Identification and Characterization of Novel Fusion Genes with Potential Clinical Applications in Mexican Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
Abstract
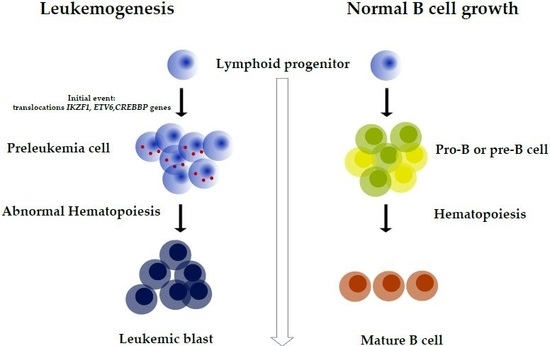
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical Features of Patients
2.2. Novel Fusion Transcripts
2.2.1. CREBBP-SRGAP2B t (16;1) (p13.3;q21.1)
2.2.2. DNAH14-IKZF1 t (1;7) (q42.12;7p12.2)
2.2.3. ETV6-SNUPN t (12;15) (p13.2;q24.2) and ETV6-NUFIP1 t (12;13) (p13.2;q14.12)
2.2.4. EP300-ZNF384 t (22;12) (q13.2;p13.31;)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients and Samples
4.2. RNA-Seq Libraries and Sequencing
4.3. Reverse Transcription–Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) for Fusion Genes
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALL | Acute lymphoblastic leukemia |
| NGS | Next-generation sequencing |
| RNA-seq | RNA-sequencing |
| IP | Immunophenotype |
| EBV | Epstein–Barr virus |
| BCP | Bicytopenia |
| SS | Septic shock |
| HLH | Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis |
| MOF | Multiple organ failure |
| TC | Toxicity |
| PN | Pneumonia |
| CR | Complete remission central nervous system relapse |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| CDS | Coding sequence |
| ETS | E-twenty-six |
References
- Pérez-Saldivar, M.L.; Fajardo-Gutiérrez, A.; Bernáldez-Ríos, R.; Martínez-Avalos, A.; Medina-Sanson, A.; Espinosa-Hernández, L.; de Diego Flores-Chapa, J.; Amador-Sánchez, R.; Peñaloza-González, J.G.; Álvarez-Rodríguez, F.J.; et al. Childhood acute leukemias are frequent in Mexico City: Descriptive epidemiology. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swords, R.; Sznol, J.; Elias, R.; Watts, J.; Zelent, A.; Martin, E.; Vargas, F.; Bethel-Ellison, S.; Kobetz, E. Acute leukemia in adult Hispanic Americans: A large-population study. Blood Cancer J. 2016, 6, e484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera-Luna, R.; Correa-González, C.; Altamirano-Alvarez, E.; Sánchez-Zubieta, F.; Cárdenas-Cardós, R.; Escamilla-Asian, G.; Olaya-Vargas, A.; Bautista-Marquez, A.; Aguilar-Romo, M. Incidence of childhood cancer among Mexican children registered under a public medical insurance program. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 1646–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullighan, C.G. The molecular genetic makeup of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program. 2012, 2012, 389–396. [Google Scholar]
- Yokota, T.; Kanakura, Y. Genetic abnormalities associated with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 721–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Greaves, M.F.; Wiemels, J. Origins of chromosome translocations in childhood leukaemia. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aplan, P.D. Causes of oncogenic chromosomal translocation. Trends Genet. 2006, 22, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hasty, P.; Montagna, C. Chromosomal Rearrangements in Cancer: Detection and potential causal mechanisms. Mol. Cell. Oncol. 2014, 1, e29904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersson, A.K.; Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Gedman, A.L.; Dang, J.; Nakitandwe, J.; Holmfeldt, L.; Parker, M.; Easton, J.; et al. The landscape of somatic mutations in infant MLL-rearranged acute lymphoblastic leukemias. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shurtleff, S.A.; Buijs, A.; Behm, F.G.; Rubnitz, J.E.; Raimondi, S.C.; Hancock, M.L.; Chan, G.C.; Pui, C.H.; Grosveld, G.; Downing, J.R. TEL/AML1 fusion resulting from a cryptic t(12;21) is the most common genetic lesion in pediatric ALL and defines a subgroup of patients with an excellent prognosis. Leukemia 1995, 9, 1985–1989. [Google Scholar]
