TOP2B: The First Thirty Years
Abstract
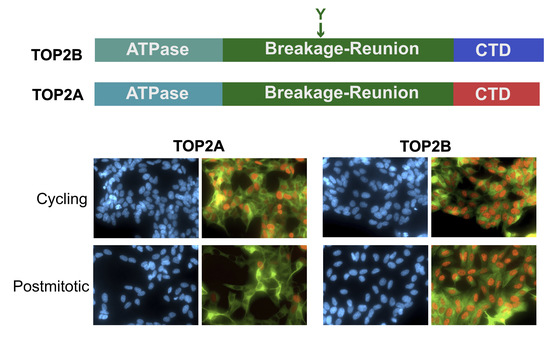
:1. Discovery of DNA Topoisomerase IIβ (TOP2B) Protein
2. Cloning the cDNA Encoding TOP2B
3. Protein Characterisation
4. Expression of TOP2B
5. TOP2B In Vivo Functions
6. TOP2B as an Anti-Cancer Drug Target
7. TOP2B Cell Biology–Cell Cycle Expression
8. Subcellular Location of TOP2B Protein
9. Protein–Protein Interactions
10. Transcriptional Roles of TOP2B
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CTCF | CCCTC-binding factor |
| CTD | C terminal domain |
| DSB | Double strand DNA break |
| t-AML | Therapy-related acute myeloid leukaemia |
| TARDIS | Trapped in agarose DNA immunostaining |
| TOP2A | DNA topoisomerase IIα |
| TOP2B | DNA topoisomerase IIβ |
| TOP2 | DNA topoisomerase II |
| ts | Temperature sensitive |
References
- Drake, F.H.; Zimmerman, J.P.; McCabe, F.L.; Bartus, H.F.; Per, S.R.; Sullivan, D.M.; Ross, W.E.; Mattern, M.R.; Johnson, R.K.; Crooke, S.T. Purification of topoisomerase II from amsacrine-resistant P388 leukemia cells. Evidence for two forms of the enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 16739–16747. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Per, S.R.; Mattern, M.R.; Mirabelli, C.K.; Drake, F.H.; Johnson, R.K.; Crooke, S.T. Characterization of a subline of P388 leukemia resistant to amsacrine: Evidence of altered topoisomerase II function. Mol. Pharmacol. 1987, 32, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Holden, J.A.; Rolfson, D.H.; Wittwer, C.T. Human DNA topoisomerase II: Evaluation of enzyme activity in normal and neoplastic tissues. Biochemistry 1990, 29, 2127–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roca, J.; Mezquita, C. DNA topoisomerase II activity in nonreplicating, transcriptionally inactive, chicken late spermatids. EMBO J. 1989, 8, 1855–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, T.D.; Drake, F.H.; Tan, K.B.; Per, S.R.; Crooke, S.T.; Mirabelli, C.K. Characterization and immunological identification of cDNA clones encoding two human DNA topoisomerase II isozymes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 9431–9435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai-Pflugfelder, M.; Liu, L.F.; Liu, A.A.; Tewey, K.M.; Whang-Peng, J.; Knutsen, T.; Huebner, K.; Croce, C.M.; Wang, J.C. Cloning and sequencing of cDNA encoding human DNA topoisomerase II and localization of the gene to chromosome region 17q21-22. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 7177–7181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, K.L.; Meczes, E.L.; Thorn, R.; Turnbull, R.M.; Marshall, R.; Austin, C.A. Mutagenesis of E477 or K505 in the B’ domain of human topoisomerase IIβ increases the requirement for magnesium ions during strand passage. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 1223–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leontiou, C.; Watters, G.P.; Gilroy, K.L.; Heslop, P.; Cowell, I.G.; Craig, K.; Lightowlers, R.N.; Lakey, J.H.; Austin, C.A. Differential selection of acridine resistance mutations in human DNA topoisomerase IIβ is dependent on the acridine structure. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 71, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, C.A.; Marsh, K.L.; Wasserman, R.A.; Willmore, E.; Sayer, P.J.; Wang, J.C.; Fisher, L.M. Expression, domain structure, and enzymatic properties of an active recombinant human DNA topoisomerase IIβ. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 15739–15746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, C.A.; Fisher, L.M. Isolation and characterization of a human cDNA clone encoding a novel DNA topoisomerase II homologue from HeLa cells. FEBS Lett. 1990, 266, 115–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Austin, C.A.; Sng, J.H.; Patel, S.; Fisher, L.M. Novel HeLa topoisomerase II is the IIβ isoform: Complete coding sequence and homology with other type II topoisomerases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1993, 1172, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, C.A.; Barot, H.; Margerrison, E.E.C.; Hayes, M.V.; Fisher, L.M. Biochemical and immunological characterization of mammalian DNA topoisomerase II. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1989, 17, 528–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsutsui, K.; Okada, S.; Watanabe, M.; Shohmori, T.; Seki, S.; Inoue, Y. Molecular cloning of partial cDNAs for rat DNA topoisomerase II isoforms and their differential expression in brain development. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 19076–19083. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, J.R.; Ayton, P.; Jones, T.; Davies, S.L.; Simmons, D.L.; Harris, A.L.; Sheer, D.; Hickson, I.D. Isolation of cDNA clones encoding the β isozyme of human DNA topoisomerase II and localisation of the gene to chromosome 3p24. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992, 20, 5587–5592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, K.B.; Dorman, T.E.; Falls, K.M.; Chung, T.D.; Mirabelli, C.K.; Crooke, S.T.; Mao, J. Topoisomerase IIα and topoisomerase IIβ genes: Characterization and mapping to human chromosomes 17 and 3, respectively. Cancer Res. 1992, 52, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lang, A.J.; Mirski, S.E.; Cummings, H.J.; Yu, Q.; Gerlach, J.H.; Cole, S.P. Structural organization of the human TOP2A and TOP2B genes. Gene 1998, 221, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sng, J.H.; Heaton, V.J.; Bell, M.; Maini, P.; Austin, C.A.; Fisher, L.M. Molecular cloning and characterization of the human topoisomerase IIα and IIβ genes: Evidence for isoform evolution through gene duplication. