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, M.; Distefano, E.; Pallottini, V.; Caporali, S.; Bruscalupi, G.; Trentalance, A. Activation of ip(3)-protein kinase c-alpha signal transduction pathway precedes the changes of plasma cholesterol, hepatic lipid metabolism and induction of low-density lipoprotein receptor expression in 17-beta-oestradiol-treated rats. Exp. Physiol. 2001, 86, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, M.; Pallottini, V.; Trentalance, A. Estrogens cause rapid activation of ip3-pkc-alpha signal transduction pathway in hepg2 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1998, 245, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castoria, G.; Barone, M.V.; Di Domenico, M.; Bilancio, A.; Ametrano, D.; Migliaccio, A.; Auricchio, F. Non-transcriptional action of oestradiol and progestin triggers DNA synthesis. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 2500–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marino, M.; Acconcia, F.; Bresciani, F.; Weisz, A.; Trentalance, A. Distinct nongenomic signal transduction pathways controlled by 17beta-estradiol regulate DNA synthesis and cyclin d(1) gene transcription in hepg2 cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 3720–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marino, M.; Acconcia, F.; Trentalance, A. Biphasic estradiol-induced akt phosphorylation is modulated by pten via map kinase in hepg2 cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 2583–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.R.; Park, J.; Yu, H.N.; Kim, J.S.; Youn, H.J.; Jung, S.H. Up-regulation of pi3k/akt signaling by 17beta-estradiol through activation of estrogen receptor-alpha, but not estrogen receptor-beta, and stimulates cell growth in breast cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 336, 1221–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.G.; Xia, C.; Zheng, X.P.; Yi, T.T.; Wang, X.Y.; Song, G.; Zhang, B. 17beta-estradiol promotes cell proliferation in rat osteoarthritis model chondrocytes via pi3k/akt pathway. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2011, 16, 564–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, R.X.; Wei, L.H.; Tu, Z.; Sun, P.M.; Wang, J.L.; Zhao, D.; Li, X.P.; Tang, J.M. 17 beta-estradiol activates pi3k/akt signaling pathway by estrogen receptor (er)-dependent and er-independent mechanisms in endometrial cancer cells. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2006, 99, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paruthiyil, S.; Parmar, H.; Kerekatte, V.; Cunha, G.R.; Firestone, G.L.; Leitman, D.C. Estrogen receptor beta inhibits human breast cancer cell proliferation and tumor formation by causing a g2 cell cycle arrest. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 423–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pravettoni, A.; Mornati, O.; Martini, P.G.; Marino, M.; Colciago, A.; Celotti, F.; Motta, M.; Negri-Cesi, P. Estrogen receptor beta (erbeta) and inhibition of prostate cancer cell proliferation: Studies on the possible mechanism of action in du145 cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2007, 263, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virgili, F.; Acconcia, F.; Ambra, R.; Rinna, A.; Totta, P.; Marino, M. Nutritional flavonoids modulate estrogen receptor alpha signaling. IUBMB Life 2004, 56, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.Y.; Santell, R.C.; Haslam, S.Z.; Helferich, W.G. Estrogenic effects of genistein on the growth of estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer (mcf-7) cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 3833–3838. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, E.; Lehmann, L.; Metzler, M.; Stopper, H. Hormonal and genotoxic activity of resveratrol. Toxicol. Lett. 2002, 136, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, H.S.; DeNardo, D.G.; Jacquot, Y.; Laios, I.; Vidal, D.S.; Zambrana, C.R.; Leclercq, G.; Brown, P.H. Stimulatory effect of genistein and apigenin on the growth of breast cancer cells correlates with their ability to activate er alpha. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2006, 99, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Du, J.; Hu, C.; Qi, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, Q.; Li, Z. Delayed activation of extracellular-signal-regulated kinase 1/2 is involved in genistein- and equol-induced cell proliferation and estrogen-receptor-alpha-mediated transcription in mcf-7 breast cancer cells. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2010, 21, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allred, C.D.; Allred, K.F.; Ju, Y.H.; Clausen, L.M.; Doerge, D.R.; Schantz, S.L.; Korol, D.L.; Wallig, M.A.; Helferich, W.G. Dietary genistein results in larger mnu-induced, estrogen-dependent mammary tumors following ovariectomy of sprague-dawley rats. Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allred, C.D.; Allred, K.F.; Ju, Y.H.; Virant, S.M.; Helferich, W.G. Soy diets containing varying amounts of genistein stimulate growth of estrogen-dependent (mcf-7) tumors in a dose-dependent manner. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 5045–5050. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ju, Y.H.; Fultz, J.; Allred, K.F.; Doerge, D.R.; Helferich, W.G. Effects of dietary daidzein and its metabolite, equol, at physiological concentrations on the growth of estrogen-dependent human breast cancer (mcf-7) tumors implanted in ovariectomized athymic mice. Carcinogenesis 2006, 27, 856–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggiolini, M.; Bonofiglio, D.; Marsico, S.; Panno, M.L.; Cenni, B.; Picard, D.; Ando, S. Estrogen receptor alpha mediates the proliferative but not the cytotoxic dose-dependent effects of two major phytoestrogens on human breast cancer cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 60, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.J.; Kim, G.H. Antiproliferative activity of daidzein and genistein may be related to eralpha/c-erbb-2 expression in human breast cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 7, 781–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, N.H.; Hwang, K.A.; Lee, H.R.; Choi, D.W.; Choi, K.C. Resveratrol regulates the cell viability promoted by 17beta-estradiol or bisphenol a via down-regulation of the cross-talk between estrogen receptor alpha and insulin growth factor-1 receptor in bg-1 ovarian cancer cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 59, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielecki, A.; Roberts, J.; Mehta, R.; Raju, J. Estrogen receptor-beta mediates the inhibition of dld-1 human colon adenocarcinoma cells by soy isoflavones. Nutr. Cancer 2011, 63, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Totta, P.; Acconcia, F.; Virgili, F.; Cassidy, A.; Weinberg, P.D.; Rimbach, G.; Marino, M. Daidzein-sulfate metabolites affect transcriptional and antiproliferative activities of estrogen receptor-beta in cultured human cancer cells. J. Nutr. 2005, 135, 2687–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulzomi, P.; Galluzzo, P.; Bolli, A.; Leone, S.; Acconcia, F.; Marino, M. The pro-apoptotic effect of quercetin in cancer cell lines requires erbeta-dependent signals. J. Cell. Physiol. 2012, 227, 1891–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cipolletti, M.; Montalesi, E.; Nuzzo, M.T.; Fiocchetti, M.; Ascenzi, P.; Marino, M. Potentiation of paclitaxel effect by resveratrol in human breast cancer cells by counteracting the 17β-estradiol/estrogen receptor α/neuroglobin pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Galluzzo, P.; Martini, C.; Bulzomi, P.; Leone, S.; Bolli, A.; Pallottini, V.; Marino, M. Quercetin-induced apoptotic cascade in cancer cells: Antioxidant versus estrogen receptor alpha-dependent mechanisms. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009, 53, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Totta, P.; Acconcia, F.; Leone, S.; Cardillo, I.; Marino, M. Mechanisms of naringenin-induced apoptotic cascade in cancer cells: Involvement of estrogen receptor alpha and beta signalling. IUBMB Life 2004, 56, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.S.; Choi, K.C.; Hwang, K.A. Genistein suppressed epithelial-mesenchymal transition and migration efficacies of bg-1 ovarian cancer cells activated by estrogenic chemicals via estrogen receptor pathway and downregulation of tgf-beta signaling pathway. Phytomedicine 2015, 22, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piccolella, M.; Crippa, V.; Messi, E.; Tetel, M.J.; Poletti, A. Modulators of estrogen receptor inhibit proliferation and migration of prostate cancer cells. Pharmacol. Res. 2014, 79, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, R.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Cai, X.; Wu, K.; Bergan, R.C.; Xu, L.; Fan, D. Genistein suppresses flt4 and inhibits human colorectal cancer metastasis. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 3225–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, K.K.L.; Siu, M.K.Y.; Jiang, Y.X.; Wang, J.J.; Leung, T.H.Y.; Ngan, H.Y.S. Estrogen receptor modulators genistein, daidzein and erb-041 inhibit cell migration, invasion, proliferation and sphere formation via modulation of fak and pi3k/akt signaling in ovarian cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2018, 18, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, Y.H.; Allred, K.F.; Allred, C.D.; Helferich, W.G. Genistein stimulates growth of human breast cancer cells in a novel, postmenopausal animal model, with low plasma estradiol concentrations. Carcinogenesis 2006, 27, 1292–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Belosay, A.; Hartman, J.A.; Song, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W.; Doerge, D.R.; Helferich, W.G. Dietary soy isoflavones increase metastasis to lungs in an experimental model of breast cancer with bone micro-tumors. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2015, 32, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, G.A.; Choi, K.C.; Hwang, K.A. Kaempferol, a phytoestrogen, suppressed triclosan-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastatic-related behaviors of mcf-7 breast cancer cells. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 49, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bratton, M.R.; Duong, B.N.; Elliott, S.; Weldon, C.B.; Beckman, B.S.; McLachlan, J.A.; Burow, M.E. Regulation of eralpha-mediated transcription of bcl-2 by pi3k-akt crosstalk: Implications for breast cancer cell survival. Int. J. Oncol. 2010, 37, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fiocchetti, M.; Nuzzo, M.T.; Totta, P.; Acconcia, F.; Ascenzi, P.; Marino, M. Neuroglobin, a pro-survival player in estrogen receptor alpha-positive cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiocchetti, M.; Cipolletti, M.; Marino, M. Compensatory role of neuroglobin in nervous and non-nervous cancer cells in response to the nutrient deprivation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0189179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPherson, S.J.; Hussain, S.; Balanathan, P.; Hedwards, S.L.; Niranjan, B.; Grant, M.; Chandrasiri, U.P.; Toivanen, R.; Wang, Y.; Taylor, R.A.; et al. Estrogen receptor-beta activated apoptosis in benign hyperplasia and cancer of the prostate is androgen independent and tnfalpha mediated. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 3123–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.G.; Katiyar, S.K.; Agarwal, R.; Mukhtar, H. Enhancement of antioxidant and phase ii enzymes by oral feeding of green tea polyphenols in drinking water to skh-1 hairless mice: Possible role in cancer chemoprevention. Cancer Res. 1992, 52, 4050–4052. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, N.; Feyes, D.K.; Nieminen, A.L.; Agarwal, R.; Mukhtar, H. Green tea constituent epigallocatechin-3-gallate and induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in human carcinoma cells. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1997, 89, 1881–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhtar, H.; Ahmad, N. Mechanism of cancer chemopreventive activity of green tea. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1999, 220, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okabe, S.; Ochiai, Y.; Aida, M.; Park, K.; Kim, S.J.; Nomura, T.; Suganuma, M.; Fujiki, H. Mechanistic aspects of green tea as a cancer preventive: Effect of components on human stomach cancer cell lines. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 1999, 90, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.Y.; Liao, J.; Kim, K.; Yurkow, E.J.; Yang, C.S. Inhibition of growth and induction of apoptosis in human cancer cell lines by tea polyphenols. Carcinogenesis 1998, 19, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Romero, I.; Paez, A.; Ferruelo, A.; Lujan, M.; Berenguer, A. Polyphenols in red wine inhibit the proliferation and induce apoptosis of lncap cells. BJU Int. 2002, 89, 950–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.N.; Almoyad, M.; Huq, F. Polyphenols in colorectal cancer: Current state of knowledge including clinical trials and molecular mechanism of action. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 4154185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, S. Effects of dietary flavonoids on apoptotic pathways related to cancer chemoprevention. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2007, 18, 427–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, H.H.; Chen, J.H.; Huang, C.C.; Wang, C.J. Apoptotic effect of 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid on human gastric carcinoma cells involving jnk/p38 mapk signaling activation. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 120, 2306–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galluzzo, P.; Ascenzi, P.; Bulzomi, P.; Marino, M. The nutritional flavanone naringenin triggers antiestrogenic effects by regulating estrogen receptor alpha-palmitoylation. Endocrinology 2008, 149, 2567–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulzomi, P.; Marino, M. Environmental endocrine disruptors: Does a sex-related susceptibility exist? Front. Biosci. 2011, 16, 2478–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozo-Guisado, E.; Alvarez-Barrientos, A.; Mulero-Navarro, S.; Santiago-Josefat, B.; Fernandez-Salguero, P.M. The antiproliferative activity of resveratrol results in apoptosis in mcf-7 but not in mda-mb-231 human breast cancer cells: Cell-specific alteration of the cell cycle. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2002, 64, 1375–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulda, S.; Debatin, K.M. Sensitization for anticancer drug-induced apoptosis by the chemopreventive agent resveratrol. Oncogene 2004, 23, 6702–6711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kubota, T.; Uemura, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Taguchi, H. Combined effects of resveratrol and paclitaxel on lung cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2003, 23, 4039–4046. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gill, C.; Walsh, S.E.; Morrissey, C.; Fitzpatrick, J.M.; Watson, R.W. Resveratrol sensitizes androgen independent prostate cancer cells to death-receptor mediated apoptosis through multiple mechanisms. Prostate 2007, 67, 1641–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luck, H.J.; Roche, H. Weekly paclitaxel: An effective and well-tolerated treatment in patients with advanced breast cancer. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2002, 44 (Suppl. 153), S15–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sledge, G.W.; Neuberg, D.; Bernardo, P.; Ingle, J.N.; Martino, S.; Rowinsky, E.K.; Wood, W.C. Phase iii trial of doxorubicin, paclitaxel, and the combination of doxorubicin and paclitaxel as front-line chemotherapy for metastatic breast cancer: An intergroup trial (e1193). J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiocchetti, M.; Cipolletti, M.; Leone, S.; Ascenzi, P.; Marino, M. Neuroglobin overexpression induced by the 17beta-estradiol-estrogen receptor-alpha pathway reduces the sensitivity of mcf-7 breast cancer cell to paclitaxel. IUBMB Life 2016, 68, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obiorah, I.E.; Fan, P.; Jordan, V.C. Breast cancer cell apoptosis with phytoestrogens is dependent on an estrogen-deprived state. Cancer Prev. Res. 2014, 7, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, S.K.; Das, D.K. Resveratrol and chemoprevention. Cancer Lett. 2009, 284, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.P.; Chien, M.H.; Chern, I.Y. Impact of lower concentrations of phytoestrogens on the effects of estradiol in breast cancer cells. Climacteric 2015, 18, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acconcia, F.; Manavathi, B.; Mascarenhas, J.; Talukder, A.H.; Mills, G.; Kumar, R. An inherent role of integrin-linked kinase-estrogen receptor alpha interaction in cell migration. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 11030–11038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollard, T.D.; Borisy, G.G. Cellular motility driven by assembly and disassembly of actin filaments. Cell 2003, 112, 453–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamir, E.; Geiger, B. Molecular complexity and dynamics of cell-matrix adhesions. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 3583–3590. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saha Roy, S.; Vadlamudi, R.K. Role of estrogen receptor signaling in breast cancer metastasis. Int. J. Breast Cancer 2012, 2012, 654698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, A.M.; Flamini, M.I.; Baldacci, C.; Goglia, L.; Genazzani, A.R.; Simoncini, T. Estrogen receptor-alpha promotes breast cancer cell motility and invasion via focal adhesion kinase and n-wasp. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 24, 2114–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giretti, M.S.; Fu, X.D.; De Rosa, G.; Sarotto, I.; Baldacci, C.; Garibaldi, S.; Mannella, P.; Biglia, N.; Sismondi, P.; Genazzani, A.R.; et al. Extra-nuclear signalling of estrogen receptor to breast cancer cytoskeletal remodelling, migration and invasion. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakravarty, D.; Nair, S.S.; Santhamma, B.; Nair, B.C.; Wang, L.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Agyin, J.K.; Brann, D.; Sun, L.Z.; Yeh, I.T.; et al. Extranuclear functions of er impact invasive migration and metastasis by breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 4092–4101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjornstrom, L.; Sjoberg, M. Mechanisms of estrogen receptor signaling: Convergence of genomic and nongenomic actions on target genes. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005, 19, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Ding, Y.; Catalona, W.J.; Yang, X.J.; Anderson, W.F.; Jovanovic, B.; Wellman, K.; Killmer, J.; Huang, X.; Scheidt, K.A.; et al. Mek4 function, genistein treatment, and invasion of human prostate cancer cells. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2009, 101, 1141–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Zhu, C.-F.; Dai, Y.-L.; Zhong, Q.; Sun, B. Inhibitory effects of genistein on metastasis of human hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 15, 4952–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onder, T.T.; Gupta, P.B.; Mani, S.A.; Yang, J.; Lander, E.S.; Weinberg, R.A. Loss of e-cadherin promotes metastasis via multiple downstream transcriptional pathways. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 3645–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, S.; Wang, J.; Wu, Q.; Qian, J.; Yang, C.; Bo, P. Genistein inhibits the growth and regulates the migration and invasion abilities of melanoma cells via the fak/paxillin and mapk pathways. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 21674–21691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.; DiLeo, A.; Niv, Y.; Gustafsson, J.A. Estrogen receptor beta as target for colorectal cancer prevention. Cancer Lett. 2016, 372, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shang, D.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhao, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y. Baicalein suppresses 17-beta-estradiol-induced migration, adhesion and invasion of breast cancer cells via the g protein-coupled receptor 30 signaling pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 2077–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benetou, V.; Orfanos, P.; Lagiou, P.; Trichopoulos, D.; Boffetta, P.; Trichopoulou, A. Vegetables and fruits in relation to cancer risk: Evidence from the greek epic cohort study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2008, 17, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, C.A.; Pera, G.; Agudo, A.; Bueno-de-Mesquita, H.B.; Ceroti, M.; Boeing, H.; Schulz, M.; Del Giudice, G.; Plebani, M.; Carneiro, F.; et al. Fruit and vegetable intake and the risk of stomach and oesophagus adenocarcinoma in the european prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition (epic-eurgast). Int. J. Cancer 2006, 118, 2559–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, M.; Tajima, K.; Mizutani, M.; Iwata, H.; Iwase, T.; Miura, S.; Hirose, K.; Hamajima, N.; Tominaga, S. Regular consumption of green tea and the risk of breast cancer recurrence: Follow-up study from the hospital-based epidemiologic research program at aichi cancer center (herpacc), Japan. Cancer Lett. 2001, 167, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Surh, Y.J. Nrf2 as a novel molecular target for chemoprevention. Cancer Lett. 2005, 224, 171–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rieger-Christ, K.M.; Hanley, R.; Lodowsky, C.; Bernier, T.; Vemulapalli, P.; Roth, M.; Kim, J.; Yee, A.S.; Le, S.M.; Marie, P.J.; et al. The green tea compound, (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate downregulates n-cadherin and suppresses migration of bladder carcinoma cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2007, 102, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, J.H.; Crotty, S.; Nelson, P.N. Phytoestrogens: Perpetrators or protectors? Future Oncol. 