- Shurtleff, S.A.; Buijs, A.; Behm, F.G.; Rubnitz, J.E.; Raimondi, S.C.; Hancock, M.L.; Chan, G.C.; Pui, C.H.; Grosveld, G.; Downing, J.R. Prevalence of gene rearrangements in Mexican children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A population study-report from the Mexican Interinstitutional Group for the identification of the causes of childhood leukemia. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 210560. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Razzaq, S.K.; Vo, A.D.; Gautam, M.; Li, H. Identifying fusion transcripts using next generation sequencing. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2016, 7, 811–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talkowski, M.E.; Ernst, C.; Heilbut, A.; Chiang, C.; Hanscom, C.; Lindgren, A.; Kirby, A.; Liu, S.; Muddukrishna, B.; Ohsumi, T.K.; et al. Next-generation sequencing strategies enable routine detection of balanced chromosome rearrangements for clinical diagnostics and genetic research. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2011, 88, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gocho, Y.; Kiyokawa, N.; Ichikawa, H.; Nakabayashi, K.; Osumi, T.; Ishibashi, T.; Ueno, H.; Terada, K.; Oboki, K.; Sakamoto, H.; et al. A novel recurrent EP300–ZNF384 gene fusion in B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2015, 29, 2445–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullighan, C.G.; Zhang, J.; Kasper, L.H.; Lerach, S.; Payne-Turner, D.; Phillips, L.A.; Heatley, S.L.; Holmfeldt, L.; Collins-Underwood, J.R.; Ma, J.; et al. CREBBP mutations in relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nature 2011, 471, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kobitzsch, B.; Gökbuget, N.; Schwartz, S.; Reinhardt, R.; Brüggemann, M.; Viardot, A.; Wäsch, R.; Starck, M.; Thiel, E.; Hoelzer, D.; et al. Loss-of-function but not dominant-negative intragenic IKZF1 deletions are associated with an adverse prognosis in adult BCR-ABL-negative acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 2017, 102, 1739–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mullighan, C.G.; Miller, C.B.; Radtke, I.; Phillips, L.A.; Dalton, J.; Ma, J.; White, D.; Hughes, T.P.; Le Beau, M.M.; Pui, C.H.; et al. BCR-ABL1 lymphoblastic leukaemia is characterized by the deletion of Ikaros. Nature 2008, 453, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Churchman, M.L.; Low, J.; Qu, C.; Paietta, E.M.; Kasper, L.H.; Chang, Y.; Payne-Turner, D.; Althoff, M.J.; Song, G.; Chen, S.C.; et al. Efficacy of Retinoids in IKZF1-Mutated BCR-ABL1 Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Braekeleer, E.; Douet-Guilbert, N.; Morel, F.; Le Bris, M.J.; Basinko, A.; De Braekeleer, M. ETV6 fusion genes in hematological malignancies: A review. Leuk. Res. 2012, 36, 945–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, R.H.; Smolik, S. CBP/p300 in cell growth, transformation, and development. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 1553–1577. [Google Scholar]
- Chrivia, J.C.; Kwok, R.P.; Lamb, N.; Hagiwara, M.; Montminy, M.R.; Goodman, R.H. Phosphorylated CREB binds specifically to the nuclear protein CBP. Nature 1993, 365, 855–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennis, M.Y.; Nuttle, X.; Sudmant, P.H.; Antonacci, F.; Graves, T.A.; Nefedov, M.; Rosenfeld, J.A.; Sajjadian, S.; Malig, M.; Kotkiewicz, H.; et al. Evolution of human-specific neural SRGAP2 genes by incomplete segmental duplication. Cell 2012, 149, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boija, A.; Mahat, D.B.; Zare, A.; Holmqvist, P.H.; Philip, P.; Meyers, D.J.; Cole, P.A.; Lis, J.T.; Stenberg, P.; Mannervik, M. CBP Regulates Recruitment and Release of Promoter-Proximal RNA Polymerase II. Mol. Cell 2017, 68, 491–503.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stankovic, T.; Marston, E. Molecular mechanisms involved in chemoresistance in paediatric acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Srp. Arh. Celok. Lek. 2008, 136, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrock, A.B.; Zhu, V.W.; Hsieh, W.S.; Madison, R.; Creelan, B.; Silberberg, J.; Costin, D.; Bharne, A.; Bonta, I.; Bosemani, T.; et al. Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Fusions and BRAF Kinase Fusions are Rare but Actionable Resistance Mechanisms to EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1312–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Tian, W.; Teng, W.; Ma, X.; Guo, L.; Fang, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Retrospective analysis of 36 fusion genes in 2479 Chinese patients of de novo acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2018, 72, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgopoulos, K.; Bigby, M.; Wang, J.H.; Molnar, A.; Wu, P.; Winandy, S.; Sharpe, A. The Ikaros gene is required for the development of all lymphoid lineages. Cell 1994, 79, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westman, B.J.; Mackay, J.P.; Gell, D. Ikaros: A key regulator of haematopoiesis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2002, 34, 1304–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, J.; Cronshagen, U.; Kadokura, M.; Marshallsay, C.; Wada, T.; Sekine, M.; Lührmann, R. Snurportin1, an m3G-cap-specific nuclear import receptor with a novel domain structure. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 4114–4126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shago, M.; Abla, O.; Hitzler, J.; Weitzman, S.; Abdelhaleem, M. Frequency and outcome of pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia with ZNF384 gene rearrangements including a novel translocation resulting in an ARID1B/ZNF384 gene fusion. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2016, 63, 1915–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Untergasser, A.; Nijveen, H.; Rao, X.; Bisseling, T.; Geurts, R.; Leunissen, J.A.M. Primer3Plus, an enhanced web interface to Primer3. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W71–W74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| Case | Age (Years) | Sex | Fusion Transcripts by NGS | Relapse | Death | Adherence | Diagnosis/Year | Initial WBC Count × 106 Cell/L | BM Blast % at Diagnosis | IP | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 74MO | 10.8 | M | BCR-ABL minor SRGAP2B-CREBBP | Yes | SS | Yes | ALL/2013 | 15,630 | 100 | Pre-B | Progressed quickly; expired in 2 weeks |
| 77MO | 17.4 | M | NF | No | No | Yes | ALL/2014 | 12,570 | 98 | Pre-B | CR |
| 197MO | 9.4 | F | EP300-ZNF384 | No | No | Yes | ALL/2014 | 2430 | 95 | Pre-B | CR |
| 199MO | 3.9 | M | NF | No | SS | Yes | ALL/2014 | 440 | 100 | Pre-B | Died after remission |
| 63MO | 2.0 | M | TCF3-PBX1 | No | SS | Yes | ALL/2015 | 7500 | 97 | T cell | Died after remission |
| 123MO | 4.7 | F | NF | No | No | Yes | ALL/2015 | 42,100 | 25 | Pre-B | CR |
| 269MO | 4.0 | F | ETV6-RUNX1 | No | No | Yes | ALL/2015 | 9200 | 98 | Pre-B | CR |
| 273MO | 14.8 | M | NF | No | No | Yes | ALL/2015 | 12,460 | 96 | Pre-B | CR |
| 289MO | 0.6 | F | MLL-AF4, GLYR1-SLC9A8a | No | No | Yes | ALL/2015 | 371,000 | 80 | Pre-B | CR |
| 374MO | 4.4 | F | NF | No | No | Yes | ALL/2015 | 20,220 | 100 | Pre-B | CR |
| 385MO | 5.5 | M | NF | ND | ND | A | ALL/2015 | 7200 | 85 | Pre-B | ND |
| 405MO | 4.6 | M | NF | No | No | Yes | ALL/2015 | 2700 | 25 | Pre-B | CR |
| 420MO | 6.0 | F | NF | No | No | Yes | ALL/2015 | 2360 | 90 | Pre-B | CR |
| 545MO | 7.2 | F | WDR74-RCC1a | No | No | Yes | ALL/2015 | 8600 | 98 | Pre-B | CR |
| 549MO | 4.9 | M | NF | No | No | Yes | ALL/2015 | 13,300 | 98 | Pre-B | CR |
| 99MO | 9.8 | F | NF | No | No | Yes | ALL/2016 | 9000 | 90 | Pre-B | CR |
| 109MO | 4.7 | F | NF | No | No | Yes | ALL/2016 | 19,900 | 96 | Pre-B | CR |
| 122MO | 12.3 | M | NF | No | No | Yes | ALL/2016 | 4700 | 96 | Pre-B | CR |
| 179MO | 1.8 | F | DNAH14-IKZF1 | No | No | Yes | ALL/2016 | 32,780 | 100 | Pre-B | CR |
| 196MO | 4.1 | F | NF | No | No | Yes | ALL/2016 | 2780 | 25 | Pre-B | CR |
| 369MO | 2.3 | M | NF | No | No | Yes | ALL/2016 | 2710 | 100 | Pre-B | CR |
| 546MO | 13.0 | M | NF | No | No | Yes | ALL/2016 | 8000 | 100 | Pre-B | CR |
| 28MO | 10.3 | F | ETV6-SNUPN, ETV6-NUFIP1 | No | MOF TC, PN, TC. | Yes | ALL/2016 | 46,300 | 99.5 | Pre-B | Progressed quickly; poorly responded to therapy, died after 2 weeks |
| 73MO * | 37.3 | F | NF | ND | ND | ND | HLH/2014 | 2200 | - | NA | NA |