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1444, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, S.L.; Jenkins, J.R.; Hickson, I.D. Human cells express two differentially spliced forms of topoisomerase IIβ mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993, 21, 3719–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ng, S.W.; Liu, Y.; Schnipper, L.E. Cloning and characterization of the 5′-flanking sequence for the human DNA topoisomerase IIβ gene. Gene 1997, 203, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lok, C.-N.; Lang, A.J.; Mirski, S.E.L.; Cole, S.P.C. Characterization of the human topoisomerase IIβ (TOP2B) promoter activity: Essential roles of the nuclear factor-Y (NF-Y)- and specificity protein-1 (Sp1)-binding sites. Biochem. J. 2002, 368, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heng, X.; Jin, G.; Zhang, X.; Yang, D.; Zhu, M.; Fu, S.; Li, X.; Le, W. Nurr1 regulates Top IIβ and functions in axon genesis of mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons. Mol. Neurodegen. 2012, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aravind, L.; Leipe, D.D.; Koonin, E.V. Toprim—A conserved catalytic domain in type IA and II topoisomerases, DnaG-type primases, OLD family nucleases and RecR proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998, 26, 4205–4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.-C.; Li, T.-K.; Farh, L.; Lin, L.-Y.; Lin, T.-S.; Yu, Y.-J.; Yen, T.-J.; Chiang, C.-W.; Chan, N.-L. Structural basis of type II topoisomerase inhibition by the anticancer drug etoposide. Science 2011, 333, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendorff, T.J.; Schmidt, B.H.; Heslop, P.; Austin, C.A.; Berger, J.M. The structure of DNA-bound human topoisomerase IIα: Conformational mechanisms for coordinating inter-subunit interactions with DNA cleavage. J. Mol. Biol. 2012, 424, 109–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, J.M.; Gamblin, S.J.; Harrison, S.C.; Wang, J.C. Structure and mechanism of DNA topoisomerase II. Nature 1996, 379, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.H.; Chan, N.-L.; Hsieh, T. New Mechanistic and Functional Insights into DNA Topoisomerases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2013, 82, 139–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.-C.; Wang, Y.-R.; Chen, S.-F.; Wu, C.-C.; Chan, N.-L. New insights into DNA-binding by type IIA topoisomerases. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2013, 23, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Ruthenburg, A.J.; Bechis, S.K.; Verdine, G.L. Nucleotide-dependent domain movement in the ATPase domain of a human type IIA DNA topoisomerase. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 37041–37047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, C.A.; Marsh, K.L. Eukaryotic DNA topoisomerase IIβ. Bioessays 1998, 20, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meczes, E.L.; Gilroy, K.L.; West, K.L.; Austin, C.A. The impact of the human DNA topoisomerase II C-terminal domain on activity. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilroy, K.L.; Austin, C.A. The Impact of the C-Terminal Domain on the Interaction of Human DNA Topoisomerase IIα and β with DNA. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e14693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linka, R.M.; Porter, A.C.G.; Volkov, A.; Mielke, C.; Boege, F.; Christensen, M.O. C-terminal regions of topoisomerase IIα and IIβ determine isoform-specific functioning of the enzymes in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 3810–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozuki, T.; Chikamori, K.; Surleac, M.D.; Micluta, M.A.; Petrescu, A.J.; Norris, E.J.; Elson, P.; Hoeltge, G.A.; Grabowski, D.R.; Porter, A.C.G.; et al. Roles of the C-terminal domains of topoisomerase IIα and topoisomerase IIβ in regulation of the decatenation checkpoint. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 5995–6010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capranico, G.; Tinelli, S.; Austin, C.A.; Fisher, M.L.; Zunino, F. Different patterns of gene expression of topoisomerase II isoforms in differentiated tissues during murine development. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1992, 1132, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandvliet, D.W.; Hanby, A.M.; Austin, C.A.; Marsh, K.L.; Clark, I.B.; Wright, N.A.; Poulsom, R. Analysis of foetal expression sites of human type II DNA topoisomerase α and β mRNAs by in situ hybridisation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1996, 1307, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkin, L.F.; Gerrelli, D.; Gold Diaz, D.C.; Santos, C.; Alzu’bi, A.; Austin, C.A.; Clowry, G.J. Distinct expression patterns for type II topoisomerases IIA and IIB in the early foetal human telencephalon. J. Anat. 2016, 228, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondapi, A.K.; Mulpuri, N.; Mandraju, R.K.; Sasikaran, B.; Subba Rao, K. Analysis of age dependent changes of Topoisomerase IIα and β in rat brain. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2004, 22, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juenke, J.M.; Holden, J.A. The distribution of DNA topoisomerase II isoforms in differentiated adult mouse tissues. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1993, 1216, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauman, M.E.; Holden, J.A.; Brown, K.A.; Harker, W.G.; Perkins, S.L. Differential immunohistochemical staining for DNA topoisomerase IIα and β in human tissues and for DNA topoisomerase IIβ in non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. Mod. Pathol. 1997, 10, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Turley, H.; Comley, M.; Houlbrook, S.; Nozaki, N.; Kikuchi, A.; Hickson, I.D.; Gatter, K.; Harris, A.L. The distribution and expression of the two isoforms of DNA topoisomerase II in normal and neoplastic human tissues. Br. J. Cancer 1997, 75, 1340–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meczes, E.L.; Marsh, K.L.; Fisher, L.M.; Rogers, M.P.; Austin, C.A. Complementation of temperature-sensitive topoisomerase II mutations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by a human TOP2β construct allows the study of topoisomerase IIβ inhibitors in yeast. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1997, 39, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, S.; Redwood, C.S.; Jenkins, J.R.; Andersen, A.H.; Hickson, I.D. Human DNA topoisomerases IIα and IIβ can functionally substitute for yeast TOP2 in chromosome segregation and recombination. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1996, 252, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grue, P.; Grässer, A.; Sehested, M.; Jensen, P.B.; Uhse, A.; Straub, T.; Ness, W.; Boege, F. Essential mitotic functions of DNA topoisomerase IIα are not adopted by topoisomerase IIβ in human H69 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 33660–33666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, R.E.; Lim, C.-U.; Cole, K.; Bianchini, C.H.; Schools, G.P.; Davis, B.E.; Wada, I.; Roninson, I.B.; Broude, E.V. Effects of conditional depletion of topoisomerase II on cell cycle progression in mammalian cells. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 3505–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akimitsu, N.; Adachi, N.; Hirai, H.; Hossain, M.S.; Hamamoto, H.; Kobayashi, M.; Aratani, Y.; Koyama, H.; Sekimizu, K. Enforced cytokinesis without complete nuclear division in embryonic cells depleting the activity of DNA topoisomerase IIα. Genes Cells 2003, 8, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Li, W.; Prescott, E.D.; Burden, S.J.; Wang, J.C. DNA topoisomerase IIβ and neural development. Science 2000, 287, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, Y.L.; Wang, J.C. Aberrant lamination in the cerebral cortex of mouse embryos lacking DNA topoisomerase IIβ. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 7123–7128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nur-E-Kamal, A.; Meiners, S.; Ahmed, I.; Azarova, A.; Lin, C.; Lyu, Y.L.; Liu, L.F. Role of DNA topoisomerase IIβ in neurite outgrowth. Brain Res. 2007, 1154, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaim, M.; Isik, S. DNA topoisomerase IIβ stimulates neurite outgrowth in neural differentiated human mesenchymal stem cells through regulation of Rho-GTPases (RhoA/Rock2 pathway) and Nurr1 expression. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, V.K.; Burger, L.; Nikoletopoulou, V.; Deogracias, R.; Thakurela, S.; Wirbelauer, C.; Kaut, J.; Terranova, R.; Hoerner, L.; Mielke, C.; et al. Target genes of Topoisomerase IIβ regulate neuronal survival and are defined by their chromatin state. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E934–E943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Bawa-Khalfe, T.; Lu, L.-S.; Lyu, Y.L.; Liu, L.F.; Yeh, E.T.H. Identification of the molecular basis of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1639–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amsterdam, A.; Nissen, R.M.; Sun, Z.; Swindell, E.C.; Farrington, S.; Hopkins, N. Identification of 315 genes essential for early zebrafish development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 12792–12797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sapetto-Rebow, B.; McLoughlin, S.C.; O’Shea, L.C.; O’Leary, O.; Willer, J.R.; Alvarez, Y.; Collery, R.; O’Sullivan, J.; van Eeden, F.; Hensey, C.; et al. Maternal topoisomerase IIα, not topoisomerase IIβ, enables embryonic development of zebrafish top2a-/- mutants. BMC Dev. Biol. 2011, 11, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dovey, M.; Patton, E.E.; Bowman, T.; North, T.; Goessling, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zon, L.I. Topoisomerase IIα is required for embryonic development and liver regeneration in zebrafish. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 3746–3753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevin, L.M.; Xiao, T.; Staub, W.; Baier, H. Topoisomerase IIβ is required for lamina-specific targeting of retinal ganglion cell axons and dendrites. Development 2011, 138, 2457–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaman, J.A.; Yamauchi, Y.; Ward, W.S. Sperm DNA fragmentation: Awakening the sleeping genome. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2007, 35, 626–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leduc, F.; Maquennehan, V.; Nkoma, G.B.; Boissonneault, G. DNA damage response during chromatin remodeling in elongating spermatids of mice. Biol. Reprod. 2008, 78, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer-Ficca, M.L.; Lonchar, J.D.; Ihara, M.; Meistrich, M.L.; Austin, C.A.; Meyer, R.G. Poly (ADP-Ribose) polymerases PARP1 and PARP2 modulate Topoisomerase IIβ (TOP2B) function during chromatin condensation in mouse spermiogenesis. Biol. Reprod. 2011, 84, 900–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, R.G.; Ketchum, C.C.; Meyer-Ficca, M.L. Heritable sperm chromatin epigenetics: A break to remember. Biol. Reprod. 2017, 97, 784–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, W.S. Regulating DNA supercoiling: Sperm points the way. Biol. Reprod. 2011, 84, 841–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, W.S. Organization of sperm DNA by the nuclear matrix. Am. J. Clin. Exp. Urol. 2018, 6, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Güneş, S.; Kulaç, T. The role of epigenetics in spermatogenesis. Turk. J. Urol. 2013, 39, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, J.L.; Hsieh, C.-M.; Chan, N.-L.; Hiasa, H. Topoisomerases as anticancer targets. Biochem. J. 2018, 475, 373–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pommier, Y. Drugging topoisomerases: Lessons and challenges. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 82–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitiss, J.L. Targeting DNA topoisomerase II in cancer chemotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heinicke, T.; Labopin, M.; Schmid, C.; Polge, E.; Socié, G.; Blaise, D.; Mufti, G.J.; Huynh, A.; Brecht, A.; Ledoux, M.-P.; et al. Reduced relapse incidence with FLAMSA-RIC compared with busulfan/fludarabine for acute myelogenous leukemia patients in first or second complete remission: A study from the acute leukemia working party of the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errington, F.; Willmore, E.; Tilby, M.J.; Li, L.; Li, G.; Li, W.; Baguley, B.C.; Austin, C.A. Murine transgenic cells lacking DNA topoisomerase IIβ are resistant to acridines and mitoxantrone: Analysis of cytotoxicity and cleavable complex formation. Mol. Pharmacol. 1999, 56, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyoda, E.; Kagaya, S.; Cowell, I.G.; Kurosawa, A.; Kamoshita, K.; Nishikawa, K.; Iiizumi, S.; Koyama, H.; Austin, C.A.; Adachi, N. NK314, a topoisomerase II inhibitor that specifically targets the α isoform. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 23711–23720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.C.; Bramley, R.L.; Cowell, I.G.; Jackson, G.H.; Austin, C.A. Proteasomal inhibition potentiates drugs targeting DNA topoisomerase II. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilroy, K.L.; Leontiou, C.; Padget, K.; Lakey, J.H.; Austin, C.A. mAMSA resistant human topoisomerase IIβ mutation G465D has reduced ATP hydrolysis activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 1597–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leontiou, C.; Lakey, J.H.; Austin, C.A. Mutation E522K in human DNA topoisomerase IIβ confers resistance to methyl N-(4′-(9-acridinylamino)-phenyl) carbamate hydrochloride and methyl N-(4′-(9-acridinylamino)-3-methoxy-phenyl) methane sulfonamide but hypersensitivity to etoposide. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 66, 430–439. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leontiou, C.; Lakey, J.H.; Lightowlers, R.; Turnbull, R.M.; Austin, C.A. Mutation P732L in human DNA topoisomerase IIβ abolishes DNA cleavage in the presence of calcium and confers drug resistance. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006, 69, 130–139. [Google Scholar]
- Cowell, I.G.; Tilby, M.J.; Austin, C.A. An overview of the visualisation and quantitation of low and high MW DNA adducts using the trapped in agarose DNA immunostaining (TARDIS) assay. Mutagenesis 2011, 26, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowell, I.G.; Austin, C.A. Visualization and Quantification of Topoisomerase-DNA Covalent Complexes Using the Trapped in Agarose Immunostaining (TARDIS) Assay. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1703, 301–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willmore, E.; Frank, A.J.; Padget, K.; Tilby, M.J.; Austin, C.A. Etoposide targets topoisomerase IIα and IIβ in leukemic cells: Isoform-specific cleavable complexes visualized and quantified in situ by a novel immunofluorescence technique. Mol. Pharmacol. 1998, 54, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Errington, F.; Willmore, E.; Leontiou, C.; Tilby, M.J.; Austin, C.A. Differences in the longevity of topo IIα and topo IIβ drug-stabilized cleavable complexes and the relationship to drug sensitivity. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2004, 53, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atwal, M.; Lishman, E.L.; Austin, C.A.; Cowell, I.G. Myeloperoxidase enhances etoposide and mitoxantrone mediated DNA damage: A target for myeloprotection in cancer chemotherapy. Mol. Pharmacol. 2017, 91, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowell, I.G.; Austin, C.A. Mechanism of generation of therapy related leukemia in response to anti-topoisomerase II agents. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 2075–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowley, J.D.; Olney, H.J. International workshop on the relationship of prior therapy to balanced chromosome aberrations in therapy-related myelodysplastic syndromes and acute leukemia: Overview report. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2002, 33, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allan, J.M.; Travis, L.B. Mechanisms of therapy-related carcinogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 943–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felix, C.A. Secondary leukemias induced by topoisomerase-targeted drugs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1400, 233–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowell, I.G.; Sondka, Z.; Smith, K.; Lee, K.C.; Manville, C.M.; Sidorczuk-Lesthuruge, M.; Rance, H.A.; Padget, K.; Jackson, G.H.; Adachi, N.; et al. Model for MLL translocations in therapy-related leukemia involving topoisomerase IIβ-mediated DNA strand breaks and gene proximity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 8989–8994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.A.; Cowell, I.G.; Zhang, Y.; Sondka, Z.; Austin, C.A. The role of topoisomerase IIβ on breakage and proximity of RUNX1 to partner alleles RUNX1T1 and EVI1. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2014, 53, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azarova, A.M.; Lyu, Y.L.; Lin, C.-P.; Tsai, Y.-C.; Lau, J.Y.-N.; Wang, J.C.; Liu, L.F. Roles of DNA topoisomerase II isozymes in chemotherapy and secondary malignancies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11014–11019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haffner, M.C.; Aryee, M.J.; Toubaji, A.; Esopi, D.M.; Albadine, R.; Gurel, B.; Isaacs, W.B.; Bova, G.S.; Liu, W.; Xu, J.; et al. Androgen-induced TOP2B-mediated double-strand breaks and prostate cancer gene rearrangements. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 668–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cowell, I.G.; Austin, C.A. Do transcription factories and TOP2B provide a recipe for chromosome translocations in therapy-related leukemia? Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 3143–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uusküla-Reimand, L.; Hou, H.; Samavarchi-Tehrani, P.; Rudan, M.V.; Liang, M.; Medina-Rivera, A.; Mohammed, H.; Schmidt, D.; Schwalie, P.; Young, E.J.; et al. Topoisomerase IIβ interacts with cohesin and CTCF at topological domain borders. Genome Biol. 2016, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vian, L.; Pękowska, A.; Rao, S.S.P.; Kieffer-Kwon, K.-R.; Jung, S.; Baranello, L.; Huang, S.-C.; El Khattabi, L.; Dose, M.; Pruett, N.; et al. The energetics and physiological impact of cohesin extrusion. Cell 2018, 173, 1165–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canela, A.; Maman, Y.; Jung, S.; Wong, N.; Callen, E.; Day, A.; Kieffer-Kwon, K.-R.; Pekowska, A.; Zhang, H.; Rao, S.S.P.; et al. Genome organization drives chromosome fragility. Cell 2017, 170, 507–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.S.P.; Huang, S.-C.; Glenn St Hilaire, B.; Engreitz, J.M.; Perez, E.M.; Kieffer-Kwon, K.-R.; Sanborn, A.L.; Johnstone, S.E.; Bascom, G.D.; Bochkov, I.D.; et al. Cohesin loss eliminates all loop domains. Cell 2017, 171, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dereuddre, S.; Delaporte, C.; Jacquemin-Sablon, A. Role of topoisomerase IIβ in the resistance of 9-OH-ellipticine-resistant Chinese hamster fibroblasts to topoisomerase II inhibitors. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 4301–4308. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dereuddre, S.; Frey, S.; Delaporte, C.; Jacquemin-Sablon, A. Cloning and characterization of full-length cDNAs coding for the DNA topoisomerase IIβ from Chinese hamster lung cells sensitive and resistant 9-OH-ellipticine. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1995, 1264, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woessner, R.D.; Chung, T.D.; Hofmann, G.A.; Mattern, M.R.; Mirabelli, C.K.; Drake, F.H.; Johnson, R.K. Differences between normal and ras-transformed NIH-3T3 cells in expression of the 170kD and 180kD forms of topoisomerase II. Cancer Res. 1990, 50, 2901–2908. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Woessner, R.D.; Mattern, M.R.; Mirabelli, C.K.; Johnson, R.K.; Drake, F.H. Proliferation-and cell cycle-dependent differences in expression of the 170 kilodalton and 180 kilodalton forms of topoisomerase II in NIH-3T3 cells. Cell Growth Differ. 1991, 2, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Padget, K.; Pearson, A.D.; Austin, C.A. Quantitation of DNA topoisomerase IIα and β in human leukaemia cells by immunoblotting. Leukemia 2000, 14, 1997–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oh, E.-J.; Kahng, J.; Kim, Y.; Kim, M.; Lim, J.; Kang, C.S.; Min, W.S.; Cho, B.; Lee, A.; Lee, K.Y.; et al. Expression of functional markers in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2003, 27, 903–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaaijk, P.; Kaspers, G.J.L.; van Wering, E.R.; Broekema, G.J.; Loonen, A.H.; Hählen, K.; Schmiegelow, K.; Janka-Schaub, G.E.; Henze, G.; Creutzig, U.; et al. Cell proliferation is related to in vitro drug resistance in childhood acute leukaemia. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 88, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, D.M.; Glisson, B.S.; Hodges, P.K.; Smallwood-Kentro, S.; Ross, W.E. Proliferation dependence of topoisomerase II mediated drug action. Biochemistry 1986, 25, 2248–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, D.M.; Latham, M.D.; Ross, W.E. Proliferation-dependent topoisomerase II content as a determinant of antineoplastic drug action in human, mouse, and Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cancer Res. 1987, 47, 3973–3979. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chow, K.C.; Ross, W.E. Topoisomerase-specific drug sensitivity in relation to cell cycle progression. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1987, 7, 3119–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markovits, J.; Pommier, Y.; Kerrigan, D.; Covey, J.M.; Tilchen, E.J.; Kohn, K.W. Topoisomerase II-mediated DNA breaks and cytotoxicity in relation to cell proliferation and the cell cycle in NIH 3T3 fibroblasts and L1210 leukemia cells. Cancer Res. 1987, 47, 2050–2055. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schneider, E.; Darkin, S.J.; Robbie, M.A.; Wilson, W.R.; Ralph, R.K. Mechanism of resistance of non-cycling mammalian cells to 4′-[9-acridinylamino]methanesulphon-m-anisidide: Role of DNA topoisomerase II in log- and plateau-phase CHO cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1988, 949, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, P.; Allis, C.D.; Sassone-Corsi, P. Signaling to chromatin through histone modifications. Cell 2000, 103, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Winkfein, R.J.; Mack, G.; Rattner, J.B.; Yen, T.J. CENP-F is a protein of the nuclear matrix that assembles onto kinetochores at late G2 and is rapidly degraded after mitosis. J. Cell Biol. 1995, 130, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, H.; Tammaro, M.; Liao, S. Collision of trapped topoisomerase 2 with transcription and replication: Generation and repair of DNA double-strand breaks with 5′ adducts. Genes 2016, 7, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, N.; Miyaike, M.; Kato, S.; Kanamaru, R.; Koyama, H.; Kikuchi, A. Cellular distribution of mammalian DNA topoisomerase II is determined by its catalytically dispensable C-terminal domain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997, 25, 3135–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mirski, S.E.; Gerlach, J.H.; Cole, S.P. Sequence determinants of nuclear localization in the α and β isoforms of human topoisomerase II. Exp. Cell Res. 1999, 251, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirski, S.E.L.; Bielawski, J.C.; Cole, S.P.C. Identification of functional nuclear export sequences in human topoisomerase IIα and β. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 306, 905–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.G.; Engel, R.; Derderian, J.A.; Jove, R.; Sullivan, D.M. Human topoisomerase IIα nuclear export is mediated by two CRM-1-dependent nuclear export signals. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 3061–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zini, N.; Martelli, A.M.; Sabatelli, P.; Santi, S.; Negri, C.; Astaldi Ricotti, G.C.; Maraldi, N.M. The 180-kDa isoform of topoisomerase II is localized in the nucleolus and belongs to the structural elements of the nucleolar remnant. Exp. Cell Res. 1992, 200, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, P.; Drake, F.H.; Loranger, A.; Huang, W.; Hancock, R. Localization of DNA topoisomerase II in Chinese hamster fibroblasts by confocal and electron microscopy. Exp. Cell Res. 1993, 204, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, K.N.; Kjeldsen, E.; Straub, T.; Knudsen, B.R.; Hickson, I.D.; Kikuchi, A.; Kreipe, H.; Boege, F. Cell cycle-coupled relocation of types I and II topoisomerases and modulation of catalytic enzyme activities. J. Cell Biol. 1997, 136, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaly, N.; Brown, D.L. Is DNA topoisomerase IIβ a nucleolar protein? J. Cell. Biochem. 1996, 63, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowell, I.G.; Willmore, E.; Chalton, D.; Marsh, K.L.; Jazrawi, E.; Fisher, L.M.; Austin, C.A. Nuclear distribution of human DNA topoisomerase IIβ: A nuclear targeting signal resides in the 116-residue C-terminal tail. Exp. Cell Res. 1998, 243, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onoda, A.; Hosoya, O.; Sano, K.; Kiyama, K.; Kimura, H.; Kawano, S.; Furuta, R.; Miyaji, M.; Tsutsui, K.; Tsutsui, K.M. Nuclear dynamics of topoisomerase IIβ reflects its catalytic activity that is regulated by binding of RNA to the C-terminal domain. Nucl. Acids Res. 2014, 42, 9005–9020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cowell, I.G.; Papageorgiou, N.; Padget, K.; Watters, G.P.; Austin, C.A. Histone deacetylase inhibition redistributes topoisomerase IIβ from heterochromatin to euchromatin. Nucleus 2011, 2, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taddei, A.; Maison, C.; Roche, D.; Almouzni, G. Reversible disruption of pericentric heterochromatin and centromere function by inhibiting deacetylases. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 3, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, M.O.; Larsen, M.K.; Barthelmes, H.U.; Hock, R.; Andersen, C.L.; Kjeldsen, E.; Knudsen, B.R.; Westergaard, O.; Boege, F.; Mielke, C. Dynamics of human DNA topoisomerases IIα and IIβ in living cells. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 157, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaly, N.; Chen, X.; Dentry, J.; Brown, D.L. Organization of DNA topoisomerase II isotypes during the cell cycle of human lymphocytes and HeLa cells. Chromosome Res. 1996, 4, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taagepera, S.; Rao, P.N.; Drake, F.H.; Gorbsky, G.J. DNA topoisomerase IIα is the major chromosome protein recognized by the mitotic phosphoprotein antibody MPM-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 8407–8411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Null, A.P.; Hudson, J.; Gorbsky, G.J. Both α and β isoforms of mammalian DNA topoisomerase II associate with chromosomes in mitosis. Cell Growth Differ. 2002, 13, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Low, R.L.; Orton, S.; Friedman, D.B. A truncated form of DNA topoisomerase IIβ associates with the mtDNA genome in mammalian mitochondria. Eur. J. Biochem. 2003, 270, 4173–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.-W.; Yasukawa, T.; Dalla Rosa, I.; Khiati, S.; Pommier, Y. Increased negative supercoiling of mtDNA in TOP1mt knockout mice and presence of topoisomerases IIα and IIβ in vertebrate mitochondria. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 7259–7267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, H.; Yamazaki, T.; Miyatake, S.; Nozaki, N.; Kikuchi, A.; Saito, T. Specific interaction of topoisomerase IIβ and the CD3ε chain of the T cell receptor complex. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 6483–6489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamane, K.; Kawabata, M.; Tsuruo, T. A DNA-topoisomerase-II-binding protein with eight repeating regions similar to DNA-repair enzymes and to a cell-cycle regulator. Eur. J. Biochem. 1997, 250, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.; Desai, S.D.; Liu, L.F. SUMO-1 conjugation to human DNA topoisomerase II isozymes. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 26066–26073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, N.J.; Hickson, I.D. Human topoisomerase IIα is phosphorylated in a cell-cycle phase-dependent manner by a proline-directed kinase. Eur. J. Biochem. 1995, 231, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, N.J.; Fry, A.M.; Guano, F.; Norbury, C.; Hickson, I.D. Cell cycle phase-specific phosphorylation of human topoisomerase IIα. Evidence of a role for protein kinase C. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 28357–28363. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Morrison, C.; Henzing, A.J.; Jensen, O.N.; Osheroff, N.; Dodson, H.; Kandels-Lewis, S.E.; Adams, R.R.; Earnshaw, W.C. Proteomic analysis of human metaphase chromosomes reveals topoisomerase IIα as an Aurora B substrate. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 5318–5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardenas, M.E.; Gasser, S.M. Regulation of topoisomerase II by phosphorylation: A role for casein kinase II. J. Cell Sci. 1993, 104, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Olsen, J.V.; Blagoev, B.; Gnad, F.; Macek, B.; Kumar, C.; Mortensen, P.; Mann, M. Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks. Cell 2006, 127, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukunaga, R.; Hunter, T. MNK1, a new MAP kinase-activated protein kinase, isolated by a novel expression screening method for identifying protein kinase substrates. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 1921–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Manville, C.M. Kinase Associated Genotoxicity. Ph.D. Thesis, Newcastle University, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Plo, I.; Hernandez, H.; Kohlhagen, G.; Lautier, D.; Pommier, Y.; Laurent, G. Overexpression of the atypical protein kinase C zeta reduces topoisomerase II catalytic activity, cleavable complexes formation, and drug-induced cytotoxicity in monocytic U937 leukemia cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 31407–31415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, B.H.; Kim, T.H.; Bae, Y.S. Mapping of the interaction domain of the protein kinase CKIIβ subunit with target proteins. Mol. Cells 2001, 12, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cowell, I.G.; Okorokov, A.L.; Cutts, S.A.; Padget, K.; Bell, M.; Milner, J.; Austin, C.A. Human topoisomerase IIα and IIβ interact with the C-terminal region of p53. Exp. Cell Res. 2000, 255, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuwen, H.; Hsia, C.C.; Nakashima, Y.; Evangelista, A.; Tabor, E. Binding of wild-type p53 by topoisomerase II and overexpression of topoisomerase II in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 234, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, H.; Goodrich, D.W. The retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein is required for efficient processing and repair of trapped topoisomerase II-DNA-cleavable complexes. Oncogene 2005, 24, 8105–8113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cridland, P.; (Newcastle University, Newcastle upon Tyne, UK). Personal communication, 2018.