2007, 3, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuttke, W.; Jarry, H.; Seidlova-Wuttke, D. Isoflavones—Safe food additives or dangerous drugs? Ageing Res. Rev. 2007, 6, 150–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Li, S.; Li, H.B.; Deng, G.F.; Ling, W.H.; Xu, X.R. Antiproliferative activities of tea and herbal infusions. Food Funct. 2013, 4, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Lafuente, A.; Guillamon, E.; Villares, A.; Rostagno, M.A.; Martinez, J.A. Flavonoids as anti-inflammatory agents: Implications in cancer and cardiovascular disease. Inflamm. Res. 2009, 58, 537–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virk-Baker, M.K.; Nagy, T.R.; Barnes, S. Role of phytoestrogens in cancer therapy. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 1132–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Polyphenol Compounds | ERα | ERα-Dependent Functions | ERβ | ERβ-Dependent Functions | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Naringenin Quercetin | Antagonize ERα rapid signaling, inducing the persistent activation of p38, the inhibition of AKT and ERK1/2 E2-dependent activation. No effect on ERα transcriptional mechanism. | Inhibit proliferation in ERα-expressing cancer cells and induce pro-apoptotic cascade. Impair the E2-dependent upregulation of Ngb and sensitize breast cancer cells to apoptotic effect of paclitaxel. | Mimic E2 effect activating p38/MAPK pathway | Induction of ERβ mediated pro-apoptotic pathway | [52,114,127,128,129,130] |
| Genistein | Agonistic effect. Trans-activation of ERα inducing the persistent activation of ERK1/2. | Induction of MCF-7 cell proliferation in vitro and implanted in xenograft mice; stimulation of E2-dependent mammary tumors’growth. Inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis in long-term estrogen deprived MCF7 | E2 mimetic effects. Suppression of the ERK1/2, PI3K/AKT activation and PCNA and NFkB expression. Downregulation of migration-related pathways such as the FAK, PI3K/AKT and TGFβ pathways. | Suppression of cancer cell growth. Inhibition of migration in ovarian and prostate cancer cells and reduction of cancer metastasis in colorectal cancer. | [118,119,125,131,132,133] |
| Daidzein Equol | Agonist | Induce in vitro MCF-7 cell proliferation Increase lung metastasis in in vivo model of breast cancer. | Agonist | Inhibit cancer cells proliferation. Suppress ovarian cancer cell migration. | [125,126,134,135,136] |
| Resveratrol | Full antagonist of ERα rapid and transcriptional mechanisms | Induce pro-apoptotic effects reducing the Bcl-2/BAX ratio. Downregulates Ngb intracellular content and sensitizes breast cancer cells to the paclitaxel pro-apoptotic effect. | Agonist | Increases Ngb levels and cell-survival in neuron-derived cells | [55,128] |
| Kaempferol | Antagonist | Suppresses EMT transition and metastic behavior of MCF-7 induced by endogenous E2 or estrogen mimetic compounds. | ND | ND | [137] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cipolletti, M.; Solar Fernandez, V.; Montalesi, E.; Marino, M.; Fiocchetti, M. Beyond the Antioxidant Activity of Dietary Polyphenols in Cancer: the Modulation of Estrogen Receptors (ERs) Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2624. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092624
Cipolletti M, Solar Fernandez V, Montalesi E, Marino M, Fiocchetti M. Beyond the Antioxidant Activity of Dietary Polyphenols in Cancer: the Modulation of Estrogen Receptors (ERs) Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(9):2624. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092624
Chicago/Turabian StyleCipolletti, Manuela, Virginia Solar Fernandez, Emiliano Montalesi, Maria Marino, and Marco Fiocchetti. 2018. "Beyond the Antioxidant Activity of Dietary Polyphenols in Cancer: the Modulation of Estrogen Receptors (ERs) Signaling" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 9: 2624. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092624
APA StyleCipolletti, M., Solar Fernandez, V., Montalesi, E., Marino, M., & Fiocchetti, M. (2018). Beyond the Antioxidant Activity of Dietary Polyphenols in Cancer: the Modulation of Estrogen Receptors (ERs) Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(9), 2624. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092624