| 159MO * | 5.8 | M | NF | ND | ND | ND | EBV/2015 | 3620 | 15 | NA | NA |
| 165MO * | 2.2 | M | NF | ND | ND | ND | EBV/2015 | 29,740 | - | NA | NA |
| 83MO * | 5.8 | F | NF | ND | ND | ND | BCP/2017 | 2390 | - | NA | NA |
| Fusion | Gene Symbol (Chromosome Band) | Nucleotides (hg19) | Gene Description | Sample | Gene Previously Reported as Potential Prognostic Indicator | In-Frame | Fusion Validated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CREBBP-SRGAP2B | SRGAP2B (1q21.1) | 144013900 | SLIT-ROBO Rho GTPase-activating protein 2B | 74MO | No reported | Yes | Yes |
| CREBBP (16p13.3) | 3929832 | CREB-binding protein (CBP) | Mutations may confer to chemotherapy resistance and possibility of relapse [15] | ||||
| DNAH14-IKZF1 | DNAH14 (1q41.12) | 225333860, 225333863, 225347499, 225354984, 225374260, 225346497 | Dynein Axonemal Heavy Chain 14 | 179MO | No reported | Yes | Yes |
| IKZF1 (7p12.2) | 50444490, 50367352, 50435762, 50444490, 50448363, 50444230 | IKAROS Family Zinc Finger 1 | Deletions and mutation were related to adverse prognosis, treatment failure, and risk of relapse [16,17,18] | ||||
| ETV6-SNUPN | ETV6 (12p13.2) | 11905512 | ETS family transcription factor, Variant 6 | 28MO | In fusion with RUNX1, the most common genetic aberration in pediatric ALL and is related to favorable prognosis [19] | Yes | Yes |
| SNUPN (15q24.2) | 75913396 | Snurportin 1 | No reported | ||||
| ETV6-NUFIP1 | ETV6 (12p13.2) | 11803093 | ETS family transcription factor, Variant 6 | 28MO | Yes | Yes | |
| NUFIP1 (13q14.12) | 45540070 | Nuclear Fragile X Mental Retardation Protein Interacting Protein 1 | No reported | ||||
| EP300-ZNF384 | ZNF384 (12p13.31) | 6788687 | Zinc finger protein 384 | 197MO | EP300-ZNF384 fusion is associated with a B-cell precursor ALL in childhood (3–4%) with better favorable response to chemotherapy than patients with MLL translocations [14] | Yes | Yes |
| EP300 (22q13.2) | 41527639 | E1A binding protein p300 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mata-Rocha, M.; Rangel-López, A.; Jiménez-Hernández, E.; Morales-Castillo, B.A.; González-Torres, C.; Gaytan-Cervantes, J.; Álvarez-Olmos, E.; Núñez-Enríquez, J.C.; Fajardo-Gutiérrez, A.; Martín-Trejo, J.A.; et al. Identification and Characterization of Novel Fusion Genes with Potential Clinical Applications in Mexican Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102394
Mata-Rocha M, Rangel-López A, Jiménez-Hernández E, Morales-Castillo BA, González-Torres C, Gaytan-Cervantes J, Álvarez-Olmos E, Núñez-Enríquez JC, Fajardo-Gutiérrez A, Martín-Trejo JA, et al. Identification and Characterization of Novel Fusion Genes with Potential Clinical Applications in Mexican Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(10):2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102394
Chicago/Turabian StyleMata-Rocha, Minerva, Angelica Rangel-López, Elva Jiménez-Hernández, Blanca Angélica Morales-Castillo, Carolina González-Torres, Javier Gaytan-Cervantes, Enrique Álvarez-Olmos, Juan Carlos Núñez-Enríquez, Arturo Fajardo-Gutiérrez, Jorge Alfonso Martín-Trejo, and et al. 2019. "Identification and Characterization of Novel Fusion Genes with Potential Clinical Applications in Mexican Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 10: 2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102394
APA StyleMata-Rocha, M., Rangel-López, A., Jiménez-Hernández, E., Morales-Castillo, B. A., González-Torres, C., Gaytan-Cervantes, J., Álvarez-Olmos, E., Núñez-Enríquez, J. C., Fajardo-Gutiérrez, A., Martín-Trejo, J. A., Solís-Labastida, K. A., Medina-Sansón, A., Flores-Lujano, J., Sepúlveda-Robles, O. A., Peñaloza-González, J. G., Espinoza-Hernández, L. E., Núñez-Villegas, N. N., Espinosa-Elizondo, R. M., Cortés-Herrera, B., ... Mejía-Aranguré, J. M. (2019). Identification and Characterization of Novel Fusion Genes with Potential Clinical Applications in Mexican Children with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(10), 2394. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102394