- Tsai, S.C.; Valkov, N.; Yang, W.M.; Gump, J.; Sullivan, D.; Seto, E. Histone deacetylase interacts directly with DNA topoisomerase II. Nat. Genet. 2000, 26, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNamara, S.; Wang, H.; Hanna, N.; Miller, W.H. Topoisomerase IIβ negatively modulates retinoic acid receptora function: A novel mechanism of retinoic acid resistance. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 2066–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, B.-G.; Solum, D.; Song, E.J.; Lee, K.-J.; Rose, D.W.; Glass, C.K.; Rosenfeld, M.G. Activating the PARP-1 Sensor Component of the Groucho/TLE1 Corepressor Complex Mediates a CaMKinase IIδ-Dependent Neurogenic Gene Activation Pathway. Cell 2004, 119, 815–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, B.G.; Lunyak, V.V.; Perissi, V.; Garcia-Bassets, I.; Rose, D.W.; Glass, C.K.; Rosenfeld, M.G. A topoisomerase IIβ-mediated dsDNA break required for regulated transcription. Science 2006, 312, 1798–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, R.H.F.; Chang, I.; Hudak, C.S.S.; Hyun, S.; Kwan, H.-Y.; Sul, H.S. A Role of DNA-PK for the Metabolic Gene Regulation in Response to Insulin. Cell 2009, 136, 1056–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matheos, D.; Ruiz, M.T.; Price, G.B.; Zannis-Hadjopoulos, M. Ku antigen, an origin-specific binding protein that associates with replication proteins, is required for mammalian DNA replication. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1578, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Morris, J.H.; Cook, H.; Kuhn, M.; Wyder, S.; Simonovic, M.; Santos, A.; Doncheva, N.T.; Roth, A.; Bork, P.; et al. The STRING database in 2017: Quality-controlled protein–protein association networks, made broadly accessible. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D362–D368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, C.A.; Barot, H.A.; Margerrison, E.E.; Turcatti, G.; Wingfield, P.; Hayes, M.V.; Fisher, L.M. Structure and partial amino acid sequence of calf thymus DNA topoisomerase II: Comparison with other type II enzymes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1990, 170, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.F.; Wang, J.C. Supercoiling of the DNA template during transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 7024–7027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakurela, S.; Garding, A.; Jung, J.; Schübeler, D.; Burger, L.; Tiwari, V.K. Gene regulation and priming by topoisomerase IIα in embryonic stem cells. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perillo, B.; Ombra, M.N.; Bertoni, A.; Cuozzo, C.; Sacchetti, S.; Sasso, A.; Chiariotti, L.; Malorni, A.; Abbondanza, C.; Avvedimento, E.V. DNA oxidation as triggered by H3K9me2 demethylation drives estrogen-induced gene expression. Science 2008, 319, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNamara, S.; Nichol, J.N.; Wang, H.; Miller, W.H. Targeting PKCδ-mediated topoisomerase IIβ overexpression subverts the differentiation block in a retinoic acid-resistant APL cell line. Leukemia 2010, 24, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Puc, J.; Aggarwal, A.K.; Rosenfeld, M.G. Physiological functions of programmed DNA breaks in signal-induced transcription. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sano, K.; Miyaji-Yamaguchi, M.; Tsutsui, K.M.; Tsutsui, K. Topoisomerase IIβ activates a subset of neuronal genes that are repressed in AT-rich genomic environment. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manville, C.M.; Smith, K.; Sondka, Z.; Rance, H.; Cockell, S.; Cowell, I.G.; Lee, K.C.; Morris, N.J.; Padget, K.; Jackson, G.H.; et al. Genome-wide ChIP-seq analysis of human TOP2B occupancy in MCF7 breast cancer epithelial cells. Biol. Open 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, W.; Kawauchi, D.; Körkel-Qu, H.; Deng, H.; Serger, E.; Sieber, L.; Lieberman, J.A.; Jimeno-González, S.; Lambo, S.; Hanna, B.S.; et al. Chd7 is indispensable for mammalian brain development through activation of a neuronal differentiation programme. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Madabhushi, R.; Gao, F.; Pfenning, A.R.; Pan, L.; Yamakawa, S.; Seo, J.; Rueda, R.; Phan, T.X.; Yamakawa, H.; Pao, P.-C.; et al. Activity-induced DNA breaks govern the expression of neuronal early-response genes. Cell 2015, 161, 1592–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naughton, C.; Avlonitis, N.; Corless, S.; Prendergast, J.G.; Mati, I.K.; Eijk, P.P.; Cockroft, S.L.; Bradley, M.; Ylstra, B.; Gilbert, N. Transcription forms and remodels supercoiling domains unfolding large-scale chromatin structures. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- King, I.F.; Yandava, C.N.; Mabb, A.M.; Hsiao, J.S.; Huang, H.-S.; Pearson, B.L.; Calabrese, J.M.; Starmer, J.; Parker, J.S.; Magnuson, T.; et al. Topoisomerases facilitate transcription of long genes linked to autism. Nature 2013, 501, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Joshi, R.S.; Piña, B.; Roca, J. Topoisomerase II is required for the production of long Pol II gene transcripts in yeast. Nucl. Acids Res. 2012, 40, 7907–7915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Joshi, R.S.; Nikolaou, C.; Roca, J. Structure and Chromosomal Organization of Yeast Genes Regulated by Topoisomerase II. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Austin, C.A.; Lee, K.C.; Swan, R.L.; Khazeem, M.M.; Manville, C.M.; Cridland, P.; Treumann, A.; Porter, A.; Morris, N.J.; Cowell, I.G. TOP2B: The First Thirty Years. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2765. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092765
Austin CA, Lee KC, Swan RL, Khazeem MM, Manville CM, Cridland P, Treumann A, Porter A, Morris NJ, Cowell IG. TOP2B: The First Thirty Years. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(9):2765. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092765
Chicago/Turabian StyleAustin, Caroline A., Ka C. Lee, Rebecca L. Swan, Mushtaq M. Khazeem, Catriona M. Manville, Peter Cridland, Achim Treumann, Andrew Porter, Nick J. Morris, and Ian G. Cowell. 2018. "TOP2B: The First Thirty Years" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 9: 2765. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092765
APA StyleAustin, C. A., Lee, K. C., Swan, R. L., Khazeem, M. M., Manville, C. M., Cridland, P., Treumann, A., Porter, A., Morris, N. J., & Cowell, I. G. (2018). TOP2B: The First Thirty Years. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(9), 2765. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092765