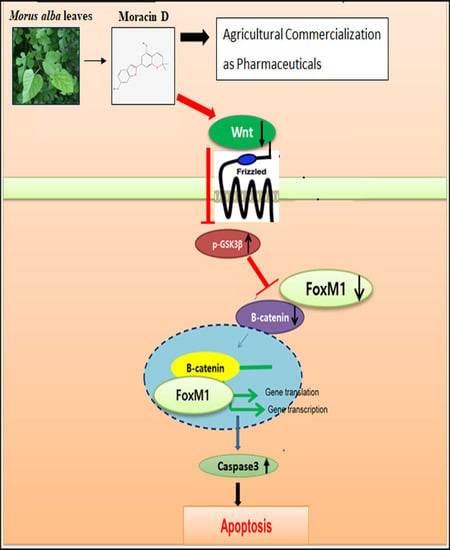
Inhibition of Wnt3a/FOXM1/β-Catenin Axis and Activation of GSK3β and Caspases are Critically Involved in Apoptotic Effect of Moracin D in Breast Cancers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cytotoxic Effect of Moracin D in Human Breast Cancer Cells
2.2. Moracin D Induced Apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 Human Breast Cancer Cells
2.3. Moracin D Effectively Attenuated the Expression of FOXM1 Related Proteins in MDA-MB-231 Cells
2.4. Moracin D Disturbed the Binding between FOXM1 and B-Catenin in MDA-MB-231 Cells
2.5. GSK3β Inhibitor SB216763 Blocked the Apoptosis Induced by Moracin D in MDA-MB-231 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Moracin D Preparation
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.4. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.5. Western Blotting
4.6. Co-Immunoprecipitation
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FOXM1 | Forkhead box |
| PARP | Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase |
| Caspase | Cysteine aspartyl-specific protease |
| Bcl-2 | B-cell lymphoma 2 |
| XIAP | X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein |
| GSK 3β | Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta |
References
- Zarei, M.; Bagheri-Saweh, M.I.; Rasolabadi, M.; Vakili, R.; Seidi, J.; Kalhor, M.M.; Etaee, F.; Gharib, A. Breast cancer research in Iran: A scientometric analysis of publications output from 1991 to 2015 in Scopus. Electron. Phys. 2017, 9, 3816–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asif, H.M.; Sultana, S.; Ahmed, S.; Akhtar, N.; Tariq, M. HER-2 Positive Breast Cancer—A Mini-Review. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2016, 17, 1609–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, R.L.B.; Han, H.S.; Gradishar, W.J. Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in triple-negative breast cancer: A review. Breast Cancer Res. Treat 2018, 169, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamy, M.; Ferreira, A.; Dias, J.S.; Braga, S.; Silva, G.; Barbas, A. Notch-out for breast cancer therapies. New Biotechnol. 2017, 39, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, N.; Shi, H. Driving better and safer HER2-specific CARs for cancer therapy. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 62730–62741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leclercq, G. Natural Anti-Estrogen Receptor Alpha Antibodies Able to Induce Estrogenic Responses in Breast Cancer Cells: Hypotheses Concerning Their Mechanisms of Action and Emergence. Int J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myatt, S.S.; Lam, E.W. The emerging roles of forkhead box (Fox) proteins in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saba, R.; Alsayed, A.; Zacny, J.P.; Dudek, A.Z. The Role of Forkhead Box Protein M1 in Breast Cancer Progression and Resistance to Therapy. Int. J. Breast Cancer 2016, 2016, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, J.M.; Peck, B.; Monteiro, L.J.; Schwenen, H.D.; Millour, J.; Coombes, R.C.; Myatt, S.S.; Lam, E.W. FOXM1 confers acquired cisplatin resistance in breast cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2010, 8, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.Y.; Jia, X.H.; Xing, H.Y.; Li, Y.J.; Fan, W.W.; Li, N.; Xie, S.Y. Inhibition of Forkhead box protein M1 by thiostrepton increases chemosensitivity to doxorubicin in T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 1457–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Cao, X.C.; Cao, J.G.; Liu, F.; Quan, M.F.; Sheng, X.F.; Ren, K.Q. Casticin induces ovarian cancer cell apoptosis by repressing FoxM1 through the activation of FOXO3a. Oncol. Lett. 2013, 5, 1605–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amado, N.G.; Fonseca, B.F.; Cerqueira, D.M.; Neto, V.M.; Abreu, J.G. Flavonoids: Potential Wnt/beta-catenin signaling modulators in cancer. Life Sci. 2011, 89, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Incassati, A.; Chandramouli, A.; Eelkema, R.; Cowin, P. Key signaling nodes in mammary gland development and cancer: Beta-catenin. Breast Cancer Res. 2010, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, R.V.; Shanley, J.; Correll, M.P.; Fieles, W.E.; Keith, R.A.; Scott, C.W.; Lee, C.M. Regulation and localization of tyrosine216 phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in cellular and animal models of neuronal degeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 11074–11079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Luo, F.; Wei, L.; Liu, Z.; Xu, P. Knockdown of glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta attenuates 6-hydroxydopamine-induced apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 487, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancinelli, R.; Carpino, G.; Petrungaro, S.; Mammola, C.L.; Tomaipitinca, L.; Filippini, A.; Facchiano, A.; Ziparo, E.; Giampietri, C. Multifaceted Roles of GSK-3 in Cancer and Autophagy-Related Diseases. Oxid Med. Cell Longev. 2017, 2017, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millimouno, F.M.; Dong, J.; Yang, L.; Li, J.; Li, X. Targeting apoptosis pathways in cancer and perspectives with natural compounds from mother nature. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila.) 2014, 7, 1081–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Khor, T.O.; Shu, L.; Su, Z.Y.; Fuentes, F.; Lee, J.H.; Kong, A.N. Plants vs. cancer: A review on natural phytochemicals in preventing and treating cancers and their druggability. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 1281–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerella, C.; Radogna, F.; Dicato, M.; Diederich, M. Natural compounds as regulators of the cancer cell metabolism. Int. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 2013, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishayee, A.; Ahmed, S.; Brankov, N.; Perloff, M. Triterpenoids as potential agents for the chemoprevention and therapy of breast cancer. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2011, 16, 980–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceylan-Isik, A.F.; Fliethman, R.M.; Wold, L.E.; Ren, J. Herbal and traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of cardiovascular complications in diabetes mellitus. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2008, 4, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, F.J.; Ho, T.J.; Cheng, C.F.; Shiao, Y.T.; Chien, W.K.; Chen, J.H.; Liu, X.; Tsang, H.; Lin, T.H.; Liao, C.C.; et al. Characteristics of Chinese herbal medicine usage in ischemic heart disease patients among type 2 diabetes and their protection against hydrogen peroxide-mediated apoptosis in H9C2 cardiomyoblasts. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 15470–15489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.X.; Liu, T.H.; Huang, Z.T.; Li, J.E.; Wu, L.L. Research progress on the mechanism of single-Chinese medicinal herbs in treating diabetes mellitus. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 2011, 17, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.G.; Matsuzaki, K.; Takamatsu, S.; Kitanaka, S. Inhibitory effects of constituents from Morus alba var. multicaulis on differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells and nitric oxide production in RAW264.7 cells. Molecules 2011, 16, 6010–6022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, T.; Hano, Y.; Fukai, T. Chemistry and biosynthesis of isoprenylated flavonoids from Japanese mulberry tree. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 2009, 85, 391–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nomura, T. Chemistry and biosynthesis of prenylflavonoids. Yakugaku Zasshi 2001, 121, 535–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, S.J.; Lu, Z.M.; Chen, R.Y.; Yu, D.Q. Structure and spectral characteristics of Diels-Alder type adducts from Morus. Yao Xue Xue Bao 2005, 40, 876–881. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Orhan, I.; Tosun, F.; Sener, B. Coumarin, anthroquinone and stilbene derivatives with anticholinesterase activity. Z. Naturforsch. C J. Biosci. 2008, 63, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagawa, S.; Gu, J.; Honda, T.; McDonnell, T.J.; Swisher, S.G.; Roth, J.A.; Fang, B. Deficiency of caspase-3 in MCF7 cells blocks Bax-mediated nuclear fragmentation but not cell death. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 1474–1480. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, X. Caspase-3 status is a determinant of the differential responses to genistein between MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1773, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foo, J.B.; Yazan, L.S.; Tor, Y.S.; Armania, N.; Ismail, N.; Imam, M.U.; Yeap, S.K.; Cheah, Y.K.; Abdullah, R.; Ismail, M. Induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in caspase-3 deficient MCF-7 cells by Dillenia suffruticosa root extract via multiple signalling pathways. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, L.; Chiang, L.; He, B.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Winoto, A. FoxM1, a forkhead transcription factor is a master cell cycle regulator for mouse mature T cells but not double positive thymocytes. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wierstra, I. The transcription factor FOXM1 (Forkhead box M1): Proliferation-specific expression, transcription factor function, target genes, mouse models, and normal biological roles. Adv. Cancer Res. 2013, 118, 97–398. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bao, B.; Wang, Z.; Ali, S.; Kong, D.; Banerjee, S.; Ahmad, A.; Li, Y.; Azmi, A.S.; Miele, L.; Sarkar, F.H. Over-expression of FoxM1 leads to epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell phenotype in pancreatic cancer cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2011, 112, 2296–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chiu, W.T.; Huang, Y.F.; Tsai, H.Y.; Chen, C.C.; Chang, C.H.; Huang, S.C.; Hsu, K.F.; Chou, C.Y. FOXM1 confers to epithelial-mesenchymal transition, stemness and chemoresistance in epithelial ovarian carcinoma cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 2349–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, U.G.; Halasi, M.; Gartel, A.L. Thiazole antibiotics target FoxM1 and induce apoptosis in human cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Cui, J.; Xie, K. Signaling of miRNAs-FOXM1 in cancer and potential targeted therapy. Curr. Drug Targets 2013, 14, 1192–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, I.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Hughes, D.E.; Ackerson, T.; Major, M.L.; Kalinichenko, V.V.; Costa, R.H.; Raychaudhuri, P.; Tyner, A.L.; Lau, L.F. FoxM1 regulates transcription of JNK1 to promote the G1/S transition and tumor cell invasiveness. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 20770–20778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, I.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Hughes, D.; Petrovic, V.; Major, M.L.; Park, H.J.; Tan, Y.; Ackerson, T.; Costa, R.H. Forkhead box M1 regulates the transcriptional network of genes essential for mitotic progression and genes encoding the SCF (Skp2-Cks1) ubiquitin ligase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 10875–10894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Chen, L.; Yie, L.; Wei, L.; Wen, T.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H. Targeting FoxM1 inhibits proliferation, invasion and migration of nasopharyngeal carcinoma through the epithelialto-mesenchymal transition pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 2402–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Lou, G.; Huang, G.; Chen, B.; Shen, X.; Gao, M.; Gong, W.; Zhou, P.; et al. LXRalpha-mediated downregulation of FOXM1 suppresses the proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncogene 2014, 33, 2888–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Quail, E.; Hung, N.J.; Tan, Y.; Ye, H.; Costa, R.H. Increased levels of forkhead box M1B transcription factor in transgenic mouse hepatocytes prevent age-related proliferation defects in regenerating liver. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 11468–11473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Halasi, M.; Gartel, A.L. Suppression of FOXM1 sensitizes human cancer cells to cell death induced by DNA-damage. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nestal de Moraes, G.; Delbue, D.; Silva, K.L.; Robaina, M.C.; Khongkow, P.; Gomes, A.R.; Zona, S.; Crocamo, S.; Mencalha, A.L.; Magalhaes, L.M.; et al. FOXM1 targets XIAP and Survivin to modulate breast cancer survival and chemoresistance. Cell. Signal. 2015, 27, 2496–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiurillo, M.A. Role of the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in gastric cancer: An in-depth literature review. World J. Exp. Med. 2015, 5, 84–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ring, A.; Kim, Y.M.; Kahn, M. Wnt/catenin signaling in adult stem cell physiology and disease. Stem Cell. Rev. 2014, 10, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Wei, P.; Gong, A.; Chiu, W.T.; Lee, H.T.; Colman, H.; Huang, H.; Xue, J.; Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; et al. FoxM1 promotes beta-catenin nuclear localization and controls Wnt target-gene expression and glioma tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 2011, 20, 427–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, B.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Du, X.; Ding, K.; Pan, J. Anthelmintic Niclosamide Disrupts the Interplay of p65 and FOXM1/beta-catenin and Eradicates Leukemia Stem Cells in Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 789–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Xue, J.; Gong, A.; Yu, G.; Zhou, A.; Lin, K.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, N.; Gottardi, C.J.; et al. Wnt-induced deubiquitination FoxM1 ensures nucleus beta-catenin transactivation. EMBO J. 2016, 35, 668–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hwang, S.M.; Lee, H.-J.; Jung, J.H.; Sim, D.Y.; Hwang, J.; Park, J.E.; Shim, B.S.; Kim, S.-H. Inhibition of Wnt3a/FOXM1/β-Catenin Axis and Activation of GSK3β and Caspases are Critically Involved in Apoptotic Effect of Moracin D in Breast Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2681. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092681
Hwang SM, Lee H-J, Jung JH, Sim DY, Hwang J, Park JE, Shim BS, Kim S-H. Inhibition of Wnt3a/FOXM1/β-Catenin Axis and Activation of GSK3β and Caspases are Critically Involved in Apoptotic Effect of Moracin D in Breast Cancers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(9):2681. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092681
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, Sung Min, Hyo-Jung Lee, Ji Hoon Jung, Deok Yong Sim, Jisung Hwang, Ji Eon Park, Bum Sang Shim, and Sung-Hoon Kim. 2018. "Inhibition of Wnt3a/FOXM1/β-Catenin Axis and Activation of GSK3β and Caspases are Critically Involved in Apoptotic Effect of Moracin D in Breast Cancers" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 9: 2681. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092681
APA StyleHwang, S. M., Lee, H.-J., Jung, J. H., Sim, D. Y., Hwang, J., Park, J. E., Shim, B. S., & Kim, S.-H. (2018). Inhibition of Wnt3a/FOXM1/β-Catenin Axis and Activation of GSK3β and Caspases are Critically Involved in Apoptotic Effect of Moracin D in Breast Cancers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(9), 2681. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092681